The replacement of baby teeth with permanent ones is a natural physiological process that every child experiences. It usually begins in preschool age and proceeds without difficulty. But parents need to approach it responsibly, since any violations when changing teeth are fraught with unpleasant consequences. This may be the formation of a malocclusion, uneven teeth, or the occurrence of a diastema (interdental gap).
In this article we will consider the correct sequence of tooth replacement, possible violations, and situations when consultation with a pediatric dentist is necessary.
Why and when do baby teeth change?
As the child grows, the dentofacial apparatus also develops. At approximately 4–6 years of age, the preparatory stage begins, during which interdental spaces appear. This prepares the place for permanent teeth in the primary dentition.
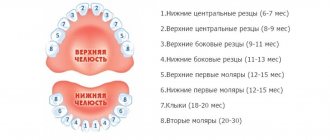
The process of replacing baby teeth with permanent teeth is a slow process, taking approximately 6 or 7 years (until adolescence). Active growth of the roots of permanent teeth activates the process of bone resorption - this is the destruction (dissolution) of milk roots, which leads to loosening and tooth loss. Standard diagram of the sequence of changing baby teeth in a child.
- Central lower incisors (5–7 years). They fall out one by one with a short time interval.
- Lateral incisors (7–8 years).
- First molars on the upper jaw, second molars on the lower jaw (9–11 years)
- Cone-shaped teeth (canines) at the age of 9–12 years.
- Second molars on the upper jaw and first molars on the lower jaw (10–13 years)
Not everyone's third molars (wisdom teeth) erupt. This is considered the norm. Most often, the optimal age for them is considered to be from 17 to 25 years.
Reference!
The later the first teeth erupted in infancy, the later they will be replaced in preschool age.
By the age of 15–16, a teenager’s permanent bite should number 28 units.
Replacement too late
In some cases, the molars are already erupting, although the milk teeth are not yet loose. Often this also leads to the appearance of certain defects. The solution to the problem is to visit a specialist to remove a baby tooth.
It also happens that molars do not appear in the standard time frame. In this case, temporary teeth may be present or fall out. Reasons for this phenomenon:
- Physiological factor. The development of tooth germs occurs properly, but their growth is too slow for certain reasons.
- Retention of molars. The tooth germs are formed in a timely manner, but the location of the permanent tooth inside the jaw bone tissue is incorrect.
- Partial primary adentia. During the development of the child inside the mother's womb, the proper laying of the rudiments did not take place or their death occurred due to inflammation.
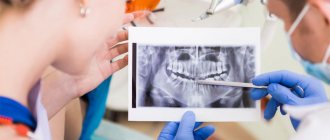
To detect such defects and determine the exact reasons for untimely replacement of baby teeth, a specialist uses x-ray examination, which allows us to determine the characteristics of the formation of tooth germs. If developmental defects are detected, children are prescribed temporary prosthetics for the period of active jaw growth. After reaching a certain age, permanent dentures are installed.
What deviations from the norm may there be?
Each child develops individually. Sometimes the timing of the replacement of certain teeth may differ from the generally accepted norm. Minor deviations are allowed up to 12 months. But sometimes the change in the primary bite begins too early or, on the contrary, the temporary teeth do not want to fall out.
Causes:
- long-term breastfeeding;
- severe infectious diseases in infancy;
- pathologies of intrauterine development.
Reference!
Dentists believe that a safer deviation is a late change in the primary occlusion than vice versa.
Let us consider in detail the common violations and their causes.
Early tooth loss
We can talk about such a pathology if a child’s baby teeth begin to fall out before the age of 5. Possible reasons:
- advanced multiple caries;
- injury;
- gum disease;
- manual loosening of the tooth.
In all these cases, consultation with a pediatric dentist is required.
Important!
Parents should record the time of tooth loss. If after 4 months the permanent tooth does not begin to emerge, then the help of a doctor is required.
In case of early unnatural tooth loss, it is advisable to conduct an X-ray diagnosis. This will help to identify possible damage to the permanent root rudiment in time and begin treatment. Otherwise, the child will need prosthetics in the future.
Late change from primary to permanent occlusion
The deadline for starting the process of changing baby teeth is 8 years. But this is considered a late shift. The disorder may be caused by:
- heredity;
- metabolic disorders;
- infectious diseases suffered in early childhood;
- mental disorders.
If after 8 years a child has not lost a single baby tooth, this is a reason to consult a doctor.
How molars grow
- First, teeth 1 through 6 erupt and the central incisors are replaced.
- Then the processes slow down as the body needs rest.
- The formation and intensive growth of molars and premolars begins.
Ideally, the appearance of permanent teeth occurs in the following sequence:
- sixth teeth;
- permanent central primary incisors;
- molar lateral incisors;
- fangs;
- “fives” instead of second premolars;
- “sevens” (11-13 years old);
- "eight" - after 16 years.
The central incisors erupt the fastest. The canines are somewhat slower, and the molars take the longest to grow. This process takes many years and requires close attention from parents, dentist and orthodontist.
Reasons for late eruption
Normally, after a baby tooth falls out, it takes 1-2 months for the permanent tooth to erupt. This is the longest period. In most cases, the rudiments of a permanent tooth can already be seen at the site of the lost tooth.
But, if a child’s toothless smile persists for 3 months or more, then this is a cause for concern for parents.
Let's consider why such dental pathology occurs:
- Retention
– a common condition that mainly affects the incisors and canines. They cannot erupt due to dense gums or because they rest against neighboring teeth. There are complete and partial retention. With the full form, a healthy root is visible in the picture, but it is completely under the gum. With partial retention, only part of the crown is visible. In this case, surgical assistance is required.
- Edentia
– a congenital pathology in which there is a lack of rudiments of permanent dental units. Can be complete or partial (sparse teeth). A rare disease. Orthopedic treatment is required as early as possible.
- Impact
– delayed eruption in this pathology is associated with a mechanical obstacle, that is, the child has a supernumerary of dental units. In this case, the permanent root simply does not have room to erupt. Impaction can only be detected using a panoramic x-ray of the jaw.
The sooner the child is examined by a doctor, the higher the chance of having an even and complete dentition.
Premature loss
This refers to the loss of baby teeth when the child has not yet reached the age of 6. Causes may include caries, special loosening and mechanical damage. If a tooth falls out long before the molar begins to grow, a space will appear in the oral cavity that will later be occupied by the remaining teeth. Eventually, permanent teeth will begin to erupt unevenly due to lack of space.
If you experience early tooth loss, you should contact an orthodontist. Often today, in such situations, prosthetic technologies are used, the main task of which is to prevent the displacement of other elements of the dentition. This solution helps prevent the development of malocclusion and the appearance of various visual defects.
Possible problems when changing baby teeth
Common dental pathologies when changing a primary dentition to a permanent one include:
- Shark teeth. A phenomenon in which baby and permanent teeth are located parallel to each other, in 2 rows. This arrangement can interfere with the normal development of the dental system. But in most cases, the temporary root becomes loose, and the “extra” tooth falls out on its own. If this does not happen, removal at the doctor's office is recommended.
- Increased pain. Sometimes a change in the milk bite is accompanied by increased body temperature, redness of the gums and severe pain. These symptoms usually accompany early or late change of teeth. Inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity may also be the cause.
- The appearance of a hematoma.
In rare cases, when molars erupt, a hematoma occurs on the gum in the form of a small bubble with an accumulation of blood. This occurs due to severe eruption, which leads to rupture of blood vessels. The gums may be pale in color. Pain and discomfort occurs. If suppuration occurs, medical attention is required.
If pathological phenomena do not go away for a long time, and the child is irritable and complains of pain, be sure to visit the dentist.
Role of parents
In most cases, changing primary teeth does not cause any particular difficulties. But if a child complains of discomfort in the gums, you can use gels that have an analgesic effect, for example, Dentinox or Kalgel.
If instead of a baby tooth there is a wound on the gum that is bleeding, you can apply a ball of sterile cotton wool to it and hold it for about 5 minutes. After a temporary tooth falls out, it is forbidden to eat food for 2 hours. On that day, it is better not to give your child spicy, salty or sour foods.
If a molar has already broken through, but the baby tooth has not yet fallen out, it is better to use the help of a dentist rather than remove it yourself.
What not to do when baby teeth fall out
Incorrect actions of children and parents can lead to the formation of malocclusion, increased pain, or the formation of crooked teeth. To avoid this, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- Don't help baby teeth fall out if they are straight and not loose. Even if, according to the child’s age, it is high time for him to have a toothless smile.
- Don't loosen your teeth with your hands. And do not pull them at home, for example, with a thread.
- Baby teeth are quite fragile in preschool age. Therefore, your child should not indulge in solid foods. The crown may break, but the root will remain in the gum.
- If a tooth falls out, do not allow your child to touch the socket with his tongue or hands. Gentle rinsing with antiseptic solutions or herbal decoctions is recommended.
If you have a fever, cough or lethargy, do not rush to resort to antiviral drugs. Poor health can be a harbinger of the imminent change of baby teeth.
Timing of permanent teeth eruption
Permanent teeth in children erupt in the same order as baby teeth:
- central incisors above and below: permanent teeth appear in first-graders - at 6-7 years from below and at 7-8 years from above;
- the lateral incisors on both jaws change to permanent ones at 7-9 years of age;
- permanent first premolars appear by 6-11 years, and second ones should be expected no earlier than 10-12 years;
- at the age of nine to twelve, the upper and lower canines appear;
- The appearance of molars usually begins at the age of six and ends at the age of 21, when the third molars erupt.
Please note: the information above is approximate, and if your baby's teeth are not appearing on schedule, there is no reason to worry. In some children, permanent dentition forms earlier, in others - later. In any case, by the time they reach adulthood, most teenagers can already boast a full set of permanent teeth, and all that remains is to wait for the “eights” - wisdom teeth. However, more and more often, recently, wisdom teeth do not appear at all, as they are rudimentary and practically do not participate in the chewing process.
Tips for parents
During the period of teeth change, you should enrich your baby’s food with foods that are rich in calcium. To prevent inflammation in your mouth, make it a habit to rinse your mouth every time you eat or have a snack. As permanent teeth erupt, offer your baby soft or liquid foods. Avoid hot drinks.
If slight bleeding occurs when a baby tooth falls out, do not use alcohol tinctures. Apply a cotton ball to the wound and do not allow food for 2 hours. In order to promptly identify possible irregularities in the eruption of the permanent dentition, it is recommended to record the date of baby tooth loss.
Beautiful, straight and healthy teeth in adults are the result of proper care in childhood. Therefore, parents should teach their child proper oral hygiene from the first tooth.
Why is it necessary to replace baby teeth with permanent ones?
The chewing apparatus is improving and developing. In infancy, it is adapted exclusively for the intake of liquid food - breast milk. But closer to six months, you can already see baby teeth in children’s mouths. They allow the baby to get acquainted with the variety of solid adult foods.
There are few temporary teeth - ten pieces in each jaw. This is quite enough for the baby to eat well and talk normally. Closer to primary school age, the jaw grows. She is ready to cope with more serious chewing loads. Then children's incisors, canines and molars begin to wobble. They are replaced by a constant shift.
What to do if a tooth does not fall out in time
According to statistics, in 20-30% of cases, children experience a “shark smile” when the permanent tooth has already erupted and is growing, but the milk tooth has not yet fallen out. Clinical studies have proven that in such a situation, parents should not hesitate to go to pediatric dentistry. The doctor will carefully examine your child's mouth and remove the temporary tooth. If you do not contact the dentist in a timely manner, double dentition can lead to improper formation of the bite, impaired diction and the functioning of the digestive system. In addition, with a “shark smile” it is difficult for a baby to bite and chew food, particles of which remain between the teeth and under the gum. As a result, inflammatory processes and caries occur. All this can be avoided by making an appointment with a specialist.
Early tooth loss
The time of tooth loss depends on the individual characteristics of the child’s body. However, premature tooth loss can be dangerous. The thing is that if a baby tooth is missing for a long time, then the neighboring teeth move, and there is simply no room left for the permanent one, which begins to grow in due course. This situation can cause a violation of the correct bite, distort the dentition and require long-term treatment by an orthodontist.
What causes premature tooth loss in children:
- various injuries;
- periodontal diseases;
- caries;
- infectious diseases suffered by a child in preschool age.
If a baby tooth has fallen out, and its permanent replacement is not expected soon, consult a dentist. In modern dentistry, there are special designs - plates that do not allow neighboring teeth to move and preserve space for a permanent tooth. Such systems do not injure tooth enamel, do not involve grinding of teeth and do not interfere with the baby while talking and eating.
Milk and molar teeth: what are their differences?
Externally, baby teeth and molars are very similar, but if you look closely, you will notice some visual differences: baby teeth are smaller in size, and the incisors and canines have a more rounded shape. The main differences are related to anatomy and structure.
- Primary teeth have thinner enamel with less mineralization.
- The root canals of baby teeth are much wider and, accordingly, more susceptible to the entry of pathogenic bacteria.
- The dentin layer of baby teeth is thinner, and the pulp is thicker.
- Milk teeth have roots, but they are less pronounced and dissolve during the process of changing the dentition.