Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
The human oral cavity has its own microflora and its own specific diseases arise. Let's talk about one of them - fibrous epulis of the gums: what kind of disease it is, what are the causes of its occurrence, how is the treatment carried out.
What it is
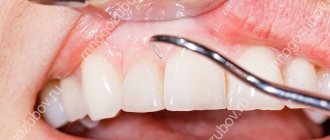
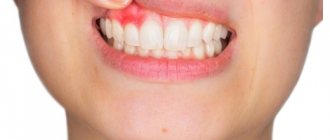
Epulis is a tumor-like neoplasm that develops on the alveolar process of the jaw. It also has other names - epulid, supragingival, giant cell granuloma. More often it is localized in the area of incisors, canines and small molars of the upper jaw, less often the tumor is detected in the lower jaw. The growth has a round or irregular shape and a wide stalk; the size of the formation varies from 3 mm to 5 cm.
Despite the fact that such a tumor looks frightening, it practically does not cause concern to the patient, unlike, for example, a burn, with the exception of a violation of aesthetics and the sensation of a foreign body in the oral cavity. Large tumors may cause difficulty chewing and swallowing food.
If epulis is accompanied by bleeding, infection may occur, which will lead to complications.
The disease mainly affects adults, but the neoplasm can also appear in children; in the latter, it occurs during teething. Studies have shown that women are more susceptible to developing epulis than men.
Prevention
There are a number of rules, the observance of which can prevent the appearance and further development of epulis:
- maintaining oral hygiene,
- avoiding, if possible, situations leading to damage to teeth, as well as soft periodontal tissues.
If there is any suspicion of the presence of epulis, you should urgently seek help from a professional of the appropriate profile. This is the only way to prevent more serious, including irreversible, consequences with a high degree of probability.
Varieties of epulis
Conventionally, there are 3 types of epulis:
- Fibrous. The neoplasm is dense, the basis is coarse fibrous tissue. Characterized by slow growth. There is no pain or bleeding.
- Angiomatous. The tumor contains a large number of blood vessels and is localized mainly in the lateral parts of the jaw. With this form of the disease, bleeding is observed even with slight pressure, for example, with a toothbrush or food. When pressed, the tumor is painless and has a soft consistency.
- Giant cell. The tumor can reach large sizes, displacing teeth that are located in the epulis growth zone. The mucous membrane of the epulis is bluish-red in color. On palpation, the neoplasm is painless, but may bleed moderately if injured.
Depending on the nature of the process, epulis can be benign or malignant. In the first case, the neoplasm is characterized by slow development and, as mentioned above, in most cases does not cause pain. The tumor size in this case rarely exceeds 10–20 mm. When the process becomes malignant, rapid tissue growth is observed. In this case, the process is often accompanied by pain, bleeding gums and affects the root canals of neighboring teeth.
The appearance of growths in a child
Most often in children, this disease manifests itself during the period when teeth are being cut . In this case, this is mostly due to trauma to the gums and mucous membranes. The angiomatous variety is most often diagnosed, but sometimes others are also found.
Parents should seek professional help from an experienced specialist as soon as possible . This is necessary to prevent the spread and growth of tumors. Girls are diagnosed several times more often.
In adolescence, the appearance of epulis on the gums of a child can be associated not only with chronic injury. It may also be hormonal disruptions during puberty . A similar failure in teenage girls can also be caused by taking inappropriate hormonal medications.
It should also be noted that in childhood it is possible to change the type of epulis, that is, the transition from one form or type to another. More often it all starts with granulomatous epulis, which, as it grows, turns into angiomatous and then into a fibrous form.
Recurrent forms are observed in a large number of cases - about 14%.
Diagnosis and treatment of epulis
Diagnosis of epulis comes down to collecting complaints, clinical examination, radiography and histological examination of the material.
The primary task in making such a diagnosis is to eliminate the provoking factor: professional cleaning of dental plaque, treatment of caries and its complications, replacement or correction of orthopedic structures according to indications. In fibromatous and angiomatous forms, dynamic observation is indicated, since after sanitation of the oral cavity and elimination of the causes of the disease, the tumor may decrease in size until it disappears completely.
Treatment of epulis is carried out surgically. The growth on the gum under local anesthesia or general anesthesia is excised with a scalpel or laser within the healthy tissue along with the periosteum. The second method is preferable, since the laser simultaneously coagulates the vessels and stops bleeding. With giant cell epulis, the area of bone tissue involved in the process is also removed. To do this, use a bur or cutter. The wound is closed with gauze with an iodoform mixture or a formed mucoperiosteal flap. If necessary, the material is sent for histological examination.
Intact teeth in the area of tumor localization must be removed with a high degree of mobility and severe exposure of the roots. If the bone lesion is extensive or epulis recurs, partial resection of the alveolar part along with the teeth is performed.
To speed up the healing of a fresh wound, the doctor prescribes compresses with medicinal ointments and rinses to the patient.
Forecast
If the causative factor that provoked the appearance of granuloma is not eliminated in a timely manner, the consequences can be very disastrous. For example, the probability of recurrence is very high even if surgical excision was performed.
Provided a comprehensive diagnosis is carried out, as well as qualified treatment, the prognosis in the vast majority of cases turns out to be quite favorable.
In addition, preventing the situation from worsening in the future is possible through proper prevention. This means preventing injury to the gums, competently performed dental prosthetics, thorough fitting of orthodontic appliances, as well as a systematic qualified examination in a professional dental office.
Preventive actions
Monitoring the condition of the teeth and oral cavity will reduce the likelihood of tumors.
- Timely sanitation of the oral cavity. Visiting the dentist for a preventive examination and professional hygiene twice a year will prevent the growth of caries, the appearance of defects in fillings and the formation of tartar, leading to gum injury and the appearance of epulis.
- Prevention of gum injury. If systematic injury to soft tissue occurs as a result of poorly fitted orthopedic or orthodontic structures, consult your doctor about this problem. He will adjust the crowns or dentures.
If these preventive measures are followed, the prognosis is favorable and epulis does not recur.
We hope that our article about epulis will be for informational purposes only. And if you want to soothe your gums, make them strong and strong, try the unique two-component mouth rinse ASEPTA ACTIVE.
This is the only rinse with a combination of chlorhexidine + benzydamine for the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases. The product has a combined effect: antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and analgesic. Instant anesthetic effect allows you to quickly reduce pain.
Causes of occurrence (Etiology)
In general, the etiology of this disease is quite natural and therefore easily explainable. Such a tumor is formed as a result of the influence exerted by local irritating factors. Injuries to the gum margin by destroyed walls of dental units, unpolished prosthetic bases, metal clasps, protruding components or ribbed edges of orthodontic structures are fraught with the progression of chronic inflammation of the productive type. Predisposing factors leading to tumor formation include pathologies of occlusion, hormonal imbalances, and narrowing of the dentition.
Clinical researches
Repeated clinical studies have proven that the two-component mouth rinse ASEPTA ACTIVE more effectively combats the causes of inflammation and bleeding compared to single-component rinses - it reduces inflammation by 41% and reduces bleeding gums by 43%.
Sources:
- Clinical and laboratory assessment of the influence of domestic therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste based on plant extracts on the condition of the oral cavity in patients with simple marginal gingivitis. Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Elovikova T.M.1, Candidate of Chemical Sciences, Associate Professor Ermishina E.Yu. 2, Doctor of Technical Sciences Associate Professor Belokonova N.A. 2 Department of Therapeutic Dentistry USMU1, Department of General Chemistry USMU2
- The effectiveness of the use of Asept “adhesive balm” and Asept “gel with propolis” in the treatment of chronic generalized periodontitis and gingivitis in the acute stage (Municipal Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk, Kaminskaya T. M. Head of the therapeutic department Kaminskaya Tatyana Mikhailovna MUZ City Dental Clinic No. 4, Bryansk
- Study of the clinical effectiveness of treatment and prophylactic agents of the Asepta line in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (A.I. Grudyanov, I.Yu. Aleksandrovskaya, V.Yu. Korzunina) A.I. GRUDYANOV, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department I.Yu. ALEXANDROVSKAYA, Ph.D. V.Yu. KORZUNINA, asp. Department of Periodontology, Central Research Institute of Dentistry and Maxillofacial Surgery, Rosmedtekhnologii, Moscow
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
Features of the course during pregnancy
During pregnancy, the female body undergoes a very complex restructuring. Hormonal disruptions and surges at this time are a completely natural phenomenon. This is why pregnant women can also often develop epulis on the gums .
The initial cause may be the same chronic injury. However, in this case, the growth of the tumor and all the processes taking place in it are significantly accelerated . This also accounts for a fairly large number of relapses. Moreover, during the period of bearing a child, new formations appear much faster.
Is it possible to use traditional medicine?
Treatment with folk remedies is allowed during the rehabilitation period after removal of the epulis. Basically, rinsing the gums with solutions that have an antiseptic, healing, and anti-inflammatory effect is used. For this purpose, decoctions and water infusions of medicinal plants are used: chamomile, calendula, sage. Procedures are carried out up to 5-7 times a day, especially after meals. In addition to decoctions of beneficial herbs, solutions of baking soda and salt are used (one teaspoon per 200 ml of warm water).
Therapy
To combat pathology, surgical, laser (as the newest surgical method), medicinal methods and traditional medicine are used as a means of complementing the main therapy.
Surgical
It is carried out when the tumor has grown significantly by completely removing it. The operation involves its dissection and takes place in several stages:
- Administration of anesthesia (depending on the epulis clinic, local or general anesthesia is performed).
- As soon as the anesthetic takes effect, the doctor, stepping back 1-2 mm from the stem of the growth, makes an incision around the soft tissue of the gums to their entire depth, capturing the periosteum.
- The flap is peeled off along its entire circumference.
- If the disease has affected bone tissue, the affected area is dissected down to healthy tissue.
- The wound surface is cleaned, washed with an antiseptic solution and covered with a swab soaked in iodoform composition.
- If the affected area is large, its edges are tightened with sutures.
Teeth located nearby are pulled out only when they are mobile (grade III) or when their roots are exposed to 2/3 of their length.
Have you discovered an abscess on your child’s gum? We'll tell you what to do. On this page: https://dentist-pro.ru/lechenie/desny/gingivit/osobennosti-razvitiya-i-taktika-gipertroficheskogo.html - you can find out the etiology of hypertrophic gingivitis.
In the next review we will talk about the approximate prices of plasma lifting in dentistry.
Laser Application
In many large dental centers, lasers are used as a surgical instrument for interventions of this type. During the operation, the patient is given infiltration anesthesia.
The advantage of using this method is that the laser simultaneously eliminates (cauterizes) the tumor and disinfects the area affected by it. As a result, the rehabilitation period is significantly reduced, and postoperative complications are reduced to a minimum.
This is how epulis on the gum is removed using a laser:
Medication
Therapy includes taking drugs that stop the growth of epulis and lead to the regeneration of its tissues. The list of prescribed medications includes:
- "Traumel S " is a homeopathic remedy that has pronounced regenerative and hemostatic effects.
It perfectly restores weakened oxidative processes in all tissues and slows down the formation of granulations. Can be taken as tablets or drops in the dosage: 1 tablet/10 drops. three times a day in a course of 10-14 days. - "Dimexide" is an anti-inflammatory, antihistamine, analgesic, antiseptic drug. Its active components, penetrating into cells, have a fibrinolytic effect, which helps curb tumor growth. Prescribed by applications: applied for 20 minutes. on the pathogenic area 4-6 times/day.
- "Miramistin" is a spray that exhibits its antiseptic activity against bacteria and viruses that cause the disease. To achieve the effect, irrigate your mouth up to 4 times during the day.
- "Vagotil" - has a pronounced sclerosing effect due to the elimination (cauterization) of the affected tissues. During treatment, a bandage is formed, moistened with the drug and applied to the problem area for 3-5 minutes. Important: the procedure can be carried out no more than 3 times a week.
- "Resorcinol" is an antiseptic, has strong antimicrobial, wound-healing, regenerating, anti-inflammatory, and antiseborrheic effects.
Its use can lead to complete removal of the growth. For treatment, an ointment of 5-10% is used, which is applied to the affected tissue twice a day.
Important: all of the listed medications can be used in treatment only after they have been prescribed by a dentist. Self-medication in this case is unacceptable.
Folk recipes
Complete treatment using only traditional recipes is impossible. They can, together with medical treatments, speed up recovery during the rehabilitation period.
All recipes are based on the use of rinses with decoctions prepared from various medicinal herbs and remedies:
- Calendula: 2 tbsp.
l. dried plant pour 1 tbsp. boiling water, leave until cool, strain and rinse your mouth up to 4 times a day. The plant has a good anti-inflammatory, wound healing and antiseptic effect. Calendula can be replaced with other equally effective plants: sage, eucalyptus, chamomile . A decoction of them is prepared in the same way. - Baking soda : 1 tsp. dissolves in 1 tbsp. warm clean water. Rinsing with it prevents further spread of suppuration, infection and inflammation. This result is achieved due to the fact that soda has a strong disinfectant, antiseptic and mild analgesic effect.
- Salts: dissolve 1 tsp in a glass of hot water. salt, but can be used only after the solution has cooled (6-8 times a day). It relieves swelling well and prevents the spread of bacteria.
All infusions used should be at room temperature, since hot ones can lead to tissue burns, and cold ones can lead to hypothermia.
Before you start using this or that drug in treatment, you need to check with your doctor to what extent its use is indicated in this case.
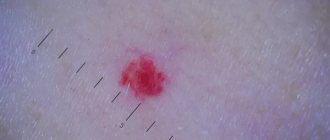
Giant cell
The name is scary, isn't it? And rightly so, because giant cell granuloma is considered the most dangerous type of disease, which threatens to develop into a malignant tumor. Epulis of this type is most often found in middle-aged and elderly women. What worries patients: the rapid increase and growth of a hard and very dense neoplasm to the touch, its bluish or dark brown tint, pain when pressing and chewing, bleeding.
Giant cell form of epulis
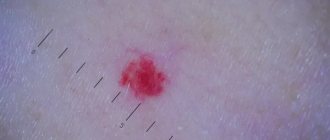
Fibrous
Fibrous epulis is the safest of all existing ones. When it appears, the damaged gum is practically indistinguishable from the rest of the mucous membrane. The tumor itself is quite dense, most often localized externally, that is, vestibular, noticeable in the smile area. It looks like a small ball or bump. This neoplasm grows extremely slowly, and the capillaries on it do not bleed.
Fibrous epulis
Reviews
Epulis in medicine is classified as a tumor neoplasm, but there is no need to be afraid of this disease. Unattractive appearance and aesthetic changes are perhaps the biggest problem during the course of the disease.
However, for many, the tumor causes a lot of inconvenience and is difficult to treat with medication. In addition to the information in this article, readers will be interested to know how the operation is performed and how long the recovery period lasts.
What medications helped reduce the tumor or get rid of it completely? Share your experience and impressions in the comments.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Complications
As a rule, qualified specialists approach the treatment of the disease with special responsibility, which helps to avoid complications. In exceptional cases, a number of consequences appear:
- relapse;
- swelling of soft tissues after surgery;
- bleeding;
- empyema of soft tissue due to infection with pathogenic bacteria.
Patients are strongly advised to follow all specialist recommendations in the postoperative period.
Do not forget about careful oral hygiene, which will prevent the risk of infection at the wound site. If complications arise, it is not advisable to delay visiting the dentist.