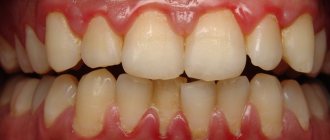
Tooth roots inevitably begin to become exposed in old age - this process is completely natural and is a reaction to the aging of the body. But old age is far from the only reason for this phenomenon, which spoils a beautiful smile and can lead to other serious illnesses in the future. Root exposure can occur at any age due to disease or pathology.
This article will talk about what to do in a situation where the gum has noticeably risen above the tooth, and you will also find answers to why this happens and what the consequences of refusing treatment may be.
For what reasons are the roots of teeth exposed?
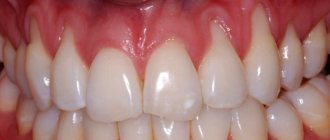
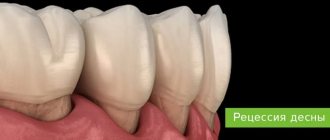
The phenomenon of exposed teeth in dentistry has a name - gum recession, but usually recession is only a symptom behind which another dental disease is hidden. Most often, it is the lower row of teeth that suffers from recession, since it bears the brunt of the load.
A common disease that causes gums to become exposed is periodontitis, during which inflammatory processes begin to occur in the periodontal tissues; if such a disease is started, it can become chronic.
Typically, periodontitis is a consequence of poor oral hygiene. Plaque and food debris that accumulate between the teeth and on the surface gradually enter the soft tissues and provoke inflammatory processes.
Inflammation significantly weakens the gums, making them weak and unable to maintain their shape. Then they descend and expose the neck of the teeth, which can lead to their loosening and loss. Periodontitis can also be caused by natural pathology.
The second most common cause of exposed roots is periodontal disease, which, unlike periodontitis, is not an inflammatory disease. During such a disease, the gums decrease in size due to atrophy of soft tissues, or disruption of metabolic processes in them.
Other reasons that cause denudation of teeth include:
- Improper brushing of teeth, namely too much pressure of the brush on the gums.
- Tooth decay close to the gums due to caries.
- Malocclusion, short frenulum of the tongue and other pathologies of the oral cavity.
- Malfunctions of the thyroid gland and gastrointestinal tract.
- Caries that has penetrated deep into the dental tissue often causes the gums to detach from the tooth.
To eliminate the defect, it is necessary to find out the cause of its occurrence. If the disease is allowed to progress, the gums will eventually recede to the point where the tooth can fall out. Considering that most of the causes of such a defect are not local, but affect the entire oral cavity, refusal of treatment can lead to the loss of all affected teeth.
Associated symptoms
The tooth consists of three parts:
- Crown.
- Neck.
- Root.
In a healthy state, only the crown should be visible, the neck should be covered by the gum, and the root should be located in the alveolus (a special recess for the root). When the process of recession begins, the neck of the tooth is exposed, but that’s not all; along with this problem, the following symptoms usually appear:
- High tooth sensitivity when in contact with extremely cold, hot, sweet, salty and sour foods, because the tooth exposed the sensitive part of the neck, on which there is almost no protective enamel.
- Noticeable darkening of the enamel spoils the appearance; the situation is also aggravated when the neck of the tooth, which is yellow, is exposed.
- Visually, the tooth appears longer.
- Feeling of discomfort in the gums. When you try to press on it with your tongue, it does not fit tightly to the tooth, but moves away from it.
- When brushing your teeth, your gums become very swollen, painful and red.
- Wide interdental gaps appear at the base of the tooth.
It should be noted that any of the above symptoms are more acutely felt in adolescence and middle age, while older people may not notice or feel that anything is wrong. Therein lies a great danger, because adult patients most often come when the situation has reached a critical point and it is almost impossible to save the tooth.
Why you shouldn’t ignore the problem - what complications this can lead to
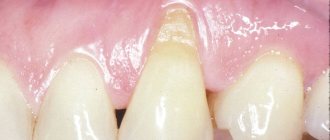
First of all, the neck of the tooth is exposed, then always after some time the root is exposed; the disease simply cannot remain at one stage. Due to the weakening of the tissue, the gums become smaller and can no longer cope with the task of holding the tooth, which is why it becomes loose at the slightest pressure.
Before the tooth falls out, deformation of the entire dentition will occur and with a high probability a tooth fracture may occur at the point of contact between the neck and crown, due to the low density of the enamel in this area.
Another almost inevitable consequence of failure to treat gum recession is a wedge-shaped defect, as a result of which the edge of the gum that is adjacent to the tooth takes on a V-shape, which immediately catches the eye and spoils the aesthetic appearance. To prevent complications, it is necessary to consult a dentist in a timely manner, find out the reason why gum recession occurs and eliminate it as soon as possible.
Symptoms characteristic of periodontal disease and periodontitis
Unfortunately, periodontitis tends to develop slowly.
. At the initial stage, periodontitis does not cause pain or other sensations. The disease develops asymptomatically, gradually destroying the periodontium. Therefore, patients, as a rule, are in no hurry to see a doctor. Periodontitis can manifest itself differently depending on the stage, and often begins with bleeding gums. At this stage, the process is still reversible; the periodontal ligament, which surrounds the tooth and connects it with its neighbors, is not affected, so that the chewing pressure is distributed evenly throughout the entire dentition and there is no overload in the periodontal tissues.
Without treatment, the process penetrates deeper
and destroys the periodontal ligament, a periodontal pocket appears, in which, in turn, plaque and stone are deposited and stimulates further progression of the process. Periodontal tissues (surrounding the tooth - gums, bone tissue) are destroyed, and the tooth begins to wobble, losing bone support in the jaw. At this stage, a change in the position of the teeth, their pathological mobility, the appearance of gaps between them, impaired chewing function, and traumatic occlusion may also be observed.
The initial period of the disease is characterized by itching, throbbing in the gums, mobility of teeth, discomfort when chewing, and bad breath. As the process progresses, the supporting apparatus of the tooth becomes looser, tooth mobility increases, the necks of the teeth become exposed and become more sensitive. The lack of adequate treatment measures at this stage leads to the loss of practically healthy teeth.
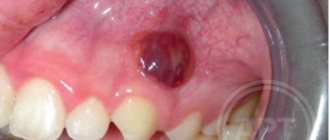
During an exacerbation, sharp throbbing pain, fever, malaise and weakness occur. There is marked redness and swelling of the gums, and pus is released from the periodontal pocket. Treatment is complex and aimed at stabilizing the pathological process.
Treatment Options for Gum Recession
After finding out the main reason that caused such an unpleasant phenomenon, treatment can begin. When treating gum recession, the primary goal is to preserve the tooth and prevent future weakening of the gum tissue.
Receding gums are always a consequence of some disease or pathological process. As for treating the recession symptom, modern medicine can offer several ways to eliminate such an unpleasant defect:
- Professional oral hygiene against plaque and deposits . In this type of cleaning, you need to focus on deposits in the gum pockets. Regularly carrying out such a procedure under the supervision of a dentist is the best way to prevent gum peeling and many other dental diseases.
- Treatment using the Vector device . This device takes teeth cleaning to a new level; the advanced German Vector technology perfectly helps to cope with the removal of tartar and plaque. The device releases ultrasonic waves that are safe for the body, but prevent harmful infusion on deposits in the oral cavity.
- Gum curettage is a procedure that helps to effectively get rid of deposits and plaque, and also, if necessary, normalize the condition of bone tissue. There are 2 options for carrying out this procedure. The first option, “closed curettage,” is recommended for patients whose periodontal pockets are no more than 5 mm deep and inflammatory processes have not yet penetrated deep into the bone. The second option is “open curettage” for pockets with a depth of more than 5 mm. In such a situation, the doctor makes a small incision in the gum, thereby peeling off a small section of it to gain access to the bone tissue and tooth root. Then the doctor carries out an antiseptic treatment; if there is bone atrophy, bone chips are planted to restore its normal state.
- Plasmolifting. This type of lifting involves the direct introduction of special autoplasma into problem areas, which is previously isolated from the patient’s blood. Before the procedure, you need to donate about 15 ml of blood, from which the doctor will separate plasma. Such plasma contains an increased number of platelets and protein. Then this liquid enters the gums through an injection and promotes its restoration.
- Vestibullasty of the gums. This method involves a surgical intervention during which a piece of healthy gum is transplanted to the site of the damaged one. After such treatment, long-term drug therapy is prescribed.
- Treatment with vitamins. In the early stages of gum recession, gum recession can be treated by taking a special set of vitamins and professional cleaning. In such a situation, the patient is usually prescribed vitamins A, D, B9, C. It is their lack that weakens the gums.
In the case when the gum recession is too advanced and the tooth is already clearly loose, it is necessary to undergo a splinting procedure (combining the moving parts of a row into a new group and fixing it in the desired position). For fixation, a thin aramid thread is usually used, which is attached to the back of the row, or a prosthesis with claw-shaped branches is installed under each loose tooth.
It is worth noting that sometimes, when the gums have almost exposed the root, the tooth is very loose and is in poor condition, the best solution is to remove it. In the future, an implant can be installed in its place, which will be indistinguishable from a real tooth. Such an implant is the only option to preserve a beautiful smile and jaw functionality.
Causes of periodontal disease and periodontitis
The causes of periodontal disease are completely unknown. Hereditary predisposition plays a certain role. Local factors, such as the impact of microorganisms on the periodontium, can only aggravate the process.
Periodontitis can be a consequence of the action of pathogenic microorganisms that accumulate in dental plaque and tartar, tooth trauma, caries, poorly performed dental prosthetics or restoration, and violations of the integrity of the tooth. Significantly increase the likelihood of developing periodontitis, poor oral hygiene, crooked teeth and malocclusion, dietary habits, and a decrease in the general immune reactivity of the patient’s body.
The main cause of gum disease is bacterial plaque.
which is a sticky, colorless film that constantly forms on the teeth. If plaque is not removed, it hardens and forms a rough, porous build-up called tartar. As the disease progresses, toxins can lead to the destruction of the tissues that support teeth. A space is formed between the tooth and the gum - a periodontal pocket, which is filled with plaque. The bone that supports the teeth is subject to constant destruction. Periodontitis can develop after inflammation of gums and gingivitis.
Treatment with traditional medicine
The practical use of traditional medicine advice is allowed only as an additional therapy and only after consultation with a doctor. Here are some proven and effective methods:
- Regular rinsing is necessary to clean and strengthen teeth and gums. The best tincture for rinsing would be a decoction of St. John's wort. To prepare it, you need to grind the dry plant and add water to it in a ratio of 1 to 4, then bring to a boil and leave to infuse for 1 hour. You need to rinse your mouth 2 times a day after basic hygiene procedures.
- Compresses. Using compresses will help reduce pain and start tissue repair processes. An effective compress can be made by mixing sea buckthorn oil and olive oil in a ratio of 1 to 1. Then dip a cotton swab into the resulting solution and apply to the problem area for 5 minutes. After which you need to rinse your mouth with water. This procedure will relieve pain.
- Massage. A good massage improves metabolic processes in the gum tissue, which promotes rapid healing. Before the procedure, you need to wash your hands, and then lightly massage the gums with your fingertips for 1-2 minutes.
Treatment without qualified medical advice may lead to a worsening of the condition. Therefore, when the first signs of recession appear, you should first see a dentist and then take treatment measures.
Prevention measures
It is impossible to completely guarantee protection against the gradual separation of the gums from the tooth, because this will happen naturally with age, but you can slow down this process. Experts in the field of periodontology and dentistry have identified several basic recommendations, following which you can minimize the risk of gum recession:
- The first thing you need to do is systematically visit the dentist 2-3 times a year as a preventative measure.
- You need to give up bad habits or reduce them to a minimum.
- Enrich your daily diet with fresh fruits and vegetables.
- Perform hygiene procedures at least 2 times a day, in the morning and before bed. If desired, you can supplement brushing with dental floss.
- If you suspect or have any symptoms of any oral disease, consult a doctor immediately.
Regular dental checkups are something that most people neglect. Therefore, you need to develop a habit that will help keep your teeth healthy.
It is important to know! If your gums are your weak spot, you need to brush your teeth very gently, using a soft toothbrush and mouthwash. A hard brush can harm the gums and cause them to separate over time.
Gum recession is not just an aesthetic problem. This phenomenon signals the presence of a more serious disease or ongoing pathological processes in the soft tissues of the gums. Any deviation from the normal state should alert you and cause a visit to the dentist.
The roots of the teeth are exposed - what to do and how to treat them
Open and closed curettage of periodontal pockets
Treatment of generalized moderate and severe periodontitis
Laser gingivotomy - surgical treatment of complex forms of periodontitis
Laser gingivectomy in the area of one tooth
Splinting teeth for periodontitis with fiberglass and tape
What can a doctor do?
Only the dentist and hygienist with a simple examination
can determine the presence or absence of periodontal disease. The essence of the study is to measure the periodontal pocket (for periodontitis) using a special probe and an x-ray. This method allows the doctor to quickly and painlessly assess the condition of your gums, propose a treatment plan to prevent further development of the disease, and develop a special self-hygiene regimen that will suit your specific situation.