What to do if teeth do not erupt “on time”?
Nothing to do. As stated earlier, the timing is quite relative and not strict data. There is such a thing as the individual characteristics of a child. Plus neonatal indicators, physical constitution, etc. Thus, the timing of the appearance of teeth in your child is normal for him. The same applies to permanent teeth.
The later the teeth appear, the healthier they will be?
Is not a fact. The timing of teething does not affect their “quality”.
What sedatives can be used during teething? Do they influence the process itself?
No, such drugs do not affect the process of teeth formation and, as a rule, have no side effects. For children with allergies, there is a sedative called Doctor Baby that does not contain lidocaine. Almost all gels contain lidocaine and inert fillers (cooling menthol, astringents and flavoring additives). You can use Dentinox, Kalgel (be careful with diathesis, because it is sweet), Kamistad (very effective, but you need to know when to stop), Mundizal, Cholisal, Solcoseryl dental paste (especially good in the presence of wounds or ulcers).
How often should such drugs be used?
Soothing gels are not antibiotics and do not need to be used according to a specific regimen. If the child is in pain, apply it, but if everything is calm, don’t. But it’s better not to use it more than 3-4 times a day and for longer than 3 days in a row.
Infant digestion
A newborn is constantly in a state of adaptation to new living conditions. Its organs and systems continue to develop, and the physiological mechanisms of defecation are also improved.
In an adult, the retention of feces in the rectum is ensured by involuntary and voluntary, that is, subject to the will, contractions of its muscles - the sphincters.
The urge to defecate occurs when stool comes into contact with the lower intestine. An adult is able to control the urge, but a newborn child is not.
The milk enters the stomach and triggers a gastrointestinal reflex, generating a wave of peristalsis throughout the gastrointestinal tract. Feces fall into the rectum and cause the urge to defecate. Not realizing that the conditions for defecation are, to put it mildly, unsuitable, the baby draws in his legs and strains. Emptying your bowels makes room for more food.
The frequency of stool in a newborn often coincides with the frequency of feedings, but it can be twice a day3. The feces have a yellow or yellow-brown color, sometimes with a greenish tint, a mushy consistency mixed with foam and inclusions reminiscent of cottage cheese, and the smell of sour milk.
Starting at about 2 months, the frequency of stools begins to gradually decrease. By the time complementary foods are introduced (by 4-6 months), most infants have bowel movements 2 times a day, and some - once every 2 days3. The feces thicken and take on a sausage shape - this is what all small children should have.
Up to contents
Is it possible to speed up teething?
Medication - no. But massaging your gums won't hurt at all. Using a clean finger, gently and gently massage your baby's gums. The baby will feel better, and the tooth will cut through faster. Just do not press hard so as not to injure the gums. You can give your child a cool spoon or pacifier to hold in his mouth. Try buying special teethers with liquid. They are placed in the refrigerator for a while, and then given to the child to chew on. All these methods are good in moderation, do not overdo it.
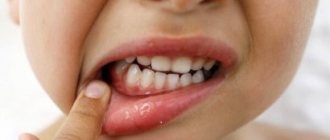
Can bad breath occur during teething and what is the cause?
The process of teething is associated with partial decomposition (lysis) of the mucous membrane under the action of salivary enzymes. We all notice that the amount of saliva increases sharply during this period. In this case, indeed, indicators such as viscosity, color and smell of saliva may change. Another factor is the presence of weak antibacterial substances in saliva, which are designed to prevent infection of the wound when a tooth cuts through the gum. A certain amount of blood also enters the oral cavity. When it decomposes, a sour (metallic) odor may appear.
A sharp increase in temperature during teething. What to do?
Teething does not cause a temperature jump to 39-40 degrees. Only a slight increase is possible, which is normal. Be careful: teething should not cause high fever, diarrhea, vomiting, complete loss of appetite, cramps or choking. If you have such symptoms, even if you attribute it to your teeth, consult a doctor. It is also not recommended to use antipyretics and painkillers without consulting him.
What is the difference between an increase in temperature due to teething and an increase due to other reasons? How long can the elevated temperature last in the first case?
It all depends on the individual characteristics of the child. Basically, hyperthermia and diarrhea are only secondary signs of the teething process, which in itself is a serious physiological turning point for a small organism. Fever is, rather, a reaction to inflammation of the oral mucosa. After all, at the site where the tooth exits, irritation forms, often a wound that can become infected. Thus, hyperthermia is caused not by the mechanism of tooth formation itself, but by side effects. After all, the eruption of permanent teeth, despite the similarity of histological and physiological changes, causes symptoms of colds and diarrhea extremely rarely. And it is quite simple to explain their appearance in children: changes in diet and diet, constant foreign objects in the mouth, microflora disturbance, weakened immunity in the nasopharynx. So, if high fever and loose stools continue for more than 72 hours, then teething really has nothing to do with it.
What to do for constipation in a newborn while breastfeeding
You need to act based on the cause of constipation. When organic constipation is diagnosed, treatment for the underlying disease is prescribed by a doctor. Solving the problem leads to normal bowel movements.
For functional constipation, doctors recommend:
Breastfeed2.
Breast milk, containing the mother’s immune factors, provides the baby’s natural protection from infections, promotes the formation of his intestinal microflora and the development of the digestive system as a whole2. In case of weak lactation and lack of breast milk and unstable stool with a tendency to constipation in a child, doctors recommend supplementary feeding with adapted milk formulas with the addition of prebiotics2. They help maintain intestinal microflora, on which digestion partly depends2.
Follow the diet of a nursing mother
The composition of breast milk directly depends on the mother's nutrition, therefore, by changing nutrition, you can influence the baby's diet4. For the functioning of the baby’s gastrointestinal tract, it is important to maintain a water regime, vegetables, fruits, cereals, wholemeal bread eaten by the mother, that is, foods high in fiber4. You should limit the consumption of foods that provoke increased gas formation: cabbage, onions, tomatoes, rice, legumes, black bread, pears, grapes, mushrooms, pickles, smoked meats and spices3.
Prunes, dried apricots and simple boiled beets will help as a natural laxative during breastfeeding for constipation in a newborn - you just need to include them in the diet.
Fermented milk products are useful for maintaining intestinal microflora2. But if a child is diagnosed with intolerance to cow's milk, the nursing mother will have to completely abandon dairy products made from it4.
Keep your child physically active
A well-organized daily routine and physical activity are the most important factors in the treatment of constipation in a child2. Physical activity is selected individually according to the age of the child2. For newborns and infants during the first 5 months of life, their natural activity and special gymnastics are sufficient2. It is very important that clothes do not restrict the child’s movement and allow him to independently improve his motor skills in the process of exploring the world.
Do a belly massage
First of all, after feeding, you must keep the baby in an upright position so that he burps air, and then lay him on his tummy.
Abdominal massage involves lightly stroking the tummy in a clockwise direction, that is, in a circle, starting from the right iliac region and ending with the left iliac region. In this case, the child should lie on his back. At the end of the procedure, you need to hold the ankle joints and press the baby’s legs one by one to the tummy. This stimulates the passage of gases and bowel movements.
Use gas-reducing products wisely
A large amount of gases stretches the intestinal walls, weakens its peristalsis and leads to colic. Dill water, light fennel tea, and simethicone-based medications can relieve symptoms associated with constipation4.
In some cases, means that help mechanically remove gases from the intestines are useful, for example, a gas tube or enemas4. However, their frequent use aggravates the problem of constipation: the baby’s gastrointestinal tract begins to “become lazy” and ceases to independently perform its functions3.
Microclysters MICROLAX®
In the complex treatment of constipation in breastfed newborns, microenemas occupy a special place. They promote bowel movements and thereby alleviate the baby’s suffering.
MICROLAX® for children from 0 years old was created for the smallest children, equipped with a special short “spout” and can be used from birth to 3 years6. The drug contains sodium citrate, which displaces water from the stool, sodium lauryl sulfoacetate, which thins the contents of the rectum, and sorbitol, which stimulates the flow of water into the intestines6.
By enhancing each other's action, MICROLAX® components are able to soften stool and facilitate bowel movements6. In this case, the effect of the drug can begin in 5-15 minutes6.
It is important that the effect of MICROLAX® is limited to the final intestine. It is not absorbed, does not enter the general bloodstream and therefore does not affect the functioning of other organs and systems6.
For ease of use, MICROLAX® is available in the form of a disposable microenema equipped with a shortened spout tip6. It is enough to break off the seal and the microenema with 5 ml of the drug will be ready for use.
Up to contents
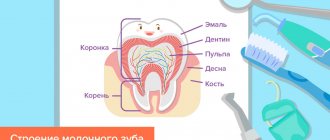
Teething in infants
Possible characteristics of teeth in children at the teething stage. Stay up to date.
The expansion of the spaces between the teeth is caused by the growth of the jaws. During the transition from baby teeth to permanent teeth, it is considered a normal condition. A wide gap between the upper anterior incisors is usually associated with a deep-lying maxillary frenulum. An orthodontist should observe and treat such a gap between the teeth;
- a blackish edging on the neck of the tooth can form when taking soluble iron supplements, as well as during a chronic inflammatory process (precipitation of bacteria from the leptotrichium group);
- yellowish-brown staining of teeth may be associated with the use of antibiotics - by the mother in the 2nd half of pregnancy or by the child himself during the formation of teeth;
- yellowish-greenish coloring is caused by severe disturbances in bilirubin metabolism, hemolytic conditions (destruction of red blood cells);
- reddish staining of tooth enamel is characteristic of a disease called porphyria - a congenital disorder of the metabolism of porphyrin pigment;
- malocclusions are formed by the uneven growth of the child’s jaws, as well as prolonged sucking of the nipples;
- Anomalies in the location of teeth occur for a number of reasons: trauma, congenital disorders of connective tissue metabolism, constitutional reasons (small jaw size), tumors of the alveolar process of the jaw.
- the absence of teeth before one year of age is extremely rarely associated with edentia (lack of tooth buds), which can be checked using radiovisiography as prescribed by a pediatric dentist.
If teeth erupt on time and in a certain order, this indicates the normal development of the child’s body. After all, this physiological process is in direct connection with the general health of the baby. Some atypical cases may indirectly indicate the presence of pathology. But only a special examination of the child can confirm or refute the assumptions made. The reasons must be identified and analyzed by a specialist.