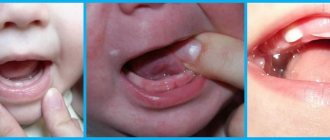
How to Reduce Teething Pain
Fever and pain can be reduced by:
- massage the gums where tooth eruption is expected;
- the gums can be lubricated with an anesthetic;
- give the child a vasoconstrictor if the child has a runny nose;
- if the temperature rises above +38C, then the child should be given an antipyretic in the form of a sweet syrup.
Usually, the eruption of baby teeth occurs without complications. In some cases, a complication may occur that is caused by:
- Presence of a dental cyst.
- When the baby tooth has not yet come out, but it is supported by a permanent tooth.
- When a fang erupts, it is out of place in the dentition.
Teething order
Diagram of the eruption of baby teeth (numbered in order of priority)
Finding out the sequence of teeth appearance in children will be useful for young parents who have already felt the joy of becoming a mother and father, or this is still to come in the future. By the end of the first year, children have several teeth. The number is determined by a number of factors. One reason is heredity.
Problems in the baby’s body that arise as a result of:
- low calcium content in the body and the formation of rickets.
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland and, as a result, a decrease in hormones in the blood.
- absence of incisors (edentia).
- dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract.
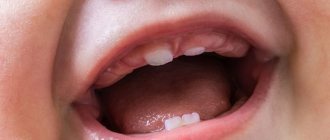
Baby teeth
While still in the womb, the rudiments of dental formations are formed in the fetus. And by the middle of pregnancy, the required number and order of appearance of one or another incisor is formed.
It must be taken into account that a child’s oral bone formations should number 20. The time of eruption of baby teeth and the order are of a purely individual nature. However, there are generally accepted norms, which are an indicator of the correct physiological development of the baby. So how do children usually grow their teeth? Let's take a closer look at this topic.
First tooth
In babies, the first pair of teeth appears on the lower jaw. Which tooth of a given pair should appear first? Pediatricians say that teeth can erupt at the same time or with an interval of several days. And you shouldn’t worry about which incisor appeared first, because there are no special rules for this. Usually, young parents are happy to see their child’s first tooth appear at 6-7 months of his life. But at the same time, the scope of the norm expands significantly - from 4 to 9 months.
Second pair
Following the growth of the lower incisors, the upper ones should appear. The order in which the right or left incisor appears first does not matter. The interval between their occurrence can vary from several hours to two weeks.
According to statistics, the upper incisor appears first on the side from which the lower one appeared. The upper teeth normally erupt at 5-11 months. Usually at eight months.
Third pair
How does a child’s teeth continue to grow? After the child begins to smile with his 4 teeth, his lateral incisors, which are located on the upper jaw, appear. The third pair of bone formations appears at 10 months. Medical experts consider it normal for these teeth to erupt from 7 months to a year.
Fourth pair
The lower lateral incisors appear between 9 and 15 months.
The child's next teeth are the upper and lower molars. Normally, they appear before the fangs. But in recent years, doctors have increasingly encountered exceptions when the canines form first. And after 2-3 months, the lower molars are also replenished in the mouth.
Molars begin to grow at the age of 1-1.5 years. Let us immediately note that molars are large formations and their eruption is accompanied by high fever, lack of appetite and capriciousness of the child.
The next stage of the teething scheme is given to the canines. Fangs usually appear between the ages of one and a half to two years. But there are cases when they are formed earlier than paired molars.
Fangs, like painters, make themselves felt through the manifestation of the following symptoms: pain and itching of the gums, symptoms of rhinitis, changes in stool. These signs disappear as soon as a new tooth appears.
The second group of upper and lower molars erupt painlessly and asymptomatically at 2-3 years. This group is the final one in the chain of primary (non-permanent) teeth. After the milky bone formations of the oral cavity begin to fall out, permanent teeth will grow.
Generally accepted teething pattern
Children at 2.5 years old should have 4 incisors and 4 molars, as well as 2 canines. This scheme looks like this: 2-1-2 (2 incisors, 1 canine, 2 molars grow from above and below from each half of the jaw).
In order to determine the normality of a child’s teeth, a special formula is provided. The calculation is carried out as follows: the number of teeth should correspond to the difference in the age of the baby in months and six. For example, at 1.5 years (17 months) this number is 11 (17-6=11). The method for determining the required number of teeth is more appropriate to use for children under two years of age, then the formula will be more accurate.
First teeth: symptoms of their eruption
The progress of teething is usually accompanied by certain symptoms. These signs are reflected in behavior and emotional state. The following manifestations are considered normal:
- secretion of saliva in large quantities. This symptom usually appears at the end of 2 months and can last up to 4.
- looseness and hyperemia of the gums – lasts for quite a long time.
- skin irritation in the lips and chin area. The appearance of an allergic reaction is caused by excessive salivation. To prevent irritation on the baby's delicate skin, parents should wipe his mouth more often and lubricate the skin with baby cream. For better absorption of the cream, it is better to apply it at night.
- The gums turn red and begin to itch. This manifests itself when the baby is breastfeeding, because he bites the nipple.
- the presence of pain disrupts the baby's sleep. For some time he will not be able to fall asleep on time, and the duration of sleep will be shorter. During this period, some pediatricians recommend giving the baby analgesics.
- Lack of appetite and refusal to eat are common problems during the teething stage. This symptom is caused by pain when eating food. The exception is the mother's breast.
- thumb sucking or the desire to chew on something. Most often, the child puts into his mouth any object that catches his eye and begins to gnaw on it. Therefore, it is necessary to ensure that toys and other items are clean.
- hematomas or bruises - medium-sized bulges on the gums with a bluish tint. There is no need to worry about their occurrence if their number is insignificant. You can apply cold compresses to the bumps. The hematomas will gradually disappear on their own.
All of the above signs have virtually no effect on the baby’s behavior and well-being, and disappear after teeth appear.
How to help a child with incisor teeth?
As soon as the baby begins to be bothered by the symptoms associated with the manifestation of incisors, parents begin to look for ways to eliminate negative phenomena. There are many tips and recommendations from specialists that can help you survive this stage of a child’s development more easily and without any consequences.
How can I make teething easier for my baby?
- You should provide your child with objects that he can chew on. This will relieve his anxiety and massage his gums.
- For this purpose, rubber toys filled with liquid or gel filler are best suited. They are designed to achieve a cooling effect on the gums. The main disadvantage of such items is that they will have to be periodically placed in the refrigerator.
- Pacifiers or bottles. The chewing or sucking mechanism helps soothe irritated gums. It should be taken into account that regular sucking and chewing of objects with an irregular shape can cause the formation of an abnormal bite. That is why it is necessary to purchase a pacifier with a special shape and made of high-quality material.
- A finger brush is a remedy for eliminating itchy gums in a baby. Recently, it has become increasingly popular and in demand among young mothers, because in addition to its main action, the brush is an assistant in caring for the oral cavity of babies.
- At home, in the absence of special care items, it is possible to use gauze swabs, which are pre-moistened in cold water. This method simultaneously eliminates itching and cleanses the oral cavity of microorganisms. Massaging the gums with a gauze swab should be done carefully, gently, without sudden movements that can injure the oral mucosa.
- Most methods are ineffective. In extreme cases, resort to medication. Pharmaceutical companies offer a huge number of special gels and ointments for topical use. It is better to select the appropriate remedy together with your pediatrician.
Eye teeth in older children
Permanent eye teeth erupt in children aged 9-12 years. Normal eye tooth eruption should occur painlessly. If pain still bothers the child, it may be caused by:
- the presence of infection in the oral cavity;
- periodontal disease;
- development of dental caries.
The eye teeth may erupt in a crooked manner. Orthodontic treatment helps correct abnormal tooth growth. If a tooth erupts and grows incorrectly, it is removed on the advice of a dentist. After removing an eye tooth, it must be immediately replaced with a prosthetic so as not to disrupt the integrity of the dentition and not to impair the process of chewing food.
How to help your child during teething
The period of teething is considered difficult for the baby and requires special indulgence, attention and care for him. Therefore, it is important to help your child get through this difficult time for him. The process of cutting through the fangs located in the top row can be called especially painful. After all, they are located near the facial nerves. When the top row of canines erupt, tears actively flow from the baby’s eyes. His parents notice that he has some symptoms of conjunctivitis.
Now in children's stores and pharmacies you can buy toys - teethers, produced specifically to facilitate the process of cutting fangs. Manufacturers fill them either with water or use a gel for this purpose. The purchased toy can be placed in the refrigerator for a few minutes and cooled; it will soothe the baby’s gums and relieve itching. Parents will also benefit from pacifiers that the baby can chew; it is better to choose arthodontic ones. You can also buy special medications at the pharmacy that relieve some symptoms. For example, a gel with an anti-inflammatory effect, which ultimately reduces the baby’s pain. But you should not select any medications on your own without first consulting a specialist. If the child’s temperature rises to 38 degrees Celsius, then after consultation with the pediatrician, you can give him medicine with paracetamol. Ibuprofen may be a good alternative. These medications are considered safe for the baby and effectively fight fever. For children under 3 years old, it is better to buy medicines in the form of suppositories or syrups. Suppositories have an effect slower than syrup, but their effect lasts longer.
How to reduce pain in an eye tooth using traditional medicine
Dental treatment of the eye tooth can be supplemented with treatment with traditional medicine. Typically, after visiting a dentist in a specialized clinic, they advise the following:
- Dissolve a teaspoon of baking soda or salt in a glass of warm water. Rinse your mouth with this solution several times a day.
- Prepare a decoction of medicinal herbs: chamomile, sage, or make an infusion of oak bark. Rinse your mouth with prepared decoctions and infusions several times a day.
The eruption of eye teeth in children should occur under the supervision of a pediatric dentist. Adults who have problems with their eye teeth should also see a dentist.
How to determine by symptoms that a child is getting his first fang
Symptoms can be detected much earlier than the baby’s first fangs appear. Usually parents notice them a few weeks before the teeth erupt, but there are also cases when symptoms appear even earlier. How can you tell if your child is growing fangs?
- The baby becomes irritable, his mood changes for the worse. He is capricious and crying.
- Parents notice strong salivation, sometimes leading to a runny nose or causing a cough.
- The gum swells and changes color where the fang erupts. The fang first appears as a small white dot located under the baby's gum.
- The child does not want to eat, sometimes he categorically refuses to eat.
- The baby doesn't sleep well.
- He often chews on various objects, trying to make them come into contact with his gums.
In addition to the above signs, parents may also observe an increase in temperature when the child begins to grow fangs. In some cases it rises to 38 degrees Celsius. The baby's stool becomes liquefied due to increased salivation. Excessive salivation also leads to vomiting.
Location
The eye teeth or canines are found in pairs on the upper and lower jaws. They occupy an intermediate position between the front and back teeth, adjacent to the lateral incisors and molars (in the primary dentition) or small molars (in the permanent dental set).
The formation of primary eye teeth begins in the second month of embryogenesis. Like other teeth, they originate from the dental lamina of the oral epithelium, but penetrate into the developing bone tissue somewhat deeper than the others. The development of permanent canines and the entire set of molars begins a little later (at about 4 months of intrauterine development), but occurs identically to the formation of baby teeth.
The canines are characterized by the following features that distinguish them from other teeth:
- The presence of a single fairly long root, which is somewhat compressed on the sides.
- A massive crown with 2 cutting edges converging at an acute angle.
- The crown has a somewhat flattened shape, in which the labial and lingual surfaces meet at the cutting edge.
- The upper canine is slightly larger than the lower one, it has a longer cutting edge and wider contact surfaces.
Such features in the location and structure of the eye teeth allow them to perform their main function well: holding food and tearing it into pieces.
What to do if baby teeth are delayed?
The absence of signs of teething in a child at a time when other children already have several teeth is not a cause for concern. The exact timing depends on several factors, including:
- genetic characteristics;
- climate and living conditions;
- feeding habits (in children who are breastfed, teeth usually appear later than in “artificial” children);
- quality of child care;
- nutrition and living conditions of the mother during pregnancy;
- the presence of chronic diseases and pathologies.
Numbering of teeth in dentistry for children
A situation where teeth are completely missing in a one-year-old child should be a cause for concern - sometimes this is a variant of the norm, and sometimes it indicates disorders in the body.
Important! The most common pathologies that can affect the timing of teething are dysfunction of the endocrine system and rickets.
Less common is a disease called edentia, or the absence of tooth buds, which can be diagnosed using x-rays.
Duration of growth
Typically, children say goodbye to their last temporary teeth at about 12-13 years of age, although the roots of baby teeth dissolve even earlier. By that time, the oral cavity already has molars that are actively growing, and their roots are at different stages of formation.
It is necessary to understand the approximate timing of growth and root formation in case of deviations. It is these indicators that are taken into account when choosing a treatment method.
Experts distinguish two main stages of development of the roots of permanent teeth:
- Stage of unformed apex.
- Unclosed apex stage.
At the first stage, the length of the root becomes maximum, but its walls are parallel to each other. The channel is of sufficient width; it ends in the area of the future apex with a bell. The periodontal gap can be seen only on the sides of the tooth root.
At the next stage, there is a gradual formation of the upper part of the root, the convergence of the root walls and the release of the periodontal fissure, the apical region of which is slightly enlarged.
Formation of permanent teeth
Molars are formed from the epithelial dental plate. The appearance of their rudiments occurs only closer to the 5th month of fetal development inside the mother’s womb.
There are two groups of molars:
- Substitutes. This includes canines, incisors and premolars, which have temporary analogues.
- Additional. This group includes molars that do not have milk predecessors.
The growth of the primordial teeth of the replacement type occurs in the same alveolus as the temporary teeth; they are located behind the lingual surface of the primary teeth. Only after some time does the volume of bone tissue increase, ensuring their insulation.
Additional teeth are formed only after a year, since for this the jaw must reach the appropriate size.
What signs are used to determine the appearance of molars?
There are several symptoms that, to a certain extent, may indicate that the child will soon have a permanent one in place of a baby tooth:
- The tooth is loose - this indicates that the root has begun to dissolve, as a result of which the fixation of the baby tooth has weakened.
- The tooth fell out - the reason for this is that the permanent tooth has already formed and pushed it out.
- A swelling appeared on the gum at the site of eruption.
- Body temperature has increased.
Take into account! The growth of permanent teeth leads to a weakening of children's immunity. Therefore, you need to give your child vitamins and take him to the dentist for preventative visits.
How does the process work?
When the time comes for teething, the baby usually becomes restless, begins to put toys and other things in his mouth, bites his chest with his gums, and begins to salivate profusely. Parents may notice a small bump on the gum filled with fluid; the mucous membrane in this place becomes red and swollen. After some time, white spots clearly appear through the soft tissues - this means that the tooth is ready to be born.
Milk and permanent teeth
Important! If the lump becomes too large and causes serious discomfort to your baby, you can ask the doctor to cut it to “help” the tooth get out.
The body's reaction to teething depends on its individual characteristics. In some children this process is asymptomatic, in others the temperature rises, a runny nose, redness of the throat, diarrhea, sleep and appetite worsen.
Attention! If teething is difficult, accompanied by fever and other symptoms, it is better for parents to consult a doctor. Typically, in such cases, antipyretic and analgesic drugs are prescribed, as well as ointments and gels that reduce discomfort in the gums.
Types of teeth
You can relieve discomfort from teething by massaging your gums (performed with a clean finger) or by purchasing a special stimulator ring at the pharmacy.
- When do children's fangs change to permanent ones?
Possible complications
"Surprises"
The problems that nature presents when infants have their first teeth do not end with the listed troubles. Sometimes other complications are possible:
- Formation of hematomas.
A bluish-colored bubble swells on the gum. Most often it resolves over time, but sometimes if the blister is too large, surgery is required. The doctor makes a small incision on the gum to remove the bloody fluid.
- The appearance of vomiting.
This may be caused by excessive salivation. However, if vomiting is accompanied by diarrhea and fever, these may be signs of rotavirus, so it is necessary to urgently show the child to the pediatrician.
- Cough reflex.
With normal teething it does not happen. The cause of the cough may be excessive saliva secretion, which causes the baby to choke.
If a runny nose appears, take your child to the doctor
- teething probably coincided with a cold.
Important:
If your baby is experiencing fever, diarrhea and vomiting during teething, take this seriously. The cause of their appearance cannot be teething. It is urgent to call a pediatrician, since the baby’s body is at risk of intoxication due to a developing infection.