Where does the abscess come from and what is its danger?
In the vast majority of cases, an abscess on the gum is associated with a tooth, often with a milk tooth. The most amazing thing is that the tooth may appear healthy from the outside, it may have a beautiful filling, and the tooth may not hurt. Why does pus still appear?
Baby teeth are less resistant to infection than permanent teeth; they are designed for a short service life, although they, like permanent teeth, have a nerve and roots. However, the roots of baby teeth begin to dissolve after five years. Caries in such teeth spreads much faster. Within three months, a cavity can form in the tooth, reaching the nerve. If caries is not treated, all pathogenic bacteria enter the dental nerve, and then, through the nerve, the microbes enter the bone. Bone is quite comfortable for microbes. They multiply there, dissolve the bone, which is accompanied by the formation of pus. If the tooth is open, there is a hole in it, pus comes out into the oral cavity. If food particles, fragments of destroyed enamel get into the tooth, or the tooth is covered with a filling without adequate treatment, pus can no longer flow freely. If the pus cannot flow out through the tooth cavity, it begins to look for another way out. The pus melts the bone and comes out under the gum. The outer covering of the gum, under which the pus has come out, swells and takes the form of a lump. Over time, the lump may burst and pus leaks out.
Once the pus is released, the lump may disappear and the gums may heal until the pus collects in large quantities again. The danger of such “bumps” is as follows:
- there is always an infection in the body (you should never forget that the abscess is not just on the gum, but in the head);
- the pus that is in the jaw dissolves the bone and can damage the growing permanent tooth.
The disappearance of an abscess next to a tooth never means recovery.
Symptoms that appear along with an abscess
- redness on the gum;
- tooth pain (optional);
- There is a hole in the tooth or there may be a filling on it;
- enlarged lymph nodes (dense “balls” appear under the lower jaw).
Sometimes a lump is discovered by chance, and the child may not be bothered by anything at all. The parent should periodically examine the child's mouth independently.
Manifestation of hyperplasia
- The color of the enamel changes. Yellow spots appear on it. Discoloration of the enamel may be accompanied by pain, but the tooth still retains its integrity.
- Underdevelopment of enamel, which manifests itself in the form of wavy enamel and furrowed depressions.
- Complete absence of enamel.
The most severe disease is the complete absence of the top layer of enamel, which can manifest itself as: tooth deformation, pain due to temperature changes, pain due to mechanical impact on the teeth.
Risk factors for the development of hyperplasia on permanent teeth:
- Disease of rickets or various infectious diseases.
- Excess of vitamins A, C, D in the body.
- Syphilis disease.
Never do
You should never heat your gum or cheek, no warm compresses or salt or other “folk remedies”! It’s better not to do anything at all before going to the doctor. After warm compresses, pus may spread not only in the jaw, but also in the cheeks, throat, and neck. Situations arise that are dangerous not only to health, but also to life.
Contraindicated
- refusal to brush teeth;
- independent opening of the abscess;
- taking medications without the consent of a doctor (except for painkillers).
The main risks of gum fistula and the risk of complications
Without proper timely treatment, fistulas often cause complications. They can affect not only the oral cavity, but also the internal organs of the baby.
There are several common risks:
- Severe intoxication of the body. Occurs because pus is constantly secreted from the wound. The pathogenic microflora that develops poses a great danger.
- Tooth loss. Sometimes it is necessary to remove only the one whose root has been affected. But cases with gradual spread of inflammation are also common, when several teeth need to be removed.
- Damage to the periosteum. It has far-reaching consequences associated with inflammation of tissues and bones, and the need for surgical intervention.
- Sinusitis. The infection quickly spreads to the human maxillary sinuses and begins to rapidly progress, covering ever larger areas.
Other dangerous potential complications include the need for perforation of the cheek, flux, removal of tonsils, and gastrointestinal disorders.
As with any other type of inflammation, the hours begin to count. Therefore, if a problem occurs, you need to seek dental help as quickly as possible.
Treatment
Depending on whether a permanent or baby tooth caused a lump on the child’s gum , the doctor carries out appropriate treatment. If a permanent tooth is damaged, seek help immediately while there is a chance to save the child’s tooth. The doctor will have to remove the nerve and fill the canals. In this case, adult dental treatment is a necessity, because if high-quality treatment and appropriate treatment are not carried out, the child may lose a tooth.
Milk teeth are removed immediately - their root system has not yet had time to form, and it is impossible to properly fill the canals. In addition, if a diseased tooth is left, the molar may grow back with defects (stains, damage.
At the Family Dentistry Center, you can remove a child’s tooth without pain or fear. All procedures in the clinic are performed under medical sedation. While the baby is sleeping peacefully and does not feel pain or discomfort, the doctor can carry out all the necessary procedures. Being able to treat your teeth while you sleep is a great way to cope with dental phobia.
The main symptoms of gum fistula in children
It is very important to understand that a child is at risk of developing a fistula at a very early stage. But often parents in precisely this situation cannot find any signs of a problem. Inflammation can indeed form without serious external manifestations.
But as the disease progresses, the symptoms become more and more severe. First of all, a small swelling appears at the site of inflammation. Over time, it begins to become more and more pronounced, turns red, and the tissues can warm up from the inside.
Symptoms change with development. Among the important indications:
- It's a dull pain. Usually it turns out to be quite strong, the child begins to complain and be capricious. It may pass for a while and this will lull your vigilance. But there is a serious risk that the sensations will soon return and be even more noticeable.
- Swelling on the gum. It may look like a small abscess, similar to those that sometimes appear on human skin.
- Cone development. Usually it is quite large in size and has a whitish tint. In the inflamed area, the pain intensifies and other unpleasant sensations appear.
- Tooth mobility. It becomes more noticeable as the disease spreads. The tooth becomes very loose, and in the later stages it can even come out of the gums.
- Discharge from the inflamed area. When you press on the gum, it begins to ooze pus and blood.
Also, in the later stages of inflammation, a strong bad breath appears, and other unpleasant symptoms may develop.
It is often possible to find a fistula even on your own during an external examination. Moreover, without a properly selected treatment program, inflammation can spread deeper into the tissue and gradually worsen.
Prevention
There are no special unique ways to prevent dental disease in children. Ulcers on the gums are the result of untreated caries. Therefore, all preventive measures are aimed at preventing caries:
- oral hygiene (make sure your baby brushes his teeth properly);
- balanced diet;
- rinsing your mouth every meal;
- preventive procedures (remineralization, fluoridation; fissure sealing);
- timely dental treatment;
- preventive examinations at the dentist 2 times a year (some experts recommend once every 3 months if the baby already has treated teeth).
Timely dental treatment for children and proper hygiene will help avoid many dental problems. Teach your child to take care of the health of their teeth and beautiful children's smiles will delight you every day!
How to treat a fistula at home
We emphasize that home treatment is only one of the auxiliary methods prescribed by a doctor.
At home, you will need to treat the oral cavity using special decoctions with a pronounced calming and antiseptic effect. You can use decoctions of calendula and chamomile, solutions of salt and soda.
Also allowed are lotions made from aloe and Kalanchoe, and the application of special ointments prepared at home. They are made using crushed chamomile herbs mixed with sea buckthorn oil.
This home treatment can significantly speed up the recovery period and reduce your child’s discomfort.
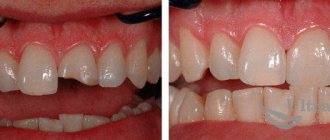
Why do the necks of teeth become exposed and how to restore gums?
Quite often, patients come to me with complaints of increased tooth sensitivity. It is impossible to drink cold water in the summer without eating ice cream.
Typically, gum recession is to blame. Let's figure out what it is and what can and should be done to enjoy delicious ice cream without discomfort.
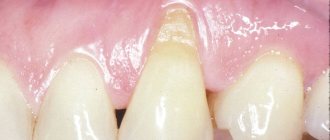
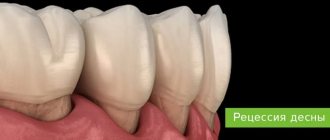
Gum recession is the exposure of the neck of the tooth, which is accompanied by aesthetic discomfort and increased sensitivity.
Why does gum recession occur?
Gum recession occurs for many reasons.
The main reasons for a recession are:
- Hygiene. Plaque and tartar that are not removed in a timely manner lead to “squeezing” of the gums and exposure of the neck of the tooth. Also, overly aggressive poor home hygiene leads to the same consequences.
- Pathological bite. When the tooth is positioned incorrectly, when the tooth is tilted in one direction or another, or when there is severe crowding, the periodontium (the complex of tissues surrounding and holding the tooth) is overloaded, which leads to a reduction in the gums and exposure of the tooth root.
Treatment of gum recession.
A very important point is that during recessions, not only gum loss occurs, but also loss of BONE TISSUE in the tooth area. Based on this, if you do not pay attention to this problem in a timely manner, it can lead to further mobility and loss of teeth.
Surgery is the main treatment for gum recession. Thanks to different techniques, the gingival contour is restored and the tooth root is closed.
If the cause of recession is associated with a pathological bite, then in such a situation it is necessary to first carry out orthodontic treatment and, after completion, resort to surgical methods.
In some cases, with proper orthodontics, the recession is closed without resorting to surgery.
Gum recession classification.
Depending on the severity of the current, recessions occur
- Mild form - the gums recede no more than 3mm.
- Medium shape - the gums drop by 3-5mm.
- Severe form – the gums recede by more than 5mm.
With regards to the coverage of the oral cavity, the pathology can have both local and generalized distribution.
Treatment of gum recession.
The main essence of the surgical technique is taking your own tissue (from the palate or the tubercle of the upper jaw) and suturing it in the defect area, thereby increasing the volume of soft tissue.
The relevance of this technique remains in both localized and generalized forms. Its advantage is considered to be effective restoration, since the materials are 100% identical. The only drawback of the manipulation is the feeling of slight discomfort for some time at the site of donor tissue collection. There are also cases when the flap does not take root in the transplanted area. As a rule, this happens due to poor hygiene and failure to follow the recommendations given by the doctor.
A favorable prognosis ensures timely seeking qualified help. Therefore, you should not put off your visit to the dentist, since the outcome of treatment depends on this.
How to stop gum recession!
- if there are dental diseases and other injuries to the oral cavity, then it is necessary to treat them in a timely manner - this applies to a greater extent to caries, which patients often bring to an advanced state (becomes complicated forms);
- regularly visit the dentist for a preventive examination: as you know, early diagnosis allows you to quickly eliminate the problem, without radical intervention, without waiting for serious health problems;
- monitor the condition of the gingival margin, avoiding injury and excessive bleeding;
- correct the bite in a timely manner;
- do not forget about strengthening tooth enamel with the help of remineralizing treatment;
- pay special attention to hygiene - effective brushing of teeth, choice of brush and toothpaste.
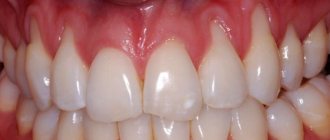
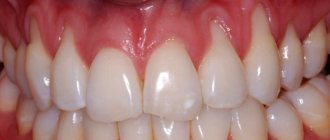
One of my works:
Preparation (closure of recession) was carried out before orthodontic treatment. After orthodontic treatment, cosmetic removal of remaining recessions is planned.