The functioning of a woman’s body changes with the onset of pregnancy, and the changes very often concern the digestive system. The expectant mother is worried about toxicosis and weakness, she develops new gastronomic preferences, and the secretion of saliva increases, which causes a lot of inconvenience. Is drooling normal? Will it go away on its own or do you need to take measures to reduce the secretion of salivary fluid?
Increased salivation: causes and treatment
Hypersalivation - what is it?
Why is there a lot of saliva in the mouth?
Salivation during sleep
Excessive salivation during pregnancy
Treatment of hypersalivation
Saliva is not just a liquid secreted in the mouth. Saliva is involved in the digestion process and protects the body from bacteria. The process of salivation is not controlled by humans. Usually about 2 liters of saliva are produced per day. Under the influence of certain factors, its amount can greatly increase. In this article we will talk about the causes of increased salivation and how to treat it.
Increased salivation is a feature of successful conception
Ptyalism refers to the list of the first signs of pregnancy. In the first trimester, the amount of saliva secreted can increase several times, which leads to exhaustion of the body. In addition, the liquid constantly affects the skin and irritates the corners of the mouth and chin.
Excessive salivation usually occurs during early pregnancy and disappears or decreases by the beginning of the second trimester, along with toxicosis. But it happens that such an unpleasant symptom is accompanied by the entire period of bearing a child, as well as a feeling of nausea.
Increased salivation is affected by hormonal changes in a woman’s body. Hormones stimulate the function of certain glands, including the salivary glands. Other manifestations will help you understand that a symptom is indeed a sign of pregnancy:
- swelling and pain in the chest;
- constant fatigue;
- frequent urination;
- sensitivity to strong odors;
- dizziness.
A test and test results for the presence of the hormone hCG in the blood will help you verify your pregnancy.
Hypersalivation may be one of the early signs of pregnancy
Why is there a lot of saliva in my mouth?
Let's consider the possible causes of increased salivation
| Oral diseases. These include: stomatitis, gingivitis, glossitis, etc. Bacteria provoke irritation of the salivary glands, hence the excessive secretion of fluid. If these diseases are not treated, inflammation of the salivary gland may occur. |
| Having dentures or braces. The structures cause irritation of the mucous membrane, which provokes excessive secretion of fluid. This problem is especially noticeable in the first two weeks after installation of the structure, when adaptation occurs. |
| Gastrointestinal diseases (gastritis, pancreatitis, stomach ulcers, etc.). The problem most often occurs against the background of increased stomach acidity. Other reasons that doctors highlight: liver dysfunction, worms, stress on the pancreas. |
| Diseases of the central nervous system (cerebral palsy, Parkinson's disease, irritation of the trigeminal nerve, migraine). A similar condition occurs when the functioning of the vestibular apparatus is disrupted and blood pressure increases. |
| ENT diseases, ARVI, inflammation of the adenoids. The person begins to breathe predominantly through the mouth, as nasal breathing is difficult. The mucous membrane dries out, causing the glands to begin to work actively. |
| Changes in hormonal levels - problems with the thyroid gland, diabetes, menopause, etc. |
| Smoking. Tobacco smoke irritates the salivary glands. They begin to produce a lot of fluid. This is why smokers have the habit of spitting. |
Causes of ptyalism
Increased salivation is one of the adverse reactions to changes in hormone levels in the body. It has been scientifically proven that estrogen acts on the epithelium of the oral cavity, causing the secretion of salivary fluid.
The reasons for the appearance of excessive drooling in the early stages of gestation have not been precisely established, but several other factors can affect the likelihood of the symptom occurring:
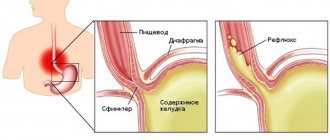
- Heartburn. This phenomenon worries almost all pregnant women. As a result of reflux, stomach acid rises up the esophagus, which leads to irritation and a sore, burning sensation. An alkaline environment, i.e. saliva, helps neutralize acid. The self-regulation mechanism is activated, the salivary glands perceive signals from the receptors of the esophagus and produce more fluid. When swallowing saliva, the acid is partially neutralized, which brings the woman a feeling of relief.
- Changes in stomach acidity. Due to the effects of acid, the walls of the stomach are irritated, and in response to this, the glands secrete more saliva, which brings acidity back to normal.
- Taste preferences. Often, from the first weeks of expecting a baby, the expectant mother becomes addicted to sour or salty foods. Due to constant irritation, the salivary glands produce more fluid.
- Toxicosis. Nausea and vomiting can be provoked by any irritant, even a smell or a sharp sound, as a result of which a woman, fearing another attack of vomiting, tries to swallow saliva as little as possible. It builds up, making it seem like you're producing more saliva fluid than usual. Also, frequent vomiting can lead to the proliferation of specific microflora in the oral cavity, which provokes the production of saliva in large volumes.
Salivation during sleep
Sometimes, when a person wakes up, he notices wet spots on the pillow. This usually happens due to extreme fatigue and sound sleep. However, if salivation during sleep becomes a pattern, you should consult a doctor.
The main factors that provoke the secretion of saliva during sleep.
- Malocclusion or missing teeth. Saliva flows out because the teeth do not close completely.
- Difficulty in nasal breathing: runny nose, deviated nasal septum, colds. All this forces you to breathe through your mouth. Since the lips do not close, the accumulated fluid flows out. This is often accompanied by snoring.
- Deep sleep.
How does it manifest?
The most common manifestation of toxicosis is vomiting , which can occur with varying frequency, depending on the severity of toxicosis.
In mild cases of toxicosis, vomiting occurs no more than 5 times a day, and may be accompanied by a prolonged or constant feeling of nausea. Vomiting occurs on an empty stomach and can be caused by food intake or unpleasant odors. In this case, the loss of body weight is either absent or small - 1-3 kg (up to 5% of body weight before pregnancy). This condition can be easily treated at home.
In more severe cases, vomiting occurs up to 10-20 times a day and is accompanied by drooling, while the woman’s general condition significantly worsens, weakness and apathy occur. A significant amount of fluid is lost through vomit and saliva, dehydration occurs, and metabolism is disrupted. The skin becomes dry, pale, blood pressure decreases, the pulse quickens, constipation occurs, the amount of urine discharge decreases, and the temperature rises. Loss of body weight can be up to 8-10 kg or more (up to 10% of initial body weight). With the progression of this form of toxicosis, a violation of water-salt, protein, carbohydrate and fat metabolism, acid-base and vitamin balance, and the functions of the endocrine glands gradually develops. In such a situation, the supply of nutrients to the fetus is sharply disrupted, and it is during this period that the laying and formation of all the main organs and systems of the baby takes place.
Drooling (ptyalism) can accompany vomiting during pregnancy; less commonly, it occurs as an independent form of early toxicosis. With severe drooling, a pregnant woman can lose 1 liter of fluid per day. Excessive drooling leads to dehydration of the body, loss of proteins, and negatively affects the mental state of a woman.
By 12 weeks of pregnancy, as a rule, the symptoms of early toxicosis disappear.
Excessive salivation during pregnancy
During pregnancy, hormonal changes occur in the female body. The main reasons why an expectant mother’s salivation increases.
- Heartburn. When the acid-base balance in the stomach is disturbed, the body begins to produce a lot of saliva. This is a defensive reaction.
- Reaction to medications.
- Toxicosis. To stop gagging, the expectant mother tries to swallow saliva less often. Therefore, it may seem that there is more saliva in the mouth than usual.
A large amount of saliva does not threaten the fetus, however, if this is a consequence of any disease, then the pregnant woman should monitor her condition.
What complications are possible?
- Impaired taste perception of food.
- Dehydration of the body.
- Insomnia, disturbance of psycho-emotional state.
- Deterioration of the skin condition on the face and body.
- Infectious diseases.
Causes of salivation
Increased salivation is considered one of the negative reactions to changes in the amount of hormones. Estrogen affects the epithelium of the oral cavity, provoking the secretion of saliva. There is no exact cause for this symptom, but there are factors that cause fluid secretion:
Bloating during pregnancy
- Heartburn - hormonal disorders lead to an increase in the acidity of gastric juice, which is why the salivary glands are more activated. Therefore, the burning sensation in the esophagus must be extinguished. The body of a pregnant woman tries to make up for the resulting deficiency with increased saliva production.
- Changes in taste - consuming sour and salty foods provokes secretion production several times faster.
- Increased appetite - the feeling of hunger leads to the activity of the salivary glands.
- Toxicosis - this symptom and nausea occur almost simultaneously.
- Smoking - unfortunately, not all expectant mothers give up this bad habit, and it is precisely this habit that causes drooling.
A viscous secretion appears in the mouth if a woman does not swallow liquid, trying to avoid gagging.
When the volume of saliva is increased and interferes with normal life, you should not force yourself to constantly swallow it. It is better to take paper napkins and spit out the liquid from time to time.
Treatment of hypersalivation
There is no single treatment method for all cases. However, you can use methods to reduce the activity of the salivary glands - sometimes they are recommended by doctors as an addition to complex therapy.
- Reception of sorbents: activated carbon, polysorb, etc.
- Taking medications prescribed by a doctor.
- Exercise therapy, massage (most often prescribed for children).
- Botulinum toxin injections.
In rare exceptions, the salivary glands are partially removed, but the downside is that there is a risk of damaging the facial nerve.
Which doctors will help you cope with this disease? Dentist, gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, neurologist, infectious disease specialist, etc.
Hospitalization
If the doctor discovers changes in the tests, the scale arrow stubbornly deviates to the left every day, and your health worsens, most likely you will have to go to the hospital . The doctors' first task will be to restore lost fluid, protein, and salts. You will be given an IV to ensure that nutrients and vitamins go directly into your blood. To suppress vomiting and nausea, drugs that block the gag reflex are used. Since, as already mentioned, the state of the nervous system has a significant impact on the severity of toxicosis, a protective treatment regime will be created in the hospital for your peace of mind. In addition, you will be prescribed medications that have a calming effect, and if there is increased salivation, medications that inhibit the action of the salivary glands. It is possible that non-drug methods will also be used: acupuncture, hypnotherapy and psychotherapy, herbal and aromatherapy. This will help reduce the number of drugs that can have undesirable effects on the developing embryo.
When, as a result of treatment, weight gain becomes obvious, daily diuresis (the amount of urine excreted), as well as pulse, blood pressure and temperature are normalized, vomiting stops or becomes less frequent, and you can return to your usual home environment. In rare cases, complex treatment over several days turns out to be completely ineffective, and then the pregnancy has to be terminated.
Based on materials from the magazine “9 months” No. 3, 2003
Causes of hypersalivation: why does saliva begin to be produced faster?
The reasons for the increased work of the glands in the oral cavity lie not only in the onset of conception. Hypersalivation also appears as a result of disorders of the swallowing reflex and defects of the oral cavity.
The last reason includes damage to the lips, cheeks in the mouth area, loss of teeth and pathological conditions of the facial muscles, in which they cannot function normally. When increased production of saliva begins, we can talk about the presence of inflammation in the oral cavity - the consequences of stomatitis or gingivitis.
When does toxicosis end in pregnant women?
Changes in hormonal levels in the body are temporary. In cases where the problem is limited to ptyalism, single vomiting or nausea without significant deterioration of the woman’s condition, toxicosis does not require any specialized treatment.
Despite this, many expectant mothers are interested in when toxicosis ends in pregnant women. If we are talking about an early form of pathology, then it goes away on its own by 15-16 weeks. With late toxicosis, symptoms disappear after delivery.