Tooth roots inevitably begin to become exposed in old age - this process is completely natural and is a reaction to the aging of the body. But old age is far from the only reason for this phenomenon, which spoils a beautiful smile and can lead to other serious illnesses in the future. Root exposure can occur at any age due to disease or pathology.
This article will talk about what to do in a situation where the gum has noticeably risen above the tooth, and you will also find answers to why this happens and what the consequences of refusing treatment may be.
Exposure of the cervix causes severe pain
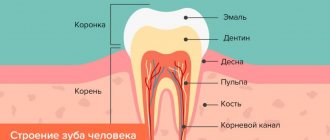
Our teeth consist of a crown part, which rises above the gum, as well as a neck and root system, which are hidden by soft and hard tissues. The neck of the tooth is the area between the crown and the roots; in fact, it is the transitional part from the crown to the root. On top it is covered by the gum, but if for some reason the gum begins to change its volume and move upward, then it can literally slide off the neck and make it very defenseless against the aggressive environment of the oral cavity, against any mechanical impact.
When the neck of the tooth is exposed, a yellow area appears near the gum
If the neck of the tooth is exposed, it is quite easy to notice upon careful examination near the mirror - you will see a yellow area (this is cement that covers the neck and roots). The cervix itself is very sensitive, it is many times more sensitive and thinner than the enamel, so after it is exposed, you will begin to experience sharp unpleasant sensations, pain from eating sour or salty, hot or cold food. Acute painful sensations can be caused by the daily procedure of brushing your teeth or even just touching a defenseless area with a brush.
If periodontitis or periodontal disease is to blame - only comprehensive treatment
The development of periodontitis is accompanied by the spread of inflammatory processes to periodontal tissue. Periodontal disease leads to a decrease in gum volume and rapid atrophy of the oral mucosa due to degenerative processes rather than inflammatory ones. In its “pure” form, this pathology is extremely rare - in 3-5% of cases. Today, it is more often considered as a complication of an advanced form of periodontitis or a consequence of its long-term treatment against the background of the aggressive course of the pathology itself. In both cases, an integrated approach to treatment is required, and it is better for the patient to immediately prepare for long-term therapy.
The treatment regimen for each patient should be worked out taking into account the individual characteristics of his clinical picture and the stage of development of the disease. Typically, such a course lasts about a year, during which some procedures are carried out once, others in a course of up to 10 visits. The complex may include the following therapeutic and preventive measures:
- diagnostics - computed tomography, tests, microflora culture, etc. diagnostic measures,
- comprehensive hygiene – removal of plaque and hard deposits, polishing and fluoridation of enamel, strengthening of mucosal tissues through the application of special hydrogels and a collagen membrane with extracts of medicinal herbs,
- splinting in case of mobility of some teeth,
- closed curettage (for pocket depths up to 4 mm) and open (for greater depths) in combination with treatment and polishing of the root surface,
- application of periodontal dressings with a pronounced healing effect,
- plasmolifting,
- injection vitamin therapy,
- laser therapy to stimulate the restoration of soft tissue cells,
- the use of medications based on hyaluronic acid to nourish the mucous membrane and stimulate its natural restoration (Revident and Revident+),
- fixation of collagen membranes (Creos from Nobel) and APRF membranes based on the patient’s own blood (an alternative to injection plasma lifting),
- the use of drugs to stimulate the growth of soft tissue (Straumann Emdogain),
- use of bone volume replenishment products (BoneCeramic from Straumann, Bio-Oss)
- training in the correct cleaning technique, selection of individual hygiene products, regular visits to the periodontist for preventive examinations.
Periodontitis is a chronic pathology, which is virtually impossible to cure completely. However, within a year of comprehensive treatment and restoration of gums, acute symptoms can be reliably relieved and stable remission can be achieved. However, you will have to continue to maintain the achieved effect, and for this you need to visit your specialist once every six months and carry out maintenance therapy according to his indications.
Pain is not the only problem that may bother you
With such a pathology, as we mentioned above, the necks of the teeth hurt. However, if you do not think about what to do in a timely manner, the problem will get worse. For example, a pathology can spread to the entire series and become generalized, then treating it later will be more difficult, and it will take a lot of time. In addition, exposing the hidden parts of the tooth will make your smile unattractive, it will lose its aesthetics, which in turn can cause psychological problems and refusal to communicate with others.
Pain also leads to another problem - you cannot eat what you want and cannot eat properly, which in turn is fraught with gastrointestinal diseases, weight loss and bad mood.
Pain impairs quality of life
The exposed necks of the teeth are defenseless not only against mechanical stress and the temperature and hardness of food, but also against the attack of bacteria. Therefore, if you do not start treatment on time, you may develop caries, pulpitis, and periodontitis.
Treatment at the dentist
If the pathological process has not yet covered a large area, treatment may be limited to:
- carrying out deep fluoridation;
- installing a filling on the root area;
- laser cleaning of areas affected by tartar;
- installation of dental crowns or veneers.
But most often, when patients come to the dental clinic, the disease has already reached the stage when only surgical treatment methods can help. Their goal: to close the exposed neck of the tooth and restore the natural contour of the gums.
Patchwork method
The most common treatment option that dentists and their patients appreciate for the short recovery period. It consists of transplanting a flap of tissue from the same gum or palate to the affected area. The disadvantages of the method include a feeling of discomfort in the area from which the tissue for transplantation was taken and a possible discrepancy in the color of the gum and the borrowed flap.
Tissue regeneration method
In this case, a membrane is introduced into the affected area, which stimulates the growth of the patient's own soft tissue. When the natural contour of the gum is restored, another operation is performed to remove the membrane. This method of gum reconstruction is very effective, but it frightens patients with the need for repeated surgical intervention.
Fortunately, technology does not stand still, and today more and more dental clinics can offer the implantation of a resorbable (absorbable) membrane. It does not require a second operation, making tissue regeneration an ideal treatment for gum recession.
100% discount on periodontist appointments!
Moscow
Exposure of the cervix may be caused by gum recession
Gum recession is a pathology in which the oral mucosa begins to change its normal volume, i.e. it atrophies, it becomes smaller, and accordingly, the hidden parts of the tooth are exposed. This phenomenon is dangerous because due to atrophy of soft tissues, the edge of the periodontium also shifts, i.e. the normal position of the tissues that are responsible for holding the tooth in its original position is disrupted.
Sometimes the opposite happens - the gum grows and increases in volume, and hyperplasia occurs. How dangerous is this phenomenon and how to deal with it? Find out from the article on the website.
With gum recession, the mucous membrane begins to decrease in volume.
Why does gum recession occur and the necks of teeth become exposed? In fact, there can be many reasons, and not all of them are as harmless as we would like. Let's look at them:
- poor oral hygiene: if plaque is not removed, pathogenic microflora will predominate in the mouth, and bacteria will begin to release large amounts of toxins, leading to tissue inflammation,
- atrophic gingivitis: this is an inflammation of the gums, in which blood circulation and nutrition of the mucous membrane are disrupted, resulting in a loss of soft tissue,
Most often, this symptom is a sign of gingivitis. - periodontitis: if gingivitis is not treated, the disease progresses and will lead to periodontitis, which is characterized not only by inflammation and exposure of the gums, but also by destruction of the musculoskeletal system of the tooth,
- periodontal disease,
- traumatic oral hygiene: for example, you carry it out using an unsuitable brush with hard bristles, an abrasive paste, or you do it too hard - pressing on the enamel and mucous membranes,
- cervical caries: if bacteria begin to attack the tooth from above, then there is a possibility that harmful microorganisms will provoke the destruction of the soft tissue of the gums,
- incorrectly installed fillings or crowns,
- incorrect bite: not only long-term neglect of bite pathologies can lead to gum recession, but also incorrect installation of orthodontic appliances,
- abnormalities of the frenulum of the upper or lower lip: abnormally located frenulums can pull poorly attached soft tissues away from the tooth,
- internal diseases of the body: for example, diabetes mellitus1, in which the blood circulation of the mucous membrane is impaired,
- metabolic disorders in the body: most often the problem is characteristic of pregnant women and women after menopause, adolescents, as well as elderly people (the appearance of gum recession in them can be a purely physiological phenomenon that arose due to age-related characteristics),
- individual physiological characteristics: for example, the mucous membrane of the gums is too thin, when due to any mechanical impact they begin to move away from the tooth.
For what reasons are the roots of teeth exposed?
The phenomenon of exposed teeth in dentistry has a name - gum recession, but usually recession is only a symptom behind which another dental disease is hidden. Most often, it is the lower row of teeth that suffers from recession, since it bears the brunt of the load.
A common disease that causes gums to become exposed is periodontitis, during which inflammatory processes begin to occur in the periodontal tissues; if such a disease is started, it can become chronic.
Typically, periodontitis is a consequence of poor oral hygiene. Plaque and food debris that accumulate between the teeth and on the surface gradually enter the soft tissues and provoke inflammatory processes.
Inflammation significantly weakens the gums, making them weak and unable to maintain their shape. Then they descend and expose the neck of the teeth, which can lead to their loosening and loss. Periodontitis can also be caused by natural pathology.
The second most common cause of exposed roots is periodontal disease, which, unlike periodontitis, is not an inflammatory disease. During such a disease, the gums decrease in size due to atrophy of soft tissues, or disruption of metabolic processes in them.
Other reasons that cause denudation of teeth include:
- Improper brushing of teeth, namely too much pressure of the brush on the gums.
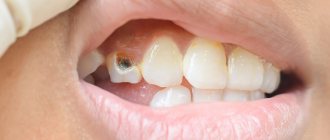
- Tooth decay close to the gums due to caries.
- Malocclusion, short frenulum of the tongue and other pathologies of the oral cavity.
- Malfunctions of the thyroid gland and gastrointestinal tract.
- Caries that has penetrated deep into the dental tissue often causes the gums to detach from the tooth.
To eliminate the defect, it is necessary to find out the cause of its occurrence. If the disease is allowed to progress, the gums will eventually recede to the point where the tooth can fall out. Considering that most of the causes of such a defect are not local, but affect the entire oral cavity, refusal of treatment can lead to the loss of all affected teeth.
Pathology can be calculated by characteristic symptoms and signs
If you see a yellow area at the junction of the crown and gums, and periodically feel sharp pain in this area, then in most cases this indicates that the neck of the tooth has become exposed. What to do? First of all, pay attention to other alarming symptoms that accompany the disease:
- swelling of the mucous membrane and bleeding,
- pain on the mucous membrane,
- hyperesthesia (increased sensitivity) of enamel,
- formation or increase in interdental spaces,
- accumulation of soft and hard plaque on the enamel and at the junction of the enamel and gums,
- visual lengthening of crowns,
- the appearance of bad breath that is not associated with eating or smoking.
With pathology, swelling of the mucous membrane appears
Diagnostics
If a patient complains of tooth sensitivity to cold, hot, sweet and sour foods, the doctor may immediately suspect hyperesthesia. The disease can be diagnosed after a visual examination of the patient's oral cavity. During the examination, the doctor may note changes in the structure of the hard tissues of the tooth, as well as changes in the condition of the periodontium. Usually there is a decrease in hard tissue at the cutting edge (front teeth) or on the chewing surface (back teeth).
Differential diagnosis of hyperesthesia lies in the ability to distinguish the symptoms of tooth sensitivity from the symptoms of acute pulpitis. In acute pulpitis, pain is prolonged, pain occurs mainly at night. With hyperesthesia, the pain is short-term, occurs directly from chemical or thermal irritation of the tooth and goes away almost immediately.
If the disease is not treated, you can lose your teeth
We have already found out why the necks of the teeth are exposed. Obviously, the disease requires treatment; it will not go away on its own, but in the absence of measures it will only progress, affecting an increasingly larger volume of first mucous and soft tissues, and then destroying the periodontium and ligamentous apparatus of the tooth. Thus, the pathology will be complicated by atrophy of bone tissue and exposure of the roots, due to which the teeth will lose stability, begin to shift, deform, loosen and fall out.
If not treated promptly, you can lose your teeth.
When the neck of a tooth becomes exposed and hurts, this is a reason to think about solving the problem, because... If this thin area is left unprotected, the tooth can become very fragile and susceptible to chipping; it can simply break as a result of strong pressure or excessive chewing load.
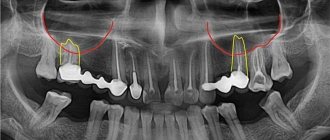
Types of dental root exposure
In addition, it is x-rays that make it possible to determine the class of recession:
- 1st class: the gums recede slightly, exposing the yellowish necks of the teeth,
- 2nd class: there is a displacement of the edge of the mucosa within 2-4 mm towards the root, the tissues in the area of the interdental septa turn pale,
- 3rd class: the mucous membrane completely exposes the necks of the teeth,
- 4th grade: there is a pronounced loss of mucous and bone tissue, x-rays show its atrophy. The neck along with the root protrudes from under the gum, and the spaces between the teeth become wider and more noticeable.
It is important to determine what exactly caused the recession, and symptomatic therapy can already be prescribed based on the diagnosis. For this reason, independent attempts to cope with the problem do not produce results, and sometimes even provoke complications.
The disease cannot be cured at home
If the neck of the tooth is exposed, then treatment at home is unacceptable. Traditional medicine methods, at best, will not give anything, at worst, they will only aggravate the situation. For such a pathology, treatment should be comprehensive and professional. Therefore, if the necks of the teeth are exposed, then the first thing to do is consult a dentist.
The doctor, first of all, will conduct a differential diagnosis between a wedge-shaped defect and caries, and determine what is causing the necks of your teeth to become exposed. Next, the specialist will carry out professional hygiene and sanitation of the oral cavity, remove plaque and deposits using special tools and preparations (Air Flow, ultrasonic scaler, brushes, floss and paste). Then, depending on the cause of the disease, treatment or a whole range of therapeutic measures will be prescribed.
Remineralization and fluoridation of enamel
When the neck of the tooth is exposed, and this process is still at the initial stage of development, the doctor may suggest that you strengthen the tissues so that they become stronger, less sensitive, and can withstand the attack of bacteria. What will the specialist do? It will apply a useful composition rich in microelements to all visible parts of the tooth.
The photo shows the remineralization procedure
Read the article on the topic: 3 options for how to carry out fluoridation to strengthen the enamel.
Use of medications
Exposure of the neck is often a consequence of gum recession, which occurs against the background of inflammation and insufficient nutrition of the mucous membrane. To restore blood circulation and relieve the inflammatory process, the doctor will individually select medications for you to take orally. It will also be necessary to apply and rinse the mucous membrane, and make lotions. Injections into the gums may be prescribed.
Filling bare areas
The procedure is possible only at the initial stage of the disease, when the pathology is not pronounced and affects only individual units.
Prosthetics
If exposure of the neck threatens fracture or destruction of the tooth under the influence of mechanical loads, then treatment will consist of prosthetic crowns. If the pathology is more of an aesthetic problem and affects the teeth located in the smile zone, then veneers or lumineers can be installed on them.
The defect can be corrected with veneers
Gumplasty
If the aesthetics of a smile is seriously compromised, the pathology is irreversible, and also leads to the inability to eat properly without pain and discomfort, then the doctor may resort to surgical methods. For example, for flap surgery. During the operation, the specialist peels off the gum and moves it to a new place, thereby achieving correction of the position of the mucous membrane.
In case of complex pathologies, a specialist can perform gum surgery
After treatment, the doctor will also be sure to select personal oral hygiene products (brush, paste) and tell you about the correct hygiene technique.
Notice
: Undefined variable: post_id in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content/themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
45 Notice
: Undefined variable: full in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content /themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
46
Rate this article:
( 7 ratings, average: 4.57 out of 5)
toothache
- Yusupalieva K.B. The effect of hyperglycemia on the condition of periodontal and oral cavity in patients with diabetes mellitus. Scientific research, 2017.
Expert “In the fight against exposed tooth necks, doctors use many methods. You may be prescribed physiotherapy, orthodontic treatment, plasma lifting and the use of protective membranes, and frenulum trimming. If pathologies of internal organs are suspected, the dentist may refer you to third-party specialists, for example, an endocrinologist.” Dentist-therapist Tatyana Vitalievna Varlamova
Consulting specialist
Varlamova Tatyana Vitalievna
Specialization: Dentist-therapist Experience: 6 years
Prevention measures
It is impossible to completely guarantee protection against the gradual separation of the gums from the tooth, because this will happen naturally with age, but you can slow down this process. Experts in the field of periodontology and dentistry have identified several basic recommendations, following which you can minimize the risk of gum recession:
- The first thing you need to do is systematically visit the dentist 2-3 times a year as a preventative measure.
- You need to give up bad habits or reduce them to a minimum.
- Enrich your daily diet with fresh fruits and vegetables.
- Perform hygiene procedures at least 2 times a day, in the morning and before bed. If desired, you can supplement brushing with dental floss.
- If you suspect or have any symptoms of any oral disease, consult a doctor immediately.
Regular dental checkups are something that most people neglect. Therefore, you need to develop a habit that will help keep your teeth healthy.
It is important to know! If your gums are your weak spot, you need to brush your teeth very gently, using a soft toothbrush and mouthwash. A hard brush can harm the gums and cause them to separate over time.
Gum recession is not just an aesthetic problem. This phenomenon signals the presence of a more serious disease or ongoing pathological processes in the soft tissues of the gums. Any deviation from the normal state should alert you and cause a visit to the dentist.
Splinting teeth for periodontitis with fiberglass and tape
Open and closed curettage of periodontal pockets
Laser gingivectomy in the area of one tooth
Laser gingivotomy - surgical treatment of complex forms of periodontitis
The roots of the teeth are exposed - what to do and how to treat them
Catarrhal and hypertrophic gingivitis symptoms and treatment in adults
Comments
The necks of my teeth are exposed and I don’t know what to do? Is it possible to somehow strengthen the gums at home to solve the problem?
Rita (07/30/2019 at 10:16 am) Reply to comment
- Dear Rita, pathology can be caused by many reasons, and in order to know which treatment method to choose, you must first accurately determine the cause. You cannot do this yourself without the help of a dentist. As for strengthening the gums, of course, to prevent the problem, you can use special pastes and rinses with herbal extracts, rinsing with herbal decoctions. Be sure to purchase an irrigator that will help you gently massage the mucous membrane every day and normalize the blood circulation process in it. Eat foods that contain vitamin C, which is very beneficial for health and rapid mucosal regeneration.
Editorial staff of the portal UltraSmile.ru (08/06/2019 at 08:55) Reply to comment
Hello, the necks of my teeth were exposed, there was not much pain in the exposed areas, I went to the dentist, work was done in those places, but the pain went away. What does this mean? Did you do a bad job as a dentist and need to do it over?
Christina (10.29.2020 at 05:58) Reply to comment
Write your comment Cancel reply
Treatment with traditional medicine
The practical use of traditional medicine advice is allowed only as an additional therapy and only after consultation with a doctor. Here are some proven and effective methods:
- Regular rinsing is necessary to clean and strengthen teeth and gums. The best tincture for rinsing would be a decoction of St. John's wort. To prepare it, you need to grind the dry plant and add water to it in a ratio of 1 to 4, then bring to a boil and leave to infuse for 1 hour. You need to rinse your mouth 2 times a day after basic hygiene procedures.
- Compresses. Using compresses will help reduce pain and start tissue repair processes. An effective compress can be made by mixing sea buckthorn oil and olive oil in a ratio of 1 to 1. Then dip a cotton swab into the resulting solution and apply to the problem area for 5 minutes. After which you need to rinse your mouth with water. This procedure will relieve pain.
- Massage. A good massage improves metabolic processes in the gum tissue, which promotes rapid healing. Before the procedure, you need to wash your hands, and then lightly massage the gums with your fingertips for 1-2 minutes.
Treatment without qualified medical advice may lead to a worsening of the condition. Therefore, when the first signs of recession appear, you should first see a dentist and then take treatment measures.
How dangerous is the problem - what complications can it lead to?
First, the neck of the tooth is exposed, but after that the root is also exposed. As a result, the periodontal tissues become weak, also decrease in size and do not hold the tooth well, which is why it begins to wobble. Even before it falls out, deformation of the entire dentition occurs, and there is a high probability of chipping and fracture of the crown, because in the cervical area the enamel is too thin to cope with the constant chewing load.
Another almost inevitable consequence of gum recession is a wedge-shaped defect. As a result, the gingival margin adjacent to the tooth acquires a V-shape, which generally spoils the aesthetics of the dentition. To avoid complications, you need to see a doctor in a timely manner, identify the cause of the problem, eliminate it and correct the aesthetic defect.
The photo shows a wedge-shaped defect
Symptoms
The main symptom of tooth enamel hyperesthesia is acute short-term pain . Usually the patient complains that the tooth feels cold, sweet, hot, sour, and begins to hurt. In this case, the pain is short-lived; literally after a few seconds the pain subsides and the tooth stops hurting. The intensity of toothache can range from mild discomfort to very severe throbbing pain. In some particularly difficult cases, patients cannot even breathe in cold air and only take warm, neutral-tasting food.
Typically, pain during hyperesthesia is a constant symptom, but sometimes temporary periods of remission are observed when the teeth do not respond to stimuli at all or the intensity of pain is significantly reduced.