According to statistics, by the age of six, approximately 70% of children have dental caries. A large percentage of young children are susceptible to developing so-called bottle caries. What kind of disease is this, why it occurs and whether it can be cured, we will tell you in the article.
In this article
- The mechanism of caries development in children
- What is bottle caries in children?
- How to treat bottle caries?
- How bottle caries is treated using remineralization method
- Treatment of bottle caries using fluoridation
- Treatment of bottle caries using the ICON method
- Is silver plating safe for children?
- Ozone therapy treatment
- What to do if there is a hole in your tooth?
- What should be done to prevent bottle caries?
The mechanism of caries development in children
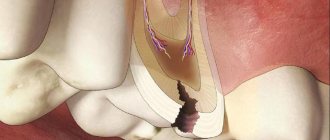
Caries is a slowly occurring pathological process in which the destruction of hard dental tissues occurs. It can affect both baby and permanent teeth and occurs in adults and children of any age.
It is known that caries develops under the influence of several factors - both external and internal. The main cause of carious lesions is the activity of cariogenic bacteria. They coat the teeth with a biofilm we call plaque. Bacteria feed on carbohydrates that enter our body with food. They ferment sugars and convert them into acids, which have a negative effect on superficial and deep dental tissues. If plaque is not removed from the surface of the enamel in time, the acids will destroy its structure and sooner or later penetrate into the dentin - the bone tissue under the enamel. Thus, it is organic acid, a product of bacterial activity, that has a damaging effect on teeth.
There are factors that increase the risk of developing caries. These include:
- a large amount of carbohydrate and sweet foods in the diet;
- multiple snacks, keeping food in the mouth for long periods of time (for example, sucking on lollipops, bottle-feeding babies at night);
- infrequent or improper brushing of teeth, which does not effectively remove plaque;
- a diet lacking healthy foods rich in calcium and fluoride.
Symptoms of the disease
The clinical symptoms of bottle caries depend on the neglect of the pathological process. The development of the disease goes through several successive stages:
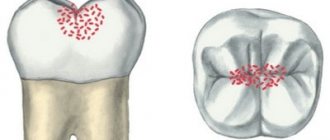
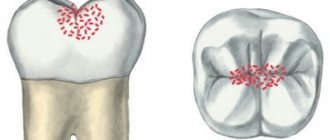
- Formation of a white spot. White spots appear on the surface of the enamel, indicating the beginning of the demineralization process. There are no other symptoms.
- Superficial lesion. The demineralization zone takes on a yellowish-caramel or darker hue. The surface of the spot becomes rough. There are no complaints of pain. A short-term reaction to sweets or sour foods is possible.
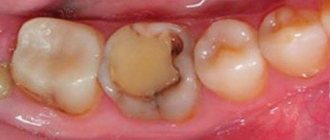
- Average caries. Inflammation spreads to dentin. Pits and grooves form on the surface of the segments. The amount of pigmentation increases. Pain appears when exposed to cold or heat. The baby may complain about food getting stuck in the spaces between the units.
- Deep caries (advanced). A large area of dentin is affected. There is pain that gets worse while eating. Sleep is disturbed, the child is capricious and cries. Upon examination, a deformation of the shape of the affected segment and a deep cavity are revealed.
What is bottle caries in children?
Childhood caries can occur for various reasons. One of the most common forms of the disease does not occur in adults, but is characteristic of young children. This is the so-called baby bottle caries. Another name is circular. What are its features and reasons?
The main cause of bottle caries can be understood from the name - long-term feeding of a child from a baby bottle with a pacifier. The disease is also typical for children who have been breastfed for a long time.
The essence of the problem is as follows. When a baby is given a bottle and breastfeeding before bedtime or nap time, baby's teeth are left with large amounts of sweet carbohydrates, a food source for bacteria. At the same time, at night the amount of saliva in the mouth decreases, which has a bactericidal effect and could at least partially protect the teeth. It turns out that all night or several hours during the day, while the child is sleeping, there are food remains in the oral cavity, which microbes happily convert into acid. At the same time, the enamel of children's teeth is not yet as strong as that of adults. Therefore, caries begins and spreads much faster. In just a few months or even weeks, it can go from early stage staining to deep dentin damage.
The peculiarity of bottle caries is that most often it affects the front incisors: whitish spots appear on them in the contact areas and near the gums. This is due to the peculiarities of gripping a bottle or the mother's breast when feeding. The circular arrangement of bottle dental caries on the front teeth, in areas of contact with food, gave it the name circular. This type of caries is often diagnosed in a one-year-old child who continues to eat from a bottle, although he can receive complementary foods from a spoon. In addition to babies of the first year of life, children's bottle caries can appear in two- and three-year-olds, who are allowed to eat sweets and drink juices more than three times a day. The mechanism of dental damage is the same as with bottle feeding.
Dangerous consequences
You know what to do if your child has bottle tooth decay. What will happen if it is not treated? Untreated disease in time will lead to serious consequences. The presence of constant inflammation will cause severe pain, due to which the baby will not be able to sleep. Intermittent sleep will cause overwork, which, in turn, will weaken the immune system and cause various diseases, including mental ones, and will also affect the overall development of the child. An infection that is not stopped in time will lead to inflammation of not only the hard, but also the soft tissues of the tooth, and will also damage the rudiments of the molars. The long absence of molars, in turn, will affect the diet, cause speech defects, malocclusion and, as a result, changes in the child’s appearance. Moreover, the infection is likely to spread beyond the mouth, to the throat and lungs and cause respiratory problems. In order to avoid such a terrible development of events, it is necessary to treat bottle caries in time, and even better, to prevent its occurrence.
Prevention measures
- In order to avoid circular caries, first of all, you need to stop feeding your baby before bed. If the child cannot sleep on an empty stomach, before going to bed, wait until the baby burps, and then thoroughly clean the baby’s mouth with a special toothbrush or napkin.
- Reduce the amount of sweets and replace high-sugar juices with water, preferably fluoridated. Fluoride is very beneficial for children's teeth, but only in certain quantities. Therefore, we recommend that you contact your pediatric dentist and, together with him, choose a toothpaste that is suitable for your baby, enriched with this substance.
- In addition, experts urge parents not to overuse sweet cough syrups - they are one of the main causes of caries. After using them, do not forget to rinse your child's mouth and brush his teeth.
How to treat bottle caries?
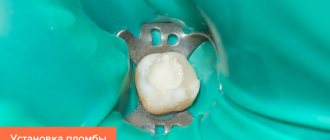
Treatment of children with bottle caries is carried out using different methods, depending on the age of the child, the stage of development of the disease, and the technical capabilities of the dental clinic. There are two main approaches to treatment - conservative and surgical. The first involves treatment without preparation, drilling the tooth with a drill, or installing a filling. These are non-invasive and completely painless methods. But, unfortunately, they are effective only in the early stages.
Much more often it is necessary to carry out surgical treatment, in which the tooth is opened and a filling is installed. This is due to the fact that in most cases, bottle caries is diagnosed too late - when the tooth already has cavities and preparation cannot be done without.
Why does tooth decay occur?
The destruction of dental tissue is due to several reasons:
- Violation of the diet and rules of nutrition. Parents often ignore the feeding recommendations of the doctor observing the child, giving the baby food at his first request (without following the regime) and placing a bottle with a sweet drink next to the baby’s crib so that the child can drink whenever he wants and not scream. Sugar is a simple carbohydrate that is the main raw material for the formation of acid, which has a destructive effect on teeth. As a result, cariogenic organisms are always provided with the raw materials to create acid.
- Poor hygiene. If you do not teach your child to brush their teeth twice a day, this may subsequently result in the formation of microbial plaque. It is better to prevent caries than to treat it: the best prevention is a properly organized diet and proper care of the gums and teeth.
- Infection with cariogenic organisms. The oral cavity of a newborn person is sterile. The cause of the appearance of cariogenic microflora can be parents who taste food with a spoon, which they then give to the child without washing it, and kiss him on the lips.
- Insufficient mineralization. The enamel of the first teeth contains practically no calcium. Proper hygiene, as well as the use of pastes that contain calcium or fluoride, gradually strengthen it. However, if you do not follow a diet and brush your teeth incorrectly, the enamel will not strengthen and will begin to lose calcium, which will inevitably lead to caries.
How bottle caries is treated using remineralization method
Early bottle caries can often be found on the teeth of children aged 10-20 months. Signs of carious lesions at this stage are white spots on the enamel and in the area of contact of the dental crown with the gum and adjacent jaw. A small child does not show any signs of anxiety, because teeth with early caries do not hurt or cause discomfort. To notice the lesion, parents should regularly examine the baby’s mouth and, if they detect changes in the enamel, immediately contact the dentist.
For early caries in children, treatment will consist of strengthening the enamel, restoring its mineral composition and stopping further pathological process.
There are different options for treating caries without a drill. One of the methods is remineralization therapy. The mineral composition of tooth enamel consists of 57% calcium and phosphorus. When these substances are not enough, gradual destruction of the enamel structure occurs. Retherapy is carried out to restore its normal mineral composition and strength. For the purpose of remineralization, the surface of the teeth is covered with gels, pastes and other preparations with calcium and phosphorus. To consolidate the result, the dentist may prescribe additional fluoride-containing medications. They reduce the solubility of tooth enamel, prevent the leaching of calcium, and increase its resistance to acid.
In order for retherapy to give the expected result, a number of conditions must be met. Firstly, remineralizing compounds are applied only to teeth that have been cleaned of plaque, because they must come into contact with the enamel. Secondly, the contact must be long-lasting. Thirdly, minerals must be present in them in the form of phosphorus and calcium ions.
Correct retherapy, which will give the best results in the treatment and prevention of bottle caries, can be carried out by a qualified dentist.
How to prevent the appearance and development of the disease? Prevention from the first months of life!
There are several measures to prevent bottle caries in children, and they are all divided into two types: measures of local protection against caries and measures of systemic prevention.
The first include:
- Brushing your teeth is important for all children who have at least one tooth. For cleaning in very young children (up to one year old), simple gauze swabs soaked in water, tea or chamomile decoction, soft brushes placed on the finger of one of the parents, and special napkins (Spiffies, Teeth Cleaners) are used. From the age of one and a half, a child can already be taught to use a children's toothbrush.
- The use of anti-caries gels for treating teeth.
<
Systemic prevention consists of the following actions:
- Compliance with the diet, avoiding night feedings and feedings after brushing your teeth.
- Correction of the diet, reducing the amount of sweets and flour products in it, increasing the amount of fresh fruits and vegetables, fish, dairy products, and herbs.
- Observe basic hygiene measures: do not lick the spoon with which the child eats, or a pacifier that has fallen on the floor. Cariogenic bacteria from the parents' mouth may be unfamiliar to the baby's body.
In general, the child should be weaned off the pacifier as early as possible and under no circumstances should it be smeared with jam or syrup. A healthy child can easily calm down and fall asleep simply with the help of his parents' affection.
And if the baby is capricious and cries for no apparent reason, this is a reason to show him to the doctor. Do not be afraid of doctors: no one better than them recognizes a disease at a stage when it is still easy to cure. And be healthy!
Treatment of bottle caries using fluoridation
A disease such as bottle caries can be cured at an early stage using simple or deep fluoridation.
The essence of fluoridation is that tooth enamel is saturated with fluoride - a substance that reduces tooth sensitivity, strengthens the enamel, and makes it less susceptible to negative external influences.
With simple fluoridation, a fluoride-containing composition is applied to the teeth, which forms a thin protective film. With deep fluoridation, in addition to fluorine, the preparations include calcium and other compounds. Their complex action promotes the penetration of beneficial substances into the enamel structure and strengthens it from the inside.
After fluoridation, teeth become less sensitive, the surface of the tooth enamel becomes smoother, less plaque accumulates on the teeth, and light and dark spots disappear.
Types of caries
- White spots appearing on the enamel. This is the very initial stage of caries, which is indicated by the appearance of white spots - foci of demineralization. At this stage, the dental tissue has not yet begun to deteriorate, and only chalky stains indicate that not everything is normal. However, if you ignore the appearance of these spots and do not contact your dentist, the enamel will continue to suffer from a lack of calcium and, as a result, deteriorate.
- Painless superficial caries - damage that affects the enamel and does not harm the underlying dentin. If such caries is not treated, it will move to the next stage.
- Medium caries is damage to the enamel and dentin underneath. If you allow cariogenic organisms to get close to the dentin, tooth destruction will occur much faster, since the bone substance of the tooth is softer in structure than the enamel.
- Deep caries, when a thin layer of dentin remains. If the dentin becomes completely thin, then caries will affect the pulp of the tooth, which will cause a lot of pain to the child.
Bottle caries is one of the types of dental damage. The term comes from a bottle of drink (usually sweet) that is often within a child's reach at night. These carious formations affect the upper incisors.
If caries is ignored and no measures are taken to eliminate it, complications may arise. Average caries, left unattended, will lead to the penetration of microorganisms into the pulp, which will cause pulpitis (characterized by severe pain that does not even allow you to sleep) and periodontitis (it is distinguished by the formation of a lump or fistula on the gum, filled with pus).
Treatment of bottle caries using the ICON method
Children over three years old with early stages of caries can be treated with a minimally invasive infiltration method. It is absolutely safe, but requires sitting still for about 20 minutes, so is not suitable for younger children.
The essence of the ICON method is that after preliminary preparation, damaged tooth enamel is coated with a sealant gel. It penetrates the pores of the enamel, seals them and prevents bacteria and acid from penetrating deep into the tooth.
Is silver plating safe for children?
The superficial form of bottle caries most often occurs in children between 16 and 24 months. At this stage of the lesion, dentin is exposed - the hard tissue of the tooth located under the enamel, the enamel becomes more sensitive. Gradually, carious spots change shade: instead of light, they become dark. Caries at this stage is also treated with remineralizing therapy, fluoridation, and infiltration. In some cases, it is advisable to carry out silvering.
Although this method is considered outdated and has a negative impact on the aesthetics of teeth (they darken), silver plating is still used in pediatric dentistry.
The essence of the method is that the surface of the teeth is coated with silver nitrate. It forms a film on the teeth that has an antimicrobial effect. Silvering does not cure bottle caries, but it can stop its development for a certain period of time.
Possible complications
If bottle caries in temporary teeth is not treated, the pathological process will soon lead to their complete loss by 3-4 years. The child cannot eat without pain or discomfort and chews food poorly.
Crumpling teeth not only upset the baby, but also pose a danger - sharp fragments can be swallowed and become injured.
The next stage after caries is pulpitis, when the infection spreads to the pulp tissue. The disease is characterized by severe paroxysmal pain that does not stop immediately after the removal of the irritant, as was the case with caries.
Then pulpitis is complicated by periodontitis - damage to the tissue behind the apex of the roots of the teeth. Often pulpitis and periodontitis affect temporary teeth at the same time, because the root canals in them are wide, and the infection is transmitted more quickly. Often this diagnosis ends in premature removal of teeth, because the inflammatory process in the thickness of the jaw threatens the health of the dental rudiments of the permanent dentition.
To prevent complications of bottle caries, it is first of all necessary to come on time for preventive examinations to the pediatric dentist. If you are highly susceptible to caries, it is recommended to visit a doctor every 3 months.
Even if the baby is still very small and is afraid of strangers and does not open his mouth, dental treatment is mandatory at any age. The dentist will definitely find an approach to the child and a method of treatment that will not bring him pain and stress.
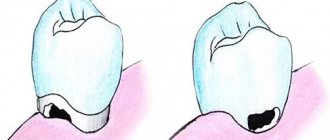
What to do if there is a hole in your tooth?
The above methods will help cure caries in the initial stage, when there is no cavity in the tooth. As soon as a hole has formed in the dentin, this means that caries has entered the medium or deep stage. In this case, treatment is carried out surgically.
The affected teeth are prepared, cleaned, dried, the cavity is prepared for the installation of a filling, and then filled with modern composite materials.
Children of any age do not like to visit dentists; some of them are difficult to even sit in a dental chair, let alone carry out treatment with a drill. This is why early diagnosis is so important, which is only possible with regular visits to the dentist.
What should be done to prevent bottle caries?
The development of bottle caries can be avoided if you monitor children’s teeth from early childhood and take comprehensive preventive measures:
- Teeth brushing begins immediately with the eruption of the first tooth. In the first year, you should use a soft brush without toothpaste or with a small amount of children's toothpaste. After a year, teeth are brushed with toothpaste; dentists also recommend using dental floss.
- In order to prevent tooth decay, you should not bottle feed your baby for a long time. When introducing complementary foods, it is advisable to immediately teach the baby to eat with a spoon from a plate. A similar recommendation applies to those children who are bottle-fed.
- Do not feed children before bed or during the day, and do not leave bottles in the crib for the baby to suck on throughout the night.
- Instead of sweet drinks, introduce your child to clean water and unsweetened tea.
- To avoid the transfer of cariogenic bacteria from an adult to a child, you should not share a spoon with children or give a child a pacifier from your mouth.
- In order to promptly notice pathological changes in the structure of the enamel and the condition of children's teeth, visit the dentist at least once every six months, even if it seems that the child has no signs of caries.
- Dental caries in children develops rapidly, and it is better for the dentist to once again confirm the healthy state of the oral cavity than to immediately detect pulpitis.
These simple recommendations will protect children's teeth from bottle caries and help maintain a beautiful smile.
Stages of development and manifestation of each form
The disease develops in 4 successive stages. Over time, teeth become more and more affected; in advanced cases, the baby may remain toothless.
Initial
Occurs in children aged 1-1.5 years. Small whitish spots are visible on the enamel. These are areas of tissue demineralization. In places of contact with the gums, whitish stripes are observed. It is not painful for the child; it is almost impossible to notice the lesion with the naked eye. It is for this reason that it is necessary to undergo preventive examinations with a dentist to detect the problem in a timely manner.
Experienced dental doctors will help determine the onset of the pathological process and take rehabilitation measures to prevent its further development.
Superficial
The enamel is partially destroyed, dentin is exposed. More often the problem is typical for children aged 2 years.
Such caries is noticeable, it looks like brownish spots. Sometimes the baby feels pain, but it occurs rarely and goes away quickly. At this stage, filling and preparation are indicated.
Average
Both layers are destroyed: dentin and enamel. If a small patient drinks or eats hot, cold, sweet, sour, acute pain appears. With subsequent rinsing and cleaning, the unpleasant sensations dull. Children become whiny and irritable.
Deep
At 2.5-4 years old, you can encounter serious damage to the teeth. The enamel is completely destroyed, the integrity of the dentin is significantly damaged. Soreness becomes a constant companion of the child, he refuses food and drink, cries. If the incisors and canines can be saved, crowns are installed. After removal, prosthetics are indicated.