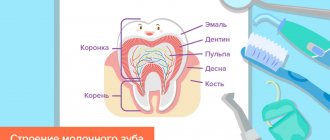
Teething in an infant is a very exciting moment in the life of the baby and his parents. And although teething is a physiological process, almost all children experience discomfort and anxiety during this period. From the point of view of a scientific approach to this problem, the difficulty lies in the fact that with all the variety of teething symptoms from mild restlessness and moodiness, increased salivation to an increase in body temperature to high numbers and signs of impaired digestion, increased colic and diarrhea, there are no sufficient diagnostic criteria to connect all these numerous symptoms to the root cause. Nevertheless, many parents and some practicing pediatricians are still ready to blame the baby’s teething for almost all the troubles that befall them in the period from 5 - 6 months to one and a half - two years, when the teething process is mainly teeth should already be completed.
Most children begin teething between the ages of 4 and 7 months. As a rule, the eruption of each tooth lasts from 2 - 3 to 8 days. During this time, it is possible to increase body temperature to 37.4 - 38.0 degrees. At the same time, high temperature (from 38.0 and above) usually lasts no more than 2 days. Nasal discharge during the period when teeth are erupting is usually transparent, liquid, and should not contain pathological impurities: pus, greens, etc. Cough during teething is caused by saliva entering the nasopharynx and larynx area, which is released in large quantities. Cough due to teething does not require treatment. Regarding diarrhea, pediatricians sometimes differ in their opinions: some believe that diarrhea (loose stool) is not directly related to teething. And yet, studies have shown that from 10 to 30% of children have frequent and/or loose stools during teething. This is also explained by the large amount of saliva secreted, which enhances intestinal motility.
What to do if teeth do not erupt “on time”?
Nothing to do. As stated earlier, the timing is quite relative and not strict data. There is such a thing as the individual characteristics of a child. Plus neonatal indicators, physical constitution, etc. Thus, the timing of the appearance of teeth in your child is normal for him. The same applies to permanent teeth.
The later the teeth appear, the healthier they will be?
Is not a fact. The timing of teething does not affect their “quality”.
What sedatives can be used during teething? Do they influence the process itself?
No, such drugs do not affect the process of teeth formation and, as a rule, have no side effects. For children with allergies, there is a sedative called Doctor Baby that does not contain lidocaine. Almost all gels contain lidocaine and inert fillers (cooling menthol, astringents and flavoring additives). You can use Dentinox, Kalgel (be careful with diathesis, because it is sweet), Kamistad (very effective, but you need to know when to stop), Mundizal, Cholisal, Solcoseryl dental paste (especially good in the presence of wounds or ulcers).
How often should such drugs be used?
Soothing gels are not antibiotics and do not need to be used according to a specific regimen. If the child is in pain, apply it, but if everything is calm, don’t. But it’s better not to use it more than 3-4 times a day and for longer than 3 days in a row.
Urticaria and food allergies in infants
26.05.2021
Urticaria in a child manifests itself as itching, redness, and blisters. It is not uncommon, but in some cases it can be dangerous. One of the symptoms of hives may be a food allergy . Its presence requires certain changes in the diet of the baby, and often his mother. What to do if you suspect a food allergy in a child and how to recognize its symptoms?
Urticaria in a child
The name "urticaria" is no coincidence, because the changes caused by it are similar to those that can be observed as a result of skin contact with nettles. Red, itchy blisters may appear in different places on the body, changing their location over the following days. Urticaria in a child is equivalent to an allergy . One of the most common is food allergies , but children, like adults, can be allergic to dusty plants, animal dander, and dust. Babies' skin is also often irritated by the use of cosmetics or washing powders.
There are several types of urticaria . Acute urticaria in a child appears on the skin as a result of a specific reason and lasts from several days to 1.5 months. Blisters on the skin can persist for more than 6 weeks. urticaria occurs . In idiopathic urticaria, the cause of the disease is unknown, which makes the treatment of skin lesions difficult.
Urticaria in a child can be dangerous if it is accompanied by swelling and rashes around the throat . It can even lead to suffocation. It is worth knowing that the cause of urticaria is not only an allergy , but also a reaction to low or high temperature, exposure to solar radiation, under pressure, as a side effect of medications.
Food allergies in infants
The hives described above are one of the symptoms of food allergies , which can be associated with digestive and breathing problems. Usually this:
- colic;
- flatulence;
- diarrhea;
- constipation;
- cough;
- juice.
Food allergies in an infant often occur when new foods are added to their diet, but can also appear in the first months of life. It is believed that the safest way to prevent allergies is to breastfeed your baby for the first six months of his life. However, it is worth noting that food allergies in a newborn can also arise as a result of foods consumed by the mother. The most common allergens include: cow's milk, eggs, grain products containing gluten, nuts, fruits such as strawberries, bananas or citrus fruits, fish and seafood.
An elimination diet is quite simple to implement when parents introduce new foods into their child's diet one at a time. Then careful observation is enough to determine the causes of food allergies . For the same reason, breastfeeding women should pay close attention to their diet and closely monitor their baby's reactions. In case of milk allergy The tendency to allergies is not always hereditary, but its presence in parents increases the likelihood of allergic reactions in the child.
Treatment of food allergies in infants
In the case of food allergies, the procedure seems clear - just avoid the factor that provokes an abnormal reaction of the immune system . However, if it is impossible to eliminate the allergenic factor, antihistamines are used. Their task is to suppress the secretion of histamine, a substance responsible for the occurrence of hypersensitivity reactions. The same treatment is used for allergic urticaria . For other types of urticaria , it is essential to make an appropriate diagnosis, which then determines treatment or specific preventive measures. Blood tests help determine the causes of hives .
Published in Allergology Premium Clinic
Is it possible to speed up teething?
Medication - no. But massaging your gums won't hurt at all. Using a clean finger, gently and gently massage your baby's gums. The baby will feel better, and the tooth will cut through faster. Just do not press hard so as not to injure the gums. You can give your child a cool spoon or pacifier to hold in his mouth. Try buying special teethers with liquid. They are placed in the refrigerator for a while, and then given to the child to chew on. All these methods are good in moderation, do not overdo it.
Can bad breath occur during teething and what is the cause?
The process of teething is associated with partial decomposition (lysis) of the mucous membrane under the action of salivary enzymes. We all notice that the amount of saliva increases sharply during this period. In this case, indeed, indicators such as viscosity, color and smell of saliva may change. Another factor is the presence of weak antibacterial substances in saliva, which are designed to prevent infection of the wound when a tooth cuts through the gum. A certain amount of blood also enters the oral cavity. When it decomposes, a sour (metallic) odor may appear.
A sharp increase in temperature during teething. What to do?
Teething does not cause a temperature jump to 39-40 degrees. Only a slight increase is possible, which is normal. Be careful: teething should not cause high fever, diarrhea, vomiting, complete loss of appetite, cramps or choking. If you have such symptoms, even if you attribute it to your teeth, consult a doctor. It is also not recommended to use antipyretics and painkillers without consulting him.
What is the difference between an increase in temperature due to teething and an increase due to other reasons? How long can the elevated temperature last in the first case?
It all depends on the individual characteristics of the child. Basically, hyperthermia and diarrhea are only secondary signs of the teething process, which in itself is a serious physiological turning point for a small organism. Fever is, rather, a reaction to inflammation of the oral mucosa. After all, at the site where the tooth exits, irritation forms, often a wound that can become infected. Thus, hyperthermia is caused not by the mechanism of tooth formation itself, but by side effects. After all, the eruption of permanent teeth, despite the similarity of histological and physiological changes, causes symptoms of colds and diarrhea extremely rarely. And it is quite simple to explain their appearance in children: changes in diet and diet, constant foreign objects in the mouth, microflora disturbance, weakened immunity in the nasopharynx. So, if high fever and loose stools continue for more than 72 hours, then teething really has nothing to do with it.
What kind of rash occurs and why does it occur?
A rash on a child’s body can appear for many reasons, not just when teething; it may also be that the parents simply gave the baby new complementary foods or he became infected with something. You need to make sure that the child is completely healthy and there are no allergenic substances around him, for example, low-quality household chemicals or food. Any of these factors can cause a child to develop a rash on any part of the body. It may appear as redness, be hard or flaky to the touch, itch or sting when touched, and may appear as clusters of pimples or blisters. In any of these cases, the first step is to visit a pediatrician.
If the rash is still not associated with any factors other than teething, you must first determine the location of its main location before moving on to treatment.
Where does the teething rash appear and can it spread beyond the baby's face?
As a rule, such a rash, which can be attributed to teething, begins in the area of the child’s head (face) and neck and looks like in the photo. It spreads in stages, from the place of first localization to more distant places on the body. The next stage is usually the arms, and then the rest of the body and legs. The rash itself feels like a very dry area, sometimes flaking, with increased skin temperature at the site of the rash. In any case, no matter what the rash looks like, it should always be under the careful supervision of parents.
If you notice a rash on your child’s face and are sure that he is absolutely not sick with anything, you should visit a doctor and consult with him what needs to be changed in the child’s routine so that the rash disappears.
Teething in infants
Possible characteristics of teeth in children at the teething stage. Stay up to date.
The expansion of the spaces between the teeth is caused by the growth of the jaws. During the transition from baby teeth to permanent teeth, it is considered a normal condition. A wide gap between the upper anterior incisors is usually associated with a deep-lying maxillary frenulum. An orthodontist should observe and treat such a gap between the teeth;
- a blackish edging on the neck of the tooth can form when taking soluble iron supplements, as well as during a chronic inflammatory process (precipitation of bacteria from the leptotrichium group);
- yellowish-brown staining of teeth may be associated with the use of antibiotics - by the mother in the 2nd half of pregnancy or by the child himself during the formation of teeth;
- yellowish-greenish coloring is caused by severe disturbances in bilirubin metabolism, hemolytic conditions (destruction of red blood cells);
- reddish staining of tooth enamel is characteristic of a disease called porphyria - a congenital disorder of the metabolism of porphyrin pigment;
- malocclusions are formed by the uneven growth of the child’s jaws, as well as prolonged sucking of the nipples;
- Anomalies in the location of teeth occur for a number of reasons: trauma, congenital disorders of connective tissue metabolism, constitutional reasons (small jaw size), tumors of the alveolar process of the jaw.
- the absence of teeth before one year of age is extremely rarely associated with edentia (lack of tooth buds), which can be checked using radiovisiography as prescribed by a pediatric dentist.
If teeth erupt on time and in a certain order, this indicates the normal development of the child’s body. After all, this physiological process is in direct connection with the general health of the baby. Some atypical cases may indirectly indicate the presence of pathology. But only a special examination of the child can confirm or refute the assumptions made. The reasons must be identified and analyzed by a specialist.