Cough
Most often, children develop a wet cough during the period of the appearance of incisors, canines and molars. His attacks are rare. This usually happens in a horizontal position when the child is lying down. It goes away in 2-3 days. But, young mothers should remember that frequent manifestations of a wet cough may indicate serious illness. You need to see a doctor to rule out bronchitis and pneumonia. If symptoms are severe, you should not delay a visit to the pediatrician.
Vomit
This unpleasant state at the birth of units can be explained.
- With strong salivation, the child does not have time to swallow saliva. It drains, accumulates in the mouth and is expelled by reverse peristalsis.
- Painful condition, crying and screaming contribute to swallowing air. It gathers in large quantities, props up the diaphragm, the little ones arch and saliva, along with food, spews out.
- Refusal to eat provokes mothers to force-feed. In such a situation, food is rejected by the body.
Vomiting can be provoked by high temperature, decreased immune status, which is fraught with the introduction of pathogenic microflora. Intoxication leads to vomiting. This is how the body cleanses itself of toxins. It is important to avoid dehydration. Remember that in a child’s body it occurs quickly. Therefore, contacting a pediatrician is mandatory.
An examination of the oral cavity will reveal a violation of the closure of the jaws and their uneven growth. This may be a consequence of prolonged use of the pacifier. Correcting the bite in children is an important component of overall health. A mandatory visit to the pediatric dentist is carried out no later than 6 months of age. The doctor will evaluate the position of the upper and lower lips, the condition of the frenulum, and the features of the maxillofacial structure.
Diarrhea
Watery bowel movements, that is, diarrhea, are also noted at the birth of the masticatory organs. If stool is not frequent, no more than 2-3 times a day, and this trouble lasts from 1 to 3 days, mothers should not worry. If you have frequent bowel movements with the appearance of blood clots, you should contact your pediatrician, especially when you experience abdominal pain. You cannot self-medicate, it is dangerous for the baby’s health. In such a situation, dehydration is detrimental. Only a doctor can make the correct diagnosis and help cope with the problem.
When teeth start cutting
There is no exact answer as to what time a child’s teeth are cut – the timing varies from person to person. However, you can focus on the average, standard periods of eruption approved by WHO:
- the lower incisors appear at 6–7 months;
- upper – at 7–8 months;
- upper lateral incisors – at 8–9 months;
- the lower ones are closer to a year.
According to the standard, a one-year-old child must have eight baby teeth.
From one year to one and a half years, the child acquires larger teeth - upper and lower molars, and from fifteen to twenty months - upper canines, which are also called “ocular.” The fact is that the optic nerve runs next to them, so these teeth are often more difficult for the child than others. Irritation of the nerve causes sharp pain and sometimes watery eyes.
It can be difficult even for a doctor to understand that the first teeth are being cut. After all, this process is often accompanied by an increase in temperature, changes in stool and mood, and refusal to eat.
When do teething symptoms appear?
The foundation of baby teeth is laid during pregnancy: doctors recommend that mothers monitor their diet and bad habits, including because all this affects oral health.
During the first six months of life, the child accumulates material for bone tissue growth. When the baby is six months old, you can expect symptoms: at this age, babies begin to erupt their upper (natal) teeth. This happens in most cases, but there are many exceptions. Surely you have heard about children who are born with “hatched” teeth. It also happens that the first incisor appears only at one year of age. Both cases are normal.
In total, 20 milk teeth should appear in the baby’s mouth by the age of three: on each jaw there are 4 incisors (4 central teeth), 2 canines and 4 molars (fourth and fifth teeth).
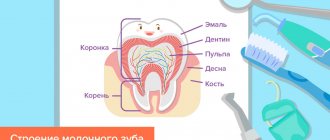
Formation of the dentition
The article tells how to understand that a child is teething, and about ways to help him with pain and inflammation of the gums. But first, a few words about the process of dentition formation.
The formation of absolutely all teeth occurs in the fifth month of intrauterine development. They remain in a “frozen” state and begin to grow immediately before eruption. Therefore, if a child has no teeth by 9-12 months, radiography is prescribed - a study that allows one to evaluate their formation and location.
How teeth are cut: the order in which they appear
Every adult can understand how a baby feels when his first teeth are cut - just remember how the so-called “wisdom teeth” appeared.
Swelling of the gums, itching and pain - you must admit, this is not pleasant. Therefore, infants often become capricious during the teething process. They may lose appetite and sleep, and even have a slight rise in temperature. The earliest time for baby teeth to erupt is at the incisors (front teeth). There are four of them on each jaw. As a rule, the lower two incisors erupt first (at 6-8 months), then the upper central incisors. The teeth appear in pairs opposite to each other, this is important for the formation of a correct primary bite. At 8-12 months, the baby develops lateral incisors (first on the lower jaw, then on the upper). At one year old, a child should have eight teeth. After this there is a short break in their appearance.
Next in the sequence are fangs. There are two of them on each jaw. The location and structure of these teeth makes their eruption especially difficult and difficult for the child. At the age of 16-20 months, fangs will appear on the lower jaw, and then on the upper jaw. Then comes the turn of the painters (large molars). They begin to erupt at 20-30 months, each child at its own time. There are a total of 20 teeth in the primary occlusion, 10 on each jaw: 4 incisors, 2 canines and 4 painters. All of them should appear by 2.5-3 years.
What affects the timing of teething?
Processes in the body are individual, including timing. The age at which the first teeth appear is determined by a number of factors:
- Heredity.
- The intrauterine period and negative factors affecting the fetus (for example, a pregnant woman taking certain medications).
- Nutrition for the expectant mother during the period of waiting for the baby and breastfeeding.
Introduction of complementary foods, etc.
How to relieve symptoms
The basic principle of medicine is to do no harm. Therefore, the first thing you need to do is consult a doctor. You cannot select medications on your own or on the advice of neighbors. And in the pharmacy you can find a lot of ointments and gels with a “cooling” effect and remedies for fever.
Teethers
There are different types of devices. Some of them are used for signs of eruption of the upper teeth, others are suitable for the frontal units or distant molars. The purpose of use is to massage the gums, which alleviates the condition of the little one. You can buy silicone and latex products that are suitable for children as young as 3 months. If mom will massage her gums, she needs a fingertip with a special brush. To help the baby scratch his teeth and play at the same time, special rattles have been created. Teethers for yearlings can be filled with gel or water. They cool the oral cavity well, which “freezes” the pain. The device may vibrate if the baby bites it.
Cream
It is used as a protective agent at the time of increased salivation. This protects the skin of the chin and chest from irritation, especially during a walk in winter.
Vertical position
Parents need to play with their baby more often and distract him from pain. Holding your child upright will reduce pain by reducing blood flow to the head.
Drinking regime
Salivation, especially increased salivation, provokes severe thirst. You need to give your baby more clean water.
Psychological discomfort is compensated by affection, care, and attention. At this time, you should not introduce new foods into the diet, so as not to expose the baby to additional stress.
Teething symptoms
- there may be a slight fever;
- anxiety - the child becomes capricious, sleeps poorly, often wakes up at night;
- decreased appetite;
- excessive salivation and, as a result, redness of the skin around the mouth;
- swelling and redness at the site of tooth eruption, possible formation of hematomas on the gum mucosa;
- increased need for the baby to chew on something: pacifier, toys, fingers.
There are children whose teeth appear asymptomatically and even unnoticed by their parents. But, as a rule, this process is accompanied by an individual combination of the signs given in the list above.
Replacing baby teeth with permanent teeth
Eruption of molars begins at the age of 6-7 years. First, the large molars are shown (usually on the lower jaw). Then the pattern of baby teeth eruption is repeated. The incisors on the lower jaw are the first to change, and at the age of 7-8 years, the incisors on the upper jaw are also replaced. At the same time, the lower lateral incisors can also change.
At 8-9 years old, the upper incisors will change. It's the fangs' turn. At the same time (9-10 years), teeth that were not in the primary occlusion - premolars - begin to grow. There are four premolars on each jaw - two on the left and two on the right. At the age of 12, the fangs on the upper jaw will change. At this stage, the formation of the height of the bite begins, which has both aesthetic and functional significance.
The last teeth (wisdom teeth or third molars) appear between the ages of 17 and 25. Only after this can we say that the formation of the dental arches is completely completed.
When replacing baby teeth with permanent molars, it is important to pay attention to the bite. It is easy to correct at a young age, while adults will have to correct it throughout their lives. By regularly visiting a pediatric dentist, you can intervene in the process of bite formation in a timely manner. In addition, a specialist can monitor the eruption of baby and molar teeth (so that it is not too early or late), give recommendations to alleviate the child’s condition, and recommend special baby suppositories or gels for teething.
When should you worry?
The listed signs of the appearance of the first baby tooth should not bother mom, dad and grandmother too much. The following symptoms may be a reason to contact your pediatrician:
- Early appearance of the first teeth. In rare cases, newborns develop teeth immediately after birth. This may indicate endocrine pathology and requires examination by an endocrinologist.
- A significant delay in teething may also indicate various metabolic disorders in children and requires medical intervention.
- Incorrect appearance order . If, instead of the baby’s first incisors, molars or fangs begin to peck, such disharmony may indicate anomalies in the baby’s development or be a consequence of illnesses that the woman suffered during pregnancy.
- Temperature above 39 degrees. When the first teeth erupt in children, the temperature rises slightly. If your baby becomes hot and the high temperature lasts for several hours, call a doctor immediately.
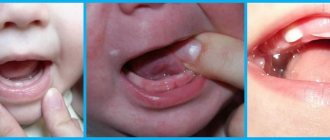
The urge to scratch the gums and drooling
Children generally tend to put everything in their mouths, but as teething begins, this need may increase noticeably. If your baby always wants to scratch his gums on something, this is a clear sign that he is teething. Make sure that the child cannot reach dangerous objects that could block his airway, and let the baby chew special teething rings.
Another sign of rapid teething is excessive drooling: in some babies it can be so intense that their clothes become wet through, and skin irritation appears around the mouth and chin. To help keep your baby comfortable and rash-free, gently wipe away any saliva from his face and change wet clothes as needed.
How to understand that teeth have started to cut?
The following symptoms will indicate that a child is getting his first baby tooth:
- severe crying, frequent whims of the baby;
- increased salivation;
- slight increase in temperature;
- frequent excitability;
- refusal of food;
- upset stomach (diarrhea).
Of course, the above symptoms individually can indicate not only that the child is getting his first teeth. For example, whims and frequent excitability in a baby can be caused by stress due to moving to a new apartment, fever by a cold, and diarrhea by an allergy to a particular product. Usually, the eruption of the first teeth in children provokes several, or even all, of these signs at once.
When do the first teeth appear?
Usually a baby's first baby tooth is at 6 months. Although some children have their first teeth appearing as early as 4 months of age, others have to wait as long as 7 months for their first incisors. By the way, both such an early and such a late appearance is considered the norm. At 6-8 months, the central lower incisors appear.
- At 8-12 months, the central upper incisors grow;
- 10-13 months – second upper and lower incisors;
- 1-1.5 years – primary molars;
- 1.5-2 years – fangs;
- 2-2.5 years – second primary molars.
Thus, by the age of two, the baby already has 18 teeth in its mouth. But it is the first incisors that cause the baby the most inconvenience.
Why does the child have a fever?
When teeth begin to cut, the child may develop a fever, which is completely normal in such a situation. What should parents do to help their baby?
- If the temperature does not exceed 38 degrees, try not to bring it down with medications; just don’t insulate or overheat the baby.
- The baby in this state is very nervous, contact with mommy is very important, so do not deny him the breast, even if it is out of your usual latching regime.
- Let your child drink water more often, because at high temperatures, dehydration occurs faster in the child’s body.
- To make the baby's teething process smoother, you need to lubricate his gums with special gels, for example Kalgel or Cholisal. After this, offer your baby a teething toy. This toy massages the gums well and distracts the baby.
- Gum massage is a very effective remedy; to do this, you need to sit the baby on your lap or simply take a position that is comfortable for both of you, and very carefully massage the gums, without pressing hard and without sudden movements.
- Try to calm the baby down, hug him, rock him, because when a baby cries, as a rule, the temperature begins to rise faster.
- If you periodically wipe the baby's body with warm water at high temperatures, paying special attention to the folds under the arms and between the legs.
Make an appointment