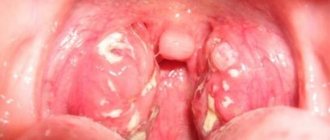
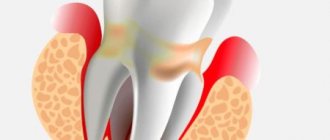
Chronic tonsillitis is a chronic inflammation of the tonsils.
The palatine tonsils (popularly called tonsils) are an important part of the human immune system.
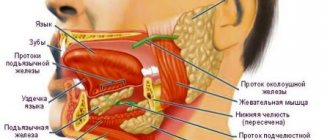
Bacteria, viruses, and microscopic fungi enter us with food and air. They settle on the mucous membranes, where they are picked up by a constant current of mucus, and this “river” flows in the direction of the oropharynx, just where the tonsils are located behind the palatine arches.
The palatine tonsils are like a sponge. They are dotted with gaps. When we swallow a bolus of food soaked in infected mucus, this mucus enters the lacunae of the tonsils. There, foreign microorganisms are attacked by the guard cells of the primary immune response: neutrophils and macrophages. The latter not only kill the infection, but also “cut” it into small molecular fragments, on which young cells of the secondary immune response—lymphocytes—are then “trained.” Prepared and trained lymphocytes emerge from the tonsils and “spread” throughout the mucous membranes of the pharynx and nose, forming a fairly reliable secondary specific defense.
Causes of chronic tonsillitis
In fact, inflammation occurs constantly in the tonsils - this is their function. But sometimes the protective resources of the tonsils are unable to cope with the infection, and then the inflammation, which gets out of control, turns into a serious disease - tonsillitis.
The acute form of tonsillitis is tonsillitis. Untreated tonsillitis often develops into chronic tonsillitis. Conversely, exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis leads to an outbreak of tonsillitis. If a person gets tonsillitis every year or several times a year, then he most likely has chronic tonsillitis.
Sometimes chronic tonsillitis can develop even if a person has not had a sore throat. This is possible if there is a source of infection that can affect the tonsils for quite a long time, for example, untreated caries or chronic sinusitis.
Operations for tonsillitis: from traditional methods to modern techniques
Indications for surgical treatment:
- The presence of episodes of exacerbation of the disease 2 or more times a year, with a predominance of purulent inflammation.
- Frequent (more than 4 times a year) exacerbations of tonsillitis, even if they occur without complications.
- Exacerbations are rare, but there are signs of complications from the heart, joints, kidneys or other organs.
- The disease is latent (hidden), but has become the cause of the development of rheumatism and other systemic diseases.
For a long time it was believed that chronically inflamed tonsils should be completely removed. This operation is called tonsillectomy. It allows you to eliminate the source of infection, but makes an uncorrectable hole in the protective lymphoid ring of the pharynx.
Currently, tonsillectomy is rarely performed, mainly in cases of severe purulent-destructive changes in the tonsils. In all other cases, ENT doctors give preference to organ-preserving operations, trying to leave an island of functionally active tonsil tissue.
But resection (partial cutting off of the tonsils) carries the risk of relapse of the disease. After all, such a procedure does not guarantee the elimination of all inflamed and infected tissue. The use of a laser improves the result due to an additional disinfecting and immunomodulating effect in the surgical area, but still does not completely solve the problem of relapses. Nevertheless, laser technologies are recognized as a priority in the treatment of tonsillitis.
Symptoms of chronic tonsillitis
The inflammatory process in the tonsils can spread to neighboring organs, and then the person may complain of nasal congestion, sore throat, dry cough, and these secondary symptoms may be predominant.
With chronic tonsillitis, there may also be complaints of pain in the joints (knees, elbows, wrists), especially in the evening and when the weather changes, fleeting pain in the heart, a feeling of palpitations without physical activity, pain in the lumbar region. The ECG may reveal arrhythmia and tachycardia.
Such symptoms are a serious cause for concern, since they can accompany the development of severe autoimmune diseases of the kidneys, heart, and nervous system, which are complications of tonsillitis. This occurs when inflammation in the tonsils causes the immune system to malfunction; as a result, antibodies are produced, but not to the causative agent of the disease, as it should be, but to the heart muscle, joint tissue and connective tissue. When the body's defense system is upset, it tries to destroy the body itself.
The insidiousness of chronic tonsillitis also lies in the fact that it can occur without obvious symptoms. In this case, between outbreaks of sore throat, the person does not complain of anything, although a focus of inflammation remains in the tonsils.
The main symptoms of chronic tonsillitis itself are:
Sore throat
With chronic tonsillitis, there is pain in the throat when swallowing, especially in the morning. The appearance or intensification of such pain can be caused by swallowing cold food or liquid.
Feeling of discomfort in the throat
There may be no pain as such, but there may be discomfort when swallowing, a sensation of a foreign body in the throat.
Low-grade fever
With chronic tonsillitis, there may be a temperature that does not decrease over a long time (37.2-37.5°C).
Bad breath
Inflammation in the tonsils can manifest as persistent bad breath.
General weakness
Typical manifestations of chronic tonsillitis are increased fatigue, sweating, weakness, and poor health.
Chronic form of tonsillitis, why the tonsils become inflamed
Infection is the main cause of inflammation of the tonsils. The acute form of the disease in 70% of cases is caused by viruses, the remaining 30% is caused by bacterial and fungal flora. Therefore, sore throats most often accompany acute respiratory infections and are seasonal.
Damage to the tonsils in chronic tonsillitis in 80% of cases is of a bacterial nature. The main causative agents of the disease:
- β-hemolytic streptococcus.
- Group A streptococcus.
- Staphylococcus aureus.
- Haemophilus influenzae.
- Rarely encountered bacteria: mycoplasma, chlamydia, etc.
Viruses in the chronic form of the disease have a predominantly provocative, destabilizing effect. Acute and chronic recurrent viral infections weaken the immune defense, which creates conditions for the activation of bacterial flora. Hypothermia, acute intoxication, and ingestion of cold or irritating food lead to the same result.
Treatment methods for chronic tonsillitis
It is very important to defeat chronic tonsillitis: otherwise, there remains a constant source of infection and intoxication of the entire body, not to mention the threat of severe autoimmune complications.
Home methods can reduce the severity of symptoms, but achieving a complete cure is difficult. Tonsillitis is a disease that is too complex in its nature and course. Therefore, if you suspect chronic tonsillitis, you should consult a doctor.
First of all, a comprehensive examination should be carried out to determine the pathogen and the stage of development of the disease.
Before treating tonsillitis, it is necessary to eliminate other sources of infection - cure carious teeth, inflammatory processes in the nose and paranasal sinuses. If your child often suffers from sore throats, then it is very likely that one of the family members is a carrier of the infection. In this case, it makes sense to get the whole family examined.
With complaints corresponding to the symptoms of chronic tonsillitis, you can contact a general practitioner (family doctor or therapist) or a specialized specialist - an otolaryngologist (ENT).
Children's appointments are conducted by qualified pediatricians and ENT doctors.
The Family Doctor clinics have the necessary equipment and a staff of qualified specialists to conduct examinations, establish diagnoses and perform all procedures in accordance with the prescribed course of treatment, and, if surgical treatment is required, to perform operations.
In the treatment of chronic tonsillitis the following are used:
Washing the lacunae of the tonsils
The course of treatment for chronic tonsillitis, as a rule, involves washing the lacunae of the tonsils using vacuum drainage. During rinsing, various anti-inflammatory drugs are used that penetrate deep into the tissue, destroying microorganisms that multiply in the tonsils.
Physiotherapy
In parallel with washing the tonsils, physiotherapeutic procedures (treatment with short-wave ultraviolet radiation, magnetic laser therapy, phonophoresis) can be prescribed.
More information about the treatment method
Antibacterial therapy
If chronic tonsillitis is caused by a bacterial infection, it is treated with antibiotics.
More information about the treatment method
Surgery
If the inflammatory process has gone far enough, surgical treatment methods are used. At JSC “Family Doctor” you can use the modern method of laser tonsillotomy. Laser tonsillotomy is a high-energy treatment of the palatine tonsils, in which only the affected part of the tonsils is removed. The tonsils themselves are preserved, if possible, which is very important for the immune system. In the most severe cases, the tonsils are completely removed.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating
How to be treated correctly
Competent treatment of chronic tonsillitis includes a set of measures to eliminate infectious inflammation and deep sanitation (cleansing) of the tonsils. This is necessary to prevent relapses of the disease, suppress allergic and autoimmune processes, and restore the protective function of the pharyngeal lymphadenoid ring.
Common mistakes when treating tonsils:
- Only local medicine for sore throat is used, with the rejection of recommended systemic antibacterial therapy.
- The drug is selected by the patient independently, without taking into account the nature of inflammation, composition and sensitivity of the microflora.
- Drugs for the treatment of chronic tonsillitis are taken haphazardly, or instead of recommended medications, a folk remedy for the disease is used.
- Early cessation of treatment, therapy is completed soon after the sore throat subsides and other symptoms of exacerbation decrease.
- Avoidance of treatment between periods of exacerbation, refusal of proposed surgery.
- Late visit to the doctor, at the stage of complications.
This approach is the main reason for the protracted and complicated course of the disease and the formation of drug resistance in pathogens. Treatment of chronic tonsillitis in adults should be carried out comprehensively, under the supervision of a physician.
When to see a doctor
Frequent cases of sore throat, prolonged recovery from respiratory infections, and persistent cough are reasons to immediately seek help from an otolaryngologist. The specialist will not only conduct a comprehensive diagnosis of the body, but will also tell you how to quickly and without consequences cure chronic tonsillitis. For additional consultations and examinations, you can contact the doctors of JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitber) in the central district of Moscow at the address: 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya lane, 10 (metro stations Mayakovskaya, Belorusskaya, Novoslobodskaya, Tverskaya, Chekhovskaya) . Experienced ENT doctors will offer an effective course of treatment for tonsillitis, taking into account the age and characteristics of the patient’s body. The selection of antibiotic drugs and physical therapy will be made based on the results of the examination and a history of diseases.
How to quickly cure a disease at home, is it possible to get rid of a sore throat forever?
Treatment of chronic tonsillitis with traditional medicine should be carried out taking into account a number of important principles:
- Constant medical supervision. Any, even the most harmless, means must be agreed upon with a doctor so that he can confirm their effectiveness. This is important because the causes of the disease can be different, as well as the manifestations, which affects the selection of remedies.
- It is not worth treating the acute form of the disease with folk remedies, so as not to cause complications. But chronic tonsillitis suggests the possibility of treatment with “grandmother’s” recipes.
- It is recommended to combine treatment with folk remedies with the use of medications prescribed by a doctor. They will help enhance the effect of medications and speed up recovery. But first you should ask your doctor about the compatibility of certain drugs with medicinal herbs and other components that make up folk remedies.
- Follow all directions given in the recipe. Do not change the volumes of components and doses.
- The treatment should be absolutely safe and harmless, so before you start, try the product: apply it to an area of the mucous membrane (for example, on the inside of the cheek) and evaluate the reaction. If nothing happens within 2-3 hours, then start using it.
- Remember that some medicinal plants may have contraindications and side effects.
To prepare products, use high-quality raw materials. Products must be fresh, and it is recommended to purchase medicinal herbs at a pharmacy.
Gargling with folk remedies
For tonsillitis, one of the effective home remedies is gargling. Here are the best recipes for rinsing solutions:
- The best recipes for treating arthritis with folk remedies at home
- Garlic rinses. Crush two large cloves of garlic, pour in 1 glass of boiled warm milk, strain and gargle while warm.
- Vinegar solutions. Dilute 1 teaspoon of apple cider vinegar in 1 glass of warm boiled water.
- Celandine rinses. 1 tbsp. Pour a spoonful of celandine herb into 1 cup of boiling water, hold for 5-10 minutes in a steam bath, strain after half an hour. Rinse with a very warm, closer to hot, solution.
- Dilute alcoholic tinctures of herbs or ready-made herbal concentrates (rotocan, elekasol) with warm boiled water and rinse, alternating them.
- Rinse collection No. 1. Take 2 tbsp. spoons of marshmallow root and sweet clover herb, 1 tbsp. spoon of anise seeds, burdock roots, calendula, chamomile and linden flowers, St. John's wort herbs, wild mallow, thyme and add 250 ml of water. Leave for 25 minutes, then strain and gargle.
- Rinse collection No. 2. Take 1 tbsp. spoon chamomile herb, calendula flowers, eucalyptus leaves, pour 400 ml of water, boil for 2 minutes, strain after 30 minutes. Start gargling at a decoction temperature of 26 °C and, gradually reducing the temperature of the solution by 1 °C, bring it after 10 days to 16 °C. Find out about gargling with soda and salt for a sore throat here.
Medicinal teas, decoctions, tinctures
Collections for the treatment of chronic tonsillitis include plants that have anti-inflammatory, antiseptic and enhances the body's immune responses. The following plant substances can provide this effect:
- Alkaloids;
- Essential oils;
- Phytoncides, tannins (tannins);
- Resins;
- Vitamins.
Traditional medicine recommends using proven herbs for tonsillitis, compiled by experienced herbalists who are well aware of all the intricacies of plant interactions. We offer several effective preparations and recipes for the treatment of chronic tonsillitis.
Antibacterial and anti-inflammatory herbal tea
Compound:
- St. John's wort;
- Calamus root;
- Calendula;
- Coltsfoot;
- Peony root;
- Wormwood grass;
- Chamomile;
- Black currant leaves;
- Dill herb;
- Thyme herb;
- Sage herb;
- Eucalyptus leaves.
Take all components in equal quantities. Pour one teaspoon of the mixture into 200 ml of water at a temperature of 18-25˚C, leave for 4 hours. After this, strain. Take the medicine 100 ml 2 times a day. Also gargle with this mixture.
Immunostimulating and antibacterial collection
Compound:
- Volodushka herb (20 g);
- Horsetail (10 g);
- St. John's wort (15 g);
- Ephedra herb (5 g);
- Wild rosemary herb (15 g);
- Chopped rose hips (25 g);
- Licorice root (5 g);
- Rhizome with Leuzea roots (15 g);
- Calamus rhizome (25 g);
- Rhizome with roots of peony evasive (20 g);
- Elecampane root (10 g).
When preparing the collection, use a pharmacy scale.
1 tbsp. Add 200 ml of water to a spoonful of the mixture, boil for 10 minutes over low heat and leave for 1 hour. Strain the infusion and take 50 ml 6 times a day, adding honey to taste.
Anti-inflammatory and antiseptic collection
Compound:
- Calendula flowers (15 g);
- Chamomile flowers (10 g);
- Licorice root (10 g);
- Ledum herb (10 g);
- Linden blossom (10 g);
- Elecampane root (10 g);
- Sage herb (15 g);
- Eucalyptus leaves (20 g).
Method of preparation: 1 tbsp. Add 200 ml of water to a spoonful of the mixture, boil for 5 minutes, then leave for 6 hours. Use the infusion for rinsing, as well as for oral administration, 1 tbsp. spoon 3 times a day.
- Benefits for joints and contraindications for using chestnut vodka tincture recipes
Propolis at a 10% concentration in butter is very effective for tonsillitis: use 10–15 g of propolis oil 2–3 times a day 1–1.5 hours before meals for 10–14 days.
Another recipe using propolis: Take 20 g of crushed propolis per 100 ml of 70% alcohol and leave for 3 days at room temperature. You can take 20 drops orally, diluted in warm water or milk 30 minutes before meals or 1.5–2 hours after meals. Use this remedy 2-3 times a day.
For chronic tonsillitis, it is useful to drink hot tea with honey and lemon, and blackcurrant juice. In general, drink plenty of warm drinks: green tea or herbal tea (with or without honey).
Herbs for tea:
- Mint (any);
- Pharmaceutical camomile;
- Rhodiola rosea (golden root);
- Raspberry branches, leaves and berries;
- Currant leaves and fruits;
- Blackberry branches and berries;
- Clover flowers;
- Elecampane;
- Althaea officinalis;
- Rose hip.
An excellent remedy for chronic tonsillitis is licorice root. In the spring, take it with ginger root (preferably raw), in the fall - with tricolor violet. Crush licorice, brew in boiling water, add ginger, cook for 2 minutes and take hot at night. You can learn about the benefits of raspberry jam by following the link.
Home inhalations
Inhalations are very helpful in treating respiratory diseases. In case of tonsillitis, they can also be used. Let's look at a few recipes:
- Add eucalyptus alcohol tincture to hot water (1 tablespoon per 1 liter of water). Breathe the steam for at least 10-15 minutes.
- Use an alcoholic infusion of St. John's wort flowers for inhalation according to the same recipe. This tincture can be prepared for future use: 100 ml of alcohol per 20 g of flowers. You need to insist for 2 weeks.
- Pour boiling water over dry crushed sage (1 cup per 1 tablespoon of herb), let it brew for 15-20 minutes. Add to hot water for inhalation (1 glass of product per 1 liter), breathe for 10-15 minutes.
- Inhalations with alcoholic tinctures of aloe and chamomile infusion are also effective.
Lubricating the throat
You can lubricate your throat with honey and aloe. Take adult aloe leaves, squeeze the juice out of them and mix 1 part aloe juice with 3 parts honey. Lubricate your tonsils with this mixture on an empty stomach in the morning and do not consume anything from food or drink for 2 hours. Carry out this course for at least 2 weeks.
Mix garlic juice with the same amount of water. Lubricate your tonsils with the resulting mixture several times throughout the day. This procedure is carried out once every 2 days.
Pour crushed St. John's wort (0.5 cup) into 250 ml of flaxseed, almond or olive oil, leave this mixture for 21 days, then strain and squeeze. Lubricate your tonsils with the product three times a day for 10 days in a row. Keep refrigerated.
- How to treat arthrosis of the shoulder joint at home with folk remedies
Symptoms and treatment of tracheitis in adults
Treatment of adenoiditis in children - features of the disease and why surgical intervention in this case brings only benefits is described here.
Consequences of a deviated nasal septum //drlor.online/zabolevaniya/nosa/iskrivlenie-nosovoj-peregorodki/diagnostika-i-metody-lecheniya.html
Compresses
For tonsillitis, wet compresses are used. They must be applied in a certain sequence:
- Cleanse your skin.
- Dry the patient with a warm, damp towel.
- Apply the active substance: to do this, take a large piece of clean gauze, roll it several times to form a thick layer, soak it in the medicine, and apply it to the throat. The area of application must necessarily include the tonsils, but not the thyroid gland.
- Cover the top with compress paper and then with a thick layer of cotton wool.
- Secure the entire structure with a bandage, scarf or handkerchief folded several times.
- Leave this bandage on for the required time (you can do it all night), it will warm your sore throat and make breathing easier.
- During the day it is better to update it every 2-3 hours.
Treatment with compresses can be carried out only after consultation with the attending physician, since in case of purulent forms of sore throat, the use of warm compresses is prohibited. In this case, they will contribute to the growth of the number of bacteria and their spread throughout the body.
We offer several of the most effective ways to prepare compresses:
- Alcohol dressing. Soak gauze in vodka and apply it to the throat, then covering it with special paper or a plastic bag, insulating it with cotton wool and wrapping it with a bandage. The alcohol must be diluted in a 1:1 ratio. For children over 3 years old, alcohol compresses (only as prescribed by a doctor) are made based on a 1:3 ratio.
- Compress of cabbage leaves and honey. Before putting cabbage leaves to your throat, lightly beat them with a kitchen hammer or cut them with a knife so that they release juice. Spread a small amount of honey on top of the leaves and cover with another chopped cabbage leaf. This bandage, which has both a warming and absorbable effect, can be left on all night.
- Cottage cheese compress. Apply 200 g of cottage cheese at room temperature to the sore throat and secure with a bandage. Leave it overnight: cottage cheese has excellent stretching properties.
- Potato compress. Boil 3-4 potatoes in their jackets, add 1 tbsp. spoon of vegetable oil, crush. Spread the resulting puree onto gauze, add a few drops of iodine on top, apply to your throat and secure. Make a compress quickly, as the iodine evaporates instantly.
- Compresses with essential oils. You can use tea tree, lavender, eucalyptus, rosemary, sage, and chamomile oils. Dilute 5 drops of oil in 200 ml of water, soak gauze in it, squeeze well and apply according to the standard algorithm. Change every 1-1.5 hours.
Such dressings can be applied to children only if there is no allergy.
Classification
Acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis) or primary inflammation can occur in catarrhal, lacunar, follicular, and less often necrotic form. Secondary acute inflammation of the palatine tonsils most often occurs against the background of existing inflammatory or infectious diseases - scarlet fever, diphtheria, typhoid fever, mononucleosis, as well as leukemia,
Chronic tonsillitis is a long-term inflammatory process in the tonsils, with rare or constant relapses of the disease. Exacerbations can be caused by viruses or bacteria, or against the background of acute respiratory viral infections, dental diseases, or a general decrease in immunity.
Features and causes of the disease
Tonsillitis occurs in acute (angina) and chronic forms. The peak incidence occurs in the autumn or spring. Children get sick twice as often as adults. Due to the structural features of the organs of the peripheral immune system, which include the tonsils of the peripharyngeal ring, they often do not perform a protective function, but themselves become a source of infection due to constant inflammation in them.
Tonsillitis occurs due to a weakened immune defense and in the presence of provoking factors. The development of the disease is promoted by:
- hypothermia of the body;
- bad habits: smoking and alcohol abuse;
- hypo and vitamin deficiencies;
- throat injuries;
- chronic inflammatory diseases of the nasal and throat cavities, paranasal sinuses;
- uncontrolled use of hormonal drugs;
- hereditary predisposition to throat diseases;
- hypoplasia of lymphoid tissues and other causes.
The disease can also provoke impaired nasal breathing and concomitant somatic diseases of various organs and systems that affect the overall reactivity of the body.
The causative agents of inflammation of the palatine tonsils are most often adenoviruses, coccal flora (streptococci, staphylococci), chlamydia, rhinoviruses, herpes viruses, parainfluenza.
Causes of tonsillitis development
The main factors that trigger the pathological process are:
- infectious diseases that the patient tried to cure with home and folk methods;
- frequent pharyngitis, which reduces the body’s immunity and causes inflammation of the throat mucosa;
- allergic reactions that weaken the body;
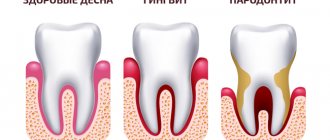
- dental diseases, treatment of which has been postponed indefinitely;
- low immunity after suffering serious illnesses or prolonged stressful situations;
- congenital pathologies of the structure of the respiratory tract, curvature of the nasal septum.
All of the listed causes of tonsillitis are summarized by one main factor – weakening of the immune system and deterioration of the body’s condition. Having lost the ability to resist infections, it becomes vulnerable to pathogenic microorganisms that cause prolonged colds and inflammation of the mucous membrane.
Risk factors
The risk of developing chronic tonsillitis of the throat increases if the patient has a hereditary predisposition to the disease. About 3% of all recorded cases are transmission of the inflammatory process from parents to children. Also, the protracted course of infectious diseases is caused by formations in the nasal cavity, polyps and sinusitis. The source of infection can be a carious tooth, gum disease, or periodontitis. Additionally, the body is weakened by poor nutrition, bad habits, constant stressful situations, and prolonged use of potent drugs.