Plaque on the teeth of children is a fairly common occurrence, primarily in cases where insufficient attention is paid to oral hygiene. Plaque itself is a collection of food debris, bacteria and elements of the oral mucosa. Initially, it has a soft structure, so removing it from the surface of the teeth is not difficult, but later it quickly hardens and cannot be removed with a simple toothbrush.
Dental plaque varies in color, from almost white to brown and black. The chemical composition of such formations is formed 80% from water, and the rest is formed by fluorides, calcium, phosphorus compounds and other elements.
Stages of plaque formation
Plaque on the teeth of children does not form immediately, but sequentially, going through several stages:
- Pellicle formation. This is an organic film of minimal thickness, the basis of which is the glycoprotein components that make up human saliva. This film is characterized by the absence of microorganisms in it.
- Precipitation of bacteria. Over time, the number of microorganisms consistently increases due to the appearance of new films, which in turn causes an increase in the thickness of deposits formed on the surface of the teeth.
- Actions of anaerobic agents. In air conditions, bacteria are active, resulting in the release of acid. This, in turn, affects tooth enamel, washing away minerals from it.
- Formation of an anaerobic environment. At this stage, the density of deposits increases to a state in which it is not possible to remove them with saliva or rinsing the mouth. The enamel is actively losing minerals.
The rate of formation of deposits on teeth is largely individual. It depends on the composition of saliva, the intensity of epithelium changes, a person’s tendency to inflammation, and so on.
Tooth enamel: general characteristics and properties
This is the hardest and most durable tissue in our body, its thickness on the outer surface reaches almost 2 mm. It consists of many layers formed at various stages of mineralization and has a crystalline structure. The chemical composition is represented predominantly by apatites, calcium and phosphorus predominate from inorganic compounds, and proteins, lipids and carbohydrates from organic compounds.
The main function is to protect dentin from external factors: mechanical, chemical and temperature stimuli. Thanks exclusively to this tissue, teeth can fulfill their main purpose - grinding and chewing food.
Despite its extraordinary strength, enamel is permeable to water and many organic and inorganic substances contained in saliva. It has been found that the degree of permeability for much-needed connections depends on several factors. If we talk about temporary occlusion, this is:
- condition of the oral cavity;
- nutritional features;
- long-term treatment with certain medications (in particular, tetracycline antibiotics);
- features of intrauterine development.
Enamel maturation
The composition of the protective tissue covering dentin is constantly changing, which is associated with age-related characteristics. Throughout the year after teething, there is an active accumulation of calcium and phosphorus, and during this period it is extremely important to receive all the necessary elements with food or multivitamin preparations. It has been proven that a sufficient content of microelements prevents the development of caries.
Main reasons
When plaque occurs on the teeth of children over two years of age, there may be several reasons for this phenomenon, but the main ones are:
- Fungal infections developing in the oral cavity;
- Dysbacteriosis;
- Lack of proper oral hygiene;
- Excessive amount of sweets consumed with a shortage of fruits and vegetables;
- Bottle feeding babies at night;
- Chewing food on one side (plaque forms on the other side).
Description of the problem
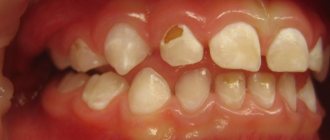
Black plaque on baby teeth has its own shape and size. Sometimes these can be dots, and sometimes stripes of different shapes (there are cases when black plaque completely covers the tooth). Plaque can appear on the outside of the tooth and on the inside. This is the result of poor oral hygiene and is formed from food debris. That is why a child should be taught to read their teeth from early childhood, and this should be done not just haphazardly, but for three minutes in the morning and evening. Black milk teeth are a characteristic feature for children aged 1 to 4 years.
The main dangers of dental plaque
Such deposits, regardless of their color, are a breeding ground for various bacteria, so they pose a danger to the child and require prompt removal. At the same time, the waste products of such microorganisms have an acidic environment, which has a destructive effect on tooth enamel.
In this case, the following diseases may become further development of plaque:
- Destruction of enamel;
- Formation of tartar;
- Caries;
- Gingivitis (inflammation of gum tissue);
- Periodontitis.
Treatment methods
If you notice a black plaque on your child’s baby teeth, then this is a reason to switch to a different diet, a healthier diet. What does the problem mean and methods for solving it:
- lack of calcium. You need to consume more fermented milk products;
- Priestley's raid. This is a reason to contact the dentist, he will carry out a cleaning;
- fluoridation. Modern technique.
Regular preventive examinations will help eliminate the problem in the early stages of development.
Possible color of plaque on teeth
- Yellow. Such plaque in most cases is the result of insufficient oral hygiene. If the thickness of the layer of formations turns out to be significant, you should consult a dentist.
- Brown color. Indicates deposits containing iron. They can be caused by taking iron-containing drugs or increased levels of this metal in drinking water.
- Green color. Characteristic of a situation where chlorophyll-containing microorganisms develop in the child’s mouth. Most often, such plaque does not form on the teeth, but on the inner surfaces of the lips and cheeks in the area of the patient’s front teeth.
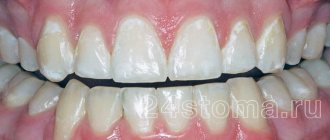
- White color. The safest of all types of plaque is white. It indicates a lack of hygiene. It is enough to regularly brush and rinse your teeth, starting from the moment the first teeth appear, and it will definitely disappear.
- Black or dark green color. It is called Prisley plaque and is very difficult to clean off. It is mainly characteristic of baby teeth, and gradually goes away as the child develops a correct bite.
The reason for the dark color of Prisley's plaque is the bacteria Actinomycetes and Lactobacillus, which create a dark pigment in the process of their own vital activity.
Today, medicine has not yet fully determined the causes of the occurrence and spread of such bacteria in the oral cavity, but it is believed that problems with the gastrointestinal tract may be the cause. In such conditions, a trip to a gastroenterologist will not be superfluous.
A number of researchers indicate that children with such plaque have a slightly changed composition of saliva, where there is much more pH, calcium and a number of other elements. As a result, such saliva is more dense in its structure.
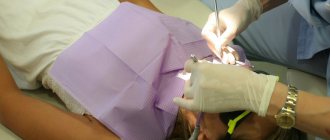
At the same time, it is impossible to remove plaque on children’s teeth on their own; you will need to go to a dental clinic.
Types of plaque
- White.
By the end of the day, all children have a small amount of harmless white residue. Abundant formation indicates vitamin deficiency, reduced immunity or insufficient hygiene. This type of plaque can be removed from a child’s teeth if you brush your teeth thoroughly every day. The presence of hard fruits and vegetables in the diet, such as apples and carrots, promotes mechanical cleaning. If no action is taken, the layer will harden, mineralize and turn into tartar.
- Yellow.
Indicates insufficient hygiene and poor nutrition. In children under two years of age, it can occur, for example, due to the consumption of sweet liquids from a bottle. It may also indicate the initial stage of caries. By choosing the right toothpaste and brush, as well as brushing your teeth more thoroughly, this problem can be solved.
- From light gray to green.
Gray - possible with abundant release of chlorophyll, sometimes acquires a greenish tint. Green - provoked by a fungus - chromogenic bacteria. Damages the pellicle, the natural protective film on the teeth. Only a dentist can help remove such plaque.
- Brown.
Indicates a fungal infection of the oral cavity and a disorder in the gastrointestinal tract. The result is darkening of the enamel. Iron supplements can also stain teeth brown. How to remove such plaque from a child’s teeth? Sometimes it goes away on its own after you stop taking iron-containing foods or medications. If the deposits have hardened, you will need professional teeth cleaning - ultrasound or chemical whitening. It is also necessary to adjust the child’s nutrition.
- Black.
Black plaque is the first harbinger of caries. Especially if it has a point character. In such cases, it is better not to postpone a visit to the dentist.
Possible complications
Some parents are in no hurry to visit a pediatric dentist because they consider it useless to treat baby teeth. This approach is explained by the fact that permanent ones will grow instead of them anyway.
Although the carious process itself does not transfer from baby teeth to permanent ones, untreated caries lesions have a detrimental effect on the condition of the latter. If you ignore superficial caries in children , complications may very soon manifest themselves:
- caries progresses rapidly in the absence of adequate therapy. This leads to the development of periodontitis and damage to the molar tooth germ. The inflammatory process significantly slows down the eruption of permanent teeth and complicates their growth;
- premature loss of baby teeth leads to the formation of malocclusion and disrupts the structure of the maxillofacial system;
- If at least one tooth is missing in the dentition, this complicates the process of chewing food. As a result, problems arise with the functioning of the digestive system.
Remember! Even the smallest stain can lead to complete tooth decay. There is no need to risk your child's health. It is much easier to visit the dentist and, if necessary, treat caries.
What kind of stone is there?
There are two types of tartar:
- supragingival;
- subgingival.
They differ from each other in location.
Supragingival calculus is easy to see, it is grayish or yellowish in color, and is easy to scrape off from the tooth. The appearance of such a stone can be blamed on the minerals found in saliva. Most often, this type of deposit is based on the front teeth and buccal surfaces of the molars of the upper jaw.
Subgingival stone can only be detected by a dentist. At Family Dentistry, the doctor will definitely conduct a diagnosis in order to detect deposits or make sure that they are absent. This type appears due to gingival fluid containing minerals. This stone is either greenish or dark brown, attached to the neck of the tooth, on the root cement, in the periodontal pocket.
Visually, it can only be seen if the disease is advanced - the deposit covers the neck of the tooth, and protrusions form.
How to get rid of white spots on teeth
First of all, it is important to consult a doctor to find out the causes of the unpleasant symptom. The pediatric dentist will determine what caused the whitish formations on the teeth, select effective therapeutic methods, and give recommendations for high-quality hygienic care and prevention.
If a carious lesion is detected at the initial stage, no serious intervention is required. In most cases, it is sufficient to use silvering (on primary occlusion), remineralization or ozonation (in the presence of permanent rows). The baby must be taught proper hygiene.
When caries is deep and painful, you cannot avoid using a drill and installing filling material. When the pathological process is advanced, depulpation and even extraction (removal) are indicated.
If an excess of fluoride is detected in a child’s body, the doctor will advise using a paste that does not contain this component. Remineralization is also indicated.
When tooth surfaces become white due to braces or other orthodontic structures, complex treatment is carried out, which includes:
- elimination of carious cavities;
- disinfection;
- replacement of simulators with new ones;
- regular dental monitoring;
- professional cleaning of food debris and accumulated plaque.
Black teeth in children: possible complications
Black teeth look unsightly. In childhood, this can affect self-esteem. Also, a person with this problem has bad breath. In addition, ignoring this symptom can lead to a number of complications. Among them:
- caries;
- periodontitis;
- increased sensitivity of teeth;
- bleeding gums;
- gingivitis.
To eliminate plaque and prevent its reappearance, it is enough to simply teach your child to follow the rules of hygiene. But it’s better not to take risks - get tested and rule out bad options.
How to clean at home?
Most children really don't like visiting the dentist, so you can try to get rid of brown plaque on your teeth at home.
Activated carbon
- You should take one tablet of coal and grind it to a powder.
- Then add a little water and stir thoroughly. You should have the consistency of a paste.
- Apply the resulting mixture to a brush and brush your teeth well with it.
- After this, you need to rinse your mouth to completely wash off the activated charcoal.
Baking soda
- You need to sprinkle a little baking soda on your baby's brush.
- Brush all teeth using gentle movements.
Baking soda is a good bleacher; in addition, it perfectly disinfects the oral cavity and can dissolve tartar.
Strawberry puree
The most “tasty” way that children really like.
- A handful of fresh strawberries should be washed and mashed.
- Apply the resulting puree to your teeth and leave for a while.
The acid contained in the berries should dissolve the brown coating.
Hydrogen peroxide
- Mix a teaspoon of 3% hydrogen peroxide with 200 ml of clean water.
- Soak a cotton pad in the solution and gently wipe the child’s teeth with it.
- After the procedure, rinse your mouth thoroughly.
Orange
This fruit contains acid that can dissolve plaque.
- The orange should be cut into slices and rubbed on the tooth enamel.
- After a few minutes, brush your teeth.
If there is damage to the gums, then this method will not work.
Attention! Any of the homemade cleaning methods should not be used very often so as not to damage tooth enamel. If the brown plaque does not disappear, the child must be shown to a doctor.
Factors influencing the development of superficial caries in children
The fundamental factors that result in superficial caries in children are:
- eating foods that contain large amounts of carbohydrates;
- non-compliance with hygiene rules: insufficient brushing of teeth, ignoring periodic rinsing with special means, etc.;
- drinking water with a deficiency of fluoride in its composition;
- deficiency of vitamins and mineral elements;
- severe systemic diseases;
- hormonal imbalance;
- ignoring professional hygiene, the need for which arises every 5-6 months.
Any of these factors or several at once are the primary causes of tooth enamel destruction.
Cleansing methods
The soft layer of contamination on dental elements is an excellent breeding ground for pathogenic microflora. It multiplies exponentially, becoming a source of infection and, as a result, the cause of caries, gum problems and gastrointestinal diseases. Dentists have learned to effectively deal with the problem. Once upon a time, cleansing was carried out manually, it was not effective enough and was accompanied by pain. Now, special devices are used for cleaning, which allow 100% destruction of pathogenic flora. Experts recommend doing this procedure at least once a year.
The most popular method is cleansing using an Air Flow device. Mechanism of action: a solution containing tiny abrasive particles is applied to the surface of the enamel layer under pressure. They gently “bombard” plaque, destroying it and washing it away. Hard tartar is removed with an ultrasonic scaler. Once cleaning is complete, the enamel is polished and a fluoride varnish is applied to remineralize it.
Important: self-medication is dangerous. Do not try to remove dirt with sharp objects (needle, knife, etc.). This is fraught with injury to the gums, chips, and the risk of swallowing the cleaning tool.