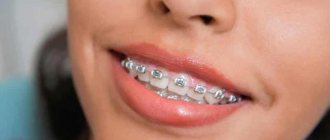
Human papillomavirus (HPV, HPV) belongs to the group of papillomaviruses and is one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases. This infection was already known in ancient Greece; Hippocrates himself studied one of the types of HPV - condylomas and gave them the name “genital warts”.
HPV is a virus that is transmitted only from person to person. Currently, about 600 types of HPV are known, some varieties can cause the growth of benign or malignant tumors.
HPV types:
- HPV, which manifests itself as warts (HPV 1-5): warts (calluses) located on the soles of the feet - HPV types 1-4;
- flat warts - HPV types 3, 10, 28, 49;
- common warts - HPV type 27.
1
Diagnosis of papillomavirus infection
2 Diagnosis of human papillomavirus infection
3 Diagnosis of human papillomavirus infection
HPV. Symptoms
The papilloma virus is constantly present in a person’s blood, but is activated only when immunity decreases. With weakened immunity, HPV begins to accumulate on the skin or mucous membrane and leads to the appearance of tumors.
At a young age, HPV manifests itself as warts that are located on the fingers, elbows, and knees. Then a papilloma grows on a person’s skin (a soft-to-the-touch round formation on a stalk, with the help of which the papilloma is attached to the skin). Most often, papillomas are located on the skin of the face, neck, armpits, and papillomas are also found on the labia.
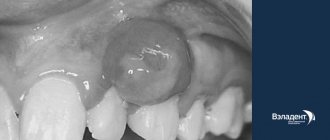
One of the most common manifestations of HPV is condyloma (uneven to the touch, soft, attached to the body with a stalk or a wide base, grows quite quickly, sometimes in a few hours).
Thus, warts, papillomas and condylomas are different signs of the same papillomavirus infection. Papilloma is a benign formation that can “show off” on a person’s face and body, not too pleasing to him aesthetically, but without causing much harm. Unlike papilloma formations, human condyloma tends to inflame and damage the skin and mucous membranes.
Condylomas
Condylomas are formations on the skin of the genitals, on the pubis, inner thighs, in the urethra, around the anus (anal condylomas) and inside the anus, having a lobed structure, flesh-pink in color, pedunculated or with a wide base, from a few millimeters to ten centimeters (eg, giant Buschke-Levenshtein condylomas).
Condylomas usually come in 2 types:
- condyloma lata, wide neoplasms with a wide base with which they attach to the skin, these neoplasms are considered a sign of secondary syphilis;
- genital warts, similar to soft pinkish bubbles with a thin stalk.
Condylomas acuminata
Genital warts are small flesh-colored formations that choose the genitals and anus as their location. In appearance, condylomas are sometimes confused with pearlescent papules, which are not a disease. Unlike pearlescent papules, genital warts are soft to the touch, attached to a thin stalk, and can be of different sizes.
Pointed papillomas are transmitted only sexually (through all types of sexual contact), therefore they belong to the group of sexually transmitted infections.
Causes of condyloma
There are various reasons for the appearance of condyloma, among which there are several main ones:
- having multiple sexual partners;
- long incubation period (time from infection to clinical manifestations);
- complex diagnostics;
- the presence of many types of PVI viruses;
- combination with other sexually transmitted infections;
- lack of protection effect using condoms from infection, etc.
1 Urethroscopy for diagnosing HPV
2 Urethroscopy for diagnosing HPV
3 Urethroscopy for diagnosing HPV
What operations are used?
Types of labial frenuloplasty:
- Frenulotomy;
- Frenulectomy;
- Frenuloplasty using the Limberg method;
- Fixation with sutures using the Dieffenbach method;
- Correction using laser.
The main type of treatment is surgical. First, the patient is given anesthesia. For children, before the injection, it is recommended to use gels with local anesthetics to numb the injection site. Thus, pain during basic anesthesia is reduced. After a couple of minutes, several injections are made into the frenulum area.
Next, a wedge-shaped incision is made and the attachment is excised. A deep incision is made on the side of the frenulum down to the bone, without touching the gum near the incisors. The resulting area is grabbed with tweezers and cut off. It is best to do this in the area of the papilla, since the level of aesthetics will be higher with this method.
At the end of the manipulation, the edges of the wound are connected to each other and sutures are applied. The patient is prescribed rinsing with antiseptic solutions and the use of healing drugs (for example, solcoseryl). You must return for examination and removal of sutures after 7-10 days.
If desired, the invasiveness of the operation can be reduced using a laser. Anesthesia is carried out using the same technique. The laser is set to pulse mode, power 1 W. Movements during tissue excision should be short and intermittent. Be sure to stretch the fabrics to achieve the best effect.
After the operation, there is no need to apply stitches, since the wound is slightly smaller in size. Instead, a special protective film is applied, which contains keratoplasty.
Recommendations after surgery include: using a toothbrush with soft bristles, rinsing with antiseptic solutions. You can also prescribe antiseptic tablets “Lizobakt” and apply “Solcoseryl” paste to the wound surface.
Contraindications to surgery
It is recommended to postpone lip frenuloplasty in the following cases:
- Diseases of the circulatory system;
- Oncological diseases;
- Stage of infection activity;
- Chronic pathologies that may affect the duration of recovery after surgery on the labial frenulum;
- Diseases of the oral mucosa.
Lip frenuloplasty is not a complicated operation and is easily tolerated even by the smallest children. Quick recovery eliminates any discomfort. After just a couple of days, the child recovers completely. And after 2 weeks, it becomes possible to correct the changes caused by the incorrectly growing frenulum.
HPV in women
HPV in women manifests itself not only as papillomas on the body, but also causes the development of cervical erosion , precancerous conditions, and cervical cancer . Condyloma in women is quite difficult to detect; it can exist in a woman’s body for a long time without any symptoms, and is discovered purely by chance at an appointment with a gynecologist. That’s why it’s so important to visit a specialist regularly, once every six months!
Symptoms of condyloma include:
- genital warts, which can appear on the genitals (condyloma on the labia, vaginal condyloma, cervical condyloma), in the oral cavity, on the skin of the anus (anal condyloma);
- disturbance in the maturation of epithelial cells (there are 3 stages of the process, the third stage is precancer);
- the development of a malignant formation from the epithelium lining the cervix.
Why changes may occur
This anomaly develops during the intrauterine development of the child. Its appearance can be provoked by:
- Intrauterine diseases of the fetus;
- Viral diseases of the mother at the very beginning and very end of pregnancy;
- Chronic diseases of the mother;
- Heredity.
Characteristic manifestations
The following manifestations are possible:
- Incorrect pronunciation of sounds;
- Violation of facial expressions;
- Difficulty brushing your teeth daily;
- Recession of gum level;
- Inflammatory gum diseases, such as gingivitis and periodontitis;
- Formation of space between the front incisors.
All this can be cured in childhood.
The first sign that is worth paying attention to is the formation of space between the front incisors during the change period. In case of physiological discrepancy, the teeth will come together after the eruption of the lateral ones. If not, then we can say that lip frenuloplasty is necessary.
In its normal state, the frenulum of the upper lip is located in the midline and is attached to the base of the interdental papilla.
If the attachment is abnormal, it will end below the base of the papilla or be completely woven into it. The cord itself may contain muscle fibers of the orbicularis oris muscle.
Development of the disease
HPV infection can occur through all types of sexual contact (vaginal, oral, rectal), while condoms are not a guarantee of protection, since condylomas can be localized on unprotected areas of the skin and the size of the virus is smaller than the pore size of condoms. In addition, the virus can also be transmitted to the baby during childbirth if the woman is a carrier of the virus.
The human papillomavirus (HPV) has a tropism for the skin and mucous membranes of the genitals, oral cavity, and anus. The amount of virus depends on the state of both the immune system as a whole and local immunity. The more productive the individual factors of the immune system are, the more actively the division of the virus is blocked, and the less of it is contained. That is, a person can be infected with HPV without having any external clinical symptoms.
Causes of papillomas
The cause of the appearance of papillomas in intimate places is the human papillomavirus (HPV), which circulates in the blood of almost every man and woman, starting from adolescence.
According to WHO, 80-90% of the population is infected with HPV. Most often, papillomas occur in young people who have a large number of sexual partners. Genital-anal papillomas are typical manifestations of human papillomavirus infection. In 90% of cases they are caused by the sixth and eleventh types of HPV.
In the daily life of every person, the following exposures increase the risk of infection:
- smoking;
- stress;
- using other people's hygiene products;
- visiting baths, saunas;
- shaking hands with carriers at the acute stage;
- decreased immunity.
Globally, the spread of HPV is influenced by many factors, including socioeconomic, medical, hygienic and geographic. The virus can stay in the body for years without showing itself. Its activation is provoked by a weakening of the protective forces of the immune system, which entails the appearance of papillomas in intimate places, both in women and men.
Pregnancy, hormonal imbalances, metabolic disorders, acute viral infections, long-term chronic diseases, poor nutrition and lack of sleep can also trigger the growth of papillomas in intimate places.
Clinical picture
Condylomata acuminata are formations of flesh-pink color, lobulated, ranging in size from 2 millimeters to ten centimeters, with exophytic growth, in which the apex of the genital condyloma is often wider than the base. Externally, the growths may resemble cauliflower or cockscomb.
The incubation period can range from 2-3 months to 2-3 years or more. The growth rate of formations varies, which is often associated with the state of local immunity, the presence of concomitant STIs, and sexual activity.
Complication after condylomas
Human condyloma is not just a harmless lobular growth on the genitals, it is a reservoir for the human papillomavirus. In recent years, cases with localization of genital warts in the oral cavity and throat have become more frequent, and there are condylomas on the lips.
The virus, accumulating in tissues, causes a change in the genome of epithelial cells of the skin or mucous membranes, which can lead to the development of severe complications. In men, HPV can lead to penile cancer . HPV in women threatens the development of cervical cancer . With these diseases, HPV is found in almost all patients.
Asymptomatic carriage of human papillomavirus (HPV)
In reality, many more people are infected with HPV than statistics show. Most of them simply do not know about it, since there are no symptoms of condyloma.
The virus may not manifest itself in any way for a long time, since the human immune system does not allow it to develop to the required extent. However, at any time, with a decrease in both general and local immunity, this can happen, and then papillomas and/or condylomas appear.
1 Laboratory diagnostics
2 Dermatoscopy
3 Extended colposcopy
Papilloma virus. Diagnostics:
- Consultation with a dermatovenerologist . Only a dermatovenerologist can make a diagnosis during an initial examination, assessing the clinical picture, conducting a test with acetic acid, and, if necessary, using the dermatoscopy method.
- Laboratory diagnostics. It is necessary to conduct a HPV test using the PCR method, which will allow you to estimate the amount of the virus, as well as determine which type of HPV is present in this case (they are divided into types with high and low risk of oncogenicity). A PCR test must also be performed on all sexual partners of a patient with genital warts. A positive test result in the absence of clinical manifestations of the disease means that treatment is necessary to suppress the development of the virus in the body.
- Urethroscopy is a study of the condition of the urethral mucosa using special endourethral endoscopes. Considering the increase in recent years in the number of patients with endourethral condylomas, this study is necessary for all patients, both men and women.
- Extended colposcopy - examination of the cervix using a colposcope and performing a test with acetic acid and the Schiller test. It is necessary for all women to undergo laboratory confirmation of papillomavirus infection, since the presence of flat condylomas on the cervix is possible.
- Immunogram is a study of the state of the immune system. This will allow for the most effective HPV therapy.
Treatment
To the question of how to treat papillomas in intimate places , modern medicine gives a clear answer: they need to be removed. Destruction of benign neoplasms can be carried out using various methods:
- electrocoagulation – exposure to high frequency current;
- cryodestruction - removal using cold treatment;
- laser removal – layer-by-layer treatment with laser radiation;
- chemical destruction - using special chemical solutions.
Classic surgical removal is also an option.
A specific scheme for how to completely and safely remove papillomas in intimate places is prescribed by a specialist in accordance with the localization of the process, the severity of the course, and concomitant diseases.
An important aspect of treating papillomas in intimate places is changing lifestyle and strengthening the immune system. An integrated approach avoids the emergence of new formations.