Traditional methods of treating periodontitis
Today, dentists can offer many medicinal methods for treating periodontitis. However, some still prefer to deal with this problem with the help of “grandmother’s recipes.” Is it worth starting treatment for periodontitis with folk remedies or is it still necessary to go to the doctor?
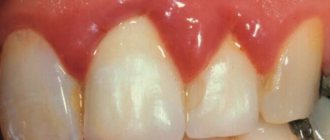
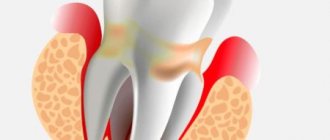
Periodontitis is an unpleasant disease from any point of view. It causes not only bleeding and painful sensitivity of the gums, loosening and displacement of teeth, but also bad breath, and also makes a person’s appearance rather unattractive. If treatment is not started in time, the acute local process will become chronic, and may even lead to tooth loss.
How to fight periodontitis
A dentist’s help with periodontitis involves making a correct diagnosis and prescribing adequate treatment, depending on the severity of the disease and the individual characteristics of the patient’s body. After carrying out the necessary medical procedures in a dental clinic, treatment of periodontitis should be continued at home. For this purpose, special solutions, medicinal herbs and various folk remedies are used.
Folk remedies
Improving and treating gums with periodontitis using folk remedies is possible only after professional sanitation of the oral cavity. If plaque and tartar are not removed, the gum mucosa will be constantly injured, and pathogens will cause inflammatory processes. Let's say you did everything right: you visited a doctor, performed professional hygienic cleaning, took a course of medication (if it was prescribed). Here's what else might help:
- Beekeeping products Honey and propolis have always been used for stomatitis - their safety and effectiveness make it possible to recommend them even to small children. And if you add viburnum or chokeberry to healing honey, you can get an excellent remedy for periodontitis. The mixture is prepared from one type of ground berries and honey in a 4:1 ratio, and is used as a dessert after meals. You can alternate viburnum and chokeberry daily. The duration of taking this tasty “medicine” is 25–30 days.
- Medicinal herbs For rinsing, a decoction of comfrey or an infusion of oak bark with linden flowers are useful. Crushed comfrey roots should be simmered over low heat for 20 minutes, then cooled and used for daily rinsing twice a day. An infusion of oak bark is prepared in the same way, but after boiling, linden flowers are added to it and allowed to brew. The ratio of oak bark and linden blossom should be 2:1. You should rinse your mouth with this infusion 4-5 times a day until the symptoms disappear completely.
- Vegetable oils A mixture can be prepared from sea buckthorn and fir oil to lubricate the gums. the procedure using it is carried out twice a day, carefully rubbing the mixture into the gums using gauze, which is wrapped around a finger. To achieve the desired effect (that is, relieve inflammation), you need to carefully, with smooth circular movements, massage the gums in this way both from the outside and from the inside.
Modern means
To treat periodontitis at home, modern pharmacological agents are also used - ready-made medicinal rinses and special toothpastes. The solutions have anti-inflammatory, disinfecting, antimicrobial and analgesic effects. Many of them contain not only chemicals, but also extracts of medicinal herbs, some contain antibiotics. Therefore, when choosing a medicinal solution or toothpaste, consult your dentist to ensure that the product is not only effective, but also safe.
Expert opinion
The use of folk remedies in the treatment of periodontitis at the initial stage is quite effective - provided, of course, that the disease is not in an acute phase and does not require urgent dental intervention, for example, to remove tartar that causes inflammation. “Medicines from the people” cope well with the problem of bacterial plaque during the prevention of various inflammatory diseases. And for chronic periodontitis, treatment with folk remedies is the most effective “weapon” from the entire arsenal of preventive measures that can prevent relapses of the disease. However, it is recommended to use folk remedies only under the supervision of a doctor, since they often cause serious allergic reactions that complicate the course of the disease. Therefore, before you undertake periodontitis treatment on your own, visit a dentist who will give you all the necessary recommendations taking into account the characteristics of your body.
Homeopathy
In cases where traditional means of therapy cause allergies or in severe general conditions of the body, homeopathic preparations . The following products have worked well:
- traumeel C
- echinacea compositum
- engystol
- mucosa compositum
These drugs stop inflammation in the periodontium and relieve swelling of the gums. They also stimulate metabolic processes in tissues and accelerate healing. Homeopathic remedies combine well in complex treatment with other medications. They are simple and easy to use. Side effects are extremely rare.
Preparations in the form of tablets and capsules are taken 1 piece 3 times a day. The duration of admission is not limited. The ointments are rubbed into the gums in the morning and evening until the main symptoms disappear permanently.
Remember! Treatment of periodontitis using traditional recipes must be agreed with the dentist. Self-medication in this case may not only not bring significant relief, but also cause a number of serious problems.
What contributes to the development of periodontal disease?
Factors contributing to the development of the disease:
- vascular disease and a tendency to form plaques;
- hormonal disorders;
- weakened immunity;
- side effects of medications;
- smoking;
- lack of vitamins;
- structural features of the gums and jaw.
Symptoms to watch out for:
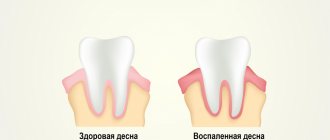
- Unexplained pale gums
- Redness
- Visible lengthening of the tooth due to the opening of the neck
- Increased sensitivity to hot and cold
- Periodic bleeding.
- Unexplained itching in the gums
- Loosening of teeth that begins with slight mobility.
Any of the above symptoms is a reason to consult a dentist. He will make a diagnosis and develop a treatment plan for periodontal disease. Whether it will be carried out entirely at home or with mandatory visits and medical procedures depends on the actual stage of the disease.
Clinical picture of the disease
Periodontitis is characterized by pronounced symptoms. If they appear, you should immediately consult a dentist. Characteristic features include:
- bad breath;
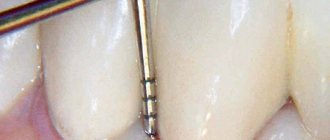
- the occurrence of pathological periodontal pockets;
- bleeding gums during brushing;
- increased tooth sensitivity to hot and cold foods;
- presence of a metallic taste in the mouth.
Treatment of gums at home
How to treat inflammation? There are many ways to treat gum inflammation at home. Dentists usually recommend antiseptic drugs with anti-inflammatory effects. The optimal treatment regimen is prescribed by the dentist after diagnosis. Let's consider the most effective treatment options.
Rinse with solutions
Rinsing with special solutions helps to quickly get rid of pain and stop inflammatory processes occurring in soft tissues. The compositions of the solutions disinfect the surface of the gums, destroying pathogenic bacteria. It is necessary to rinse your gums after every meal, 2 to 4 times a day. Some drugs in this group are used in pure form, others must be diluted in water.
To treat inflamed gums, dentists usually prescribe the following solutions:
- Furacilin;
- Chlorhexidine;
- Miramistin;
- Rotokan;
- Stomatophyte;
- Malavit;
- Listerine;
- Chlorophyllipt.
The listed drugs are usually used to prevent diseases of the oral cavity, reduce pain and reduce inflammation, but do not apply to independent means of treatment. Therefore, rinsing is usually prescribed in combination with other procedures.
Causes of periodontal disease in adults
Periodontal disease is a systemic disease that indicates not so much problems in the oral cavity, but rather malfunctions in the functioning of various organs. In most cases, pathology develops due to poor circulation in the gums. This is due to age-related changes, deterioration of immunity or certain diseases: diabetes, atherosclerosis, malfunction of the endocrine system, etc.
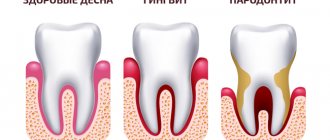
Differences between periodontal disease and periodontitis
Patients often confuse the names, and therefore turn to dentists, complaining of periodontal disease. In 90-93% of cases, ordinary periodontitis is detected. It is widespread. Our disease is rare.
Periodontitis manifests itself through:
- pain on palpation, when brushing teeth;
- bleeding;
- redness of the gum margin;
- swelling;
- cyanosis.
In severely advanced cases, there may also be headaches, fever and severe toothache. All this leads to refusal of food and hygienic cleaning of the oral cavity.
By place of development:
- localized - a small lesion affecting only one tooth; often results from mechanical damage to tissue;
- generalized - damage to several teeth also affecting the gingival and bone tissue.
According to the nature of the course:
- acute - characterized by sudden pain attacks and rapid development of symptoms;
- chronic periodontitis is the transition of untreated acute periodontitis to a chronic form, in which pain and other symptoms practically disappear, but the disease progresses and deforms the tissue.
Symptoms
This pathology has not only obvious signs (like the formation itself, which is visible without special equipment ), but also symptoms that do not appear externally, but are recorded solely from the patient’s words:
- the patient's field of view narrows ;
- visual acuity decreases;
- when looking at objects, their contours blur ;
- there is pain syndrome ;
- the eyes may become cloudy , and floating “spots” and dots appear before the eyes;
- redness of the conjunctiva is observed .
In patients with increased intraocular pressure, such symptoms are more pronounced and cause more discomfort.
Teeth in danger: how to recognize the disease
Thanks to advertising, even children know about caries. But periodontal diseases are still a closely guarded mystery. Let's eliminate this gap. Periodontitis is an inflammatory disease that affects the tissue around the tooth and gums. As a result, loose teeth and other unpleasant “bonuses” appear.
Periodontitis - symptoms:
- gums bleed, especially under stress (chewing hard food, brushing);
- sensations of itching and pulsation under the gums;
- bad breath even after hygiene procedures;
- the mucous membrane around the teeth changes color;
- dark hard deposits on the enamel;
- periodontal pockets and tooth mobility appear.
Signs of the chronic form:
- inflammation and swelling of the gums;
- the mucous membrane becomes bright red;
- discharge of pus from periodontal pockets;
- throbbing severe pain;
- weakness, general malaise, possible fever.
We continue to understand the features of the disease: to understand whether you belong to the “risk group”, you need to know where gum inflammation comes from.
Periodontitis - causes:
Insufficient oral hygiene is the most common reason. Residues of food, falling under the gums, provoke the formation of microbes and the development of inflammation.
Food poor in vitamins and microelements.
- The predominance of soft food on the menu. The gums do not receive the necessary “massage” and there is insufficient blood flow.
- Complications of gingivitis and stomatitis.
- Weakened immunity, chronic diseases (diabetes mellitus).
- Very tight fit of teeth to each other (crowding).
- Allergies to medications and chemicals.
It’s simply amazing when some patients want to get rid of an illness that takes years to develop in a few days. People ask how to treat periodontitis with folk remedies and sincerely believe that this is a panacea. We responsibly declare that “grandmother’s spells”, miraculous rinses and ointments will at most ease the pain, but will not stop the development of the disease.
Professional dentistry involves complex treatment of periodontitis - more complex and lengthy, but effective.
- Consultation with a periodontist is the first step. The doctor will make an accurate diagnosis and determine a further treatment plan. After the x-ray diagnosis, the specialist will be able to answer the questions: is it possible to save the teeth or will some have to be parted with;
- will tell you how to treat periodontitis , how much the procedure will cost;
- coordinates treatment and prosthetic options;
- will determine the sequence of methods in the clinic.
Preparations for the treatment of periodontal disease
Medications are rarely used in the treatment of periodontal disease, since bacterial inflammation rarely accompanies the disease. If necessary, the following drugs are prescribed:
- Carotinoly-M is an antioxidant of animal origin. Rejuvenates gums, saturates them with vitamins A, D, E, F.
- Heparin ointment thins the blood, stimulates microcirculation of periodontal tissues, and saturates them with oxygen.
- Troxevasin in gel form improves blood circulation, strengthens the vessels of the periodontal tissues, and has a strong anti-periodontal effect.
- Aloe extract. The course includes 20-25 injections into the gums every other day. The drug enhances cellular metabolism.
The duration of treatment is determined by the periodontist. As a rule, therapy lasts from 10 days to several months.
Antibiotics for periodontal disease
Patients are often interested in whether antibiotics are used for periodontal disease in adults? In the initial stages, this is not necessary, since there is no inflammatory process. However, severe degrees of the disease are sometimes accompanied by inflammatory complications. Here, treatment of periodontal disease with antibiotics is considered justified. What antibiotics do doctors usually prescribe for periodontal disease with inflammatory complications? These can be various drugs that help quickly stop inflammation.
How to cure periodontal disease forever?
Treatment of any disease begins with diagnosis. In the case of periodontal disease, which is often asymptomatic, the following procedures are performed to make a final diagnosis:
- examination of the oral cavity;
- probing of the gingival sulcus;
- X-ray examination (orthopantomography);
- biomicroscopy of the gums to determine the degree of microcirculation impairment.
The main factor confirming the presence of periodontal disease is a uniform decrease in the height of the interdental septa with alternating foci of osteosclerosis and osteoporosis in the deep parts of the alveolar process and the body of the jaw, as well as in other bones of the skeleton. As a rule, all these manifestations are displayed on an x-ray. The patient will also need additional consultation with a general practitioner and an endocrinologist to identify and treat metabolic disorders, diseases of the cardiovascular or endocrine systems, which often accompany the disease.
How to get rid of periodontal disease and finally prevent bone tissue destruction? Unfortunately, it is impossible to completely say goodbye to the disease. For this reason, treatment of dental periodontal disease is usually aimed at slowing down the process of periodontal dystrophy and preventing tooth loss, tissue inflammation and purulent bone damage.