In order for your teeth to be not only beautiful, but also healthy, you need to take care of them from early childhood. However, oral hygiene alone is not enough to prevent the development of various problems such as tooth decay or plaque. At least once every six months, the baby should be taken to the dental office for examination and preventive procedures. But how can this be done if he panics at the mention of doctors and clinics? In the article we tell you what to do, how to teach a child not to be afraid of the dentist and force him to treat his teeth, we share useful life hacks, how to ensure the right psychological mood.
Where does fear come from?
Dentophobia is the name given to the fear of treatment at the dentist. If it is present, a person seeks the help of a specialist only in extreme cases, when there is no longer any possibility of enduring the pain. Children also suffer from it. At a young age, fear is usually caused by already acquired negative experiences. At the same time, it is not the dentists themselves who may frighten the baby, but the “white coats” in general. If you do not overcome this phobia in childhood, it will spread into adulthood, and then it will be almost impossible to get rid of it.
If you don’t know how to force your child to go to the dentist, but he refuses to have his teeth treated, first of all you need to find out the reason for what is happening. Most often, fear occurs for the following reasons:
- the baby sees a doctor for the first time or experiences severe pain;
- there are character traits - suspiciousness, shyness, indecisiveness;
- Previously, the baby had already been forcibly held in a dental chair for some procedures, a negative experience was ingrained in his head;
- the parent could not explain why it is important to go to the dentist, why all these manipulations are needed.
Note that young children almost always react negatively to examination of the oral cavity. This seems something unnatural, and that is why it is perceived so hostile. The general goal of parents is to convince the baby that there is nothing wrong with what is happening. On the contrary, it will help him be healthy and beautiful.
In addition, it is important to combat the fear of “white coats.” The baby should not be afraid of doctors, because in any case he will have to contact them. Not necessarily for treatment - preventive examinations in kindergarten and school have not been canceled.
How to determine caries in a child?
Unfortunately, caries does not depend on age and can appear even in very young one-year-old children immediately after the eruption of their first teeth.
Dentists distinguish 4 stages of caries, depending on the depth of damage to the enamel, each of which has its own specific symptoms:
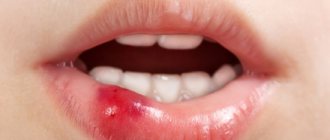
- Stain stage
- destruction affected only the upper layers of enamel, which changed its color - turned white or darkened. There are no indentations on the enamel yet. At this stage, caries can only be noticed visually; the child does not make any complaints. If the spot changes color over time and becomes darker, even black, this means that the disease is progressing. - Superficial caries
- the lesion has not yet gone beyond the enamel layer, but there is a noticeable depression on the tooth. The color of the enamel has changed - it is darker or whitish. The child still has no complaints; sometimes the tooth may react briefly to sweet or sour foods. - Medium caries
is diagnosed when dentin destruction has begun - i.e. tooth tissue under the enamel. At this stage, a depression is already noticeable; food debris can get stuck in it - this is what the child most often complains about. The tooth begins to react with pain to changes in food temperature. Your child may have bad breath. - Deep caries
affects all tooth tissues and actually reaches the pulp. There is a large carious cavity in the tooth, but sometimes it is not visible under the thin top layer of enamel. Often at this stage, pulpitis can no longer be avoided (see below). Due to the wide dental canals, the child may not feel much pain. The pain intensifies in response to an irritant (mechanical load, change in temperature, etc.) and goes away after cleaning the cavity and rinsing with water. The child is lethargic, may refuse to eat, and the temperature rises especially in the evening hours. The child refuses to chew on the painful side, but often cannot tell which tooth hurts.
Basic mistakes
Fear is not born out of nowhere. Every phobia has a root cause. And, no matter how bitter it may be to realize this, it is often the parents who become the creators of fears. Remember, even an accidentally dropped word can make a tremendous impression on a child and influence his life.
Below we look at the most common mistakes that inexperienced mothers and fathers make:
- Going to the dentist even if you have problems. Of course, in such a state (when the tooth aches and hurts), it will be extremely difficult for the baby to trust a stranger. That is why it is necessary to take him for routine examinations - for adaptation.
- Lack of motivation to undergo treatment. From an early age it is important to develop positive health-saving attitudes. If developed in childhood, they will remain forever and will help a person adhere to the principles of a healthy lifestyle.
- Use of violence. Never force your baby to do anything. A quality dialogue and search for compromises are always necessary.
- Well, a convenient time to visit. All visits to the hospital should be arranged at a time that is convenient for the visitor.
Well, the main thing is deception. Do not lie about the absolute painlessness of the procedure if you know in advance that this is not so.
Features of childhood caries that parents need to know:
1. Rapid development of the disease.
Weak enamel and wide canals in baby teeth lead to rapid progression of caries, which can progress to the mid-stage in a few weeks. And from the beginning of the inflammatory process in the pulp to the purulent form, no more than 24 hours can pass.
2. Childhood caries has no age restrictions
.
Children of any age suffer from caries, including children in their first year of life.
3. Children may often experience very aggressive forms of the disease that are not typical for adults.
Multiple carious lesions, when almost all teeth are affected by caries, as well as rapid forms of development of the disease, the so-called. Generalized caries occurs more often in children than in adults. Children also suffer from special forms of caries that do not occur in adults. Circular caries affects all surfaces of the tooth in a circle, which often leads to a fracture of the crown and the need for tooth extraction, and planar caries, which develops only on the surface of the tooth, affects the entire tooth enamel, but does not go deep into the underlying tissues.
First visit
Above we have already partially touched on the importance of initial experience, now let’s talk about it in more detail. The child’s subsequent attitude towards the dentist and dental treatment in general depends on how the session goes.
What is important? No coercion. Don't try to force yourself to love the dental office. Usually such actions only cause negative reactions.
The most effective way is to lead by example. When you yourself are not afraid of dentistry and understand the importance of all the procedures performed, the baby will absorb your mood and will not worry.
In addition, so that the child is not afraid, it is good to go to the pediatric dentist. Those dentists who work with adults often lack the tact and sensitivity required at a young age.
Introductory visit
For convenience, we attach a detailed scenario of how the first visit should go:
- Acquaintance. The doctor cannot immediately begin with treatment or perform any complex manipulations. His task is to win over the patient.
- Gloves. Wearing them is not recommended, as is using intimidating tools and devices. The best option is to organize a short tour of the office with a story about what is needed and why.
- Dialogue. All actions must be accompanied by explanations. The unknown scares the baby.
- Leisure. In some clinics, cartoons are played or toys are provided for young patients. This is a good solution to shift your focus.
Please note that we are talking about a routine preventive examination.
Appearance
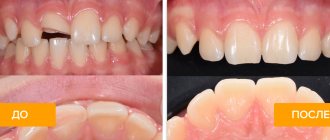
What do teeth that have undergone restoration look like? Look at the photos below. If everything is done correctly, the new teeth will not differ from your own teeth located next door.
Photos before and after
The psychological aspect in the matter of dental restoration is of considerable importance. If a child feels the mocking attitude of peers, this can lead to disturbances in the formation of personality, character, and a decrease in the level of self-esteem. With such a burden it will not be easy for him to start his adult life. Consider this if you are simply going to remove a decayed front tooth. Maybe it’s still worth fighting for it?
What to do when a child is very afraid and does not want to have his teeth treated: how to persuade him to go to the dentist
Some modern techniques, developed jointly with psychologists, involve exciting adventures, while others involve a preliminary study of possible problems. Below we talk about the most successful and popular practices that can be easily adapted to Russian reality.
Playing doctor
This is a unique tool for understanding the world around us, especially in childhood. Even the most unremarkable and disgusting things seem more attractive and interesting if they are presented in a positive playful way. Turning a standard trip to the dentist into a real adventure is an art. However, if you don’t want your baby to develop dental phobia, this is exactly what you should do.
Below are the most successful entertainment scenarios:
- Offer to treat your favorite toy's teeth. The child will be so interested in the process that he will want to check the condition of his own.
- Role-playing game. Something from the “mother-daughter” category, only “doctor-patient”. First, the parent will act as a dentist - just to explain and tell how everything works. And then the baby will try on this image. Such tricks help dispel fears before visiting the office.
- A fairy tale about the good doctor Aibolit. Before your visit, you can watch the old cartoon.
Of course, this is not a complete list of all games. You are free to invent and propose your own. The main thing is to create a comfortable psychological environment.
Reward and encouragement
Just as bad behavior in a dental clinic should be discouraged, good behavior should be rewarded. It is best to give the gift to the doctor so that he, in turn, gives it to the baby. Such a simple manipulation will win the favor of the little patient.
However, gifts should not become a management tool. During each visit, the child is introduced to the culture of health care and is more responsible about the state of the oral cavity.
Cartoons during treatment
Watching your favorite cartoon during a visit will help you take your mind off what the doctor is doing and concentrate on something more pleasant. This technique is actively practiced by dentists at Dentic Kids.
Own example
Of course, cartoons, games, gifts are all very good. But remember, nothing works better than a worthy personal example. If you yourself literally faint at the mere mention of the need to see a dentist, it is unlikely that you will be able to develop a love for this specialist in your children. That is why, before raising them, it is important to work through your own fears and phobias.
If, on the contrary, you understand the importance of dental treatment and endure any procedures, then it would be a good idea to go to the session with your baby. There he will see your positive attitude and will quickly be charged with the right mood.
Reasons for the growth of the second dentition in a child
Double or “shark” teeth in children appear when the baby tooth and the rudiment of the molar are located at different points in the oral cavity. When a new set erupts, the baby tooth remains in place. A tooth grows above a tooth, which not only does not look aesthetically pleasing, but also interferes with the development of the rest of the row.
The most common reason why teeth do not change is improper breathing. A lot depends on how a child breathes. Breathing disorders lead to problems with bite, deterioration of posture and changes in facial shape.
A child’s jaw develops correctly only when he breathes correctly through his nose. The tongue in this position presses on the palate from the inside. A natural semicircular shape of the jaw is formed, in which there is enough space for all the molars. This is why it is so important to teach your child to breathe through his nose to prevent the growth of the second row of teeth.
What to do if your tooth already hurts
It’s easy to talk about preventive procedures and routine examinations. The child is not in any danger, he does not experience acute pain, and he can resist going to the dentist’s office only for some personal reasons. In such situations, you have enough time and resources to change his mind, dispel his fears, and help him get into the right frame of mind. But what to do when the tooth is already aching? Pain and discomfort are not exactly what instills a love for dentistry.
My child is afraid to have his teeth drilled, how can I take him to the dentist? If there is no time for persuasion, try to talk to him like an adult. Explain everything that is happening, tell him why he is experiencing discomfort, and then offer a solution. Imagine the dentist in some kind of fairy-tale light, give him the role of a wizard who will make it so that it no longer hurts.
There is no point in deceiving your child that everything will go smoothly and painlessly. Having encountered a lie once, he may gradually begin to treat your words with greater caution, and in some cases, lose trust.
Thus, the key to solving the problem is confidential negotiations and discussions without secrets or embellishment.
What are baby teeth used for?
Not just for chewing, although that is their most obvious function. They also participate in the formation of the facial skeleton and ensure proper growth and development of the jaw bone. Contrary to popular belief, baby teeth have roots. They are thinner and shorter than those of permanent ones, but nevertheless perform an important function: they hold the teeth in the jaw bone and “transmit” the force during chewing to it. Gradually, as the child grows, his diet should expand and include more solid foods (meat, vegetables, fruits). Then the jaw apparatus will develop correctly and perform its direct function - chewing. If baby teeth are removed too early, long before the permanent ones erupt, the chewing process, and with it the formation of the bite, is disrupted.
That is why early removal of baby teeth can lead to consequences such as narrowing (insufficient development) of the jaw and the formation of crowding of already permanent teeth.
How not to be afraid of the dentist for children 10 years old and older
While it is still possible to agree on something with a child, it is much more difficult to do this with a teenager. Age plays a huge role - it is difficult and critical; it makes you distrustful of adults and often enter into conflicts with them. Your main task as a parent is to establish a warm relationship with your own child. It is necessary to explain: his choice is respected and taken into account. Next, by creating a favorable psychological environment, you can position your child to visit the dentist’s office.
However, everything is not so simple here either. Sometimes fear is caused by unpleasant experiences in early childhood. You can hardly get by with just one conversation. How then? Let's look at some tips from dentists on what to do if a child is terrified of going to the dentist:
- Talk through all the procedures to be done. Often the unknown is much more frightening. A detailed discussion of all manipulations helps to dispel some of the fears.
- If your teen refuses a visit and the situation is not an emergency, do not insist on treatment. Perhaps he just needs a little time to collect his thoughts and make up his mind.
- Form positive self-preservation attitudes and motivation for regular and timely dental examinations. Try to instill a love for beautiful snow-white teeth, an even smile, and fresh breath. When all this is valuable to the child, he will want to take care of his oral health.
- Don't refuse support. By law, the parent has the right to be in the office during the procedure. Don't neglect it. In your society, the teenager will feel protected, and, therefore, everything will go more smoothly.
Well, and, of course, one cannot fail to mention the role of a specialist. He must have quite a wealth of practical experience in order to be able to win over a young patient and gain his trust.
Classic method of caries treatment
If caries has already developed, then it will have to be treated using the standard method, using drilling of the carious cavity and filling it. And the parent’s task is to prepare the child for this procedure , to form a positive attitude towards the doctor. Today, in order to arouse children's interest in treatment, children's doctors install colored fillings, which the child can choose according to his own taste. This is quite a strong motivation for a child, who can then show off his beautiful teeth to his friends. Treatment with a drill provides pain relief for small patients.
Moreover, before the injection, the doctor numbs the injection site with a special gel. The treatment procedure should not exceed 30 minutes, otherwise the child will get tired. Frequent breaks in the treatment procedure are required.
If the baby behaves very restlessly, then doctors recommend giving him a tablet of children's Tenoten for resorption 20 minutes before the appointment. The medicine significantly reduces anxiety , improves mood and removes fear.
In modern dental centers, parents can be offered a sedation procedure for children who are not amenable to treatment, categorically refusing it. Using a mask with nitrous oxide, the child is put into a shallow sleep , after which anesthesia and then treatment are carried out.
As a last resort, anesthesia is used, but only according to the pediatrician's indications. In order not to lead children to deep caries, you need to know preventive measures against it.
Tips on how to persuade your child to go to the dentist and have their teeth treated
In conclusion, we will briefly summarize all of the above and formulate the main recommendations for parents:
- If possible, plan to visit the dentist in the morning. If the visit is scheduled for a later time, the baby may “wind up” himself, become capricious, become nervous and whiny.
- Do not escalate the situation before going to the dentist. Even if there are some minor problems and troubles, try to ignore them in order to minimize psychological discomfort. If the child is upset, this will only worsen his condition at the time of the procedure.
- Discuss what procedures will be performed in the dental office. And then try to switch the baby’s attention to some abstract topics. This will allow you to wait for your appointment without panic and unnecessary nerves.
- Take a responsible approach to choosing a clinic and specialist. It is best if this is a person who works directly with children.
- Do not be nervous. Yes, we should not forget that a lot also depends on the psychological state of the parent. If you are tense and tense, the child will feel it and quickly move into the same phase.
- At the end of the procedure, be sure to praise the baby and encourage him in some way. This will provide a good foundation for the future. If positive memories remain in your memory, it will be easier to decide on your next visit to a specialist. If the baby is overwhelmed with emotions, let him speak out and tell him everything.
- Visit the dental office regularly. It is recommended to do this at least twice a year. Why such frequency? Firstly, it allows you to promptly identify and eliminate existing problems. And, secondly, it helps the baby adapt and get used to it.
- Do not discuss treatment of your own teeth in front of your child. Especially if your experience was negative.
- Do not intimidate a young patient with a doctor. A visit to the dentist doesn't have to be a daunting experience.
Summarizing all of the above, we can conclude that the psychological attitude is of enormous importance. Parents often use doctors (including dentists) as a tool of intimidation - “If you don’t listen, I’ll take you to the doctor!” This is a fundamentally wrong position, entailing a lot of different problems and difficulties. To prevent your baby from panicking at the sight of a white coat, you need to talk through and work through all possible situations with him. As a parent, you must explain why dental care is important and the consequences of not getting proper treatment. But this should be done softly and delicately; under no circumstances should you press. We hope that our article on how to prevent your child from being afraid of the dentist helped you find answers to all your questions and was useful!
How restoration is done
The method in pediatric practice is chosen by the dentist. Its choice is determined by clinical feasibility. He is guided by the degree of destruction of the crown. The wishes and financial capabilities of the parents are then taken into account by him.
In what cases is each method used:
- a filling is placed if only one wall is destroyed;
- if two walls are missing, then it is carried out with depulpation;
- if three are missing, a crown is installed;
- in the absence of all the walls of the coronal part, and the roots are healthy, restoration is carried out using a crown and a reinforced structure.
Modern dentistry makes it possible to restore even almost completely damaged teeth.
Types of child reactions to dental treatment
The types of reactions listed below are not a professional psychological classification, but rather reflect the experience of a pediatric dentist.
- Conditionally normal reaction. The child fulfills all requests of the doctor and parents. Doesn't cry, doesn't scream, even when discomfort occurs, he behaves calmly.
- Closing in on oneself. The child does not comply with the requests of the parents and the doctor and remains silent. You may not be able to sit in a chair at all.
- Crying and hysterics. The child not only cries, but may call him names and try to hit the doctor and parents.
In the first case, treating a child is not difficult; these children can be given anesthesia and perform all manipulations. This is how children usually react to treatment after 7-9 years of age. They can already articulate their fear. If everything is explained to them correctly, there will be no problems with the manipulations.
In the second case, it is not always possible to carry out treatment, but you can try to establish contact with the child and introduce the child to the office.
In the latter case, manipulation is very difficult. If assistance is urgently needed, anesthesia or a visit to the maxillofacial department is required.