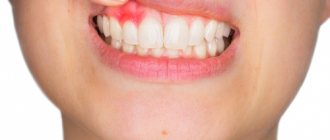
Often, patients seek help from a dentist with the problem of gum discoloration. The seriousness of this disease lies in the fact that blue discoloration of the periodontium in some cases can occur against the background of any somatic disease. In some cases, blue gums may be associated with problems in the oral cavity. Timely detection of pathology and timely measures taken are the key to quickly eliminating the disease without developing complications.
Important information about diseases and factors that cause blue gums in adults
When blue gums near a tooth are discovered, or generalized (along the entire row) changes in the shade of the oral mucosa become noticeable, then there is no time for jokes. Many are beginning to wonder what this might be connected with. And we will tell you about the most common – dangerous and not very compelling reasons for this phenomenon.
The reasons for blue gums can be different.
Summary -
In this article, we briefly listed the main stages of treatment necessary to quickly relieve inflammation. Removing dental deposits from teeth and anti-inflammatory therapy will relieve redness, swelling, bleeding of the gums, the gums will become denser, pale pink in color, and bad breath will disappear. However, the treatment of a disease such as periodontitis does not end there.
In the case of deep periodontal pockets, and when the gums move away from the teeth, it can be assumed with a high degree of probability that splinting of mobile teeth will be required, as well as one of the surgical methods for treating periodontitis (for example, flap surgery or open curettage of the gums). During flap surgery, a thin strip of marginal gum is removed, which is loose and not attached to the teeth and, accordingly, this reduces the depth of periodontal pockets, as well as the rate of progression of periodontitis.
Sources:
1. Dental education of the author of the article, 2. Based on personal experience as a periodontist, 3. National Library of Medicine (USA), 4. American Academy of Periodontology (USA), 5. “Therapeutic dentistry. Textbook" (Borovsky E.V.).
Possible dental causes
Some dental patients notice that they have blue gums after tooth extraction. Indeed, this is not uncommon. Often the phenomenon is caused by traumatic effects on tissues, vessels and capillaries during surgical procedures. And such a symptom may not necessarily occur only after root removal, but also after procedures such as anesthesia, incisions, suturing, and gum retraction. Changes in mucosal swelling can often be seen after the following operations: gingivectomy, vestibuloplasty, osteoplastic procedures, implant installation.
Important! After surgery, blue gums in an adult are most often discovered due to too large-scale intervention or traumatic actions of the doctor. And also if the patient has a history of various chronic diseases, for example, hypertension, diabetes, or poor blood clotting. In this case, there is a high risk of hemorrhages in the tissue and the formation of various hematomas.
If there is blue gum near a tooth, this may be due to other dental factors:
- poor-quality prosthetics: after installing structures that do not correspond to the anatomical characteristics of the patient, or are too “driven” under the gums, hematomas may form, since the tissues are compressed too much and cease to be properly supplied with blood,
- the presence of crowns with a metal component in the mouth: materials based on alloys of base metals can, over time, interact with saliva and oxidize, leaving blue gum above or below the tooth. Blue gums can even appear from a metal-ceramic crown,
Gums may remain blue after whitening
- teeth whitening carried out by an inexperienced dentist, cosmetologist, or, more often, by the patient himself (for example, at home, using inappropriate means and folk recipes). In the process, a doctor or home “experimenter” may leave soft tissues without proper protection, apply too much product and not remove the excess, overexpose the composition and thereby provoke a burn,
- inflammatory periodontal diseases: gingivitis, periodontitis and periodontal disease,
- purulent processes in the affected teeth, mucous membrane, bone tissue: for example, gumboil, enlarged cyst or granuloma, abscess, osteomyelitis,
- the presence of removable dentures in the mouth: at the initial stage, they can put pressure on the mucous membranes, injure and irritate them, and impair blood circulation in the tissues. During operation, such problems arise in the absence of timely corrections and against the background of inevitable atrophy of the jaw bone,
- complications after surgical interventions: for example, alveolitis after tooth extraction. This may also be inflammation of the tissue around the implant, indicating mucositis or peri-implantitis,
- cervical caries.
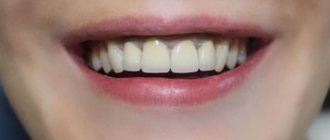
“5 years after wearing a metal-ceramic bridge, my gums became blue, and they become exposed when I smile. It was very ugly. After that, she stopped opening her mouth wide at all. She hardly smiled. Complexed. And when the bridge cracked a few years later, the dentist suggested replacing it with zirconium dioxide so that there would be no blue discoloration. It cost me a lot more, but now everything looks very natural and doesn’t interfere with my smile.”
Marina Olegovna, review from the dental portal gidpozubam.ru
Blue gums after installation of metal-ceramic crowns
What can cause your gums to turn blue?
So, why can individual areas of the gums change their color, and where do such blue spots appear on the mucous membrane? This could be due to many different factors. So, for example, if we are talking about a child, the reason may be the eruption or change of baby teeth. In adults, a similar symptom is sometimes provoked by certain diseases of periodontal tissue or the oral mucosa as a whole. Also, the area near the tooth may turn blue due to unsuccessful prosthetics or malfunctions in the internal systems of the body. Let's look at possible provoking factors in more detail.
Why do my gums turn blue?
Causes of blue gums in a child
The time when a baby's first teeth emerge varies in each situation individually. When an already formed rudiment erupts, inevitable injury to soft tissues occurs, and, as is known, a large number of vessels are concentrated in them. Due to a violation of the integrity of the mucous membrane, blood enters the soft tissues, and a hematoma forms. If the child is one year old and a bruise appears on his gum, namely in the place where the tooth should appear, there is nothing to worry about.
“And sometimes the teeth start to break through with a bruise. We had the same thing with the side ones. I remember looking in the morning and a blue spot appeared on my daughter’s gum. I thought that she had hit herself somewhere, so I decided to observe. And after a while a white stripe appeared.”
Marina7, Irkutsk, from correspondence on the woman.ru forum
Among the pathological causes of the formation of blue areas in the mouth in children, experts in the field of pediatric dentistry and pediatrics identify the following conditions:
- inflammation of gum and periodontal tissues: the most common cause of blue discoloration is gingivitis - inflammatory processes that spread in the gums without disrupting the periodontal attachment. Redness turning blue is observed in localized areas, mainly in the cervical area. At the same time, the child becomes whiny and capricious, and his appetite is impaired. If left untreated, the next stage may be periodontitis,
Gingivitis in a child can cause blue gums - diseases of the mucous membrane: often stomatitis leads to blue gums - an inflammatory disease, the development of which is accompanied by the appearance of painful rashes on the gums, the inside of the cheeks, lips, palate and tongue. In this case, a change in the color of the soft tissues is noted around the tumors. Associated symptoms include severe pain in the oral cavity, as well as a sharp increase in body temperature.
Stomatitis is common in infants
It is worth noting that most often the diseases described above are diagnosed in children with weakened immune defenses. However, the main enemy of oral health is poor oral hygiene. Plaque and dental deposits are the key cause of most dental ailments.
Why does the mucous membrane turn blue in adults?
In adults, the gums most often turn blue after poor-quality dental intervention, as well as against the background of periodontal diseases and systemic pathologies of the body as a whole. Thus, the most common cause of hematoma is unsuccessful prosthetics. A small blue spot may appear above the crown if it is pushed too far under the gum. As a result, microcirculation will be disrupted, a blood clot will form, swelling and hypoxia of the mucosa will appear. Much less often, a similar situation occurs during restoration with filling materials, when the composite is carelessly applied to the gum1.
On a note! There is an opinion that the soft tissues surrounding the structure may turn blue due to metal-ceramics. This is a common misconception based on the assumption that the metal is oxidizing. In fact, changes in the gums around the crown only indicate its incorrect installation. The metal in the crown does not oxidize and certainly does not rust. To create such orthopedic structures, a special alloy is used, which fully meets all the necessary requirements.
In some cases, darkening of gum areas may indicate the development of certain pathological conditions of internal organs and systems. These include the following factors:
- thin blood vessel walls or blood clotting problems,
- violation of microcirculation,
- gingivitis and periodontitis,
- deficiency of vitamins and microelements in the body,
- anemia.
Blue gums in adults may occur after the installation of crowns.
In the case of anemia, a lack of iron, vitamin B12 and other vital substances in the body leads to a decrease in the level of hemoglobin in red blood cells. As a result, the patient experiences pallor of the skin and mucous membranes, including the appearance of cyanosis.
What internal diseases may the symptom indicate?
If you have blue gums, then the reason for this phenomenon is pathological changes occurring in the body against the background of various systemic diseases. Thus, due to diseases of the blood, heart, and metabolic disorders, blood vessels become thinner and capillaries become fragile, and internal local bleeding occurs.
Doctors say that a similar symptom sometimes occurs against the background of iron deficiency conditions, that is, with anemia. For kidney disease and thyroid problems. And in diabetes mellitus, when the processes of nutrition and tissue regeneration are disrupted, even minor traumatic injury can lead to the formation of long-term non-healing hematomas.
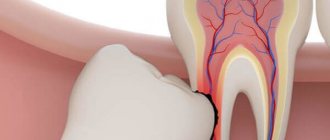
Why does the gum move away from the tooth?
A prerequisite for the destruction of the periodontal attachment is the presence around the necks of the teeth - soft microbial plaque or supragingival tartar. The formation of dental plaque occurs due to irregular oral hygiene. In some patients with periodontitis, tartar may not be visually visible, because... when the attachment of the gum to the tooth is destroyed, it can already be localized below the level of the gum (then it is called “subgingival”).
But usually the destruction of the attachment of the gums to the teeth is always preceded by a long period of chronic inflammation of the gums, during which the patient is only bothered by periodic bleeding of the gums, possibly bad breath, redness or cyanosis of the gingival margin, as well as swelling of the gingival papillae. These symptoms are characteristic of gingivitis, an inflammatory disease of the gums in which the attachment of the gum to the tooth is not yet broken.
The lack of professional treatment for gingivitis (usually patients during this period self-medicate using antiseptic rinses and toothpastes for bleeding gums) leads to destruction of the attachment of the gums to the teeth. As a result, so-called periodontal pockets (gingival pockets) are formed between the teeth and gums, and patients in this case may complain that their gums have moved away from their teeth.
Stages of gum inflammation (gingivitis and periodontitis) –
Conclusions: Figure 10 shows the differences between gingivitis and periodontitis, and that with periodontitis, the gums are not attached to the teeth to the full depth of the periodontal pockets (from 3 to 6 mm or more). Therefore, if your gum has moved away from a tooth, there is simply no point in delaying a visit to the dentist, unless, of course, your goal is to remove these teeth in the near future. And in this case, there is no method of self-medication (magic rinses or ointments for gums) that would allow you to save the situation without going to the dentist.
In the absence of professional treatment of gums by a dentist, such teeth will first become mobile, then they will begin to fan-shaped and shift in different directions (under the forces of chewing pressure). In Fig. 11-13 you can see advanced forms of periodontitis in patients who, unfortunately, turned to the dentist too late. The teeth in these photographs have a very high degree of mobility and many of them only need to be removed.
Consequences of lack of treatment -
Other factors leading to the problem
Another reason why an adult’s gums may turn blue is a burn. It is not difficult to get it if you eat too spicy foods, hot soups and sour drinks. A bad habit such as smoking can also contribute to this.
The symptom may indicate chemical burns, when delicate tissues are damaged due to the use of aggressive compounds unsuitable for the oral cavity. For example, alcohol, manganese, iodine, peroxide.
Very often, pathology occurs due to bruises and injuries received in the area of the maxillofacial apparatus. And the safest reason that can explain the blueness of mucous membranes is the consumption of drinks and dishes with food or natural dyes that give pigment to the teeth, gums and tongue. For example, blueberries, blackberries, soda pop, plum wine and plums. Fortunately, you can easily get rid of this problem by thoroughly cleaning your mouth with a brush and paste.
The gum has moved away from the tooth: treatment
If the gum has moved away from the tooth, treatment will largely depend on the severity of the inflammation. For example, if a patient seeks help at a fairly early stage of inflammation (when the depth of periodontal pockets does not yet reach 3 mm and there is no tooth mobility), significant success can be achieved in the treatment of periodontitis and the process can be completely stopped. Advanced cases of gum inflammation will require much more complex treatment and serious financial costs. Next we list the main stages of treatment.
1) Consultation and x-ray diagnostics –
It is necessary to begin treatment with a consultation with a periodontist and a panoramic photograph of the teeth, which will allow you to create an optimal treatment plan taking into account the condition of your teeth and gums. The image will allow you to determine the amount of destruction of bone tissue around each tooth, the location and depth of periodontal pockets, and will help guide the patient in the need for splinting of mobile teeth, the need for prosthetic replacement of missing teeth, and make the correct diagnosis.
An example of a panoramic image of a patient with periodontitis –
Looking closely at the image, you may notice that the level of bone tissue (the bone looks in the image as fine-mesh looped tissue and normally should reach the necks of the teeth) is reduced in different teeth by 1/4 to 4/5 of the length of their roots. The patient has decayed teeth that need to be removed, as well as carious teeth that require treatment (24stoma.ru). The level of bone tissue is most reduced in the front teeth of the upper and lower jaw, which in this case was the result of not only inflammation of the gums, but also the absence of the chewing group of teeth.
To treat gums, it is best to contact not ordinary dental therapists or hygienists, but periodontists. These are the dentists who specialize in gum treatment. The first and most important stage of treatment will be ultrasonic teeth cleaning. Next, a course of anti-inflammatory therapy is carried out, which in most cases can be successfully carried out at home.
2) Removal of dental plaque –
First of all, it is necessary to remove the cause of inflammation - microbial plaque and dental deposits. They are removed from the teeth using an ultrasonic scaler (Fig. 15), usually over several visits. It is simply impossible to remove all dental deposits in just 1 visit in a patient with periodontitis, because... It takes a lot of time to remove subgingival dental plaque, which is localized in periodontal pockets below the gum level.
It is subgingival dental plaque that poses the main danger for further progression of inflammation, so sometimes it is necessary to prescribe the patient even 3-5 times. Learn that without professional cleaning, all other stages (for example, anti-inflammatory therapy, splinting) will be completely meaningless.
Most dentists and hygienists won't bother with finding and removing subgingival calculus...as experience has shown. Therefore, it is very important to find a competent specialist. Anti-inflammatory therapy is prescribed immediately after 1 session of removing tartar, and within the first 24 hours you will be able to notice changes in the appearance of the gums. In parallel with the reduction in gum swelling, their volume will also decrease, which will allow you to see new portions of dental plaque and remove them during subsequent visits.
Removing dental plaque with ultrasound: video
You can see in the following photos what happens when subgingival tartar is removed poorly. The first photograph shows that the gums are visually in good condition, although a periodontal probe revealed the presence of a periodontal pocket about 5 mm deep. The second photograph was taken after the gums were detached from the teeth, and it shows a very large amount of destruction of bone tissue, which arose due to the presence of small subgingival tartar on the surface of the tooth root.
3) Anti-inflammatory therapy –
The course of anti-inflammatory therapy usually lasts 10 days. In most cases, it is carried out by the patient himself at home, after doctor’s prescriptions and patient education. However, if the patient has deep periodontal pockets with purulent discharge, the doctor may additionally prescribe washing the periodontal pockets, which is done using a syringe and antiseptic solutions. In some cases, antibiotic therapy may also be prescribed for periodontitis.
Anti-inflammatory treatment regimen - usually a complex is prescribed, consisting of an antiseptic mouth rinse and application of gel to the gums. The procedures are carried out 2 times a day (morning and evening, after meals and subsequent oral hygiene), for 10 days. Most often, a complex of the following drugs is prescribed:
- rinsing with Chlorhexidine (instructions)
- “Cholisal-gel” applications (instructions)
In patients with periodontitis, the correct choice of treatment agents is very important. For example, a standard 0.05% solution of chlorhexidine, sold in pharmacies for 40 rubles, is advisable to use only for superficial inflammation of the gums (gingivitis), but for periodontitis it is better to use a 0.2-0.25% concentration of this antiseptic. It is a big plus when such a solution contains not only a good concentration of chlorhexidine, but also other active ingredients (for example, aluminum lactate for bleeding gums or extracts of medicinal plants).
Antiseptic mouth rinse is carried out after breakfast and oral hygiene, rinse your mouth for 1 minute. After this, the gums need to be dried with a dry gauze pad to remove excess saliva, and an anti-inflammatory gel should be applied to the gum edge. The gel is applied in front of a mirror using a finger, and usually only on the front side of the teeth. After such treatment, it is not recommended to eat for 2-3 hours, and also not to drink for 30 minutes. There are a lot of remedies for treating gums, and we hope that our next articles will help you understand their diversity -
→ The best antiseptics for mouth rinsing, → Rating of the best gels for treating gums.
4) Oral hygiene training –
If you have not yet forgotten the beginning of the article, then remember that the cause of periodontitis and destruction of the dental-gingival attachment is unsatisfactory oral hygiene, which leads to the accumulation of microbial plaque and tartar on the teeth. Therefore, in addition to the basic treatment that we described above, it is very important to constantly maintain high-quality oral hygiene.
Good hygiene doesn't mean just brushing your teeth twice a day, that's not enough. Good oral hygiene includes brushing your teeth after every meal, not snacking on cookies or candy between meals, and regularly using dental floss. You can read about absolutely all the recommendations in the article at the link above. Below, you can watch the video on how to properly use a toothbrush and dental floss.
How to use dental floss and brush correctly -
In the presence of periodontal pockets and mobile gingival margins, it is important to carry out hygiene below the gum level. This can be done using special devices - home irrigators. Special attachments allow you to rinse at home not only areas of the oral cavity that are difficult to reach for hygiene, but also periodontal pockets below the level of the gingival margin. Irrigators can use both ordinary boiled water and special medicinal solutions.
Possible associated symptoms
Typically, blue gum above or below a tooth is not the only symptom that something is wrong. Typically, people with a similar problem note other warning signs:
- mucous membranes swell and begin to bleed, may move away from the necks of the teeth,
- itching and soreness in the gums occurs: the discomfort intensifies with pressure, any mechanical impact, while eating food,
- a nearby tooth hurts, it can also become mobile,
- body temperature rises,
- there is a strong foul odor coming from under the gums, pus may be released,
- Plaque intensively accumulates on the necks of teeth.
Symptoms
Changes in gum color are usually accompanied by the following complaints:
- pain when brushing teeth and chewing food;
- itching;
- swelling of the mucous membrane;
- periodontal bleeding;
- accumulation of abundant plaque on the teeth;
- formation of tartar.
Symptoms depend on the cause of the disease and on the individual characteristics of the body. Eliminating the cause of gum discoloration is the first thing to start treatment with.
When does it make sense to go to the doctor?
Of course, in any unclear situation this will be the best solution. However, many people prefer to wait a few days, observe the condition of their blue gums and evaluate their overall health. And this is not prohibited if you do not have a rapid increase in body temperature and positive dynamics are observed.
In what cases should you urgently consult a doctor?
In cases where blue gums persist for longer than 3-5 days, with severe pain, high fever, loss of appetite, a change from a local process (when the gums turn blue in the area of 1 tooth) to a generalized one (the pathology spreads to neighboring elements of the row, increases in size, grows ) you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
How to prevent the problem
High-quality care and systematic teeth cleaning are two basic rules, the observance of which will, to a certain extent, protect oneself from inflammatory and carious processes. In addition, do not forget that every time after eating you need to thoroughly rinse your mouth and use dental floss. It is also important to choose the right toothpaste and brush, especially if you have sensitive gums. And of course, don’t forget to visit the dentist regularly.
If a bluish spot appears on your gum, do not put off your visit to the dentist. The longer you ignore the problem, the higher the likelihood of developing truly serious complications.
- Balakhnichev, D.N. The influence of fixed orthopedic structures on the periodontium of abutment teeth, 2011.
What can dentists offer in the fight against gum pathologies?
When a person discovers blue gums, he probably asks the question: what to do? The first step is to see a dentist. The doctor will examine your mouth and identify possible problems.
If the cause is poor-quality or incorrectly installed crowns or dentures, they will need to be adjusted or replaced. In case of dental diseases and detection of purulent processes against this background, it may be necessary to open, drainage and antiseptic treatment of tumors, clean the root canals, apply medicated pads and install a sealed filling at the end.
In case of periodontal inflammation, a specialist will definitely prescribe comprehensive treatment[1]. It is aimed at eliminating symptoms, restoring gum tissue and preserving teeth, which, in advanced stages of periodontitis and periodontal disease, can become loose and fall out. What procedures will be required: professional oral hygiene to remove bacterial plaque, anti-inflammatory and restorative therapy for gums in the form of rinses, lotions, antibiotic therapy. Some patients are also prescribed plasma lifting and periodontal gels with growth factors.
Expert opinion
Marina Igorevna Tarabanovskaya
Specializations: Dentist-therapist, periodontist
Experience: 10+
“In case of periodontal diseases, it is important not only to undergo treatment, but also to adjust the lifestyle that the patient usually leads. It is necessary to follow a certain diet, stop smoking, and purchase a suitable brush, toothpaste and mouthwash for daily hygiene. And be sure to undergo professional hygiene and examination by a dentist at least twice a year. Otherwise, the pathology will constantly worsen, and the patient risks losing all his natural teeth ahead of time.”
Traditional medicine tips
Many medicinal herbs have proven themselves to be excellent in the fight against inflammation in gum tissue. Infusions and decoctions are made from them, which are then used to rinse the mouth several times a day. Antiseptic plants that additionally have pronounced anti-inflammatory properties include chamomile, sage, and oak bark. Some sources provide recommendations for treating the mucous membrane with aloe juice or honey to relieve pain. In order to restore soft tissues after an incorrectly installed orthopedic structure, stimulation of blood circulation is required. A decoction of nettle leaves, as well as propolis ointment, helps with this.
Chamomile infusion is great for rinsing
It is important to understand that any folk recipes can be used only after consultation with the treating specialist. Otherwise, you can provoke the development of a serious complication and only make everything worse. And certainly traditional medicine cannot become a full-fledged alternative to drug therapy. The use of medicinal plants is justified only as an additional measure.
Treatment of a darkened tooth
Darkening of the tooth near the gum requires immediate consultation with a doctor, regardless of the cause. If you leave the disease to its own devices, you can face more dangerous and serious consequences.
The doctors at our regional dental clinic are ready to help. We use modern equipment, progressive therapeutic practices and always put the patient's comfort as a priority. Therefore, treatment of a darkened tooth will be quick and effective. Don’t let the disease lead to dangerous consequences - make an appointment with the dentist!