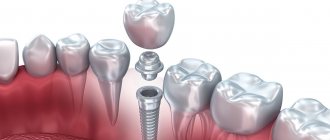
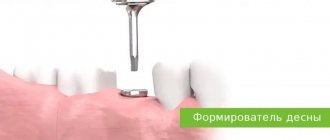
After the installation of a titanium implant is completed, it is necessary that it be completely covered with bone tissue and mucous membrane: this ensures the conditions for its successful engraftment into the bone. But situations arise when the edge of the implant becomes visible due to bone and gum deficiency. Such defects are eliminated by performing bone grafting and gingivoplasty - operations to increase the volume of tissue around the implant.
In order not to trigger a pathology that significantly impairs aesthetics, it is important to notice the initial manifestations of this complication in time.
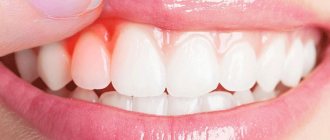
Why is the gum exposed under the implant?
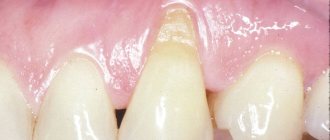
Implant exposure is a fairly common occurrence. More common with two-stage implantation. A characteristic sign is the exposure of the metal rim of the abutment under the prosthesis, resulting in the formation of a black stripe . Usually the defect makes itself felt some time after the operation.
Common causes of complications:
- using an implant with a polished neck that remains above the bone surface after screwing in;
- too thin mucous membrane;
- overtension of the gingival flap;
- temporary crown pressure;
- poor quality oral care after implantation;
- mechanical trauma to the gums (toothbrush, hard food);
- improper formation of the gingival margin;
- subsidence of the bone as a result of long-term use of artificial teeth.
Signs of artificial root rejection
The fact that the implant has not taken root or the osseointegration process is disrupted may be indicated by the persistence of symptoms of inflammation a week after surgery. Pain, redness of the gums, and swelling in the first five days are normal, as is a slight increase in temperature. But if more than 7–10 days have passed after installation, but the listed ailments do not go away, but increase, you need to rush to the doctor. In some cases, the patient only feels the mobility of the structure; there may be no other symptoms.
Sometimes implant rejection does not occur in the first month after installation, but in a delayed period, when it would seem that the rod has acquired a stable position. This can be caused by bacterial processes, prosthetic errors, or injuries.
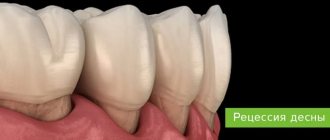
What methods are used to treat recession?
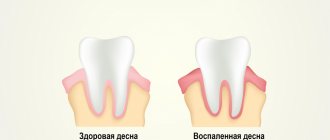
Gum recession is manifested by exposure of the root system. The problem negatively affects the appearance and is fraught with the development of pathologies.
In dental practice, there are two ways to treat recession:
- Elimination of the defect using soft tissue plastic surgery . This allows you to adhere to the two-step technique, as well as prevent the development of the infectious process. However, surgery cannot be avoided. Plastic surgery is performed by augmenting the gums.
- Transition to a one-stage operation protocol. The plug is removed and an abutment is placed in its place. This option does not guarantee the possibility of infection and loosening of the implant, since a two-stage implantation method was initially chosen.
How to identify postoperative complications? Characteristic symptoms of implant rejection
The first thing to know about implant failure is that it does not necessarily start immediately after surgery. It may take months or even years after the implantation of a denture before the first symptoms of rejection appear. However, the first signs that the implant is not taking root may appear during the healing period, which can greatly complicate the diagnosis.
The following symptoms indicate problems with implant healing:
- swelling of the gums and swelling at the site of implantation (may appear during the healing period even if implantation is successful);
- inflammatory process in the gum, change in its color, unpleasant odor from the installation site;
- bleeding at the implant site (possible in the first few days after successful implantation);
- discharge of pus from the gums at the implantation site;
- strong pain.
As you can see, some of the symptoms are characteristic of the normal course of the postoperative period. Therefore, in order not to miss the onset of inflammatory processes and not to start the rejection process, it is important to inform the doctor about all changes in the condition in the postoperative period.
Plastic surgery of soft tissues if a dental implant has come out of the gum
The procedure for correcting the gingival contour and improving the structural and functional state of the periodontium is called gingivoplasty . Allows you to restore the aesthetic appearance of the jaw when implants are exposed in case of recession.
When and in what cases is it carried out?
After implantation, the patient may experience mucosal deficiency and incomplete coverage of the surface of the titanium rod. It looks ugly and causes a deep feeling of discomfort. Plastic surgery of soft tissues is a reasonable way out of this situation. It is indicated if:
- there is a strong tension on the flap;
- the installed crown puts pressure on the gum, blocking its growth around the implant;
- The patient suffered an injury during hygiene procedures or eating food that requires surgical correction.
The procedure has certain risks. Sometimes the doctor has to put a plug on the artificial root. This does not guarantee that infection cannot enter the bone bed. When the rod is exposed, the development of resorption of bone structures is possible.
How is surgery performed if the implant is visible from the gums?
The goal of gingivoplasty is to build up the mucosa to completely cover the surface of the implant. This is done by adding your own tissues from other parts of the oral cavity. The operation is performed by a periodontist under local or general anesthesia, at the patient’s choice.
Before the procedure, a preparatory stage must be carried out, including the elimination of caries, relief of existing inflammatory processes, and removal of tartar.
Extension is carried out:
- in a selected area, usually the palate, a flap of mucous membrane is peeled off;
- applied to the exposed area;
- bone correction is performed if necessary;
- stitches are placed.
Afterwards the graft engraftment stage begins. After 10 days, the sutures are removed, and when tissue fusion is complete, the gum is incised to gain access to the structure and change the former to the abutment.
Possible complications
Gingivoplasty, like any surgical procedure, has its risks. Complications include:
- development of an allergic reaction to the administered anesthetic;
- recurrence of gum recession (requires re-building after 5-6 months);
- swelling of the operated area;
- painful sensations;
- bleeding;
- hematomas.
This is due to the abundant blood circulation of the tissues of the maxillofacial area. Therefore, with the slightest surgical intervention, especially on the lower dentition, severe swelling and bruising appear, which are not as dangerous as they look. After a couple of days their severity decreases, and after a week or two there is no trace left of them.
The appearance of pain in the first hours after the procedure is considered normal. It can be easily managed with analgesics. If the painful sensations increase and do not go away three days after gum growth, then you need to consult a doctor. Perhaps we are talking about the development of a serious pathological process.
Minor bleeding is acceptable in the first hours after the intervention. Intense hemorrhage, in addition to injury to a large vessel, may indicate a blood clotting disorder, which is dangerous. Preoperative examination, including this indicator, is important.
Numbness of the face after the anesthesia wears off is a rare but unpleasant phenomenon. This is a sign of serious nerve damage. Restoring its functions usually takes at least 4 months and requires treatment.
Possible complications
Dental implantation is a complex operation that requires careful preparation. As a rule, complications arise after poor-quality prosthetics or non-compliance with the recommendations of the attending physician. One of the most common problems is exposure of the neck of an adjacent tooth. Normally, it should be covered with gum tissue. Exposing the area between the crown and the root is a reason to contact the dentist. If the necessary measures are not taken in time, the following complications may occur:
- mobility of the dental unit,
- periodontal pockets,
- tooth root caries,
- inflammation of tissues with suppuration,
- fistula on the gum.
Implantation using a one-stage installation method - solving the problems of implant exposure
The one-stage method of installing an artificial tooth is popular due to the immediate aesthetic result. The procedure is carried out in one stage, including the following actions of the doctor:
- examination of the patient for contraindications;
- sanitation of the oral cavity, elimination of existing problematic issues;
- removal of the desired tooth;
- preparing a bone bed for a titanium root;
- screwing in the implant;
- installation of abutment and temporary crown.
Once healing is complete, the temporary prosthesis will be replaced with a permanent one.
How does normal “engraftment” of an implant proceed?
Normally, almost immediately after installation of the implant, the process of fusion with bone tissue begins. This is the same osseointegration that implant surgeons talk about. It occurs in three stages:
- Elementary. Lasts up to four weeks. During this period, loose spongy bone tissue forms around the implant. Chewing loads should be limited for now.
- Intermediate. Takes on average 17 weeks. By the end of this period, all the spaces between the titanium rod and the surrounding bone areas are filled with denser, hard tissue.
- Final. Lasts up to 1.5 years. The root substitute finally fuses with the bone and forms one whole with it.
The implant acquires sufficient stability in the bone even before osseointegration is complete. Approximately three to five months after installation of the artificial root, it can be loaded with a crown.
What to do to prevent receding gums after implant placement
You can avoid unpleasant situations by following simple rules:
- take medications prescribed by the doctor in a timely manner;
- rinse your mouth regularly with antiseptic solutions;
- treat the operated area with care;
- stop smoking;
- do not eat hard, sour, hot, cold foods;
- avoid thermal procedures, such as baths, saunas, hot baths;
- treat sutures with a special ointment prescribed by a doctor;
- brush your teeth twice a day (in the morning - after breakfast, in the evening - before bed);
- use an irrigator, floss.
To identify problem areas in a timely manner, you should visit your dentist periodically.
Provoking factors
Recession is clinically manifested by exposure of the neck of the structure. A black stripe appears in the interaction zone, which can become an entry point for infection.
Pathology develops as a result of medical error or objective factors.
The list of objective factors includes:
- After tooth extraction, the vestibular plate becomes susceptible to resorption. The thinner the plate, the more susceptible the gum tissue is to loss.
- Thickness of the mucous membrane layer. The tissue covering the alveolar ridge bone during unit extraction suffers from recession.
- The degree of resection of reimplant bone. Resorption of bone tissue provokes loss of gum tissue.
The list of subjective factors includes:
- Implant diameter. It is recommended to use structures with a platform diameter of up to 5 mm.
- Position of the rod in the bone. The direction of the implant axis must coincide with the value of natural units.
- Duration of installation of the prosthesis. Complete formation of the gingival level is completed after four weeks. Prosthetics started earlier than the specified period can provoke a recession.
- Failure to maintain the distance between the rods and the outer surface of the cortical bone.
- Contamination of the area of interaction between the implant and periodontium.
- Medical errors during implant fixation, non-compliance with technology.
A patient can provoke the onset of gum recession by his actions:
- Poor care of dentures.
- Smoking and other bad habits.
- Damage to gums when brushing teeth or eating.
Some experts are of the opinion that implants with belts in the area of interaction with the soft shell can provoke recession. However, there is no confirmation of this information.
Existing correction options
The choice of method for correcting the slipped gum margin is determined by the clinical situation. There are three variants of pathology:
- Apical edge migration. The bone volume is maintained in sufficient quantity. The implant is stable.
- Migration with bone deficiency. Stability has been maintained.
- Loss of gum tissue, bone resorption, implant mobility.
The first two clinical situations require periodontal plastic surgery. In the third case, the implant is replaced and tissue deficiency is filled.
What to do if an implant or part of it falls out?
What to do if a tooth implant falls out of your gums? Go to the clinic where the operation took place. The doctor will perform a thorough examination, order an x-ray, and possibly prescribe other types of diagnostics. It is necessary to assess the current state of the bone tissue and, of course, the integrity of the structure.
If you contact us on time, the implant can be saved and the inflammation can be stopped by taking medications and treatment. If the degree of damage is high, reimplantitis may begin, and then the artificial tooth will have to be removed. Re-implantation of the implant will be possible 1-2 months after the course of treatment.