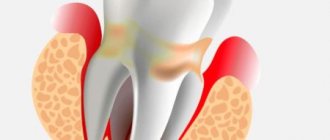
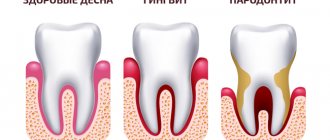
Periodontal disease is a chronic disease of the oral tissues that is non-inflammatory in nature. The disease affects the gums, periodontal areas, alveolar processes; characterized by gradual tissue atrophy, which leads to changes in the hard areas of the teeth and exposure of the dental necks.
The difference between periodontal disease and periodontitis is the absence of an inflammatory process. In the first case, inflammation does not develop in the oral cavity, but is present in advanced forms of the disease, when the patient’s immunity is weakened.
Signs of periodontal disease
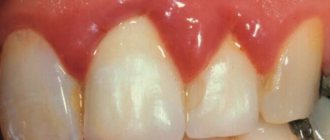
The disease has an asymptomatic period of development, the symptoms become pronounced after the transition to moderate severity, when the periodontal tissues become very thin. Visual detection of symptoms is complicated by the presence of tartar, which hides the necks of the teeth and does not allow assessing their condition. A diagnosis can only be made after professional cleaning by a dentist.
The number and severity of symptoms depend on the stage. Signs of the disease include:
- exposure of tooth roots;
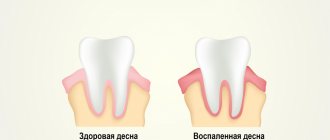
- the appearance of a pale tint in the gum tissue;
- increased sensitivity of the patient’s teeth to cold and hot foods;
- darkening of tooth enamel;
- development of sclerotic changes in bone tissue;
- the appearance of gaps between teeth;
- discomfort and itching in the gum area;
- loss of stability, loosening of teeth.
Inflammation and bleeding of the gums during periodontal disease are rare and are present in advanced stages of the disease.
To make a diagnosis, the dentist prescribes an x-ray examination, which allows you to determine the presence of sclerosis of bone tissue, the degree of development of gum atrophy and identify foci of osteoporosis.
Causes
The causes of periodontal disease are not yet fully understood. Most likely, there is a whole complex of factors contributing to the occurrence of the disease.
First of all, the cause may be a hereditary predisposition to periodontal disease. According to current research on this disease, there are several factors that, regardless of each other, can trigger the development of the disease. These include: hereditary predisposition; malocclusion; bruxism; age-related disorders of gingival circulation, tooth wear; hypovitaminosis A, C and P; insufficient oral hygiene; complications of dental treatment that caused tissue damage; negative impact of physical and chemical factors; tartar; somatic diseases (atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, etc.); chewing overloads remaining after tooth extraction. It is noteworthy that tartar, which often forms during periodontal disease, is more a consequence than a cause of the disease.
Stages of periodontal disease
Periodontal disease can be acute or chronic. Depending on the degree of spread of the pathology, there are the following types of disease:
- localized - the necks of the teeth are exposed in a separate area;
- generalized - pathological processes develop throughout the dentition.
Periodontal disease develops over several years; depending on the patient’s condition, the disease is divided into stages:
- Early - the presence of initial changes in tissues, which can be determined by the dentist during examination;
- The first is increased sensitivity of teeth to hot and cold foods, receding gums;
- The second is pronounced exposure of the dental necks, sensitivity, the formation of gaps between the teeth and the appearance of dental cement instead of enamel;
- The third is severe receding gums, gradual loosening of teeth;
- The fourth is the advanced stage: the teeth become very loose, making it difficult to eat. At this stage, tooth loss occurs.
Salt treatment
One of the most effective and proven means for the treatment of periodontal disease is salt. It stimulates restoration processes in periodontal tissues, relieves inflammation and prevents the formation of tartar on the surface of the enamel.
When treating, it is better to use sea salt, which is rich in iodine compounds and fights the disease even more effectively.
To prepare the solution, dissolve 1-2 teaspoons of salt in a glass of warm boiled water and rinse your mouth for 2-3 minutes. The procedure should be repeated after each meal at least 3 times a day.
Salt massage has proven itself well. Lightly moisten a soft toothbrush with water and then dip the ends of the bristles in fine salt. Then massage the gums and teeth for 3-4 minutes, paying special attention to areas with periodontal disease. There is no need to rinse your mouth after the procedure. The massage must be repeated once a day before bedtime.
When used regularly, sea salt is a reliable remedy for preventing disease at home.
Treatment
The treatment procedure depends on the stage of the disease and includes the following steps:
- Diagnostics at the dentist, making a diagnosis and taking an x-ray of the jaw;
- In-office dental cleaning to remove hard deposits, antibacterial therapy of the oral cavity;
- Orthopedic treatment of loose teeth to strengthen them. Splinting and prosthetic techniques are used to reduce the load on damaged teeth;
- Physiotherapeutic treatment - procedures to restore blood circulation to the gums and prevent relapses of the disease;
- Gum tissue augmentation is carried out when the necks of the teeth are severely exposed.
Self-treatment is impossible. Home remedies are not able to get rid of the causes of the disease. If you notice the first symptoms, contact your dentist.
Toothpastes
You can also cure periodontal disease at home using special toothpastes with an anti-periodontal effect. Unlike conventional dental hygiene products, medicinal pastes contain antimicrobial components, minerals and plant extracts. They have a beneficial effect on the condition of the gums, improve blood microcirculation, relieve inflammation, and stimulate periodontal renewal.
Medicinal toothpastes for the treatment of diseases:
- LACALUT Active
- PRESIDent Active
- Splat Green tea
- Parodontax
- Forest balm
- Parodontol Active
You should use medicated toothpastes only after consulting your dentist. They are used to brush your teeth twice a day for 3 minutes using massage toothbrushes. Courses of treatment last 30-60 days with breaks between them of 2-3 months.
Treatment with antibiotics, dental ointments and gels
Drug therapy is possible after professional teeth cleaning as prescribed by a doctor. Antibiotics should be taken in recommended doses in the absence of inflammatory processes in the oral cavity.
In some cases, during treatment, injections are prescribed simultaneously with the drugs Traumeel and Lincomycin.
To relieve symptoms, the dentist prescribes gels and ointments:
- "Metrogil Denta" is an anti-inflammatory, analgesic agent;
- "Cholisal" - a gel to combat gum inflammation;
- "Kamistad" - for the prevention of gingivitis, relieving swelling, eliminating pain;
- “Gengigel” is a gel that increases blood circulation and promotes the regeneration of soft tissues;
- "Stomatofit" - to relieve severe pain;
- "Asepta" - to stimulate tissue regeneration processes;
- "Solcoseryl" is an antiseptic with a healing effect.
Basic treatment methods
Correct and complete treatment for periodontal inflammation is prescribed directly by a periodontist. The treatment complexes at the initial stage of treatment include such manipulations as removing dental plaque and excess fillings, sharpening sharp tooth edges and eliminating bite defects.
To rid the oral cavity of dental deposits, dentists carry out professional cleaning using a chemical method (using acids, alkaline preparations), sonic (influencing deposits with ultrasound or sandblasting), or mechanical methods (using special periodontal hooks, probes, excavators). In addition to removing tartar, the oral cavity is simultaneously treated with one of the antiseptic solutions (hydrogen peroxide 3%, chlorhexidine bigluconate). Next, the doctor should help the patient choose basic hygiene products (toothpaste and brush, suitable hardness), mouth rinse and dental floss. As a rule, preference is given to products that have antibacterial properties and also contain herbal complexes.
If there are inflammations with purulent contents in the mouth, in this case it is appropriate to use medications containing antibiotics (most often presented in the form of gels and powders).
It is worth remembering about additional physical treatment methods, such as gum massage, leech treatment and physiotherapeutic procedures. For example, darsonvalization for periodontal disease normalizes metabolism and stops the atrophy of gingival tissue, the use of electrophoresis with calcium gluconate reduces sensitivity in the area of exposed tooth necks, and massage helps accelerate blood flow to the gums, which improves their metabolic processes.
Is it possible to cure periodontal disease forever?
Treatment of the disease is carried out comprehensively with the involvement of specialists in the field of dentistry, immunology, endocrinology, gastroenterology, and therapy. The essence of treatment is to eliminate symptoms, strengthen teeth and prevent relapses. Additionally, restoration of lost tissue is carried out.
It is problematic to cure periodontal disease in the last stage, but contacting competent doctors will help get rid of unpleasant sensations and stop the further development of the disease, preserving your teeth.
Splinting
A treatment method used to strengthen loose teeth. Splinting involves combining individual teeth into a single orthopedic structure in the form of a block to reduce their mobility.
Prosthetics
Prosthetics for periodontal disease are carried out in combination with other treatment methods; it is possible to install several types of dentures, depending on the condition of the gums. Removable prosthetics helps reduce the load on areas affected by periodontal disease: installing clasp, nylon dentures that do not rub the mucous membranes and have a fastening system that does not damage the supporting teeth.
In some cases, permanent bridge structures are used to strengthen a number of teeth located one behind the other.
Prosthetics does not eliminate the cause of the disease. Without an integrated approach, tissue reduction will continue, and after 3-5 years the patient will need replacement prostheses.
How to treat periodontal disease and periodontitis
With the exception of local periodontitis caused by traumatic factors, both diseases are completely incurable, but timely diagnosis and proper treatment can transform the disease into a stable state and preserve teeth for many years.
The main thing in the treatment of periodontitis
- If there are traumatic factors, it is important to eliminate them as quickly as possible
- solve existing orthodontic problems
- Since in the case of periodontitis, poor hygiene is the main cause of the disease, it is necessary to carefully observe daily hygiene and, on the recommendation of a doctor, do professional oral hygiene
- lead a healthy lifestyle
Read the article To prevent periodontitis, do professional hygienic teeth cleaning 2 times a year.
If, in case of gingivitis, professional hygiene with the use of ultrasonic cleaning will help normalize the situation with the gums, then in the case of the formation of subgingival deposits and periodontal pockets, treatment using the Vector device is recommended, and possibly surgical intervention (closed/open curettage and flap operations).
Read the article Prevention and effective treatment with the Vector device
The main thing in the treatment of periodontal disease
- since often insufficient blood supply to periodontal tissue is associated with cardiovascular and endocrine diseases, it is necessary to begin treatment with a specialized specialist
- Hydromassage with an irrigator, finger massage of the gums and physiotherapy will help improve blood circulation
- it is very important to lead a healthy lifestyle
- Special attention should be paid to oral hygiene so that periodontal disease is not accompanied by inflammatory processes, which can significantly accelerate the destruction of bone tissue.
Since periodontitis and periodontal disease are accompanied by a loss of bone tissue that holds the teeth, lost teeth should be restored without delay so as not to create an increased chewing load on the remaining ones and to prevent free space in the dentition.
To stabilize the position of the teeth, splinting may be required, which will distribute the load more evenly across the dentition.
Question answer
Is periodontal disease inherited?
Yes, this is a chronic disease that can be inherited and be asymptomatic, destroying tissue, but without causing discomfort to the patient.
Is periodontal disease transmitted through kissing?
No, this is not a contagious disease that cannot be contracted through airborne droplets, through shared utensils, kissing, etc. This is a systemic disease that causes disruption of internal organs and is not transmitted from person to person.
Should teeth be removed if there is periodontal disease?
When the disease reaches an advanced stage, the dentist prescribes treatment in the form of strengthening the gums, building tissue, stimulating regeneration and blood circulation. Removal is carried out in the absence of alternative treatment methods.
Is there bad breath?
Yes, when interdental spaces appear, food particles get into them, which serve as a breeding ground for the development of bacteria that cause an unpleasant odor.
Treatment and prevention of periodontal disease
Depending on the stage of the pathological process, treatment of gums for periodontal disease includes: removal of soft and hard supragingival and subgingival dental plaque; instrumental treatment of bone pockets and altered root surfaces; filling of root defects; grinding off areas of teeth that block jaw movement; layer-by-layer infiltration; creation of a mineral depot of bone tissue (using electro- or phonophoresis with calcium preparations); restoration of a bite damaged by periodontal disease; elimination of secondary deformations. Orthopedic methods for the treatment of periodontal disease include selective grinding, installation of temporary and permanent splinting devices or fixed prostheses (bridges, crowns, pin structures and others), direct splinting and prosthetics.
In combination with dental treatment of periodontal disease, the patient is prescribed gum massage to prevent trophic disorders. To reduce the pain sensitivity of the teeth, special fluoride-containing compounds are applied to the exposed necks. As for drug treatment, vitamins B, A, P, C, E, as well as folic acid are mandatory prescribed (they can be injected into the gums or by electrophoresis).
Competent comprehensive treatment allows you to preserve the beauty of your smile and the integrity of your teeth even with periodontal disease. Preventive measures are aimed at maintaining the health of the dental system and the body as a whole. Periodontists recommend eating well, eating more fruits, raw vegetables, seafood; Take daily care of your oral cavity, use dental floss to remove food debris from the interdental spaces; treat systemic diseases in a timely manner; undergo regular medical examinations with a dentist and have your teeth professionally cleaned; quit smoking.
Back to articles
Rules for applying gels and ointments to the gums
Before applying one or another dosage form to the gums, it is necessary to consider a number of rules of use:
- Clean your mouth . To do this, you can use toothpaste and a brush. Additionally, you can rinse your mouth with special products. To clean the interdental spaces, it is recommended to use dental floss.
- To apply topical treatments, you need to use cotton swabs . Applying the medicine with your finger can lead to additional injuries to the mucous membrane and infection.
- Apply the gel in smaller quantities than ointment . The quantity and frequency of application is strictly according to the instructions for the drug.
- Ointment for the treatment of periodontal disease must be applied using sterilized gauze strips . It is necessary to apply the ointment to the strip, carefully spread it in an even layer and apply it to the affected area. It is advisable to secure the gauze pad with a sterile cotton wool roll.
- When treating with ointments, you can use special dental films . If such films are used, the ointment should not be applied to the very edge of the gauze strip.
Features and rules of use
Before applying the gel or ointment to the gum area, it is necessary to prepare the oral cavity for the procedure.
Clean your mouth with a toothbrush and paste. Rinse with dental fluids intended for rinsing. It is also recommended to use interdental devices to clean the spaces between teeth.
Before applying ointments or gels, you should carefully read the leaflet for use and strictly follow the instructions: