Find out when your child's first teeth should grow. And why sometimes children have no teeth a year.
All mothers are excitedly waiting for the baby to finally have his first teeth. In addition, there are plenty of reasons to worry, because the process of teething often occurs with discomfort. The baby experiences increased salivation, worsening mood, fever, diarrhea, and discomfort.
But what follows is not about the symptoms, but about why children develop teeth later than the rest of their peers. We will also find out when children's primary and permanent teeth should appear.
When does a child cut his first tooth?
According to pediatricians, the timing of teething is individual for each baby. In some children they appear at 2-3 months, while in others at 9 months or a year. Oddly enough, this phenomenon is considered the norm. The main thing is that by the time your daughter or son reaches the age of three, she already has 20 baby teeth in her mouth.
Every mother should prepare both mentally and physically for such a responsible task.
- You will have to be patient with your child's whims. Surround your child with affection, care, love.
- Do daily cleaning, keep toys clean, and also maintain your and your child’s hygiene. After all, babies during such a period often put everything in their mouths; your task is to prevent the child from catching an intestinal infection.
- To make teething easier, you can buy special teethers (gum massagers). They have an anti-pain effect.
- Special gels are good for gum pain relief. Just don’t think that they help teething. They only relieve inflammation, relieve some pain and soothe irritated gums.
- If a child's temperature rises above 38, then visit a pediatrician. The cause of elevated temperature can be not only teething, but also various diseases.
IMPORTANT: Before using gels to soothe gums during tooth growth, consult with your pediatrician which drug is best to use.
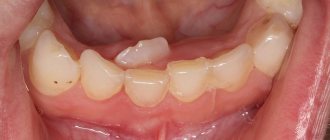
If a new tooth does not grow in place of a baby tooth
The loss of baby teeth, as well as their appearance, does not occur simultaneously, but in accordance with the development of the jaws and the growth of permanent replacement. The concept of a protracted renewal is quite relative, because for some the radical will show itself in a week, and for others in a month or two. And in the second case, we are not always talking about deviation.
Often baby teeth are “pushed out” by molars, which almost immediately make their way out, but if a child’s tooth falls out and a new one does not grow and is not visible, you need to wait a few weeks.
Reasons to see a doctor:
- lack of replacement 2-3 months after the loss of a baby tooth;
- swelling and redness of the gums, pain without signs of germination of a molar;
- sequential loss of other teeth without the appearance of new ones.
Reasons why a child’s tooth does not grow for a long time:
- Infectious diseases, including past ones.
- Lack of calcium in the body.
- Oral diseases.
- Mechanical injuries.
A child’s tooth has fallen out and is not growing, but the situation does not correspond to the reasons indicated? Perhaps the delay is provoked by poor ecology, incorrect or poor-quality diet, stressful situations, or even genetic preconditions.
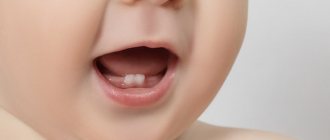
Why a one-year-old child has no teeth: reasons
Vitamin D and calcium have virtually no effect on the timing of the appearance of the first teeth. These factors have a greater impact on the quality of teeth and enamel. The reasons why a baby has no teeth at one year can be:
- genetic factors, if the parents had late teeth, then their baby is also likely to have the same problem
- oddly enough, even climatic conditions can influence this process; in a warm climate zone, children’s teeth grow better
- a lot depends on the quality of water, nutrition
- Severe infectious diseases negatively affect the rate of tooth growth
- lack of vitamins and calcium can slow down this effect
If at the age of one and a half years the baby does not have a single tooth, then he needs to undergo a comprehensive examination. Sometimes teeth do not grow due to pathology - adentia .
The main reasons for missing teeth
There are various physiological and pathological mechanisms that prevent the timely appearance of teeth. The main reasons for this situation are discussed below.
- Deviation in physical development. This is the most favorable option - teeth will appear soon, only the process is slightly delayed. This is a fairly common case in premature babies.
- Lack of calcium and vitamins in the baby’s body. Improperly introduced complementary foods or the use of non-adaptive mixtures leads to a deficiency of microelements. All organs and systems of the child’s body, including teeth, suffer from this. When normal nutrition is restored, teething will occur, but with a delay, sometimes significant.
- Edentia. This is a hereditary pathological condition characterized by the absence of tooth germs. In this case, chewing function can be restored artificially using implants.
- Mechanical damage to the gums. Sometimes parents make a serious mistake when trying to speed up teething on their own. They deliberately injure the gums, which leads to scars. This not only does not help, but on the contrary, it sharply slows down the process of teeth appearing.
A dentist will help determine the specific cause. Therefore, if there is a delay in the eruption of the first teeth, you cannot postpone a visit to the doctor.
What to do if a child does not have a single tooth in one year?
Previously, it was considered a deviation from the norm if a baby does not have a single tooth per year. Doctors first of all suspected that the baby had anemia or rickets. This version has now been refuted. Studies have shown that many children start teething at 1-1.2 years of age. However, parents should not be careless and just wait for the process to manifest itself. When your child turns 1 year old, be sure to tell your pediatrician about the problem that has arisen.
He, in turn, should establish the reason for the delay in tooth growth. If it is heredity, he will tell you when to come back for an appointment. He will prescribe the use of vitamins necessary for teeth growth and advise on how to feed the baby correctly. If not, he will send you for tests or to a dentist. You may be asked to do:
- biochemical tests of urine, blood
- ultrasound examination of organs
- check your thyroid gland
IMPORTANT: To exclude a disease such as adentia, the dentist will order an x-ray of the lower jaw. If the diagnosis is confirmed (there are no teeth rudiments), then after a while dentures are installed. However, do not get upset right away - this pathology is extremely rare.
Late teeth in children - a problem or the norm?
We have already described in detail what a child’s first teeth are in the article “A Child’s First Teeth – Joy and Responsibility”, what complications there may be during this period of the baby’s development, on a separate page of the site we provide a visual aid on how children’s teeth come in, a photo and a growth chart milk teeth.
In special medical articles, our dentists provide advice and recommendations on how to make this time easier for your baby, how to properly care for the mouth and first teeth (“A pediatric dentist is a must-have best friend from an early age”). Separately, we also focused on the question: what time do children start teething? We repeat - this process is very individual and depends on many factors: heredity, the mother’s lifestyle and nutrition during pregnancy, the baby’s nutrition and the individual characteristics of his body.
Timing of teething in children
Sometimes children are already born with one or more teeth (on average, 1 case per 2-2.5 thousand babies). There is nothing wrong with this, just like with the very early eruption of baby teeth - before 3 months. Parents are even more concerned about late teething in children under one year old. We would like to point out that this is a completely normal condition. The generally accepted standard is 5-7 months - this is the average age of appearance of baby teeth. But the first teeth can appear at 9, 10, 11 months. This is especially true for babies who were born prematurely. And in very premature babies, their first teeth can be delayed even up to 15-18 months. And there's nothing wrong with that. It’s just that when the time comes, the teeth will appear, and, as a rule, by the age of three, such children have a full set of milk teeth, catch up with their peers in all other indicators.
It was previously believed that late teeth in children were often a consequence of rickets and anemia, but modern research has shown that this is not the case. Of course, a lack of calcium and microelements also affects the dental system, but the timing of teething in children is a genetically determined feature of the body. Just like the wrong order of appearance of baby teeth. Even if there are gaps in the dentition, before the eruption of a full set of baby teeth, this is not considered a pathology.
If your child is 10 months old and has no teeth , don’t worry. See our dentist - he will dispel your doubts. But if at the age of 3-4 years the baby is missing several milk teeth, consult an orthodontist at the Utkinzub clinic, who will find out the cause of the pathology and determine measures to avoid such problems with permanent teeth.
How many baby teeth should a child have?
Above we looked at when the first teeth can erupt. Based on this, it is clear that all monthly data on dental growth are approximate. After all, some children don’t get their first tooth until they are one year old, or even later.
According to the rules, the first incisors can appear at 6-8 months. And by the age of two and a half, the baby should have grown 20 baby teeth. The remaining indigenous 10-12 grow up to 32 years. The latest ones are wisdom teeth, they are the ones that cause us a lot of trouble with their appearance.
IMPORTANT: For some people, the norm is 28-30 teeth, the remaining 4 never appear.
How many teeth should a child have at 6-7 months?
During this period, the child sometimes develops lower and upper central incisors - 2-4 teeth. Signs of the appearance of incisors, however, like other baby teeth, can be:
- cough, runny nose
- elevated temperature
- swelling of the gums
- diarrhea, vomiting, constipation
- drowsiness, tearfulness
- diathesis
However, all these symptoms disappear after 2-7 days, when the gum inflammation subsides.
How many teeth should a child have at 10-11 months?
Your baby has already grown up, at 10-11 months, he knows his loved ones very well and begins to be shy about strangers. He crawls with more confidence now. Begins to overcome various obstacles. He likes to study, explore the new world, climb on and off the soft sofa on his own. In addition, he gains 2 more upper lateral incisors, so in total the baby already has 6, and sometimes 8 teeth. You need to take proper care of them.
- Do not accustom your child to sweets; give such treats to your baby in moderation to avoid tooth decay.
- Give water after meals.
- Try not to put your baby's spoon in your mouth to avoid transferring harmful bacteria.
- Keep the pacifier clean.
IMPORTANT: If your child’s teeth grow in the wrong order, they are of an unusual color, or there is an unpleasant odor from the oral cavity, then contact your pediatric dentist.
Causes of delayed teeth emergence
A lot depends on nutrition: breastfed babies depend on the quality of breast milk. Babies who grow up on artificial formulas receive slightly more vitamins and minerals, because the formulas contain a clearly calculated amount of nutrients.
- If a child does not have a single tooth at 1 year of age, this may be a consequence of some previous disease: intestinal dysfunction, impaired metabolism, as well as insufficient calcium and vitamin D.
- Teeth may be delayed due to the special course of pregnancy; perhaps the mother suffered complications during the gestation period./li>
- Eruption after 12 months may mean that the tooth is not positioned correctly in the gum, for example, it is growing horizontally.
- Congenital absence of tooth buds in a baby. These are either hereditary disorders or a congenital pathology caused by a disruption in the normal course of pregnancy. It happens very rarely.
How can parents understand that at 12 months the baby’s teeth are simply delayed and they need to be patient, and when should they sound the alarm?
Pediatric dentists allow the first teeth to be delayed for 6 months, so if after the baby’s 1st birthday not a single baby tooth has grown, you should wait a little longer. Try to find out from your relatives about the timing and characteristics of the appearance of the first milk teeth in their childhood, perhaps this is just a family trait.
But if the teeth are already delayed by more than 6 months, and the baby’s gums do not even think of swelling, then you should contact a pediatric dentist. The specialist will conduct an examination and advise what needs to be done to help teeth appear faster.
In addition to the above reasons, the appearance of teeth after 12 months may be affected by the following:
- The teeth are located very tightly in the gums.
- There are diseases of the endocrine system, for example, hypothyroidism, due to which the activity of the endocrine glands is reduced.
- The baby suffered serious systemic diseases.
In this case, the pediatric dentist will recommend a biochemical blood test; the baby will need to have the thyroid gland examined, including an ultrasound examination. After the results are obtained, the dentist will be able to prescribe the necessary course of treatment.
Make an appointment
How many teeth should a child have per year?
According to the formula for calculating the number of teeth, at 12-13 months the baby should already have 8 teeth. 4 on top, 4 on bottom. The formula looks like this:
Ν = Κ - 4, where Ν is the number of teeth; Κ is the baby’s age in months, and 4 is a constant value .
IMPORTANT: This is the year you will need to go to the dentist with your daughter or son for the first time, even if the child has no reason to worry about the health of the mouth and teeth.
Pathological causes of delay
If a child’s teeth have fallen out and new molars do not grow for a long time, the reasons for the delay should be sought in pathologies:
- Retention is a complete or partial delay in eruption. Partial retention is observed when the crown of a molar tooth appears in the socket of a milk tooth, but growth stops there. Often the cause is early loss of a baby tooth, accidental or surgical. That is, a replacement for him has not yet been formed.
- Adentia – absence of teeth. This rare problem is common in older people, but can also occur in children. As a rule, it is triggered by taking strong medications during pregnancy.
How many teeth should a child have at 1.5 - 2 years old?
Having reached 1.5 years of age, a child may have only 4 teeth, although according to the above formula he should have 13-14 teeth. It’s okay - this is considered the norm; in such cases, dentists advise giving the baby hard cheese to chew to stimulate their growth.
Already at this age, your baby should be taught to take care of the oral cavity. Use your example to show how you brush your teeth. Give your child a toothbrush and let him repeat the movements after you, only without the toothpaste.
How many teeth should a child have at 2.5 years old?
At 2.5 years old it is considered normal if your child already has 20 teeth. Moreover, these baby teeth last up to 5-6 years. There are various atypical situations; if they arise, you need to visit an orthodontist or dentist.
- Very early appearance of teeth sometimes indicates the presence of pathologies in the endocrine system.
- Late growth of teeth is caused by genetic factors, diseases of infectious origin, the presence of rickets, and disruption of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Incorrect position of the incisor, unusual, damaged appearance of the tooth indicates violations of the bone component, incorrect location of the axis of the incisor.
Diagram of teeth in a 3 year old child
Let us now summarize when and in what order the upper and lower primary teeth appear.
- The lower two central incisors appear at 6-10 months of age
- The upper two incisors usually grow in 8-12 months
- The upper two lateral incisors will appear at 9-13 months
- The two lateral incisors from below grow in 10-16 months
- The two upper molars will grow in at 13-19 months
- Two lower molars will appear at 14-18 months
- The upper canines usually grow in between 16 and 22 months.
- The lower two canines will erupt in 17-23 months
- The lower two second molars grow in at 23-31 months
- The upper two second molars grow at 25-33 months
Thus, by the age of three, the baby should already have 20 milk teeth.
How many teeth should a child have at 4 years old?
In children of 4 years of age, the number of teeth remains the same as at 3 years of age, that is, 20 milk teeth. Interdental spaces may already appear. Parents should wean their children from bad habits that can cause the growth of crooked permanent teeth.
At this age, you should give up the pacifier, do not allow the child to suck fingers, etc. If any problems arise, take your child to the dentist.
How many teeth should a child have at 6-8 years old?
Already at the age of 6 years, future schoolchildren begin to lose milk teeth and grow permanent ones instead. This process lasts several years, gradually. First, the lower front incisors change, the permanent ones appear instead, then the upper ones. It is during these two years that the 4 front incisors will change.
IMPORTANT: Teeth need care, to avoid the well-known caries, buy your child toothpaste with fluoride, let him brush his teeth 2 times a day.
Adentia - symptoms and treatment
Complications of adentia are psychosocial, neurological, dental, and sometimes systemic in nature.
In the complete absence of teeth, atrophy of the alveolar processes occurs first. This leads to a violation of the aesthetics of the smile, as a result of which people with this disease develop psychological problems.
Why does bone tissue decrease in the absence of teeth?
When teeth are lost, the chewing load is transferred to the mucous tissue and bone support of the gums. Due to the load, the blood supply to this part of the masticatory apparatus is disrupted, venous stagnation occurs and vascular tone decreases. Redistribution of pressure also leads to the activation of osteoclasts (cells that destroy bone tissue) and damage to cancellous bone.
When there is edentulism in one jaw, the antagonizing (opposite) teeth in the dentition are crowded or piled on top of each other. In this case, individual teeth are located outside the dentition or are impacted.[2]
Changes are observed in the composition of oral fluid.[19] These disorders create favorable conditions for the occurrence of diseases of the dental system, which, at times, the body’s adaptive mechanisms are no longer able to cope with:
- the rate of saliva secretion decreases;
- the reaction of the environment changes;
- the amount of protein in the oral fluid decreases;
- indicators of antibacterial and antiradical protection change.
In 100% of cases of secondary adentia, macroglossia occurs over time, i.e., enlargement of the tongue: its microvascular bed undergoes changes.[20]
The periodontium of the remaining teeth experiences functional overload, in particular, the endurance of the periodontium of the teeth limiting the defect decreases.[23] This leads to the formation of pathological bone pockets, atrophy of the dental alveoli and localized gingivitis.
Violation of the closure of the dentition causes pathological changes in the structure of the temporomandibular joint: the movements of the articular heads are limited, the histological structure of the tissues changes.
The mutual influence of the structures of the masticatory apparatus creates the prerequisites for the formation of neurological phenomena. One of the most diverse manifestations is Costen's syndrome. It may be accompanied by:
- pain, mainly in the parotid region;
- congestion in the ear and hearing loss;
- dizziness;
- violation of taste sensitivity.
Due to the lack of chewing teeth and insufficient mechanical processing of food, disorders associated with digestion are formed - gastritis, colitis, stomach ulcers.[22]
With all this, experience shows that increasing the medical literacy of the population reduces the number of cases of possible complications, which obviously leads to an increase in the level of dental health of the population.[27]
How many teeth should a child have at 14 years old?
- Teenagers of this age have already lost their baby teeth, but their permanent teeth are about to grow in. In total, there should be 28 of them available.
- Sometimes the growth process drags on for up to 15 years. But wisdom teeth never grow back. At the age of 14, unfortunately, 28% of adolescents have dental anomalies.
- Either they grow crookedly and sideways, or they protrude from the general row of teeth. You cannot cope with such problems on your own. Please note that already at this age the correct taste is formed.
- To solve the problem, visit an orthodontist. The sooner you go to him, the easier it will be to resolve this unpleasant situation.
How to eliminate teething problems?
To ensure that your baby does not have any disorders, it is important to think about the future newborn even when planning a pregnancy. Therefore, prepare for this systematically.
- Treat your teeth in advance, eat right, take vitamins, and do not limit yourself in consuming foods rich in calcium.
- Get outside more often, make sure you have normal hemoglobin.
- Do not drink strong drinks or smoke under any circumstances.
- Do not self-medicate, do not take medications that your doctor has not prescribed to you.
After childbirth:
- Make sure your baby gets adequate nutrition
- strengthen your baby, take daily walks
- Contact your pediatrician promptly if you notice any changes in your child’s health.
- take care of your child's hygiene
IMPORTANT: Monitor your baby’s immune system as a whole. Diseases may cause teething problems.
Teething disorders - symptoms and treatment
In case of teething problems, symptomatic treatment is carried out. Its purpose is to eliminate pericoronitis, oral abscess and osteomyelitis.
Treatment of pericoronitis
Treatment of pericoronitis is carried out on an outpatient basis. If the tooth germ is positioned correctly and there is enough space for the dental arch, then surgical treatment is the most preferable option. The mucous membrane in the area of the tooth crown is completely excised. As a result, access to the chewing and lateral surfaces of the crown appears. The operation is performed under anesthesia and can be performed either with scissors or a scalpel, or with more modern methods: cryodestruction, laser and electric knife.
pericoronarotomy can be performed - an operation during which the mucous membrane above the tooth crown is dissected. As a result, tooth surfaces that were previously covered by a hood of mucous membrane are exposed.
After surgical treatment, drug therapy :
- Antibacterial agents are selected individually, taking into account the microflora. It can be:
- Inhibitor-protected penicillins that destroy anaerobic and aerobic microorganisms. Amoxicillin with clavulanic acid is most effective.
- Lincomycin and Clindamycin act against Staphylococcus aureus.
- Metronidazole is not effective against facultative anaerobes and aerobes, but together with other antibiotics it will help cope with mixed microflora.
- Cephalosporins act only together with Metronidazole and Clindamycin, since almost all anaerobic microorganisms are insensitive to them.
- The latest generations of fluoroquinolones are effective against gram-positive bacteria, but each drug has its own level of activity.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Antihistamines [10].
- Detoxification therapy consists of drinking plenty of warm drinks rich in vitamins, such as compotes and fruit drinks. Sometimes in difficult situations, an isotonic solution is administered intravenously.
To alleviate local symptoms and reduce inflammation, baths with antiseptic solutions are used: a pale pink solution of potassium permanganate, 0.01% Miramistin solution or 0.05% Chlorhexidine.
Treatment of oral abscess
Treatment for an oral abscess includes surgery and medication. Depending on the location of the abscess and the general condition of the patient, it can be performed in a clinic or in a hospital. During the operation, the purulent-inflammatory focus is opened, the postoperative wound is treated with antiseptics and drained.
After surgery, medications must be prescribed. They are similar to those used to treat pericoronitis. To detoxify, it is recommended to drink plenty of alkaline liquids, such as mineral water and cranberry juice.
For several days after the operation, the wound is bandaged daily and treated with antiseptics.
Treatment of osteomyelitis
If osteomyelitis is detected, the patient is immediately hospitalized. The erupting tooth is removed, and all purulent foci are carefully treated. Antibacterial drugs are administered intravenously. For detoxification, saline solutions are used, which are also administered intravenously.