What is a targeted dental photograph?
Another name for the procedure is targeted intraoral contact radiography - this is a simple and fast method of X-ray diagnostics in dental practice. Research is carried out in clinics using analog X-ray machines or digital radiovisiographs. The doctor gets the opportunity to examine both the condition of the tooth being examined and those located nearby.
- Carry out diagnostics. For example, detect the development of an inflammatory process.
- Evaluate the results of the therapy. This is necessary not only in the treatment of pulpitis, caries or other dental diseases, but also in preparation for prosthetics.
When using analog X-ray equipment, an image is created on film and then transferred to special paper. A digital device allows you to obtain an electronic photograph. If necessary, any area of the image can be enlarged on the monitor for a more thorough examination.
- Interproximal. Allows you to diagnose pathologies of the crown part of the tooth, detect the presence of carious cavities, as well as defects that can form under fillings and crowns.
- Periapical, allowing to assess the condition of bone tissue. This type of imaging helps monitor the quality of therapy provided.
The radiation dose for a dental x-ray is 2-3 μSv, which is very small. For comparison, with fluorography we receive a radiation dose of 500-800 μSv.
How to do dental x-rays
The procedure is carried out by a doctor in a specially equipped room. The implementation mechanism takes place in 4 stages:
- The patient sits in a chair. The doctor examines the problem area.
- A special apron is placed on the patient to reduce the adverse effects of x-rays.
- The doctor fixes the head of the subject to obtain a clear image.
- On the affected area inside the oral cavity behind the teeth or on the front side, using a digital visiograph, the doctor directs the beam.
The whole process takes 3 minutes. After 15 minutes, you will be given a photograph of your teeth on film or electronically (if necessary).
There may be the following reasons for taking a photo:
- Clarification of the development process of pulpitis, periodontal disease and caries;
- Check after removal of damaged teeth;
- Checking the quality of treated teeth;
- Determining the specific structure of teeth before installing a crown or bridge;
- Checking neoplasms.
During endodontic treatment, at least 3 photographs of the tooth are taken: 1. Photograph of the teeth at the diagnostic stage. It is necessary to determine the condition of the tooth, the shape and number of roots, and the treatment method.
2. A photograph at the stage of tooth treatment with endodontic instruments inserted into the tooth canals. The picture is displayed on the computer screen.
3. Control image after completion of treatment to check the sealed tooth canals.
Permissible radiation dose for dental x-rays
The radiation dose for a targeted photograph for a person is 3-5 μ3v. During the year, an adult is allowed to receive up to 1000 microns. Consequently, a patient can take from 80 to 90 images per year using an X-ray machine. The radiovisiograph will make it possible to take up to 400 images. This indicates the harmlessness of this manipulation.
Pros and cons of the diagnostic method
The use of a dental visiograph has a number of advantages compared to analog X-ray machines. First of all, it is an opportunity to get a clear picture of the tooth and the tissues around it. It is convenient to store the resulting images on a computer or other electronic media, printing them if necessary. A digital image allows a more detailed assessment of the clinical picture, since the image can be enlarged several times. In addition, digital dental radiography is a safe procedure. If necessary, multiple procedures may be performed. For example, during implantation, control images are taken before and after each implant is installed. And also after complete completion of prosthetics. The equipment used is characterized by a reduced level of radiation exposure. The dose of radiation that the body of the person under study receives is so small that it does not cause any harm to health. Most often, it does not exceed the natural background recorded in some megacities. Despite the large number of advantages, this method has disadvantages. For example, the image can be performed only in 1 plane covering a small area of tissue. Therefore, the maximum effectiveness of the method is achieved at the stage of early diagnosis or to control the quality of therapy already carried out.
X-ray diagnostics in pediatric dentistry
Author: Pauwels R
Extraoral radiography in pediatric dentistry
Extraoral radiography means that the probe and x-ray machine are placed outside the patient's mouth. The X-ray source and image receiver are combined to obtain the desired image quality. There are two ways to obtain extraoral radiographs: the first is to work with a stationary X-ray source and image receiver, and the second is to synchronously move the X-ray source and image receiver in opposite directions. The first method produces a planar radiographic image, while the other method produces a volumetric tomographic image. The latter implies a selected layer or a focused image layer, which ideally contains all the tissues of interest to the physician. A more detailed explanation is provided below.
Panoramic radiography
Panoramic tomography of the oral cavity, depending on the country, may be called panorex, pan, orthopantomogram (OPG), and dental panoramic radiography (DPT). They all refer to the same technique and the same image.
Equipment details
This method involves the X-ray source and image receiver moving synchronously in opposite directions, with the image receiver passing as close to the patient's face as possible. Thus, a selected layer of a certain thickness is created. The thickness of the layer depends on the width of the X-ray beam. The narrower the beam, the thinner the cut. The latter means a sharper image, but of course there is a limit.
Since the human head is not a sphere, a single point around which the probe and X-ray source rotate will not provide optimal imaging results. Therefore, the devices are designed in such a way that several turning points are used, which closely follow the shape of the dental arches. So the highlighted panoramic image layer is actually a 3D horseshoe-shaped slice through the patient's head with the jaws in the focused image layer.
Some machines allow you to adjust this shape, while others do not. The latter are usually cheaper and assume that all patients are standard. Obviously this is not true, and that the better the jaw shape is replicated, the better the image will be.
The X-ray beam used in panoramic radiography is a vertical, narrow slit-shaped beam that can be adjusted (collimated) in height according to the height and age of the patient (adult or child). This collimation is important in pediatric X-rays because it reduces radiation exposure and prevents radiation exposure to unnecessary parts of the head and neck. The X-ray beam is also tilted slightly upward (8–12°), which explains why structures in the neck or, for example, a forgotten necklace, will be projected onto the patient's chin in the final image (Figure 1). The fact that the X-ray beams are directed upward and do not pass through the patient from the front means that the use of a protective apron to protect the underlying thyroid gland is not required. In fact, a protective apron placed high on the patient's neck will unfortunately result in image artifact and the need to redo the exam without the apron. The latter will lead to an increase in radiation exposure to the patient; Therefore, when taking panoramic radiographs, it is better not to wear a radiation protective apron on the patient. However, local laws should always be observed.
It should also be emphasized that tilting the X-ray beam upward causes distortion.
Execution steps
Interproximal radiography is one of the types of intraoral examination that allows you to obtain a picture of 1 section of the oral cavity with an image of the upper and lower dentition. To obtain the image, a special holder is secured between the closed teeth. It allows you to identify interdental caries and various changes in bone tissue due to gum disease. And also check the correct installation of crowns, dentures or fillings. An X-ray of the tooth is taken by a doctor in an office specially equipped for this. Before taking an X-ray of a tooth, the doctor gets acquainted with the problem and studies its location.
To obtain a clear image of the problem area, the patient's head is fixed in the required position. The process of visiography takes a matter of seconds, but during this time the patient is required to remain completely still. The video in this article shows how to take targeted photographs of teeth so that the image is as informative as possible. Using a digital sensor, the radiologist directs a beam of rays to the required area. The photograph is taken either from the inside of the mouth or from the face. During the manipulation, the patient does not feel any pain or discomfort.
The original digital image differs from the traditional film image because it is processed using a special program in a few seconds and transferred to the monitor screen.
General information
An X-ray examination that allows you to get a real clinical picture of one or more teeth located nearby. A simple and reliable method for accurate diagnosis, used in most dental clinics.
Problems that can be solved by analyzing a targeted X-ray image:
- making an accurate diagnosis;
- drawing up a treatment plan with monitoring the dynamics of the condition;
- assessment of the degree of development of pathology;
- assessment of the restoration of hard tissues and the condition of the dental canals;
- assessment of the actual condition of blood vessels, soft tissues, rudiments;
- identification of pathologies in a latent course;
- identifying the area affected by caries, as well as identifying the source of inflammation.
Targeted X-rays are done using a digital radiovisiograph, which minimizes the radiation dose. The equipment produces a direct beam beam that directly affects the area being examined. The technique is absolutely safe for health.
Features of the procedure in children
Contact intraoral radiography can be prescribed for children in cases where tooth damage cannot be examined in any other way. The technique allows early detection of disturbances in the process of teething, bone tissue diseases, and prescribing effective treatment. In addition, this method allows you to control the implementation of orthodontic manipulations if the child has problems with the formation of the jaw.
The study is carried out in the same way as in adult patients. Children under 2 years of age are recommended to undergo x-rays only in case of urgent need. For example, in case of injury during childbirth, to monitor the development of the jaw, or after a fall from a height, to assess the integrity of the teeth.
Indications for use
Factors that determine recommendations for radiovisiography include:
- Pain in the dental area.
- Routine diagnostics prescribed to detect pathologies.
- The need to identify the degree of bone loss before implantation.
- Identified diseases of gum tissue, including periodontal disease.
- Determination of the severity of mechanical damage received.
- The need to control the growth of “eights”, or wisdom teeth.
- Checking the quality of root canal cleaning.
The procedure is mandatory before installing prosthetic structures or orthodontic devices, as well as when planning surgical intervention.
Restrictions and contraindications
How often a dental x-ray can be taken can only be determined by a doctor, guided by the severity of the problem and the patient’s condition.
It is forbidden to take dental x-rays during pregnancy, especially in the early stages. A woman needs to take care of the condition of her teeth in advance in order to eliminate the need for treatment while carrying a child. X-rays are contraindicated for children under 2 years of age.
In case of urgent need, an x-ray can be performed, but not earlier than the second trimester. The only exception is when emergency assistance is needed. Manipulation must be carried out using all possible means of protection. The period of breastfeeding is not a limitation for the study.
Interpretation of a dental radiograph
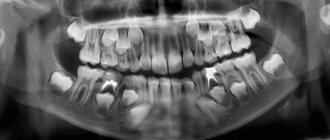
Only a dentist or radiologist can decipher and describe a dental image. The image shows the tooth: its root, internal canals, shape, anatomical features.
- Examines the rigidity, density and uniformity of the bone structure. Evaluates the location of each element of the dentition.
- Determines the presence of signs of clearing or darkening, indicating the development of an inflammatory process, cysts, granulomas, neoplasms.
- Depending on what the dental x-ray shows, a diagnosis is made.
Carious formations in the picture look like light areas of various shapes with unclear boundaries. The development of pulpitis is characterized by bone damage. The image shows a violation of its homogeneity in the interroot space. With the development of periodontitis, a granuloma appears in the area of the tooth root in the form of a darkened round shape with clear contours. With periodontitis, the image shows a decrease in the density of the bone structure, a decrease in the height of the partitions between the elements of the dentition, and the formation of “pockets.”
Kinds
Contact (pariapical)
It is carried out to obtain an image of the tooth in its true size - from the crown to the root and the hole in which it is located. As a rule, it is used to diagnose pathologies in the area of the tooth root. It also allows you to detect abnormalities in the structure of bone tissue. It is worth noting that this technique is ineffective if it is necessary to examine the condition of periodontal tissues.
When performing contact radiography with a conventional X-ray machine, film sizes of 2x3, 3x4 cm, 5x6 and 6x8 cm are used.
Interproximal
Justified in cases where it is necessary to obtain a clear and undistorted intraoral image to diagnose interdental or cervical caries and determine the degree of bone tissue resorption. Three or four photographs are taken to examine all teeth.
Occlusal (bite)
This technique is used if there is a need to examine several teeth at once (four or more), diagnose dystopic (improperly located in the dentition) and impacted teeth, study the condition of the hard palate, salivary glands, and detect neoplasms and cysts.
Occlusal radiography has proven its effectiveness in examining the dental system in children, as well as in cases where it is not possible to use the contact method due to an increased gag reflex, jaw injuries, and TMJ dysfunction. The main difference is that a film measuring 5x6 or 6x8 cm does not fit into the patient’s oral cavity, but is fixed between the closed teeth.
Long focal length
It differs from contact in that it allows you to get a clear picture of not only periodontal tissues, but also periodontal tissue (this method is actively used in periodontology). This result is achieved by using a device with a more powerful X-ray tube.
Digital radiography (radiovisiography)
Separately, mention should be made of the technology that is based on the use of a radiovisiograph. This computer device allows you to obtain targeted images of teeth with minimal radiation doses - ten times less than conventional film X-rays.
The resulting images are immediately displayed on the computer screen and then transferred to the attending physician's office, saving time.
Images can be stored for an unlimited time, they can be copied to digital media, or sent by e-mail for consultation with other doctors.
Where can I take a photo and how much does it cost?
Targeted radiography can be performed in any specialized medical institution. The average cost of the procedure is about 400-450 rubles. Some clinics include in the cost of conducting several studies at once, which involve monitoring the treatment being carried out.
All categories of patients, both adults and children, can take a targeted photograph of a tooth. The procedure is prescribed with caution to pregnant women and infants under 2 years of age.
A referral for a radiovisiographic image is given by a dentist. The resulting image makes it possible to determine the presence of a problem, confirm or refute the diagnosis, and prescribe treatment. To monitor the patient’s condition during treatment, the doctor may recommend taking a second photo of the tooth.
X-ray equipment
To obtain a targeted image, two types of equipment are used:
- X-ray machine of an outdated model;
- digital radiovisiograph (modern version).
The first allows you to get a film image that distorts the image quality. Using an innovative device, you can obtain an electronic image of high quality and resolution. For convenience, it is possible to enlarge the image with detail of the required areas.
The main advantage of the radiation machine is considered to be the minimization of radiation exposure (three times lower compared to the outdated version).
Using a digital camera you can take two types of photographs:
- Interproximal. It is used to assess the condition of the crown when treating caries with fillings, as well as to assess the correctness of prosthetics.
- Intraoral. It is performed to identify caries of nearby teeth and assess the quality of fit of the installed filling. This image is the most informative; it allows you to diagnose caries in the initial stages and identify periodontal pathologies.
How is the procedure performed?
X-rays are taken in a special room, and the procedure consists of several stages:
- The patient sits in a chair. The patient is wearing a protective apron to minimize the negative effects of x-rays.
- The doctor fixes the head in such a way as to obtain an image in the required area and asks the patient to sit still.
- The beam is directed onto the inner or outer surface. The procedure itself takes a few minutes, and it takes 10-15 minutes to prepare an electronic or printed image.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages of a targeted photograph performed using modern equipment:
- Safe diagnostic procedure.
- Clarity and image quality.
- The ability to zoom in on the desired area to see the details.
- Print the photo.
- Improving conditions for clinical research.
- Reducing the duration of the procedure.
Dentists consider this diagnostic method to be one of the most accurate and informative, since with the help of such an image it is possible to identify latent pathologies, as well as diseases in the initial stages, when they do not cause discomfort and are not visible to the naked eye.
The method under consideration also has disadvantages:
- limited scope of the study;
- photographs are taken from only one angle;
- a small viewing area, which allows you to evaluate no more than three teeth;
- inability to identify cracks in the buds and determine perforation.