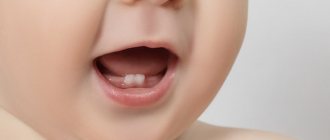
Norm or pathology
Can teeth be cut at 3 months? The earliest age for the eruption of the first elements is considered to be three months of age. Dentists consider it normal for the first teeth to appear at 3 months of age. If the incisors appear earlier than the expected period, then the child should be shown to a therapist. The early appearance of elements on the surface of the gums may signal hormonal disruptions occurring in the body.
The appearance of baby teeth on the surface is accompanied by a number of distinctive symptoms:
- Pain in the gums. Because of this, the child puts fists and foreign objects into his mouth. At this moment, it is important for adults to ensure that there are no small toys or objects near the child that could get into the respiratory tract.
- Deterioration of the oral cavity. The gums swell and redden, becoming more sensitive to external irritants. In some cases, due to teething, the child may experience slight redness of the throat.
- Irritability and increased tearfulness of the baby. The symptom is associated with constant pain in the area of the eruption of the element. At this moment, children become more active and faster.
- Disorders of the digestive tract, manifested by loose stools, regurgitation, and rare bouts of vomiting.
- Temperature increase. The symptom is due to the fact that when teething, the newborn’s body is vulnerable to bacterial and viral pathogens.
Symptoms of baby teeth erupting
Each baby reacts individually to the eruption of baby teeth, however, there are characteristic symptoms by which parents can understand that this is happening:
- heavy salivation;
- redness and swelling of the gums;
- itching
Severe itching and sometimes even painful sensations make the child capricious. He becomes restless, which disrupts his sleep. To somehow relieve the itching, children put toys in their mouths and intensively rub their gums. Children often refuse to eat or eat with less appetite. What does the gum look like when teeth come in? Changes in the condition of the gums are one of the criteria by which parents can differentiate teething. The gums in this place look inflamed - they turn red, swell, and immediately at the site of tooth eruption they become white.
However, the biggest concerns about the child’s condition are cough, runny nose, and fever during teething. Indeed, the appearance of baby teeth in its symptoms can resemble colds, and it is difficult for parents without experience to understand whether the baby is sick or is just teething.
First of all, you need to understand that both fever and cough during teething in children are acceptable reactions. Cough, hoarseness, and runny nose are most often the result of excessive salivation. For the same reason, during teething, babies develop a rash on the chin and around the mouth.
Another frequently asked question from parents is what kind of stool can a child have when teething? During a particularly acute period of teething, babies may have weak stools, which is associated with general irritation of the nervous system and has nothing to do with eating disorders.
However, it must be taken into account that when babies are teething, they are more susceptible than usual to various infections. If unpleasant symptoms (fever, diarrhea, cough) do not go away on their own after 2-3 days, the child should be examined by a doctor.
How long does teething take for babies?
With normal development and growth, baby teeth erupt within a few days (2-8 days), and the most unpleasant symptoms usually appear within about 2 days.
The period of formation of the primary occlusion ends at 2-3 years, and at this moment the baby has 20 primary teeth.
Problems and complications when the first teeth appear
Sore gums, fever, poor appetite and indigestion are, although unpleasant, acceptable symptoms during the eruption of baby teeth.
In some cases, children experience complications:
- long delay - can be either a genetic feature or pathological adentia (if the child has not formed the rudiments of teeth);
- formation of a hematoma (cyst) - in this case, the gum above the growing tooth acquires a dark purple tint, then a lump or hematoma appears in this place, which may be due to both difficult eruption (the tooth cannot cope with the mucous membrane) and other reasons;
- violation of the order of teething;
- aphthous stomatitis - rashes on the mucous membrane in the form of purulent ulcers;
- enamel hypoplasia – occurs in babies under 10 months of age;
- malocclusion - improper closure of teeth, crowding, possible problems with the eruption of permanent teeth in the future.
If your baby experiences “difficult eruption” of primary teeth or you encounter the listed complications, you should definitely consult a pediatrician. If the formation of a primary occlusion is clearly incorrect, consult an orthodontist.
Scheme for cutting elements for children
Dentists have drawn up a specific scheme for the formation of primary occlusion in children. However, it is necessary to remember that each baby’s body is individual, and the teething dates established by doctors may deviate up or down by several months. Pathological signs of bite formation in babies include early eruption of incisors (up to 3 months of age) and the complete absence of elements in the oral cavity by 12 months.
The standard scheme for the formation of bite in children is as follows:
- 5–7 months – lower front incisors;
- 8–10 – upper incisors;
- 10–12 – upper lateral incisors;
- 11–13 – lower lateral incisors;
- 12–15 – upper and lower molars;
- 17–22 – canines (upper, then lower);
- 25–30 – upper and lower molars.
Pattern of tooth growth in infants
If a child is cutting teeth at 3 months, then these should be the front pair of incisors. If the side elements are shown first, then it is necessary to show the baby to the dentist. The symptoms corresponding to the process depend on the characteristics of the child himself. In some children, the elements appear completely unnoticed, in others they cause crying, fever, etc.
Alarming symptoms
Many signs of teething are harmless and go away on their own once the incisor comes to the surface. However, some signs may indicate the addition of bacterial or viral diseases against a background of weakened immunity.
Reviews of Dentokind for teething up to one year
Normal signs of the condition include:
- Profuse salivation. The symptom is observed in almost all children under three months. It does not require treatment for the child.
- Skin irritation near the chin. The symptom is caused by increased salivation during teething. It is enough to use an emollient cream every day at night to eliminate skin redness.
- The child's desire to breastfeed frequently. During feeding, the baby scratches its gums on the mother's nipple.
The list of alarming symptoms of teething includes:
- refusal to eat (more than 3-4 feedings);
- persistent diarrhea (may indicate an incipient intestinal infection);
- constant crying of the child.
Small bruises (hematomas) may appear in the eruption area. They dissolve quite quickly if you apply a compress to the problem area.
What to do when teething: advice for young parents
Now that you know what is happening to your child, you can draw up a rough action plan aimed at making the process of the appearance of the first teeth as easy as possible for the baby.
Tips for moms and dads:
- 1
Stay calm. It’s not easy for a child anyway, and your anxiety and irritation will only negatively affect the baby’s well-being. - 2
Surround your baby with love and tenderness. Remember that small children feel calm and safe only in the arms of loving parents.
- 3
Provide your baby with special gum toys that will help relieve itching and make teething easier.
- 4
Turn on the increased antibacterial protection mode (frequent ventilation, sterilization of toys, pacifiers, etc.), since during this period the child can easily catch an infection.
If your baby's gums are bothering you a lot, you can use a special teething gel. This product has a mild anesthetic effect, relieves itching and pain. Regarding the choice of gel, it is better to consult your pediatrician. He will tell you which drug is suitable for your baby’s age and has a safe composition.
What to do when the temperature rises? Doctors recommend avoiding the use of antipyretic drugs, as the body fights infections by raising the temperature. If hyperthermia is very high, you should consult a pediatrician, he will recommend what medications and in what dosage can be given to the baby. Under no circumstances use folk remedies or medications without first consulting a doctor!
Factors affecting tooth growth
The speed of formation of a mixed bite depends on several circumstances:
- baby's genotype;
- performance of the thyroid gland;
- gender;
- severe infectious and viral diseases suffered in the past;
- duration of natural feeding;
- the presence of congenital diseases.
You also need to monitor the period of eruption of molars. They should come out to the surface of the gums only after the milk unit falls out. Otherwise, a mandatory visit to the dentist will be required. Early loss of milk elements is also undesirable, as this negatively affects the proportions of the baby’s jaw and his bite in the future.
Reasons for the atypical timing of the eruption of elements
Only a dentist can accurately determine the causes of abnormal teething in children. However, there are several common violations that lead to the problem:
- improper metabolism;
- lack of calcium in the body;
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- gastrointestinal pathologies;
- incorrect direction of the tooth axis.
Anomalies of the dentition can be associated not only with the timing of the appearance of elements, but also with the color, location, and size of the units in the row. If a child is already born with teeth, they are usually removed. Such situations are diagnosed quite rarely, and they indicate intrauterine disorders in the baby.
How to help your child: recommendations from Amel Dental doctors
To cope with the discomfort caused by the eruption of permanent teeth, it is enough to massage the child’s gums. If your gums are inflamed, a teething gel will help relieve the inflammation (your dentist will help you choose the right one).
What to do if complications develop?
- 1
Bite problems in children are easier to eliminate than in adults, so if there are defects, you should consult an orthodontist.
- 2
Caries requires immediate treatment, otherwise there is a chance that the child will lose a tooth in childhood.
- 3
If dental growth is delayed, you should immediately see a doctor. One of the main reasons for delayed eruption of permanent teeth in children is immune disorders.
Ways to alleviate the condition
The formation of a bite is often accompanied by an increase in temperature. Therefore, parents should always have antipyretic drugs in their medicine cabinet (Panadol, Nurofen, Ibuklin). They not only reduce the temperature, but also relieve pain associated with tooth growth.
The love and attention of parents will allow the child to cope with the problem. The baby should be put to the breast and picked up as often as possible. Special teethers with gel will help satisfy your baby’s desire to scratch his teeth.
You need to choose small devices so that the child can comfortably hold it in his hand.
Pediatricians advise cooling teethers with cold water before giving them to a child. Instead of toys, you can give your baby chilled pieces of apple or carrot. At the same time, parents should carefully monitor that the baby does not bite off the product and does not choke on it. In parallel with this, local anesthetics can be used.
On the pharmacological market there are many drugs in the form of a gel that relieve pain during the appearance of teeth - Kalgel, Kamistad, Cholisal. Additionally, the gels have an anti-inflammatory effect, which also alleviates the child’s condition. The analgesic effect occurs 2-3 minutes after using the drug.
Teething or infectious disease
However, most modern pediatricians agree that such symptoms in an infant as: long-term, over 2-3 days diarrhea, cough, vomiting, fever (increase in body temperature above 38.5 degrees) are most often caused by infection, and not just teething teeth. Therefore, with any of the above symptoms, it is necessary to examine the child by a pediatrician, and only after other causes of increased body temperature have been excluded, efforts should be concentrated on helping the baby to reduce the discomfort from teething.