General information
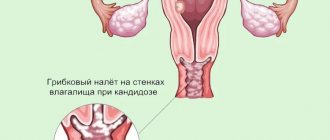
Candidiasis in children is a common disease among children. Normally, small amounts of fungi are part of the opportunistic microflora and are constantly present in the body. If the child’s immunity is strong, microorganisms are safe for health. In weakened children, the fungus begins to multiply uncontrollably, affecting the mucous membranes, skin, and genitals. If candidiasis is left untreated, serious health problems can follow. The main task of parents in the fight against the disease is to establish good nutrition and strengthen the child’s immunity.
How to avoid relapse of candidiasis?
Candida is an opportunistic microorganism that is usually present in the microflora of intimate areas. In order not to provoke its excessive reproduction again:
- strengthen your immune system;
- do not wear tight synthetic underwear;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- take enough vitamins, reduce the amount of fast carbohydrates;
- reduce the amount of foods and drinks that contain mold and yeast;
- use contraception;
- avoid stress.
During treatment for thrush, you will have to adjust your diet
Regardless of lifestyle, thrush can develop:
- when hormonal levels change (pregnancy, taking birth control pills, endocrine diseases);
- after operations;
- as a result of antibiotic therapy;
- during serious illnesses;
- with vaginal dysbiosis;
- after hypothermia.
Symptoms of candidiasis
Most often, candidiasis occurs in newborns and preschool children.
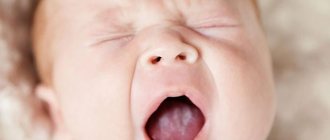
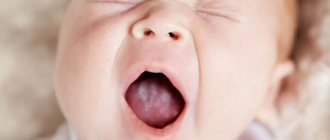
The older the child, the less often the disease is diagnosed. The favorite place for thrush to appear is the oral mucosa. A cheesy coating appears on the gums, palate, and inside the cheeks, and the baby feels pain and itching when eating. Along with these symptoms, candidiasis in children is also characterized by other signs:
- redness of the mucous membrane;
- ulcers that open after removing the cheesy plaque;
- loss of appetite;
- general weakness;
- white coating on the tongue.
The child does not eat well and is often capricious, since any touch to the mucous membrane causes pain.
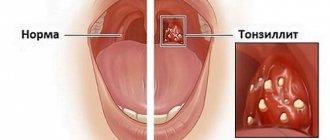
In advanced cases, bleeding wounds open at the site of the removed plaque. There is another common form of candidiasis - fungal tonsillitis. It develops as a result of improper treatment of protracted sore throat. Characteristic symptoms of the disease are a cheesy coating on the tonsils and a burning sensation in the throat.
When the skin is infected with fungi, dense spots, redness, and blisters appear on it. In adolescents, thrush often affects the mucous membrane of the genital organs, and the disease is more typical for girls. Vaginal discharge becomes white and thick. In boys, the head of the genital organ turns red, and a discharge similar to sour cream appears in the area of the urethra. Cystitis and urethritis may develop.
If fungi infect the digestive tract, the child begins to suffer from colic, and food is difficult to digest. The baby suffers from constipation and pain in the lower abdomen. If fungi colonize the respiratory organs, the child often suffers from bronchitis, pneumonia, and ARVI. If internal organs are damaged, treatment should begin immediately, in consultation with a pediatrician.
Candidiasis of the intestines and other digestive organs
After Candida damage to the skin and visible mucous membranes, candidiasis of the gastrointestinal tract in infants ranks third. Carriage of microorganisms is quite common when the pathogens do not cause disease. Good immunity inhibits the development of the infectious process. But under certain circumstances, weakened children may develop candidal esophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus), gastroduodenitis (inflammation of the stomach and duodenum), enteritis (inflammation of the small intestine), enterocolitis (inflammation of the small and large intestines).
Factors contributing to the development of gastrointestinal candidiasis
The following factors contribute to the development of intestinal candidiasis:
- An imbalance between Candida colonization in the intestines and defense mechanisms that prevent excessive growth of microorganisms.
- The presence of physiological intestinal dysbiosis.
- Features of the structure of the mucous membrane in newborns. Failure of its protective and secretory functions.
- Long-term antibiotic therapy leads to the death of “good” bacteria and excessive growth of opportunistic flora, including fungi.
Signs and symptoms of candidal esophagitis
The disease may be asymptomatic or have nonspecific manifestations. Classic typical manifestations of candidal esophagitis are recorded extremely rarely. The infectious process develops in children born to mothers with vaginal candidiasis on the second day of life. Lack of appetite, refusal to breastfeed, excessive regurgitation containing whitish lumps, vomiting and rapid increase in dehydration are the main symptoms of the disease. Toxicosis is slightly expressed.
The basis of diagnosis is fibroesophagogastroscopy and culture of vomit on nutritional media in order to identify fungi of the genus Candida.
Rice. 10. Microscopy reveals pseudomycelium of Candida b and budding cells (photo on the left); when inoculating the vomit, an increase in colonies of pathogens is noted (photo on the right).
Signs and symptoms of intestinal candidiasis
Intestinal candidiasis in children occurs with symptoms such as lack of appetite (sometimes infants completely refuse to eat), regurgitation and vomiting, pain, bloating and rumbling in the abdomen, and loose stools. The vomit contains greenish or whitish mucus, and the stool contains yellowish-greenish mucus and white lumps. The smell of stool is normal. Symptoms of toxicosis are mild or absent. Microscopy of vomit and feces reveals fungal mycelium and budding pathogen cells. Candida is isolated from feces in crops in quantities of more than 10 4–5 CFU/ml.
In more than half of infants, intestinal candidiasis is combined with lesions of the skin around the anus, buttocks and visible mucous membranes.
Rice. 11. Often in infants, intestinal candidiasis affects the skin around the anus and buttocks.
Treatment of candidiasis of the gastrointestinal tract
In the non-invasive form of candidiasis, fungal cells do not form pseudomycelium and do not germinate the intestinal mucous layer. They multiply intensively in the lumen of the organ, disrupting cavity and parietal digestion. Treatment in this case is carried out with antifungal drugs that are not absorbed from the intestinal lumen - Nystatin.
In the invasive form of intestinal candidiasis, candida germinates the epithelial layer and penetrates beyond the basement membrane. The pathogens then enter the lymphatic system and bloodstream and spread throughout the body. In this case, Flucanazole, Ketoconazole and Intraconazole are effective.
The drugs are completely absorbed in the upper gastrointestinal tract.
If treatment is ineffective in children in intensive care units, Amphotericin B is used intravenously to treat candidiasis. For intestinal candidiasis in newborns, the drug is rarely used due to its high toxicity.
To correct the composition of intestinal microflora, probiotics are used. Immunocorrectors are used according to indications.
Causes of candidiasis
The main cause of candidiasis in children is a yeast fungus of the genus Candida, present in the human microflora. But to activate it and increase the number of microorganisms, a number of factors are required:
- weakened immune system;
- frequent viral and colds;
- thyroid diseases;
- diabetes;
- hypovitaminosis;
- taking hormonal drugs or antibiotics for a long time;
- chronic diseases;
- HIV infection;
- intestinal dysbiosis.
The disease often occurs in premature infants and weakened children. If the mother's birth canal has been affected by candida, the baby, passing through it, becomes infected. The risk of developing candidiasis in such a newborn is much higher.
Treatment of thrush after taking antibiotics
Long-term or improper treatment with antibacterial drugs is one of the common causes of the development of childhood oral candidiasis.
Potent medications destroy all bacteria, harmful and beneficial, which provokes an imbalance of microflora in the body. Many parents believe that modern broad-spectrum antibiotics cannot cause dysbiosis. This is not true; there are no absolutely safe antimicrobial drugs. All of them negatively affect the balance of microflora to a greater or lesser extent.
Treatment of thrush after taking antibiotics is no different from treatment of other forms of the disease. Local antifungal and painkillers, antiseptics, antihistamines, and vitamins are prescribed.
But in addition, you definitely need to take medications to restore the microflora :
- Linux . Capsules contain live bacteria. Can be taken by children of any age.
- Bifidumbacterin . The drug contains live bifidobacteria and is produced in different forms, which allows you to choose a medicine for a child at any age.
- Trilact . Probiotic in emulsion form. It is allowed to give to children over 18 months.
Linex
Bifidumbacterin
Trilact
Reference! Useful lactobacilli for the intestines are also contained in some products - biokefir, hard cheese Slavyansky, Olympus, Imunele yogurt, Actimel.
Diagnosis of candidiasis
A pediatrician usually has no problems diagnosing thrush on the oral mucosa.
This is a common disease with characteristic symptoms, so an experienced specialist can easily identify it. In particularly difficult cases, when diagnosing a sore throat, sputum analysis may be required to identify the pathogen. The situation is more complicated with the diagnosis of candidiasis on the genital mucosa. In this case, you will have to take a smear for microflora, which will show the presence of inflammation and help identify the causative pathogen.
Thrush on internal organs is even more difficult to detect: external symptoms may be absent. Blood, urine, and stool tests may be required to detect mycosis.
How to treat thrush in a child?
The disease is treated at home. Local medications are used and only as prescribed by a doctor: pediatrician or dentist! Special antifungal agents are used in the form of solutions, sprays, gels, and drops. For maximum effectiveness of therapy, the drug must remain in the oral cavity (on the mucous membrane) for as long as possible. Therefore, the main way to use them is by rinsing or lubricating.
Treatment is long, up to 2-3 weeks.
It is important!
Often thrush in the mouth of infants is associated with candidiasis of the skin of the nipples and areola in the mother. In this case, the woman experiences redness, irritation, and a burning sensation on her chest. In this case, treatment should be comprehensive, for mother and baby.
Treatment of candidiasis
The goal of treatment for candidiasis in children is to eliminate symptoms and prevent further proliferation of fungi in order to reduce their number. General recommendations for strengthening the baby’s body are as follows:
- reduce the consumption of sweet, salty and flour foods, which create a favorable environment for the growth of candida;
- take vitamin complexes, including folic and ascorbic acids, probiotics to normalize microflora;
- give the child drugs to strengthen the immune system;
- For newborns on artificial nutrition, switch to medicinal mixtures containing probiotics and vitamins.
If candidiasis has affected the oral cavity, treatment of the mucous membrane with antifungal agents is prescribed:
- a solution of baking soda, fucorcin or brilliant green;
- Miramistin (antiseptic);
- Clotrimazole (antifungal ointment);
- Nizoral, Pimafucin (antimycotic medications);
- spray for sore throat, stomatitis.
It is recommended to lubricate nails infected with fungus with iodine, antifungal ointments Clotrimazole, Decamine, Mikoseptin and varnishes. If the vagina is affected in girls, antifungal suppositories are recommended. You should not select medications yourself. It is better to consult a doctor and get examined. Self-medication can only worsen the baby’s condition. If thrush, despite the measures taken, does not go away, you may need to consult an immunologist, because This condition is usually associated with weak immunity.
Types of fungal infections
Fungal infections can appear at any age. Infants most often encounter this problem - redness and peeling appear. The symptoms are similar to those of an allergic reaction, so therapy is often carried out, which is ineffective.
The clinical picture depends on the type of disease:
- Because Candida thrives in moist and warm environments, it multiplies in the diaper area of babies. This manifests as intense, large-scale redness with scaly edges.
- Oral thrush is characterized by the appearance of a tight, gray-whitish film in the cheeks and throat. This type of disease is also caused by Candida and is most common among infants.
- Ringworm is accompanied by severe itching, the appearance of round bald spots and blackheads. There is excessive hair fragility, which results in bald spots.
- Vaginal (genital) candidiasis also occurs in childhood, although much less frequently. The victims may be babies in the first weeks of life, whose mother gave them Candida at birth. Babies still have their mother's female sex hormones (estrogens) in their bodies. They appear to inhibit the regenerative ability of the mucous membranes, which in turn contributes to the progression of the disease.
Pet-borne dermatophytes should not be underestimated. The head and torso are affected. The main carriers are cats, as well as guinea pigs and rabbits. Accompanied by severe itching, redness and excessive dryness.
Table - Classification of mycosis pathogens
| Pathogen name | Localization area | How it manifests itself |
| Tinea capitis or Microsporum (microsporia or “ringworm”) | Scalp | Ring-shaped, sharply limited red spots appear, in which the hair either breaks or falls out. Sometimes the scalp starts to ooze due to weeping. Small red pustules may appear. |
| Tinea corporis (dermatophytosis) | Torso and upper limbs | It appears as pale red areas with characteristic peeling. In addition, there is unbearable itching. Therefore, it is important to start treatment as soon as possible to avoid spreading the fungus to other parts of the child’s body through scratching. |
| Tinea pedis (onychomycosis) | Nail plates | The filamentous fungus damages the toes or nails and gives them a characteristic yellowish coloration. The plates with onychomycosis become thick and brittle, with a “loose” structure. With the exception of visual changes, symptoms such as itching do not appear, so onychomycosis is usually diagnosed in the later stages of progression. |
Prevention of candidiasis
To avoid thrush, follow the disease prevention measures:
- Mothers in labor are advised to sanitize the birth canal before giving birth. To do this, the woman takes a smear, based on the results of which the doctor determines the need for treatment. If candidiasis is diagnosed, vaginal suppositories with antiseptics are prescribed. This measure will prevent the baby from becoming infected with fungi.
- Follow the rules of hygiene in the maternity hospital.
- Breastfeed your baby only unless there are medical indications for bottle feeding. In the latter case, you need to choose the right mixture together with your pediatrician.
- Limit the consumption of sweets and sugar in children over one year of age. Try to keep your diet varied, healthy and nutritious.
- If the baby is weakened, strengthen the immune system with hardening procedures, proper nutrition, physical exercise, etc.
Candidiasis is an unpleasant but treatable disease. Timely consultation with a pediatrician, the correct course of therapy and compliance with preventive measures will allow you to forget about thrush for a long time. SM-Doctor specialists are always ready to help your child in the fight against candidiasis.
Stages of development
The severity of thrush symptoms depends on the stage and severity of the disease.
| Stage | Characteristic manifestations |
| Lightweight | The oral mucosa is red and swollen, and rashes appear. A white coating forms on the tongue and cheeks in the form of small islands; at the initial stage, it is easily removed with a spoon. |
| Average | White plaques with a cheesy consistency cover the entire surface of the tongue. Bleeding ulcers and seizures appear. The child cries often and has poor appetite. |
| Heavy | A gray or pale yellow plaque covers not only the entire oral mucosa. But it also spreads to the lips, throat, and tonsils. The plaque is not removed; with strong pressure, bleeding ulcers appear. Additional symptoms are fever up to 38.5 degrees and above, weakness, drowsiness. The child stops eating and constantly complains of severe pain in the mouth. |