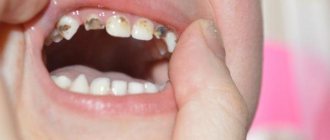
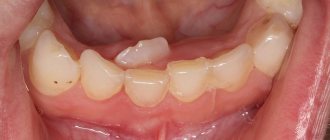
Temporary teeth
Timing of teething
Dental buds are formed during the period of intrauterine development. The eruption of the first teeth begins at the twenty-fifth week of the baby’s life. The lower incisors appear first, followed by the upper ones by eight months. The age at which baby teeth, called premolars, erupt varies from one to two years. The last to appear are the canines and second premolars, which occurs from sixteen to thirty months.
This teething schedule is optimal, but it is impossible to determine the exact timing. The process depends on the characteristics of the child’s body, the health of the mother during pregnancy and genetic factors.
Timing of teething in children in the table
| Type of tooth | Lower jaw | Upper jaw |
| Medial incisor | 6 – 10 months | 7 – 12 months |
| Lateral incisor | 7 – 16 months | 9 – 13 months |
| Fang | 16 – 23 months | 16 – 22 months |
| First premolar (baby molar) | 12 – 18 months | 13 – 19 months |
| Second premolar (baby molar) | 20 – 31 months | 25 – 33 months |
The order of teething in children
The teeth follow the principle of pairing, for example, if one fang appears, a second one should be expected soon. The sequence of teething is determined by nature based on the practical significance of dental units for survival.
The front teeth of the lower row grow first, then the upper ones come. The lateral incisors disrupt the order of teeth eruption; their appearance begins with the upper jaw. Then comes the eruption of chewing teeth - the first premolars. The last to emerge are the canines and molars. The process of teething in children is completed by the age of 2-3 years.
Diagram of baby teeth eruption in children
Molar Differences
Often the surface of each molar tooth is shaped like a triangle. There is a certain number of tubercles on it, which take an active part in chewing food. The number of such tubercles may vary. Usually there are three, but sometimes there are more.
Such mounds are connected to each other by special ridges. On the upper and lower jaws the structure of these elements is different. In the upper dentition, the apex of the surface triangle is directed towards the tongue. This form is called a trigon. On the lower jaw, the apex of such a triangle is directed towards the cheek, which is called the trigonid. The size of the first and second types of teeth is practically the same.
Permanent teeth
Timing of teething in children
The first permanent teeth appear several months before the baby teeth fall out—the molars, or “sixes,” erupt. This occurs at the age of six. By the age of eight or nine years, it is the turn of the incisors. When a child is ten to twelve years old, premolars and canines erupt. Next come the second molars, the eruption of molars is completed by adulthood.
Important!
Wisdom teeth appear much later, after twenty years. However, their complete absence is also the norm.
Timing of teething in the table
| Name | Lower jaw - time of eruption | Upper jaw - eruption time |
| Medial incisor | 6 - 7 years | 7 - 8 years |
| Lateral incisor | 7 - 8 years | 8 - 9 years |
| Fang | 9 - 10 years | 11 - 12 years |
| First premolar | 10 - 12 years | 10 - 11 years |
| Second premolar | 11 - 12 years | 11 - 12 years |
| First molar | 6 - 7 years | 6 - 7 years |
| Second molar | 11 – 13 years | 12 - 13 years old |
| Third molar | 17 – 21 years old | 17 – 21 years old |
Teething order
The pairing principle also applies to permanent dental units. The correct sequence of teething is important for the formation of the bite; it is necessary to carefully monitor the time of loss of baby teeth and the order of growth of molars.
The lower molars appear first, then the upper ones. Next, the temporary teeth of the lower jaw fall out, the permanent teeth erupt, and only then the upper dental units are replaced.
This schedule for teething in children is not universal, but if there are significant deviations, you should consult a specialist.
Features of the structure of molars
Molars have a characteristic structure. On the upper jaw they have three roots and four canals. The lower jaw has two roots and three canals. Moreover, the number of canals also differs depending on the location of the individual tooth. Thus, the first of them often have one more channel than the next two.
The main characteristic feature of this type of teeth is the area of their chewing surface. They bear the heaviest load when chewing food particles. The molars themselves also have differences among themselves, which are associated with the structure of the jaw.
Signs of teething
Symptoms of teething in infants
The appearance of baby teeth is a little more difficult than that of permanent teeth, since the baby has not yet encountered pain and cannot understand what is happening to him. Teething in children under one year of age is accompanied by the following signs.
- The most common symptom of teething is fever. An increase to 38 degrees within three days is normal.
- Swelling of the gums. Often, when children are teething, their gums swell, their sockets itch, and they have a desire to chew hard objects. It is important to prevent the child from damaging the mucous membrane; it is better to buy a special teether to relieve discomfort.
- Decreased appetite. Children refuse to eat due to stress or itchy gums.
- Teething syndrome. Neurosis, tearfulness, anxiety, poor sleep and whims may indicate the imminent appearance of the first tooth, even if the child does not experience pain, fever or swelling of the gums.
Important!
An increase in white blood cell levels during teething should not be a cause for alarm. This is a common occurrence associated with a weakened immune system.
Symptoms of eruption of permanent teeth
A change in temporary bite is accompanied by other unpleasant sensations. The process has the following characteristics.
- Root resorption and loss of baby teeth. A sure signal of the appearance of a new tooth in the coming months.
- Increase in jaw bone size. Permanent teeth are larger than baby teeth, the jaw grows, creating conditions for a change in bite.
- Pain in the gums. Redness and swelling of the mucous membrane are a reaction to teething.
Important!
Body temperature above 38 degrees, cramps, refusal to eat and difficulty breathing are not symptoms of the appearance of milk and permanent teeth. These are signs of an infectious disease. It is necessary to urgently consult a doctor.
Causes for concern
When a child remains without teeth after turning one year old, parents should take him to the doctor. Of course, the time at which chewing organs appear may vary. For example, in boys this process occurs more slowly than in girls. But, there are situations when medical consultation is absolutely necessary.
- An urgent visit to a pediatrician is necessary at a high temperature of more than 39 degrees.
- The baby should be shown to a doctor if symptoms such as frequent diarrhea and vomiting develop.
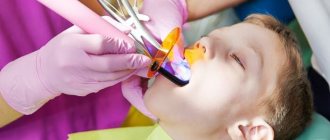
- An orthodontist is consulted if a malocclusion is suspected. Perhaps, after the eruption of incisors, canines, and molars, he needs therapy. In such situations, braces are used for children while the jaw apparatus is pliable.
- A specialist should examine a newborn whose units appeared in the prenatal period.
- A dentist is consulted if the organs are not formed in the dentition.
Therapy may consist of strengthening the health of the toddler, performing special exercises, and massaging the gums.
Painful teething: advice for parents
When faced with teething in children, many parents are at a loss. First of all, you need to call an ambulance and determine the reason for the baby’s poor health. If symptoms are confirmed, the specialist will prescribe medications for teething - antipyretics and painkillers.
You can treat your gums yourself with an anesthetic gel with a cooling effect to reduce itching and swelling of the mucous membrane. Ice will also help. To reduce gum irritation, there are special silicone fingertips made of hypoallergenic material.
Folk remedies for teething will effectively relieve painful sensations - a decoction of chamomile, sage, tincture of valerian and honey will soothe inflamed tissues.
Painkillers for teething are contraindicated in children; this can worsen their health.
Important!
Without a doctor's recommendation, antibiotics and other strong teething medications can cause an allergic reaction.
What should mom do?
When teeth erupt out of order, every parent should take this fact seriously. Pediatricians advise feeding your baby in a balanced manner. For six-month-old children, mother's milk is not enough. Complementary foods should be introduced gradually. Mothers should properly allocate time for wakefulness and sleep, and visit the doctor according to the schedule. A vitamin complex may be prescribed. It is prohibited to select medications on your own, since only a doctor can give an objective assessment of the baby’s condition.
If the chewing organs do not appear according to the calendar, specialists prescribe certain tests to determine the cause of the failure. Mom should not neglect the doctor's recommendations. Its instructions should be followed exactly to stimulate the appearance of units. To do this you need:
- Include foods rich in vitamins in your diet;
- Correctly create a daily routine and monitor its implementation;
- Conduct comprehensive physical exercises with children;
- Regularly visit a doctor for preventive purposes;
- Treat illnesses in a timely manner;
Taking medications without a doctor's recommendation is dangerous and detrimental to a child's health. Only care and affection, proper care and feeding will allow you to raise a healthy child.
Deviations in teething
Minor changes in the timing and sequence of dental growth should not cause alarm. However, significant deviations from the norm in teething are a cause for concern.
- The tooth does not appear for a long time. Reason: genetic predisposition to long eruption or lack of rudiments.
- Too early appearance of teeth. Caused by disruption of the endocrine system.
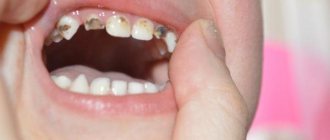
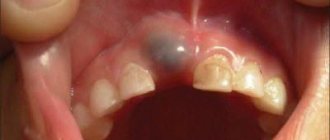
- Black or brown enamel surface color. Indicates high iron levels, poor salivation, or chronic inflammatory processes in the child’s body.
- Incorrect row position. Bite pathologies indicate a hereditary factor or deformation of the maxillofacial bone.
Typical problems.
The most typical problem between the ages of 3 and 6 years is the development of caries of primary teeth in the area of the first and second primary molars. The narrow interdental spaces between the first and second primary molars, which are difficult for a child to reach, are an ideal place for plaque to accumulate. As a result, caries forms on the surface of the teeth hidden from the eyes of parents (between the 4th and 5th milk teeth). Being unnoticed, the carious process quickly progresses, complicated by inflammation of the nerve of the tooth (pulpitis).
With poor oral hygiene and a large number of carious teeth, caries of the permanent molar (6th tooth) often develops, high-quality treatment of which is only possible by a pediatric dentist.