Necrosis is a serious pathology accompanied by the death of gum tissue. It is quite rare in dental practice. The danger of this process lies in its irreversibility, asymptomatic course in the early stages of development and serious complications that it can lead to if the necessary measures are not taken in time. Find out what can trigger necrosis of gingival tissue, what the dead areas look like, what symptoms should alert you and where to go if they are identified.
Gum necrosis
Causes of necrosis
Types of gum necrosis and treatment
Symptoms of the disease
Diagnosis of the disease
Prevention of the development of gum necrosis
Gum necrosis (from the Greek nekros - dead) is the death of tissue that occurs due to cessation of blood circulation. This disease is difficult to detect at an early stage, as its symptoms are barely noticeable. Another danger is that this process is irreversible. Therefore, if the doctor has diagnosed gum necrosis, it is important to take appropriate measures as soon as possible to prevent the development of pathology. In this article we will look at the causes of necrosis, its types, and also tell you how to avoid it.
How dangerous is this pathological phenomenon?
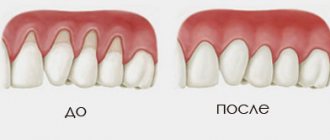
If you start the process, it will inevitably lead to irreversible consequences. The affected tissues do not have a chance to recover, and the further the necrosis goes, the higher the likelihood of losing teeth and losing chewing function. The addition of infections can provoke the development of osteomyelitis of the jaw - purulent-necrotic destruction of bone tissue structures. Less commonly, the pathological condition is complicated by general blood infection - sepsis.
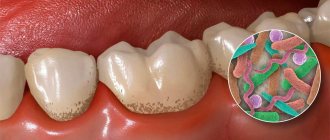
You need to understand that necrotic areas in the oral cavity become a suitable environment for the proliferation of harmful microorganisms. The problem is that the initial stages of the pathology are quite difficult to diagnose. If the problem has already become pronounced, it will be much more difficult to treat.
Necrotic areas in the oral cavity become a suitable environment for the proliferation of harmful microorganisms
Causes of necrosis
Table 1. Causes of gum structure destruction
| Causes of necrosis | How it manifests itself |
| Insufficient oral hygiene | Plaque forms, which leads to the development of gingivitis, periodontitis, and periodontal disease. |
| Injury to the gums due to malocclusion or ill-fitting dentures | This disrupts blood flow and blood circulation stops in certain segments. |
| Hormonal disbalance | During pregnancy, adolescence, with diseases of the endocrine system and blood. |
Sometimes the disease can occur due to prolonged exposure to cold, high temperatures or arsenic, which is part of the dental pastes used in root canal treatment. For example, if a temporary filling does not close the dental canal tightly, the paste can come out, causing tissue necrosis.
Types of gum necrosis and treatment
The treatment plan is developed individually for the patient and depends on the type of necrosis.
Table 2. Treatment plan depending on the type of anesthesia
| Type of gum necrosis | How to determine | Treatment |
| Dry | Dead areas dry out and decrease in volume. There are no signs of inflammation or intoxication. | The affected areas are removed, the surrounding tissues are treated with antiseptics. After the procedure, the doctor prescribes drug therapy. |
| Wet | It is considered the most dangerous form. Accompanied by swelling and increased hyperemia. | They open purulent foci, cut out dead tissue, dry the gums, and carry out antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity. After – drug therapy |
Once the necrotic process has stopped, bone grafting may be required to improve aesthetics.
Loss of dental tissue due to erosion
Tooth erosion
- progressive loss of dental tissue (dentine and enamel) of an insufficiently studied nature.
Some authors suggest that the cause of tooth erosion, like the wedge-shaped defect, arises solely from the mechanical action of the powder and the toothbrush. Others believe that the appearance of erosion is due to the large amount of consumption of citrus fruits and their juices. In any case, our dentists will be able to help in any clinical situation - they will provide high-quality treatment and save you from dental erosion.
A significant role in the mechanism of progression of erosion of hard dental tissues is assigned to increased function of the thyroid gland, and, in particular, endocrine disorders. According to experimentally obtained data, one of the main symptoms of this disease is considered to be a decrease in saliva viscosity and an increase in its secretion. It has been proven that tooth erosion occurs in patients with thyrotoxicosis twice as often as in people with normal thyroid function. At the Dantley Clinic, our dentists will perform remineralization as a treatment option for erosion. The number of patients with erosion of hard dental tissues increases by 20% with an increase in the duration of the disease by just one year.
Erosion is the loss of dental tissue, which will continue to progress without medical intervention. Dental tissues are affected and thinned on one or more sides of the tooth.
Erosion of hard dental tissues mainly manifests itself on the symmetrical surfaces of the lateral and central incisors of the upper jaw, as well as on small molars and canines of both jaws. Erosion practically does not occur on large molars and incisors of the lower jaw. The lesion is most often observed in middle-aged people, and is characterized by a long course - up to 10-15 years. In St. Petersburg, the Dantley Clinic provides remineralization and restoration of teeth to patients of all ages. Over time, a large number of teeth become involved in erosion. Due to the significant impact of adverse factors, including environmental ones (Chernobyl disaster, etc.), the number of cases of dental erosion in fairly young people (18-25 years old) is significantly increasing.
Manifestation of tooth erosion
It is a round or oval enamel defect located in the transverse direction of the more convex part of the labial (vestibular) surface of the dental crown. The bottom of the erosion is shiny, hard and smooth. The gradual expansion and deepening of the boundaries of erosion leads to the loss of part of the dentin and all of the enamel.
There are two transitional stages of damage:
- initial (enamel erosion);
- pronounced (erosion of dentin and enamel).
According to the depth of the lesion, three degrees of the disease are distinguished:
first degree (initial)
- only the superficial layers of enamel are affected;
second degree (medium)
— the entire thickness of the enamel is affected, dentin is not involved in the pathological process;
third stage (deep)
— the entire thickness of the enamel, as well as the surface layer of dentin, is affected.
According to the course of the disease, two stages of erosion are distinguished - active and stabilized, but both of them are characterized by a chronic course. With any type of erosion, our dentists will carry out remineralization or filling, reducing the chronicity of the disease to zero.
The active stage is characterized by:
- rapid loss of hard dental tissues;
- increased sensitivity of the affected area to external irritants (sweet, sour, hot, cold, building up to erosion).
The stabilized stage is characterized by:
- slowly progressive loss of hard dental tissues;
- lack of increased sensitivity of the diseased area;
- possible transition from a stabilized stage to an active one.
Treatment of tooth erosion
Local treatment of the active stage:
- The goal is to stabilize the process. This result is achieved through additional remineralization of hard dental tissues using calcium electrophoresis or applications. Daily applications of a 10% potassium gluconate solution are prescribed for 15 minutes for 15-20 days. After which, for 3 days, a 2% sodium fluoride solution is applied to the area of erosion for 3 minutes. And the treatment is completed by coating the diseased surface with fluoride varnish. A 10% calcium gluconate solution is used for electrophoresis. The duration of the procedure is 5-10 minutes. After the electrophoresis session, a swab moistened with a 2% sodium fluoride solution is applied to the area of erosion. The entire course of treatment is 10-15 procedures.
- Fluoridation - restoration and strengthening of enamel with fluoride-containing and mineral substances.
- Filling erosion with composite materials fully restores the defect, the teeth look beautiful and natural.
- If there is a large area affected by erosion, it is worth making artificial crowns.
Local treatment of the stabilized stage:
- Phosphorus and calcium preparations, microelements and vitamins are prescribed internally.
- The task is tissue depigmentation. For this purpose, over the course of two or three visits, the affected surface is treated with an abrasive paste with a high fluorine content. Whitening, filling and restoration of the defect area are also used.
Symptoms of the disease
Signs of the disease differ depending on the stage.
Early.
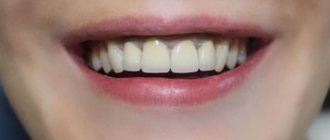
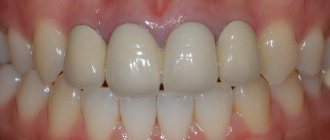
The tissues are slightly affected, darkening of the enamel and pale gums may be observed.
Average
. Swelling of the interdental papillae, a gray coating forms on the mucous membrane, and bad breath appears.
Heavy.
Swelling of the gum tissue - it turns black and ulcers appear on it. Appetite disappears, body temperature rises to 39 C°.
Last
. The epithelium dies, severe pain is felt in the gums, the necks of the teeth are exposed, and the dental units become loose.
Diagnosis of gum necrosis
Often the problem is identified during an examination by a dentist, without any complaints from the patient. In some cases, symptoms are present: pain, bleeding, flushing, bad breath.
Other signs of the disease may include:
- swelling of the mucous membrane;
- digestive problems;
- problems with swallowing;
- deterioration of health.
During diagnosis, the doctor does an X-ray examination and conducts an instrumental examination. The image allows not only to identify the necrotic process, but also to determine the stage, possible complications, etc.
Prevention of the development of gum necrosis
Interventions are often based on maintaining oral health and preventing dental diseases.
- Regular teeth cleaning and professional hygiene.
- Quitting bad habits (smoking, alcohol).
- Timely correction of the bite to prevent trauma to the mucous membrane and accumulation of dental plaque.
- Balanced diet, taking vitamins if necessary.
- Timely treatment of diseases of teeth and gums, gastrointestinal tract, endocrine diseases, etc.
After treating necrosis, it is important to prevent its reappearance. Proper oral care and mandatory visits to the dentist once every six months will help with this.
Classification
The course of the disease caused by infection can be acute, chronic or subacute.
According to location they are distinguished:
- osteonecrosis of the lower jaw;
- necrosis of the upper jaw.
By type of infection:
- endogenous - infection occurs as a result of dental diseases;
- hematogenous - pathogens enter the jaw through the bloodstream.
Also distinguished:
- medicinal (bisphosphonate);
- traumatic.
The American Dental Association defines the following stages of disease development:
Stage 0
– toothache that radiates to the temporomandibular joint or sinus. Mobility of teeth, with intact periodontium. The appearance of fistulas, cysts, fluxes.
Stage 1
– exposure of a section of bone without severe pain
Stage 2
– exposure of a section of bone, accompanied by pain and inflammation
Stage 3
- exposure of a section of bone that extends beyond the alveolar (the one in which the tooth is located) bone. With necrosis of the lower jaw, the jaw is affected down to the lower edge. Bone tissue atrophy occurs. This is the stage of pathological fractures. With necrosis of the upper jaw, the zygomatic arch and maxillary sinus are affected. Numerous fistulas are formed.