Dangerous symptoms How to relieve pain?
Allowed painkillers When can teeth be treated? Is it possible to take an x-ray Prevention Toothache during pregnancy is a common occurrence. During this period, changes in the hormonal background of metabolism occur, and the woman’s body becomes very vulnerable. Pregnancy often serves as a catalyst for oral problems. Teeth begin to react to cold and hot. Painful sensations occur during hygienic cleaning, and gums may bleed. The acidity of saliva increases, the dentition is exposed to increased bacterial load.
There are more than enough reasons for toothache. Even with regular oral care and visits to the dentist, almost half of women during pregnancy experience caries, gingivitis, periodontitis, stomatitis and other inflammatory dental pathologies. If your tooth hurts during pregnancy, you should immediately go to the dentist.
Toothache cannot be tolerated, especially during pregnancy. Painful attacks negatively affect the functioning of the nervous and cardiovascular systems and can provoke involuntary contractions of the uterus and even premature birth. The opinion that it is undesirable to treat teeth during this period is a dangerous misconception. Even initial caries during pregnancy progresses much faster. Modern dentistry offers many effective means and treatment methods that are safe for the expectant mother and baby. The doctor selects treatment individually, according to the clinical picture and stage of pregnancy.
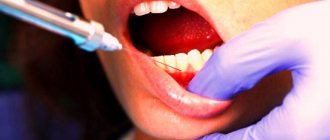
What symptoms should you consult a doctor for?
Any acute inflammatory diseases of teeth and gums are subject to urgent treatment. Even the smallest carious cavity is a source of infection, potentially dangerous for the developing fetus. If a carious tooth is not treated in a timely manner, pulpitis and periodontitis may develop, accompanied by severe pain and other symptoms.
You should immediately go to the dentist if the following symptoms appear:
- tooth reaction to cold, hot, sweet;
- pain (sharp, aching, throbbing);
- bleeding gums;
- pain when biting, chewing;
- redness, swelling of the gums;
- bad breath;
- purulent discharge
Urgent help
necessary for injuries - fracture of the tooth root, chips, cracks of the coronal part, damage to the pulp.
In the normal course of pregnancy, in the absence of risk factors for the mother and fetus, treatment of emergency or potentially dangerous conditions is carried out at any stage (in any trimester). The main contraindication to treatment is the threat of miscarriage. Each trimester has its own characteristics that determine the choice of treatment method.
Contraindications and limitations to treatment
A contraindication to dental treatment for a pregnant woman is any procedure that can directly or indirectly harm the body and cause premature birth. Such procedures include the following:
Implant treatment
Both healthy fetal development and complete implant healing require large amounts of calcium. During pregnancy, the body is unable to produce enough mineral to support both processes. Even taking vitamin and mineral complexes sometimes does not give the desired effect. Therefore, every gram of calcium counts.
An additional danger during treatment is the need for X-ray monitoring of the implant installation, as well as the prescription of medications during the recovery period. The latter can have a general toxic effect not only on the pregnant woman’s body, but also on the developmental processes of the fetus.
Professional whitening
During bleaching, the enamel is damaged, which due to pregnancy may be somewhat depleted in mineral composition. Due to the fact that most of the calcium produced goes into the fetus's body, it may not be enough to restore the top layer of enamel. The result is increased sensitivity and microcracks.
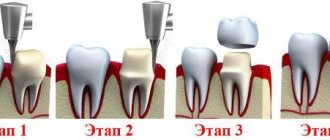
Prosthetics
Installation of fixed dentures requires special preparation: preparing the tooth and forming a stump for the crown, removing the dental pulp, filling the root canals. The installation of crowns is contraindicated for pregnant women in the 1st and 3rd trimesters. In the 2nd trimester, in emergency situations, removable prosthetics are allowed.
Tooth extraction
Removal of teeth that are not the cause of discomfort (impacted or dystopic) is contraindicated during pregnancy. If there is a possibility of rescheduling the operation and there are no obvious clinical signs (pain, redness and swelling of the gums), then in order to prevent the development of infection, it is better to refuse the procedure before delivery.
Emergency cases requiring immediate tooth extraction:
- Fracture of the root or crown of a tooth.
- Pulpitis of wisdom teeth.
- Carious lesions of the tooth root.
- Periodontitis.
- Tooth root cysts.
- Destruction of more than 50% of the tooth, accompanied by unbearable pain.
Antibacterial therapy
Antibiotics during pregnancy are prescribed strictly according to indications and taking into account the duration of pregnancy. For treatment, those groups of drugs that do not have a teratogenic effect are selected.
How to relieve pain yourself
Rinsing with a soda solution (1 teaspoon of soda per glass of warm water) will help temporarily relieve toothache during pregnancy. You need to rinse your mouth more often, every 2 hours. In addition to soda, you can use Furacilin solution, decoctions of medicinal herbs - chamomile, oak bark, yarrow.
Not recommended
use herbs containing essential oils (sage, eucalyptus, peppermint, cloves, etc.), they can cause severe uterine cramps.
Severe dental pain during pregnancy can be treated with a suitable anesthetic. Steroid-based drugs and drugs that penetrate the placental barrier are contraindicated.
Causes of labor pain
According to many years of observations by doctors and data from physiologists, many women experience almost no pain during contractions and pushing, behave quite actively or can even sleep. This cannot be called a phenomenon, since the source of labor pain is based in the cerebral cortex and is often activated by fear or confidence that pain is about to come.
In fact, when psychological factors are eliminated, expectant mothers experience only a pulling sensation in the lumbar region, where the nerve node is located. It innervates all the endings responsible for the female internal organs. Also, unpleasant mild pain appears in the lower abdomen at the moments when contractions occur. The reasons that more than seventy percent of women experience severe pain during labor lie in the structure of the female body, a sedentary lifestyle and prejudice.
Scientists who studied the life of small peoples of the Amazon and the Far North, where signs of civilization are practically invisible, were amazed at the ease with which native women give birth to children. They work physically, quite hard, until the onset of contractions, then retire for a while and return with the child in their arms. There are no signs of suffering on their faces. This happens, according to researchers, due to physical activity and the lack of psychological impact on girls.
In the cultures of such peoples, the process of pregnancy and childbirth is perceived as a taken-for-granted act, to which no special significance is attached. And every girl knows from childhood that, just like her mother, aunts and sisters around her, she will become pregnant and give birth to a baby. Of course, if complications arise, the woman most often dies, but in those cultures death is an absolutely natural phenomenon that is not given much importance.
In civilized countries, girls are taught from childhood, on a subconscious level, from the TV screen and from the pages of books, that pregnancy and childbirth are fraught with many dangers and the process of giving birth to a child is accompanied by enormous pain. Added to this is the sedentary lifestyle of most women, overeating and chronic diseases. All these factors together create the preconditions for a painful birth.
Take the first step
make an appointment with a doctor!
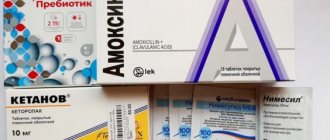
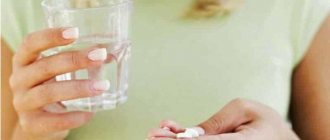
What painkillers can pregnant women use for toothache?
The most suitable painkillers approved by WHO are Paracetamol, No-shpa
(or its analogue
Drotaverine
).
Children's gels will help reduce pain - Kamistad
,
Kalgel, Dentol-baby
. These are specialized products designed to reduce pain during teething. They pleasantly cool the gums and relieve inflammation.
You must understand that taking medication is a last resort before seeing a doctor. Tablets will temporarily relieve pain, but will not get rid of the underlying problem. Pregnancy is not a disease, but a special physiological state, so treating teeth during pregnancy is not only possible, but necessary.
Drug pain relief
For drug pain relief during childbirth, analgesia and anesthesia methods are used. They differ in that during analgesia they use drugs that only partially reduce pain, while during anesthesia the patient is completely anesthetized, often with the loss of motor functions and consciousness.
Analgesia is provided both during contractions and during childbirth, and anesthesia is most often used during a cesarean section, that is, during childbirth. Epidural anesthesia occupies a special place in this classification - it is used both to relieve pain during contractions and for anesthesia during childbirth or during surgery.
Take the first step
make an appointment with a doctor!
When is the best time for pregnant women to have their teeth treated?
If a woman took a responsible approach to pregnancy and had her teeth treated in advance, she still needs to visit the dentist regularly for preventive examinations. This will allow you to detect pathology at an early stage and use the safest treatment methods. When performing any dental procedure, not only the woman’s well-being matters, but also the duration of pregnancy. Each trimester has its own characteristics and risks that determine the choice of treatment method.
First trimester
1st trimester
– period
from 1 to 12 weeks
inclusive. At this time, the formation of organs and structures of the embryo occurs. The placenta does not yet protect the fetus well enough from external influences, and the woman’s body undergoes serious changes: hormonal, physiological, metabolic. Any interventions, including medications, can negatively affect the pregnancy process and the health of the baby.
If a pregnant woman has a toothache in the 1st trimester, treatment is carried out mainly using gentle methods
(ICON, ozone therapy, air abrasive method). For pulpitis, periodontitis, accompanied by acute pain and purulent discharge, local anesthesia based on articaine (Ultracaine, Melivastesin, Mepifrine, Skadonest) is used.
Second trimester
2nd trimester
– period
from 13 to 24 weeks
.
This is the safest time
for dental treatment, gum treatment, professional hygiene and other dental interventions. The tissues, organs, and systems of the fetus have already been formed; the placenta reliably protects the baby from external factors. All planned procedures are recommended to be performed during this period.
Third trimester
3rd trimester
– the period
from 25 weeks to childbirth
, quite difficult for a pregnant woman.
The stress on the body increases, the placenta becomes more susceptible to external factors. Treatment is carried out exclusively for acute conditions
that are dangerous for the mother and child. Planned procedures are postponed until the baby is born.
If there is a need for dental treatment in a pregnant woman, a new generation of anesthetics based on articaine is used. The components of these drugs do not penetrate the placental barrier, do not affect the uterine and placental blood flow, do not increase the tone of the uterus, and are safe for the expectant mother and child. An alternative to local anesthesia is treatment under sedation (during sleep).
2nd trimester screening
Health control is extremely important for the expectant mother. Regular examinations and tests prescribed by the doctor are necessary to ensure that the pregnancy is proceeding normally and the child is developing correctly.
This is the purpose of the second screening during pregnancy. The optimal time for its completion is in the 18th week, the recommended time interval is from the 17th to the 20th week. During screening, a woman will need to undergo blood and urine tests and an ultrasound. Doctors focus on:
- hormonal examinations;
- monitoring the function and condition of the kidneys;
- hemoglobin level in the blood to eliminate the risk of iron deficiency anemia;
- anatomical ultrasound examination of the fetal anatomy.
“In the first trimester, we do an analysis of the level of glucocorticoid hormones,” explains Evgeniy Petreikov. — In the second, we take this hormone again and look at the dynamics. If abnormal glucocorticoid levels are detected, replacement therapy should be prescribed as early as possible to reduce the risk of developmental delays, late miscarriage and premature birth.”
To exclude the risk of developing diabetes mellitus in pregnant women, a glucose tolerance test is performed from the 24th to the 28th week. Even if a woman has no prerequisites for developing the disease, she still needs to be examined. The expectant mother is asked to drink a glucose solution and blood is taken after an hour and two hours. Based on the obtained blood glucose levels, a “sugar curve” is constructed. If it passes above normal values, gestational diabetes mellitus is diagnosed. It requires mandatory monitoring by doctors and the woman herself.
pixabay.com/
Is it possible to do x-rays?
Contrary to popular belief, X-rays can be taken during pregnancy. For this purpose, computer radiovisiographs are used. The radiation dose received by the patient when using a visiograph is minimal. If possible, the study should be carried out in the 2nd trimester
, excluding cases where urgent help is required - severe, acute pain in the teeth during pregnancy. X-ray examination is carried out observing all possible means of protecting the fetus.
“Fighting” radiation on the visiograph, women calmly fly south to eat fruit and bask in the sun. Not knowing that during a 2-3 hour flight a person receives 20-30 μSv. This is a radiation dose equivalent to 10-15 images on a visiograph. Ionizing radiation differs from light rays only in wavelength and has a damaging effect only under certain conditions.
Introduction
Migraine is a common primary form of headache (TH), which manifests itself in the form of repeated attacks, often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, photo- and phonophobia.
The prevalence of migraine, according to various estimates, ranges from 2.6% to 21.7%, and the average rate is 14.7% [1]. In Russia, the prevalence of migraine reaches 20.8%, which is approximately more than 30 million people [2]. The prevalence of migraine in women is more than 2 times higher than that in men, and the highest prevalence of migraine within the female population occurs during reproductive age [3]. For this reason, issues of tactics for managing patients with migraine during pregnancy are of high relevance. Issues of pregnancy planning, as well as rules for taking medications for pain relief and approaches to preventive treatment of migraine during pregnancy are discussed very often.
Epidural anesthesia
Advantages
Epidural anesthesia is absolutely safe for the child; its use completely anesthetizes and relieves sensitivity, which is why it is often used during a cesarean section. The patient remains conscious, but feels absolutely nothing, however, with the introduction of small doses of anesthetics, some women feel uterine contractions.
An epidural anesthesia procedure is performed under local anesthesia in the lumbar region, then the doctor uses a thin long needle to insert a catheter into the spine, more precisely into its epidural space, through which a dose of anesthetic is administered, if necessary. After the procedure, you need to lie down for fifteen minutes, during which time the medicine will begin to act. The catheter is not removed until labor is over; patients are usually not recommended to get out of bed and lie down, but there is also a mobile version of epidural anesthesia.
According to reviews of patients who have undergone childbirth with this type of anesthesia, pain is practically not felt, especially if an additional dose of medication is administered in a timely manner. However, there are strict contraindications for this procedure:
- Various neurological diseases;
- placental bleeding or any other origin;
- use of anticoagulants or bleeding disorders.
And finally, refusal of such a procedure is also a categorical contraindication.
Side effects
Typically, when a woman thinks about the side effects of this type of pain relief, she thinks about paraplegia, spinal nerve damage, or respiratory arrest. However, these complications are rather exceptions. The main danger is the long-term consequences: headaches, severe back pain that can last for months. Drug therapy for such pain usually does not produce results and it only goes away over time. While the medication is in effect, the patient may experience chills, trembling, decreased blood pressure, and difficulty breathing. You must tell your doctor about all the symptoms so that, if necessary, he can prescribe symptomatic treatment. Difficulty breathing occurs quite often during epidural anesthesia. This is a consequence of too large a dose of the administered drug and requires the use of an oxygen mask.
Take the first step
make an appointment with a doctor!
According to the latest data from medical studies, the use of epidural anesthesia in almost half of the cases led to various difficulties during childbirth. Since the woman in labor cannot control the birth process and does not understand when to push. In forty percent of cases, this led to protracted labor, forceps on the baby's head and traumatic brain injuries to the child. The high probability of ruptures of the perineum and vagina during such childbirth also does not add advantages to such anesthesia.
Approximately forty-five percent of women who undergo it experience this reaction to epidural anesthesia. This is quite a lot and before agreeing to such a procedure, you need to carefully weigh and think it over.