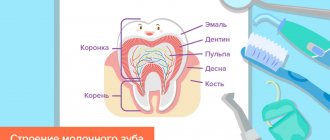
Pathologies of hard dental tissues are not always the result of caries and other inflammatory processes. A wedge-shaped tooth defect only superficially resembles an old carious lesion. The mechanism of development of this pathology is different and not fully understood.
With a wedge-shaped defect, the enamel is deformed at the place where the dental crown adjoins the gum. At first it is a rough, matte hole, then the planes of the lesion close together and are shaped like a wedge (the letter V).
Why a wedge-shaped tooth defect develops is still unknown. There are several theories and they all consider excessive stress on tooth enamel.
Content:
- Why is the position of teeth in a row disturbed?
- Can a crooked tooth fall back into place?
- Consequences of crooked teeth in children
- When should you go to the dentist?
- Devices for correcting uneven teeth
- Prevention Tips
Uneven teeth in children are not only an aesthetic defect. Unfortunately, dental problems can have serious consequences. These include: eating disorders due to improperly chewed food, dysarthria, caries. Due to the uneven arrangement of units in the dentition, plaque accumulates on the enamel due to insufficient hygiene. This leads to the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria, which provokes the formation of caries. That is why you should be careful about your teeth from an early age. My child has uneven teeth, what should I do? It is necessary to visit the pediatric dentist at least twice a year for a preventive examination. Recommended age: children over three years old.
How is filing of front teeth performed?
The technique of filing teeth varies depending on the condition of the oral cavity, the current diagnosis and treatment goals. Teeth filing begins with a detailed diagnosis. The specialist evaluates the feasibility of the procedure and identifies the teeth that need correction. For an accurate diagnosis, an examination is carried out, the causes of the disease are studied, and a treatment method is determined. The procedure consists of simple steps:
- Determination of the working area. For this, wax plates or special aerosols are used. The use of additional means allows you to mechanically highlight or paint an area that stands out from the general row and prevents the normal closure of teeth. In particularly advanced situations, it will be necessary to create a plaster model of the client’s jaw;
- Anesthesia if a large layer of hard tissue is to be removed;
- Direct filing with a diamond bur. On chewing teeth, the enamel is removed in the areas of protruding cusps. In the case of incisor processing, multidirectional movements are used to create the correct tooth shape;
- Grinding the surface, using products to replenish the deficiency of enamel minerals, as well as drugs to reduce sensitivity and strengthen dental tissue.
After filing, the thickness of the enamel changes, so sensitivity often increases. This phenomenon is temporary and for some time after treatment it is better to refrain from eating too hot or cold food. If the problem does not go away, it is better to consult a dentist.
Why is the position of teeth in a row disturbed?
Why do teeth grow unevenly? There are several reasons, the main ones are listed below.
- Hereditary predisposition. If parents or other close relatives first developed dental problems in childhood, the risk of acquiring an uneven row of teeth increases significantly.
- Deficiency of calcium, phosphorus and other nutrients in the body. The cause may be both nutritional deficiency and digestive tract disorders.
- Pathology that arose in the antenatal period. Due to excess or lack of amniotic fluid, entanglement with the umbilical cord, and the influence of teratogenic drugs, birth defects appear.
- Diseases of the upper respiratory tract, leading to changes in the function of external respiration.
Factors such as irrational and unhealthy diet, pathology of jaw and dental growth also influence. All this leads to the child’s teeth growing unevenly.
Dental hypoplasia - symptoms and treatment
Hypoplasia is a malformation of the hard tissues of one or an entire group of teeth [13]. It can be congenital or acquired. It develops when the rudiments of milk or permanent teeth are formed. It is not a carious lesion.
Hypoplasia is accompanied by a heterogeneous color of the enamel, its thinning and changes in relief - depressions of various shapes and sizes (from dots to grooves and pits). When teeth erupt, they immediately differ: there are white, yellow or brown spots on their surface.
Otherwise, such dental damage is called hereditary hypoplasia, aplasia, dysplasia or brown enamel dystrophy, and the affected teeth are grooved or plaster [1].
Statistics
Hypoplasia is the most common non-carious lesion of hard tooth tissues - enamel and dentin. It occurs in 50% of children with chronic metabolic disorders that arise before or after birth [10].
As a dental examination of the Russian population in 1999 showed, the prevalence of non-carious lesions among children 12 years old is 43.5%. At the same time, systemic enamel hypoplasia accounts for 36.7% [1].
The most common form of the disease is systemic hypoplasia - damage to all teeth in the permanent or primary dentition. It accounts for 90.6% of all types of hypoplasia [1]. More often, the defect affects the cutting edges or cusps of the teeth. In three out of five cases it develops in children under 9 months of age.
In foreign literature, hypoplasia of molars and incisors (lateral and anterior teeth) is called Molar Incisor Hipomineralisation (MIH) [1]. This form of the disease is common throughout the world [18]. The increase in its incidence of MIH can be explained by stress, deterioration of the general condition of the body, and the negative influence of the environment and food [17].
Causes and risk factors
The development of hypoplasia is associated with metabolic disorders at the time of formation of tooth buds. This is facilitated by external and internal negative factors that affect the body of the expectant mother or her already born child.
Intrauterine factors include:
- Rh conflict (incompatibility of the negative Rh factor of the mother and the positive Rh factor of the child);
- toxicosis and other disorders in the body of a pregnant woman;
- rubella, toxoplasmosis during pregnancy;
- taking tetracycline by a pregnant woman (or a child) [5].
Internal factors associated with child diseases:
- Down syndrome, cerebral palsy and other lesions of the central nervous system (they are both the cause of hypoplasia and associated pathologies) [4];
- rickets or infectious diseases in a child (measles, scarlet fever);
- hypo- and vitamin deficiency;
- changes in mineral and protein metabolism in dyspepsia (digestive disorders) and diseases of the endocrine glands (usually the thyroid gland) [3];
- penetration of infection from the inflammatory focus of a baby tooth into the germ of a permanent tooth.
External factors:
- prematurity, low birth weight of the newborn [16];
- artificial feeding of a child;
- local impact on the tooth germ, for example, birth trauma;
- trauma to the jaws and rudiment at the time of tooth formation.
If pathological factors affect the fetus, hypoplasia of baby teeth develops. If this happens in early childhood, the rudiments of permanent teeth are already affected.
Can a crooked tooth fall back into place?
The main question is: does the structure of teeth change over time? Can crooked teeth in childhood cause malocclusion in the future? It is impossible to answer the questions posed unequivocally. The fact is that under the influence of the above reasons for the formation of uneven teeth, the structure of the molars changes. A wide gap forms between the teeth or they grow close to each other. A child has uneven teeth: what to do? First of all, don't panic. In childhood, active growth of the dental apparatus is observed. It is in the period up to 18 years that they are most sensitive to the treatment. At the first suspicion of the formation of uneven teeth, you should immediately seek advice from a pediatric dentist.
Why wedges form on teeth and what to do about it
The defect can develop on both the upper and lower jaw, on one or more teeth. Most often, canines and premolars are affected - namely, they experience a large chewing load. The disease develops gradually and unnoticed. Over time, the defect deepens into the dentin, and the person feels pain. If the problem continues to be ignored, the base of the tooth becomes so thin that it can break.
A wedge-shaped defect appears in people of different ages, including teenagers. However, the older the person, the greater the risk of developing pathology.
The moment of appearance of the wedge-shaped defect cannot be tracked independently. But if you undergo regular examinations with a dentist, treatment will begin on time and will be completed with minimal time and money.
At first glance, a wedge-shaped defect can be confused with cervical caries. The affected teeth are marked with triangular-shaped spots and depressions, up to 4 mm in depth in the acute stage of development.
As for where wedges on teeth come from, there are three generally accepted theories:
- Chemical. The culprit is aggressive acids from food, drinks and resulting from an imbalance in the acid balance of the oral cavity.
- Mechanical. The defect is caused by an external load.
- Physico-mechanical. Pathology develops in response to improper chewing load.
Consequences of crooked teeth in children
Due to the fact that a child's teeth grow unevenly, many problems may arise in the future. The fact is that the speech apparatus is formed quite early. From the first months, the child learns to speak correctly, pronounce individual letters and even words. If a baby has dental problems, they will immediately manifest themselves from the first years. The first and most common complaint is the smile. The child will be embarrassed about his smile due to the incorrect position of his teeth. In addition, due to dense dentition, the quality of hygiene procedures decreases. In some cases, additional flossing may be necessary each time you eat. If a child's front teeth grow unevenly, they may even experience headaches. Pain in the neck area is also a common occurrence. This pathology occurs due to excessive tension in the temporomandibular apparatus.
Example 3
| Before orthodontic treatment | After orthodontic treatment |
Here, orthodontic treatment with braces has significantly improved the appearance of the teeth, but when everything is “not very good,” then little things do not attract attention. When the teeth were aligned, the uneven edges of the teeth became very noticeable (1), and the asymmetrical corner of the second incisor also stood out (2). Since this problem is easily solved, and the necessary specialist is in the same clinic, then why leave any imperfections? A comprehensive approach to dental aesthetics is necessary for the best results.
This is what happened as a result of the work of an aesthetic dentist after orthodontic treatment:
In this case, laser teeth whitening and restoration of the front teeth with light-curing material Estelite (Japan) were performed.
When should you go to the dentist?
What to do if a tooth grows unevenly? The only correct answer is to seek help from specialists at a dental clinic where children's doctors are seen. You should be examined at least twice annually to monitor the dynamics of the process. You should go to the dentist if your child has unevenly set teeth. After the conversation and diagnostic measures, the dentist will be able to give an accurate answer. Treatment may require special devices that should be worn for a long time. Mouthguards, braces, trainers and other devices for changing malocclusion will help cope with the problem.
How to prevent the development of a defect
If the wedge-shaped defect is not treated, the disease will develop and the tooth will collapse. But treatment methods have their drawbacks, they are not durable enough and do not guarantee that the pathology will not invade neighboring teeth.
To avoid an unpleasant disease, you need to take into account risk factors and take care of your own health and dental condition.
The most important preventive measures:
- brush your teeth correctly and choose oral hygiene products;
- undergo regular examinations in good dental clinics;
- trust dental manipulations only to a trusted orthodontist;
- correct the bite in time;
- promptly treat periodontal diseases;
- exclude soda and sour juices. Eat fresh foods containing enough vitamins and minerals;
- promptly identify and treat diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, nervous and endocrine systems.
Devices for correcting uneven teeth
There are several reliable and effective treatment methods. They differ from each other in some respects. To choose the best option, you should talk to a pediatric dentist who treats children’s teeth. Trainers and removable plates.
They can be used from an early age. Recommended age is 4-6 years. In this case, it is necessary to wear trainers every day; they are often worn at night. The significant difference is that the device is removable.
Aligner trays.
They begin to wear them at the age of 16.
You need to wear them constantly and take them off only when eating. Braces.
They are given mainly to persons over 18 years of age. They need to be worn for a long time, on average about two years.
Prevention Tips
How to prevent the formation of an uneven bite? There are some tips:
- provide the child with proper and balanced nutrition according to his age from the first years of life;
- closely monitor the child’s health;
- prevent the formation of incorrect habits, such as constant chewing on one side or sucking fingers;
- Carry out thorough oral hygiene every day.
It should also be noted that once a child reaches 1 year of age, he should be weaned off pacifiers. The fact is that mechanical action changes the structure of a child’s front teeth. The pacifier can be replaced with special vestibular plates that repeat the anatomical features of the structure of the child’s teeth.
Example 2
In this work, after orthodontic treatment, a chipped corner of the second upper incisor on the right (2) and an asymmetrically short incisor on the left (1) became more noticeable; the teeth had an uneven color, the upper front tooth was darker (3). It was not possible to change the color of the front tooth only by bleaching, since the dark tooth was previously depulped and darkened from the inside. After some teeth whitening to brighten them overall and restoration of the four upper teeth with veneers, the smile became perfect. By installing veneers on the teeth, we solved several problems at once: evening out the color of the front teeth, eliminating chips and uneven edges, and correcting the length of the second incisor.