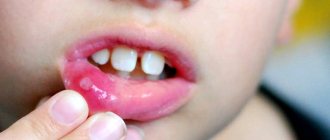
During pregnancy, the expectant mother should take care not only of herself, but also of the child, because the health of the child’s teeth can be influenced even before birth.
While waiting for the baby, the expectant mother should eat a balanced diet in order to receive a sufficient amount of vitamins and microelements, and after the birth of the child, breastfeed.
It strengthens the baby's immunity and helps to develop properly. But what to do if, after the appearance of the first teeth, you notice that the enamel on children’s teeth has begun to wear off? The structure of tooth enamel contains calcium hydroxyapatite. Children have a certain supply of calcium from birth, but if it is not enough, the tooth enamel begins to deteriorate.
Tooth wear in children: causes
A child’s teeth wear out for the following reasons:
- congenital abnormal bite;
- bruxism (the child often grinds his teeth in his sleep);
- sensitive and fragile tooth enamel due to certain diseases (hypoplasia, etc.);
- genetic predisposition.
Strong abrasion of tooth enamel is caused by straight and deep bites, leading to accelerated exposure of dentin. One of the reasons for the appearance of malocclusion is disturbances in the development of the jaws, which increases the load on the teeth.
A child’s teeth can also wear out due to systemic diseases that reduce the resistance of body tissues: endocrine disorders, diseases of the central nervous system, etc.
Tooth wear can go through several stages.
Restoration of worn teeth
Restorative treatment is carried out while preserving at least half of the hard tissues of the tooth. The technique takes place in several stages:
- Preparation. Necessary to identify the causes of diseases and their elimination or minimization, as well as the protection of remaining teeth. During preparation, an occlusal splint is made and installed if the patient suffers from bruxism. If necessary, the doctor prescribes consultations with various specialists, explains the rules of oral hygiene, and sanitizes foci of infection.
- Evaluation of the preparatory stage. After some time, the patient comes for an appointment, and the doctor assesses the condition of the teeth, checks whether the patient followed all the recommendations correctly, and discusses the upcoming treatment with him.
- Restoration. It is carried out in a certain order. First, the teeth are prepared, then the teeth on the upper jaw are restored, and only then on the lower jaw. Using a table of anthropometric data for each tooth, the doctor gives the patient's new teeth a certain length and shape.
- Observation. After successful treatment, the doctor observes the result for some time. In the first year, the patient should come for an appointment once a month, then less and less, but not less than once every 12 months. If any defects are identified, they are repaired or other treatment methods are applied.
This type of treatment, like any other, requires the patient to strictly adhere to all recommendations, give up bad habits, eat right, regular examinations by a specialist, and carefully observe hygiene skills.
Degrees of tooth abrasion
- Stage I – the enamel of the cutting edges of the child’s incisors and canines and the upper part of the chewing cusps and molars is erased, the dentin is partially affected.
- Stage II – severe abrasion of the chewing tubercles with exposure of dentin tissue.
- Stage III – the height of the tooth crown is reduced to 2/3 of the normal size during wear.
- Stage IV – abrasion of the tooth to the level of the neck. The crown of the tooth is almost completely erased.
If 1 – 2 teeth of a child are worn out, then this is local abrasion; if several teeth or the entire dentition are affected, then this is generalized abrasion.
Increased tooth wear - symptoms and treatment
Increased (pathological) tooth abrasion is an intense loss of hard tissues, which can lead to almost complete wear of the crown part of the teeth. It can be caused by congenital characteristics, somatic diseases, bad habits, abnormalities in the position of teeth, incorrect dental treatment and other factors. At the initial stage, the changes are almost unnoticeable, but as the disease progresses, the patient himself may notice a decrease in the length of the crowns of the teeth and a change in the shape of the chewing surfaces.
According to Alekseev, the author of scientific works and the book “Pathological abrasion of teeth,” increased abrasion of incisors, molars and premolars is detected in 4% of people aged 25–30 years. At the age of 30–40 years, almost 23% of patients seek orthopedic help due to increased tooth wear, at 40–45 years old - 35%, at 50–60 years old - 26%, after 60 years this figure decreases to 12% [2][ 13].
Physiological abrasion of the cusps of premolars and molars, the cutting surface of the front teeth in the process of chewing food is a natural process that is observed in every person. With age, the enamel wears off more intensively, and due to the natural mobility of teeth, facets are formed on the chewing surfaces, which are manifested by a decrease in the volume of hard tissues. The speed of this process depends on the strength of the enamel, bite and eating habits. Age-related changes in the temporomandibular joint and periodontal tissue can also cause tooth wear. Reducing the size of crowns serves as a compensatory reaction, allowing, under conditions of slowing metabolic processes, to maintain hard tissues in a normal state [1].
Causes of increased (pathological) tooth wear
The reasons can be general (pathological habits, work hazards, genetic abnormalities, chronic diseases) and local (bite pathology, tooth loss, bruxism, diet high in acids).
In some patients, pathological tooth wear is caused by harmful or professional habits: gnawing seeds or nuts, holding tools in the teeth, biting off threads. The characteristics of the enamel in these people correspond to the norm, but excess load leads to premature wear of the dental crowns. Even the strongest teeth need to be protected at a young age.
Other causes of pathological abrasion of enamel:
- malocclusion;
- bruxism (teeth grinding);
- loss of several teeth;
- wearing incorrectly made dentures, the shape of which does not correspond to the anatomical features of the patient’s oral cavity and does not ensure normal contact between the chewing surfaces;
- constant exposure of teeth to sand, soot and other solid particles;
- fluorosis (destruction of enamel associated with excess fluoride);
- amelogenesis imperfecta (hereditary disorder of the formation of tooth enamel);
- acid necrosis (destruction of enamel in patients who excessively consume acidic foods, as well as those in contact with acids in hazardous industries, as a rule, can be combined with enamel erosion);
- thyroid diseases;
- pathology of the pituitary gland;
- improper brushing of teeth [3].
Various malocclusions lead to a certain pattern of tooth wear:
- with a straight bite, the chewing surface of the molars and the cutting part of the incisors are intensively worn away;
- with a deep bite, the tissue of the front teeth decreases especially quickly, the lateral movements of the jaw in such people are limited, therefore the molars and premolars retain masticatory cusps even in adulthood;
- with an oblique bite or an anomaly in the position of part of the teeth, the process occurs asymmetrically with the abrasion of individual teeth.
When teeth are lost, the load during chewing is distributed unevenly and the remaining teeth take it upon themselves. This leads to their premature wear. If a person chews food on one side of the jaw due to dental disease, the wear of the crowns will be asymmetrical.
Another reason for premature enamel wear is improper installation of removable dentures . If the teeth, which are the supporting points for clasps (hooks for fixing the prosthesis), are not protected by artificial crowns, they will quickly wear out.
Increased tooth wear is observed in representatives of some professions:
- in persons engaged in physical labor, the pathology is associated with strong clenching of the jaws when lifting heavy objects;
- among foundry workers - with dust and gas contamination in the air;
- Chemical industry workers who come into contact with acids develop acid necrosis of the enamel.
Abnormal abrasion of enamel may be associated with diseases such as thyrotoxicosis , chronic cholecystitis, urolithiasis , and endemic fluorosis. They lead to the fact that the enamel loses its natural strength and quickly wears off even with minor mechanical stress. Diseases of the nervous system , one of the symptoms of which is bruxism, also have a negative impact
Pathological abrasion can be caused by hereditary anomalies, one of them is amelogenesis imperfecta . With this pathology, the quantity and mineralization of tooth enamel is disrupted and its density decreases. Accordingly, it will wear off faster than in people with healthy teeth [5].
With pathological tooth wear, it is first of all important to identify the cause; some patients need not only dental care, but also treatment of the underlying disease or lifestyle changes.
Pathological abrasion: consequences
Pathological abrasion – rapid reduction of enamel and dentin, teeth become shorter, sensitivity increases. How to understand that tooth wear has become pathological, and what could be the consequences?
- The surface of the child’s teeth becomes distorted and destroyed, and the edges of the tooth enamel become sharp. This can injure the tongue, as well as the delicate mucous membrane of the cheeks and lips.
- The height of the teeth changes (if the disease progresses), which leads to malocclusion and deformation of the lower part of the child’s face.
- The position of the temporomandibular joint may change, and this can injure the jaw.
- The sensitivity of tooth enamel increases.
As a result, pathological abrasion of teeth occurs
The pathogenesis of the disease involves several factors, both external and internal.
| Endogenous factors | Exogenous factors |
| Metabolic disease. Gastrointestinal diseases. Pathology of the endocrine system. Bruxism (teeth grinding). | Patient's nutrition. Nature of working conditions. Incorrect prosthetics. |
The greatest influence on the abrasion process itself is exerted by occlusal forces, which have the following characteristics:
- The amount of chewing force. It is determined by the strength of the masticatory muscles, which can range from 80 to 400 kg. It is necessary to take into account that teeth are under stress not only when chewing food, but also when swallowing, and a person performs several thousand swallowing movements per day.
- Duration. During the day, the occlusal surfaces of the teeth come into contact with each other for half an hour, but with pathology, this figure can increase significantly.
- Application point and direction. The occlusal force is directed at right angles to the chewing surface of the tooth. Normally, the contact area is several square millimeters, but with pathology it can increase several tens of times, which leads to greater efforts when chewing.
In the presence of harmful production factors, bruxism, fluorosis and other reasons mentioned above, all characteristics of occlusal forces change for the worse, which leads to tooth abrasion.
What to do if your child's teeth are worn out
Treatment for tooth wear is developed individually. At the appointment, the pediatric dentist analyzes the causes of the pathology, determines the stage of erasure, the nature of the disease and the characteristics of the development of the child’s body.
Loose teeth - reasons
The main provoking factors of pathological mobility of dental units can be:
- Inflammatory and non-inflammatory gum diseases - gingivitis, periodontitis, periodontal disease. One of the most common causes of mobility.
- Chronic diseases: psoriasis, diabetes, thyroid dysfunction, some types of metabolic disorders, arthritis, osteoporosis.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the immune system.
- Bite pathologies.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Hypovitaminosis and hormonal changes.
- Taking certain medications.
- Advanced root caries and other types of “dental” diseases (periodontitis, cyst, granuloma, etc.).
- Injuries, bruxism, unhealthy diet, bad habits.
In addition, in cases where the front teeth are loose, we can talk about non-compliance with hygiene standards - in the absence of proper care, hard plaque accumulates in the root part of the teeth, which gradually provokes inflammation of the gums and disruption of the dentogingival bonds.
If you have a problem similar to that described in this article, be sure to contact our specialists. Don't diagnose yourself!
Why you should call us now:
- We will answer all your questions in 3 minutes
- Free consultation
- The average work experience of doctors is 12 years
- Convenient location of clinics
Single contact phone number: +7
Make an appointment
Having noticed the high mobility of their own dental units, many people are interested: if a tooth is loose, can it be saved? It all depends on the cause of mobility, the degree of oral health and the general condition of the body. In any case, timely visit to the dentist significantly increases the chances of preventing edentia.
If there is nothing left of the tooth
It happens that people put off visiting a doctor for so long that only emptiness remains in place of the crumbling unit. If the roots are preserved, a crown can be installed. If they are absent or are in an unsatisfactory condition for prosthetics, the patient is offered implantation. This is a dental operation during which a titanium pin is implanted into the jaw bone. After its healing, an abutment and an artificial crown are installed on top.
If the client refuses implantation, a dental bridge can be installed. But then you will have to depulp and file the healthy teeth located on both sides of the empty space.
Treat crumbling teeth on time, then you won’t have to spend a lot of time, money and effort on restoring them. At the first symptoms of a destructive process, contact your dentist.
What to do if your teeth start to crumble badly
The first thing you need to do is make an appointment with a dentist and come to the appointment. The doctor will conduct an in-person examination and determine the cause of the pathology. Further actions will directly depend on the provoking factor.
If it's all about caries, then it will be filled. To do this, the hole will be closed with modern filling material , which will qualitatively strengthen the walls of the crown. The patient will be told how to properly care for their oral cavity to avoid illness in the future.
If the defect occurs due to mineral deficiency, remineralization is carried out. During the procedure, the crown is treated with a special composition enriched with calcium, phosphorus and other useful compounds. Afterwards, a composite or ceramic veneer is installed to hide the chip.
If you have fluorosis, you should stop using water with a high fluoride content. Existing irregularities can be corrected using dental crowns or inlays. For minor damage, veneers and lumineers will help.