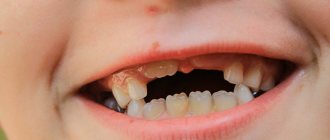
A child's teeth grow in two rows
With proper development of the jaw at the right age, permanent teeth begin to erupt and put pressure on the roots of the milk units.
Under this influence, the roots dissolve - the baby tooth becomes mobile, it wobbles and then falls out. This is a normal change in bite, the algorithm of which is known to most. But in rare cases the situation develops differently:
- when the germ of a permanent tooth and the root of the milk tooth are located in parallel planes, there is no pressure on the roots, and the permanent tooth grows in close proximity to the milk tooth;
- when the permanent one erupts quickly, and the roots of the milk unit have not yet resolved, the tooth does not fall out, and the permanent one has to bend and grow at an angle;
- when a child has a supernumerary set of teeth.
Various reasons - one result: the child’s teeth grow in the second row, threatening to ruin the permanent bite.
How many teeth should a child have?
By the age of three, a child usually already has a full set of twenty primary teeth, and until about 6 years old, their number remains unchanged. Adolescents aged 13 to 18 years should normally have from 28 to 32 molars (depending on the presence of eights, which may erupt after 21 years or not appear at all).
What to do when teeth grow in two rows
With “shark” jaws, the most reasonable solution seems to be the removal of excess milk units. And they did this for a long time. The result of hasty decisions showed that hasty removal of primary incisors and fangs leads to the opposite result and the formation of a malocclusion. After this, pediatric dental surgeons began to see children only as prescribed by the orthodontist - after professional consultation with a specialist.
An orthodontist is the first doctor you should go to when teeth grow in two rows. The doctor will assess the prospects for the formation of the dentition, send you for an x-ray to accurately determine the rudiments of permanent teeth and make the right decision. And this will not always be immediate removal of a baby tooth!
Based on the results of the diagnosis and examination, the orthodontist can advise:
- increase the amount of solid food in the child’s menu - provide the missing pressure on the baby tooth, causing it to loosen and fall out;
- wait for the natural change of teeth so that the permanent unit moves into its intended place under the influence of other teeth and under the pressure of the tongue muscles;
- remove primary incisors and canines to forcefully free up space.
The latter purpose is typical for parallel growing teeth and firmly standing primary units, since this is the only case when there are no natural prerequisites for root resorption and normal bite changes.
Child's front teeth
Since a child’s front teeth usually erupt earlier than the rest, they can be used to track how the baby’s body tolerates this process. It can occur in different ways: some children are practically not worried, while others, on the contrary, experience stress and discomfort. Swelling of the gums at the site of the future tooth, itching and pain, as well as a slight increase in temperature are the main negative aspects associated with the appearance of the first teeth. When teething baby molars, children may experience runny nose and cough.
Causes and consequences of dental pathology
Abnormal two-row growth is possible for many reasons:
- heredity;
- chronic colds and decreased immunity;
- unhealthy diet with a predominance of soft foods and purees;
- lack of vitamins and useful elements;
- premature removal of milk units;
- disturbance in the location of tooth germs.
With timely treatment, the orthodontist will easily straighten the bite and place each tooth in its proper place. If you delay visiting a doctor, the consequences can be serious:
- malocclusion;
- problems with hygiene and the development of caries;
- facial deformation due to jaw imbalances;
- ugly smile.
A sign of a potential shark jaw is the absence of gaps between the teeth in a 4-6 year old child. Insufficient space is the first prerequisite for the appearance of a second row of teeth in children and a signal for an attentive parent.
It is easy to see an incorrectly growing tooth, especially in the lower jaw. During the period of change in bite, dentists recommend monitoring the process - periodically conducting home or professional examinations and listening carefully to the baby. Complaints of discomfort in the mouth, inconvenience of chewing and pain indicate the need to visit a dentist to assess the condition of the oral cavity.
Teeth in children: order of eruption of baby teeth
The eruption of baby teeth in children is a strictly individual process for each child. Normally, there are deviations of 5-6 months from the stated standards. Most babies begin to cut their first teeth at 6 months, but there are cases where this process begins already in the first three months or only after a year. Moreover, it is not at all necessary that the rudiments be visible at the initial stage. Children's teeth can start cutting in at six months, and the first white bumps will be noticeable by one year.
Standard timing of baby teeth eruption
As a rule, this process begins faster in girls than in boys. In babies with rapid development, the first teeth can be seen at 3-4 months, but it is normal for the process to begin before the age of twelve months. If the timing of the eruption of baby teeth does not correspond to the norm, this is a reason to consult a dentist.
A delay in the natural process may be due to the following factors:
- lack of calcium in the body;
- problems with physical development;
- lack of thyroid hormones;
- metabolic problems;
- edentia – complete absence of the rudiments of baby teeth;
- rickets;
- hereditary predisposition.
Attention! The fact that a child of 1 year is missing primary teeth is not a pathology. Perhaps this is an individual feature. Sometimes parents simply cannot determine the presence of rudiments (the child closes his mouth and does not allow adults to examine the oral cavity). Then a consultation with a pediatric dentist is required, who will conduct a physical examination, assess the condition and give recommendations.
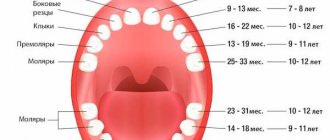
The order of eruption of baby teeth
The standard teething scheme for babies is as follows:
- the incisors in the center come first;
- lateral incisors emerge;
- next – the first molars;
- then fangs;
- The second molars emerge last.
As practice shows, in many children the teeth from below begin to grow first, but there are often cases when the first incisors and molars have already emerged from above, but not yet from below. If an examination by a pediatric dentist and pediatrician shows normal results, you just need to wait a little.
The misconception is that the more calcium in a child’s diet, the faster his teeth will erupt. Many parents begin to introduce cottage cheese, milk porridge, and hard cheese into complementary foods too early, supposedly to speed up this process. In no case should you follow this example to avoid excess calcium in the body and other health problems. Nutrition should be complete, varied, healthy. The time will come, and the teeth will erupt naturally.
By the age of two and a half, the child should have all his teeth: on each half of the jaw there should be two molars, one canine and two incisors. Baby teeth come out symmetrically to each other, there should be 20 units in total, that is, 10 on top and bottom.
Formula for calculating the number of teeth for children under 2 years of age
There is also a formula that can be used to count baby teeth. The order of teething is as follows: the child’s age in months minus six months - the number of teeth is obtained. For example, if a child is 15 months old, then we subtract 6 from 15 and get 9. Accordingly, the baby normally has 9 teeth that have erupted at the moment.
What if the baby was born with teeth already erupting?
It also happens that children are born with already erupted teeth, or they come out in the first few weeks of life. In such cases, it is necessary to seek help from a pediatrician and dentist. Sometimes the presence of incisors and molars interferes with natural breastfeeding, and the child is transferred to artificial feeding, or is fed with a bottle of breast milk and a pacifier.
How can you tell when your child’s teeth have started cutting?
Symptoms of the emergence of the first incisors and other dental units are as follows:
- the baby becomes restless;
- there is excessive salivation;
- the child actively begins to put toys and foreign objects into his mouth;
- baby sucks fingers;
- often asks for a breast or pacifier;
- day and night sleep is disrupted;
- the child becomes whiny and irritable;
- there is a refusal to eat;
- temperature rises;
- The gums are slightly swollen.
Attention! The fact that you do not see the first rudiments of a tooth (a white dot on the gum) does not mean that it is not erupting. On the contrary, the process of coming out is the most painful, and when the tooth appears on the surface, the baby’s condition returns to normal.
Pediatric dentists at the Zuub.rf clinic are ready to provide advice and medical assistance to children during teething. If your child is worried about his teeth, or you have suspicions about the order in which his baby teeth come out, a medical examination with a doctor will definitely help! The dentist will examine the condition of the child’s teeth, give detailed recommendations and rule out pathologies often “contrived” by parents.
If you have the symptoms described in this article, be sure to make an appointment at our clinic.
Don't self-medicate! Even the smallest problem, if not treated correctly, can significantly complicate your life.
By contacting us, you can be sure that:
- Get high-quality and free consultation .
- You will receive the best prices for treatment and the opportunity to receive a special promotional price.
- Only modern equipment and materials will be used.
- You will be treated by professional doctors with many years of experience.
- We offer treatment on credit or in installments. There is also the possibility of obtaining a tax deduction.
- We work seven days a week and without a lunch break, from 9 a.m. to 10 p.m.
+7
Diseases of baby teeth
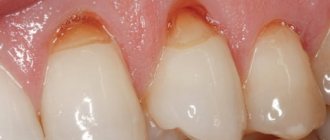
The most common troubles are caries (including bottle caries), pulpitis, periodontitis.
You should be alerted to any changes in the color of the enamel, spots, dots (both dark and white) on the child’s teeth, redness or swelling of the gums. But you don’t have to be afraid of uneven teeth at first: when chewing solid food, the baby teeth will move a little and gradually take the right place.
The causes of diseases in primary teeth are not very different from the causes of problems with permanent teeth. This:
- insufficient care for them (lack of proper hygiene),
- eating disorders,
- undermining of the immune system due to other diseases and taking certain medications.
It is a mistake to think that you can't take too much care of your baby teeth because they will fall out anyway. A diseased tooth in the mouth is a breeding ground for pathogenic bacteria, which not only destroy other teeth, but also negatively affect digestion and ENT organs. A prematurely lost baby tooth is also a problem, as it does not allow the baby to fully chew food or articulate sounds well. In addition, neighboring teeth try to occupy the vacated space - they move. And when a permanent tooth begins to grow here, it simply does not have enough space in the dentition and will have to grow sideways. That’s why it’s imperative to keep an eye on your baby teeth and treat them on time!
We ourselves, out of ignorance, introduce some pathogenic bacteria into the baby’s oral cavity. Suffice it to remember my grandmother’s method of disinfecting a fallen pacifier: lick it and put it in the baby’s mouth. How many times have we done this? Did you feed the child with your spoon? Did you take turns biting an apple or a bun with him? Imagine for a moment the state of your teeth and the newly formed, not fully formed, delicate teeth of the child. What danger did you expose them to?
Foreign microflora is especially harmful to a child under 2 years of age, while temporary teeth are maturing in his mouth and their enamel is very vulnerable.
Leftover food also contributes to the rapid proliferation of bacteria in the oral cavity. A by-product of their activity is acid, which eats away the enamel of a baby tooth, leaving its delicate base - dentin - without protection. Then it’s a matter of little things: microorganisms penetrate the dentin and destroy it. This is how caries occurs. Outwardly, a diseased tooth may look normal for quite some time: a small black dot (the site of the lesion) is not too noticeable. But inside it can already be severely damaged, since caries of baby teeth, due to the softness of their tissues, develops much faster than permanent teeth.
There is also the so-called “bottle caries” - this is a brownish plaque on the front teeth. It is very resistant and cannot be cleaned with a brush. Such teeth rot quickly. This caries is called “bottle caries” because it is a consequence of feeding the baby from a bottle with sweet drinks and juices at night and throughout the night. Carbohydrates are known to be the best food for bacteria. Receiving such wonderful nutrition, pathogenic bacteria rapidly multiply and take over the entire territory available to them. It will be very difficult to force them to give up their positions. The development of “bottle caries” is also facilitated by the fact that at night the natural protector and cleaner of teeth – saliva – is almost not produced. While you are sleeping peacefully, your baby’s fragile little teeth are under powerful attack and are not protected by anything! Is it worth it to buy yourself a vacation at such a price?
Dangerous complications of caries are pulpitis and periodontitis.
Pulpitis is an inflammation of the pulp (the core of the tooth, filled with vessels and nerve fibers). In children, the pulp is practically insensitive, so they may not feel the usual sign of pulpitis - sharp pain. As a result, pulpitis of baby teeth may not be noticed even by an attentive parent, and the role of preventive examinations by a dentist is irreplaceable here.
If bacteria pass through the root of a baby tooth and enter the gum tissue, inflammation begins - periodontitis. Severe pain and fever are already guaranteed here. The gums become red and swollen. Periodontitis is a serious disease, and a child should never be exposed to it.
By visiting your dentist in a timely manner, you can avoid all these troubles. Caries is very easy to treat. Here, however, the first question comes to mind: where exactly to turn. It turns out that the approach to the treatment of baby teeth in different clinics is very different.
Traditionally, caries of primary teeth is treated “in a hurry”: a small child usually does not really want to endure while the doctor picks around his mouth, so the doctor tries to somehow clean the damaged area and fill it with quick-hardening material. As a result, the affected teeth remain untreated and may soon become inflamed again or completely collapse. Sometimes you even have to put crowns on baby teeth.
“The Nutcracker” uses all the possibilities of modern medicine to provide comprehensive care to the smallest patients: from composite materials to “laughing gas” and Sevoran anesthesia. We are convinced that the treatment of primary teeth should be of high quality, and the child’s impressions of the clinic should be the most pleasant.