In order to maintain the beauty and health of a child’s teeth, parents, first of all, need to know their structure, as well as have an idea of how temporary teeth differ from permanent teeth, and what care they require. This will help you avoid many mistakes, saving your baby from unpleasant sensations and negative emotions, and you from unnecessary troubles and worries.
The structure of the tooth.
A tooth is a bone located in the alveolar process of the jaw and consisting of various hard tissues (enamel, dentin, cement) and soft tissues (dental pulp). Anatomically, the following parts of the tooth can be distinguished:
- crown of the tooth (the part of the tooth protruding above the gum);
- tooth root (part of the tooth located in the jaw);
- neck of the tooth (a conventionally distinguished part of the tooth, which is a transitional area from the crown of the tooth to the root, covered with a thin layer of enamel)
The crown of the tooth is covered with enamel, the hardest tissue in the body, consisting of hydroxyapatite crystals. Beneath the enamel is a softer, more porous tissue called dentin. On the crown of the chewing tooth there are tubercles and fissures. Fissures are natural depressions on the chewing surface of the teeth between the cusps. Deep fissures are often the cause of the development of the carious process, because... a lot of plaque remains in them.
Inside the tooth there is a cavity containing pulp. The pulp of a tooth, in common parlance, the “nerve” of a tooth, is a neurovascular bundle consisting of blood vessels and a nerve. The neurovascular bundle provides nutritional function and replenishment of the composition of tooth tissue.
Each group of teeth differs in their structure, shape and function:
- incisors - involved in biting off food;
- fangs - provide “tearing off” and holding food;
- molars and premolars - are involved in grinding food to create an optimal digestive bolus.
Anatomy of different types of temporary teeth
- Incisors.
- Fangs.
- Molars.
Eight temporary incisors have the same structure - a fairly flat crown and 1 root. The incisors of the upper dentition, like the rest of the teeth, are larger than the lower ones. In the center, the incisors have one canal, and in 93% of cases, the lateral ones have two.
The four temporary canines are distinguished by a slightly sharp crown on all sides and the longest root. The crown of the canine preceding the permanent one is shorter and convex. The root has a rounded shape in cross-section and a slightly curved apex towards the buccal direction.
Each of the eight teeth of this type has a multi-cusped chewing surface and ends in several root canals. These are the largest teeth in childhood. The second molars are always larger than the first, which cannot be said about similar molars.
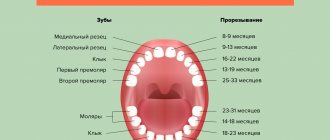
Teething in children.
Diagram and table of timing of eruption, location and loss of baby teeth in children
In humans, like almost all mammals, teeth erupt twice during life. The first teeth that appear in a child at the age of 6 - 9 months are called “milk” because of their color, as they have a soft white (milky) color.
Before appearing in the oral cavity, the tooth stretches the mucous membrane (the tooth can be easily felt with a finger), after which it breaks through it and appears in the oral cavity. In some children, a small bluish “bump” with transparent contents forms in the place where the baby tooth is about to erupt. This is an eruption cyst that forms over the future tooth. Despite the menacing name, in most cases, this goes away WITHOUT intervention from a doctor. The cyst breaks through and the long-awaited tooth appears. The cutting of a child’s first teeth is always a special and joyful event for parents, but it is often accompanied by unpleasant sensations and itching of the gums: therefore, the child is capricious and whiny, may sleep poorly, and puts everything in his mouth to “scratch” the gums and speed up the teething process. There may even be a slight increase in body temperature in a child due to teething. To represent the sequence of teeth erupting in a baby’s mouth, a diagram of the eruption of baby teeth in children is given. You can learn more about the sequence of eruption and replacement of baby teeth by reading the article “Teeth in children from 0 to 3 years old. When do children’s first teeth appear and cut?”
At the age of five years, the gradual replacement of milk teeth with permanent ones begins: under the “pressure” of new permanent teeth, the roots of the milk teeth dissolve and the milk tooth falls out (more precisely, the crown of the tooth falls out, since the root has dissolved). This is why, after a baby tooth falls out, it has no roots—hence the popular belief that baby teeth have no roots. At five years of age, the first permanent chewing tooth behind all the baby teeth is often the first to erupt. Parents often perceive this tooth as a milk tooth, since its eruption is not accompanied by the loss of any milk teeth: it seems that the child has 24 milk teeth.
The replacement of baby teeth with permanent ones is completed at the age of 13 years. By this age, a child usually has 24 teeth in his mouth, 6 teeth on each side of the jaw: central and lateral incisors, canine, first and second premolars and a molar. Next, the teenager’s second and third molars erupt. The latter is often called the “wisdom” tooth and it does not erupt until the age of 17–18 years. In some people, wisdom teeth do not erupt at all, as they are rudimentary.
Prevention
The classic question: “When should you start brushing your teeth?”
At once. From the very first eruption. Here, of course, you will have to select games with children so that this does not turn into an unpleasant procedure. Let him try different types of toothpastes, brush his teeth with a plastic horse, and the like. To start, it is convenient to use silicone brushes that fit on your finger. And you still need to keep an eye on them, even if they already brush their teeth themselves. Believe me, they often brush their teeth terribly. Buy a plaque indicator - it's a dye. You can simply rinse your mouth with it and rinse with water. Uncleaned plaque will remain brightly colored. Unfortunately, so does the language for a while. Therefore, you can simply apply it to your teeth with an ear stick.
Difference between baby teeth and permanent teeth.
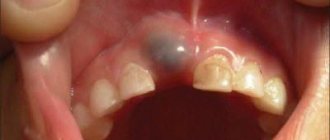
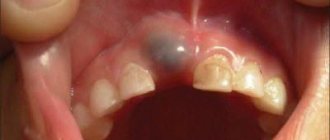
PHOTO: Caries of primary front teeth. The enamel of baby teeth is thinner and less mineralized, which makes it less resistant to caries.
Unlike permanent teeth, the “lifespan” of primary teeth is much shorter. Resorption of tooth roots begins 2-3 years after their eruption in the oral cavity and continues until they fall out.
Contrary to popular belief, baby teeth, just like permanent teeth, have roots and a nerve (pulp). The roots hold the tooth in the bone. Under the milk tooth is the germ of a permanent tooth. As the permanent tooth erupts, it stimulates the resorption of the roots of the baby tooth, and by the time the baby tooth falls out, only the crown remains.
Since baby teeth (like permanent teeth) have a nerve (pulp), they can hurt if an infection from a carious cavity enters the tooth cavity, causing the development of pulpitis (inflammation of the nerve of the tooth).
392measures and structure.
- Primary teeth are smaller than permanent teeth and have less massive roots;
- Baby teeth have a more complex anatomical structure of root canals, which leads to a more labor-intensive treatment process than in permanent teeth;
- The hard tissues of primary teeth are less mineralized and less resistant to abrasion and the development of caries.
- the hard tissues of baby teeth are much thinner than those of permanent teeth: the inflammatory process quickly reaches the nerve of the tooth;
Soft foods will cause tooth decay
This is the second consequence of feeding exclusively soft cereals and purees, when it is time for the child to chew solid food.
A colleague already talked about this in a post about caries. When we chew hard stems or gnaw on roots, we clean off plaque. In addition, there is a micro-massage of the gums, which improves their blood circulation and prevents the formation of tartar under the gums. The child should chew intensively and not drink instant cereals, jelly and banana puree. As a rule, if you see a child with severe multiple caries, then his diet will almost certainly consist of soft buns, cookies and all sorts of instant cereals. Well, in general, hygiene is also not very good.
Why are baby teeth needed?
Milk teeth are involved in the development of functions in the child such as chewing and pronunciation of sounds. Without them, chewing hard food would be impossible. The aesthetic component plays an important role.
Also, baby teeth hold space in the dentition for permanent teeth. The eruption of primary teeth stimulates the primary growth of the jaws. The second wave of jaw growth begins during the period of replacement of baby teeth with permanent ones. Early removal of primary chewing teeth leads to the displacement of neighboring teeth into the area of the missing one and the formation of crowding of teeth in the future!
Jaws don't grow because of soft food
One of the options for underdevelopment of the lower jaw. Specific “bird” profile.
The same patient. Stereolithography of the skull.
Reducing the load below the intended one leads to two very unpleasant consequences. The jaws begin to lag behind in development. As a result, lower and upper micrognathia is formed - underdevelopment of the jaws. The photos above show a very tough case. Most often this is a consequence of concomitant genetic disorders. But even on a less impressive scale, this is a wild headache for orthodontists. You can simply move and tilt individual teeth. It is almost impossible to adjust the position and size of the jaws, especially in adulthood. You will have to break bones, reshape the position of muscles, joints, tongue and much more.
Tooth development.
The formation of the rudiments of baby teeth in the fetus begins at 4–5 months of intrauterine development. That is why the mother’s illnesses during this period lead to disruption of various stages of dental development, for example, a violation of the mineralization of the tooth occurs. As a result, the enamel can become weak and brittle. Taking certain medications during this period can also affect the development of teeth. For example, if the mother was treated with tetracycline antibiotics, the child’s teeth will be dark yellow or even brown (so-called tetracycline teeth).
Enamel mineralization begins in the prenatal period and continues for 6 months after birth. Mineralization of the crown part of the teeth has time to take place in utero, while mineralization of the cervical region of the incisors, canines and molars continues after birth, in completely new and not always favorable conditions. The mineralization process can be negatively affected by the nature and diet, social living conditions and various diseases of the child (acute respiratory infections, intestinal infections and functional diseases). That is why the cervical area is the most vulnerable and typical place for the occurrence of “bottle” caries of primary teeth.
Possible complications after nerve removal
Parents often associate complications that arise after removal with the low level of professionalism of the dentist who performed the procedure. They begin to ask another question: is the nerve always removed correctly? Perhaps this procedure is associated with certain risks? Indeed, this kind of thing happens. The need to seek re-treatment may arise in several cases:
- Re-infection, which became possible due to insufficient treatment with an antiseptic.
- Destruction of the installed filling, which was caused by a poorly performed filling procedure.
- Compression of the tooth root by an installed filling.
- A root fracture that can occur if the dentist works too hard with various instruments on the surface of the pulp.
Of course, this doesn't happen very often.
However, if the child complains that the pain does not go away, but rather gets worse, you should visit the clinic again. Never ignore your child’s words that something hurts! Moreover, never resort to painkillers. After all, pain is a consequence. To get rid of it, you need to look for the cause. And only a qualified dentist with enough experience can do this. Moscow metro station Zvezdnaya, Danube Avenue, 23
Features of the root system of children's teeth
The structure of all dental canals includes coronal, middle and apical (apical) parts. The first, represented directly adjacent to the mouths, is the largest and widest. The middle part connects the coronal region with the apical zone of the root. The apical region is located below and often has a number of anatomical features: pathological or physiological resorption, fusion of several canals, lateral placement or open structure of the hole, strong narrowing or bending, ramification (branching), etc. The narrowest part of the root is located at the dentinocemental border. At a distance of 0.5-1 mm from the radiological apex there is a physiological opening. At an early age, root canals do not have a perfectly round cross-section. Only with age, due to the deposition of replacement dentin, its internal space takes on the shape of a circle.
Features of the treatment of pulpitis in the case of unformed roots
A feature of the treatment of pulpitis in the case of unformed roots is the impossibility of completely extracting the pulp and treating canals along the entire length of the root.
. Therefore, in this case apply:
- biological treatment method,
- amputation method of treatment.
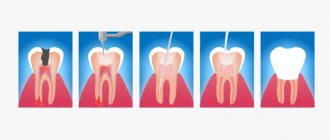
Biological method of treating pulpitis of a baby tooth (conservative).
This method involves preserving the entire pulp in a viable state , however, it has many contraindications and requires adherence to ideal asepsis and antisepsis during work in order to avoid repeated pain.
First, under anesthesia, the carious cavity is cleaned of necrotic tissue, and a medicinal paste is applied to the bottom of the cavity or directly onto the exposed pulp for several days. After the pain stops, a permanent filling is placed. Thanks to the biological treatment method, the tooth remains alive, that is, the preserved pulp allows the tooth tissue to be supplied with nutrients, maintaining high strength .
Amputation methods for the treatment of pulpitis of primary teeth
Amputation methods for the treatment of pulpitis in primary teeth with unformed or absorbable roots consist of removing the pulp .
Amputation can be: Vital – i.e. removal under anesthesia and without arsenic. This method is most often used in modern pediatric dentistry rather than the outdated method of devital amputation.
Devital amputation is a method of treating pulpitis, which involves first “killing” the pulp, and then mummifying it with potent and often toxic pastes. To cure pulpitis with this “old” method, you need not one visit, but three or even more. Long-term results, taking into account many years of experience in using this method, most often turn out to be negative.