Improper and irregular oral care means there is a high probability of getting some kind of infection, which can lead to gum disease. Gum papilloma is a form of oral disease that requires immediate treatment. It may also occur on the lips, tongue, larynx, and throat. Papillomas can be quite painful, and their development threatens inflammatory processes in the oral cavity.
Causes of papilloma
This disease is caused by papilloma, a viral infection that has a long latent, that is, hidden, period. The time during which the disease does not manifest itself after the virus enters the body takes from two months to five years. This is the main danger of such a disease, because in such cases immediate intervention by a surgeon is required, and delay can cause death. The main reason for the formation of papilloma on the gums is a decrease in human immunity.
HPV prevention
The most effective method of preventing infections and complications caused by the human papillomavirus is vaccination. It is carried out before the onset of full puberty and before the start of sexual relations. The optimal age is from 9 to 11 years.
Other preventive measures are:
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle;
- balanced healthy diet;
- timely treatment of abrasions, scratches and other skin damage;
- informing children and adolescents about the dangers of smoking, since tobacco use increases the risk of oncogenic mutations of the virus;
- regular preventive examinations.
It is very important to monitor the child’s health and support immunity in accessible ways. Active physical activity, hardening, and outdoor games are encouraged, allowing the formation of an adequate immune response to environmental factors. It is advisable to abandon home self-medication and uncontrolled use of medications, since incorrect actions can reduce the natural defenses of the child’s body and lead to the activation of HPV.
Symptoms of the development of gum papilloma
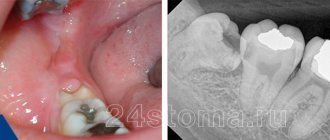
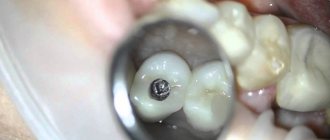
Papilloma is a benign tumor in the form of a characteristic growth. This formation can come in different sizes and shapes. Papilloma on the gum may not manifest itself in the form of pain or discomfort that bothers a person. This growth can be detected when visiting the dentist with complaints about teeth or gums, when the doctor conducts a professional examination of the entire oral cavity.
Papilloma is felt by the patient as a foreign body, which, depending on its size, creates a feeling of discomfort. It prevents the free position and movement of the tongue, which provokes distortion of the speech apparatus. With a significant increase in papilloma on the gum, it becomes difficult to chew food.
HPV symptoms
The papilloma virus infects the skin and mucous membranes, causing the proliferation of the epidermis and the appearance of pathological neoplasms:
- papillomas;
- warts;
- condylomas.
They look like small skin growths ranging in size from 1 to 5–8 mm, sometimes there are growths reaching 1–2 cm. Basically, such formations imitate healthy skin in color, but there are elements of dark brown and white shades.
The main places of distribution of papillomas:
- face and neck;
- external genitalia and groin area;
- the inner surface of the elbow and knee bends;
- soles of feet;
- fingers and skin around nails.
On the mucous membranes, elements can appear in the larynx, nasal passages; in girls, sometimes there are formations localized on the cervix.
Types of formations
There are several types of papillomas.
- Vulgar (common) warts. They are the most common type of neoplasm. They have a “leg”, rise noticeably above the surface of healthy skin, reaching a diameter of up to 1–2 cm. Sometimes hair grows from the central part of the wart. Such formations do not bother the child with pain or itching and appear on the arms, back or legs.
- Flat or juvenile papillomas. They look like small pigmented plaques of a fuzzy round shape, do not extend beyond the skin and form in groups. Such elements are characterized by a smooth surface and selectivity: they appear on the face, neck, legs, sometimes hands, but never in the armpits, genitals or skin folds. Occurs in children older than 5–6 years.
- Condylomas or genital papillomas. These elements resemble small papillae. They are pink in color and form in areas with thin skin: in the genital area, on the mucous membranes.
- Plantar warts. They affect the feet, occur under the big toes and visually resemble small round calluses.
Another variant of formations is filamentous warts or acrochords. They are similar to regular ones, but differ in elasticity and more compact sizes up to 5–6 mm. They prefer to appear under the mammary glands, in the groin, armpits, and are found on the neck and face.
The dangers of human papillomavirus
Some of the representatives of these microorganisms are harmless to humans, while others can provoke the growth of cancer cells. HPV is classified into two main types:
- Strains with high oncogenic risk. Such variants of the virus provoke the development of condylomas on the mucous membranes and in the genital area. Under unfavorable circumstances, they can cause an oncogenic mutation.
- Strains with low oncogenic risk. Viruses of this type cause warts, plantar lesions and juvenile papillomas. The risk of cell degeneration is minimal.
The greatest danger lies in girls: studies conducted in the USA have proven that 98% of cases of cervical cancer are associated with this virus. There is also a risk of developing cancer of the vagina, ovaries, anal canal, larynx, pharynx, and in boys, the genitals. Papillomas located in the anus and genital area require special attention.
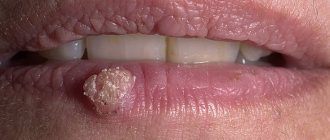
What do papillomas look like on the inside of the lip?
Photo of papillomas on the inside of the lip
As a rule, a person is not aware of the presence of the papilloma virus in the blood until visual evidence of this appears in the form of neoplasms on the skin or mucous membranes.
Papillomas on the lips of the mouth look like rough growths that resemble miniature papillae, round or oblong. They have a flat base or thin stem. In color they practically do not differ from healthy mucous membranes of the mouth and lips; they may have a whitish coating. The size usually does not exceed 12 mm.
Neoplasms can be isolated or form groups. In the latter case, they resemble a cockscomb or a broccoli floret.
Such growths do not cause pain unless they are injured. They are soft and mobile, elastic. However, if we are talking about pointed papillomas, then they are easy to injure. This can lead to an inflammatory process, suppuration, and the addition of an additional infection.
Papillomas on the inside of the lip are reactive and neoplastic. Reactive ones can grow due to regular irritation or injury, which is inevitably present in the oral cavity (food, teeth, sharp objects). Neoplastic papillomas are a collection of nodular growths that merge and form a large tumor.
Often, papillomas on the lip mucosa can form in children. The larger the tumor, the more problems it causes for babies. Thus, children cannot pronounce certain sounds due to discomfort in the oral cavity, the correct growth of molars may be disrupted, papillomas sometimes grow and affect the throat, tonsils, vocal cords, which poses a real threat to life.
Treatment methods for papillomas of the nasal cavity and nasopharynx
It is advisable to remove papillomas found in the nasal cavity and nasopharynx. Papillomas that have caused at least some concern must be removed.
Removal of papillomas
Removal of papillomas is best done using modern high-tech methods. This is radio wave removal or laser removal. This removal is easily tolerated by the patient. The technology ensures rapid healing, the risk of re-formation of papilloma is minimal.
Removal of papillomas of the nasal cavity with a laser or radio wave scalpel with Surgitr is carried out at JSC “Family Doctor”.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating
Classification of fibroids
Pathology is divided into several types according to criteria. This includes the density of the benign neoplasm, the nature of its origin, as well as the severity of clinical manifestations.
Dense fibroma
Characterized by a solid consistency. This is due to the fact that the contents are quite hard fibers of connective tissue. They include a small number of cores. Formations of this type are most often found on the gingival surfaces and palate.
Soft fibroma
The fibrous structures are thin and freely located, so their clusters are characterized by a high degree of softness. This type is most often observed on the tongue and the inside of both cheeks. Benign neoplasms of a mixed type, combining the signs of all the varieties listed above, can be found on the sublingual part and on the mucous membranes of the floor of the oral cavity. For example it could be:
- Fibrolipoma. It is hard to the touch because it contains fibrous fibers. It can be eliminated surgically, with laser, or radio waves.
- Fibrohemangioma. As a rule, it is provoked by infectious processes occurring in the child’s body. It is extremely rare in adults. It never degenerates into malignant tumors. Most often it is treated surgically, in some cases it can resolve on its own.
Fibroma from irritation
This is not a tumor formation in its usual form, but the result of reactive hyperplasia. Chronic pathology is characterized by the development of focal lesions, which are caused by systematic mechanical action and subsequent injury.
The most common cause is installed crowns, fillings, and dentures. In the latter case, the disease is called prosthetic granuloma. The orthopedic structure exerts continuous pressure on the alveolar process, leads to its resorption, moves forward and contributes to the formation of compactions, which are associated with the inflammatory process.
The risk group includes not only patients who have undergone prosthetics, but also people with untimely cured caries, in adulthood, with foreign objects in the oral cavity (for example, with piercings). Studies have shown that women are more prone to such hypertrophic transformations than men.
Symmetrical fibromas
Doctors diagnose such tumors in the area of the third molars in the areas between the gums and the roof of the mouth. The tumor is hard to the touch and resembles a bean in shape.
It should be noted that this type of compaction does not apply to true fibromatosis. These are just overgrown tissues in the gingival membranes, accompanied by the process of scarring and other changes of a similar nature.
Lobular fibroma
It occurs as a result of reactive hyperplasia with systematic trauma to delicate sensory fibers with prostheses or other orthopedic structures. The main distinguishing feature of such formations is their rough, textured surface. When palpated, tubercles are felt.
Fibrous epulis
This is a dense growth of pinkish tissue that does not cause pain or other discomfort. The edges are often hyperemic, have clear boundaries and irregular shape. The base is quite wide.
The vestibular part of the gums is usually affected. There are cases of neoplasms occurring in the interdental spaces in the form of a saddle with spread to the intraoral surface.
Quite often, a dental unit located in a pathological area has a poorly fitted metal crown, extensive carious lesions, or a prosthetic clasp. It is these structures that are the provoking factor in the occurrence of a chronic inflammatory process with the formation of granules, which over time are transformed into mature connective fibrous fibers.
In dentistry, there are also angiomatous epulis. They are brighter in color, somewhat softer to the touch and bleed. In this case, blood appears not only at those moments when the surface is affected mechanically, but regardless of the presence or absence of a traumatic factor. When conducting diagnostic studies, many vascular branches are detected in the pathological area.
Laryngeal papilloma
04.06.2021
Most often, papillomas appear in older people and young children, but by the beginning of puberty they tend to disappear. Laryngeal papilloma is a dangerous infectious disease caused by the HPV virus. Single or papillary projections on the vocal cords resemble curly cauliflower in appearance. The danger of the neoplasm is that, despite the fact that papilloma is benign, with complications it can develop into a malignant tumor and block breathing at any time.
Recommendations for the presence of papillomas on the larynx
You cannot remove papillomas on your own. This may lead to the beginning of a new mechanism for their degeneration inside the body, since on our own we cannot find out what the nature of the neoplasms are. The presence of papillomas and warts is the first sign of a malignant tumor !
Symptoms of laryngeal papilloma
At first, a person may not even suspect that he has contracted such a disease, because the disease is hidden and does not manifest itself for a long time. Quite striking symptoms of this disease are hoarseness, leading to loss of voice, roughness and rigidity of the vocal cords, gradual difficulty breathing, and as the tumor increases, it can turn into suffocation, difficult inhalation or exhalation, expectoration of blood , shortness of breath, long cough at night, imperceptible pale or transparent growths on the mucous membrane, small compactions.
Routes of infection
Since laryngeal papilloma is a disease that has signs of an internal nature, you can become infected in three ways, namely:
- During sexual intercourse, petting or oral sex during unprotected intercourse, secretory glands are released. A sick person may not suspect that he is carrying the HPV virus (genital);
- with a handshake, salivation, kiss (contact or airborne);
- During childbirth , the papilloma virus (genital) can be transmitted to the baby in the womb.
Factors influencing the further development of the disease
Without exposure to negative factors, HPV lives in the body from 10 months to 10 years. The following factors can provoke the development of a neoplasm in an infected person:
- frequent allergies ;
- surgery or injury to the larynx;
- poor resistance to stress;
- chronic ENT infections caused by microorganisms or viruses;
- hormonal disbalance;
- bad ecology;
- presence of serious infectious diseases;
- heredity;
- presence of bad habits;
- inappropriate nutrition;
- avitaminosis;
- overweight or underweight.
Laryngeal papilloma can form not only due to the above symptoms, but also due to the presence of parasitic cells inside the body. Why exactly do parasites become the source of many fatal diseases? If warts, papillomas, a large number of moles, pimples , bruises and redness appear on the body, this may be evidence that there are parasites in the body and this person is susceptible to developing dangerous diseases.
Treatment of papilloma on the larynx
The primary and most successful treatment option is surgical removal . But today there are 2 ways to treat the disease: progressive and surgical . They work best together. The progressive technique is used in the early stages and represents the prevention of the body, restoration of the respiratory tract and irradiation of the growth after the introduction of the drug the blood Immunological and antiviral drugs are also prescribed. If the conservative method does not help, then mini-surgeries using the latest endoscopic technologies are used. They are: dissection of high-frequency radio waves, removal with ultrasound , supply of ionized gas to the tissue and complete drying of the papilloma, liquid nitrogen at low temperatures, exposure to current using an electrode. After a successful operation , antibiotics, immunological and vitamin medications are prescribed.
It is important to remember that at the first symptoms you need to urgently visit a doctor , since the disease is secretive and difficult to recognize immediately. Laryngeal papilloma is a benign tumor and the chance of a full recovery is high, the main thing is to consult a doctor and carry out correct and effective treatment.
Published in Otorhinolaryngology, Surgery Premium Clinic
Symptoms of papillomas of the nasal cavity and nasopharynx
If papillomas are located inside the nasal passages, the disease may manifest itself with the following symptoms:
Stuffy nose
Papillomas can grow, and at some point a person begins to feel nasal congestion.
More about the symptom
Postnasal drip syndrome
Papillomas can cause postnasal drip syndrome. The nasal cavities contain glands that produce mucus. If a person does not have a runny nose, little mucus is produced. It serves to moisturize the nasal passages and binds dust and bacteria that have entered there. Sometimes a person sneezes or blows his nose, thereby removing mucus from the nose. Papillomas can reach significant sizes, blocking the mucus path. In this case, mucus begins to accumulate and then flow down the nasopharynx (this is postnasal drip syndrome). As a rule, an accumulation of mucus in the throat is felt in the morning, after a night's sleep.
Nosebleeds
When mechanically damaged, papillomas can cause nosebleeds.
Rehabilitation period after excision of papilloma in the oral cavity
After surgery for papilloma with any of the destructive methods, a recovery period follows, which includes drug treatment and compliance with a number of recommendations of the attending physician (treatment of the oral cavity with medications, proper nutrition, etc.).
As a rule, drug therapy after cauterization of papilloma includes taking antiviral and immunostimulating drugs, as well as vitamins. In the presence of infectious diseases that can provoke an exacerbation of HPV, appropriate medications are prescribed to combat this pathology. Complex treatment will block the virus, speed up the healing of mucous membranes and prevent infection of the postoperative wound.
You can remove papilloma in the oral cavity using one of the destructive methods in our specialized medical center, where experienced and highly qualified specialists work. After the necessary examination, taking into account the patient’s wishes and medical indications, the doctor will select the most appropriate tactics to combat warts. An individual approach to the patient, high professionalism of doctors and the use of advanced equipment will ensure successful and safe treatment of papillomas in the oral cavity.
Attention!
This article is posted for informational purposes only and under no circumstances constitutes scientific material or medical advice and should not serve as a substitute for an in-person consultation with a professional physician.
For diagnostics, diagnosis and treatment, contact qualified doctors! Number of reads: 6328 Date of publication: 08/06/2018
Dermatologists - search service and appointment with dermatologists in Moscow