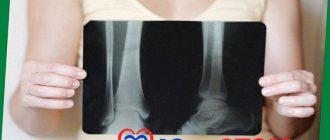
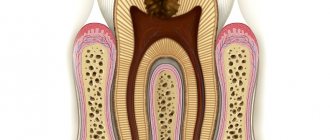
A tooth abscess is an acute infectious process accompanied by the accumulation of pus in the inner or outer surface of the alveolar processes (the area of the bone of the upper and lower jaws in which the tooth sockets are located). A tooth abscess can be periapical—flowing around the apical third of the tooth root—or periodontal—developing inside a periodontal pocket. The main symptom of an abscess is acute pain and swelling of the jaw. Treatment consists of removing purulent exudate and anti-inflammatory treatment of the canals. If the inflammation cannot be stopped, the tooth will have to be removed.
When to see a doctor
Since an abscess is an infectious disease, it has pronounced symptoms. You need to go to a specialist as early as possible. An infection diagnosed in time is easier to treat. Evidence of the spread of infection may include:
- A whitish or reddish swelling on the gum.
- Spread of swelling from the gums to the soft tissues of the face.
- Formation of an ulcer with purulent contents at the site of swelling.
- Severe throbbing pain while brushing teeth or eating.
- The appearance of an unpleasant odor from the mouth, which cannot be eliminated by ordinary daily hygiene products.
- Bitter taste in the mouth.
If there is no treatment and the infection continues to spread, general symptoms will also appear. Body temperature rises, the patient may complain of sleep disturbances, lack of appetite, and depression.
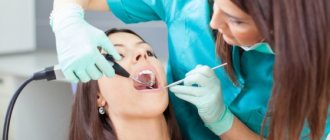
If even some of these symptoms appear, come for a consultation with a dentist at the ARDC clinic. The doctor will conduct a diagnosis and clarify the diagnosis.
Signs of illness
It is almost impossible not to notice the presence of pathology - the symptoms are always very clear. Anyone, even those far from the medical field, can understand that something is wrong with their gums.
- First there is an acute toothache. It becomes more pronounced if you press on the unit, touch it, or knock on it. It intensifies if the patient drinks or eats something hot or cold.
- Soon the gums swell. Even the cheek may swell. This indicates that the inflammation is spreading quickly.
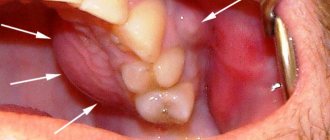
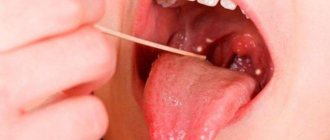
- A bulge forms on the gum. At first it is red or with a bluish tint. But it also happens that it is not there, and pus simply begins to ooze from the gums.
Due to the purulent masses, the patient has an unpleasant taste and a foul odor appears from the mouth. It is not possible to remove it using standard hygiene products - a toothbrush and toothpaste, since pus continues to actively form after brushing your teeth.
An advanced abscess contributes to an increase in body temperature, decreased appetite, and decreased performance. In many patients, the cervical lymph nodes become enlarged.
Why does a tooth abscess develop?
The main cause of abscess development is bacteria. They are always present in the oral cavity, but in order for an infectious process to develop, provoking factors are needed. The development of an abscess can be provoked by:
- Violation of the rules of daily hygiene. Bacteria multiply quickly in the favorable environment of dental plaque. When there are a lot of them, a pathological process develops.
- Dental procedures. During tooth extraction, an antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity is performed. When this treatment is insufficient or the procedure was carried out in violation of antiseptic rules, pathogenic bacteria can penetrate the tissue.
The risk of developing a tooth abscess increases if the patient has a weakened immune system or has systemic diseases, for example, diabetes, cancer. Chronic tonsillitis often provokes the development of a purulent process. This is due to the fact that with chronic inflammation of the upper respiratory tract, there is a focus of infection in the body. It may spread to other areas.
Patients with dental problems are also at risk:
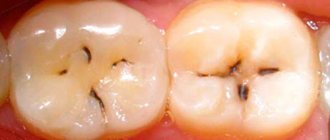
- Caries.
- Mechanical damage to the enamel (chips, cracks).
- Periodontal diseases.
- Gingivitis.
What to do when you have an abscess
What to do if a tooth breaks: immediately seek help from a dentist. When a fistula forms and the purulent contents drain, the person’s well-being improves and the intensity of pain decreases. However, the pathological process, when the lesion is opened independently, continues to progress and can lead to complications: mediastinitis, thrombophlebitis, sepsis, meningitis, etc.
Therefore, it is important to promptly treat inflammatory diseases of teeth and periodontium. How much it costs to treat pulpitis and other pathologies at North-Eastern Dental Center No. 1 can be found on the corresponding page of the official website.
Types of abscess
The type of abscess is determined by its location. Based on this feature, periodontal and periapical types are distinguished. Both can occur in acute or chronic form.
- Periodontal abscess. Develops in the space between the gum and the crown of the tooth. In the acute form there are pronounced symptoms - an abscess on the gum, severe pain when closing the teeth. In the chronic form, such pronounced symptoms are not observed. In case of chronic periodontal abscess of a tooth, a fistula develops at the site of purulent inflammation.
- Periapical abscess. The source of infection is located inside the tooth. Often this type of disease develops as a complication of periodontal disease. The process proceeds as follows. Pus begins to accumulate at the top of the tooth root. If the suppuration is deep and the pus cannot come out, it continues to spread inside the gums, under the mucous membranes. The bone is gradually affected and begins to deteriorate.
Stages of development of gum abscess
| Disease stage | Description |
| Initial | The beginning of inflammation. If the immune system is functioning well, the process may stop on its own. Symptoms are absent or mild. If the immune defense is insufficient, bone or soft tissue begins to melt. Hyperemia of the mucous membrane and discomfort appear. |
| Subacute | The inflammatory process intensifies. Pus accumulates in the pathological area (near the root, inside the periodontal pocket, near the gingival papilla). The pain intensifies. The tooth reacts to irritation. |
| Acute | Progression leads to abscess formation: a cavity with pus forms in the central zone of infiltration. The clinical picture is clearly expressed: the pain is constant, sharp, swelling appears. A lump appears on the surface of the gum, inside of which there is purulent exudate. Inflammation spreads to the submandibular lymph nodes. |
| Chronic | The abscess on the gum spontaneously opens and the contents of the cavity come out. Signs of acute inflammation subside. |
After tooth extraction
Tooth extraction is a dental operation during which the gums are injured. If antiseptic rules have been violated or the patient does not provide the necessary postoperative care, infection can enter the wound. Bacteria will multiply quickly. Suppuration forms. If there is no treatment, the abscess affects the soft tissue.
Suppuration as a result of medical error after removal is rare. At the ARDC clinic, dentists use modern equipment, consumables, and medications. You can be confident in the quality of the procedure and compliance with the treatment protocol.
Improper postoperative care is a more common cause of abscess after removal. After the operation, the dentist must give recommendations on how to care for the wound. Careful adherence to all these rules will reduce the risk of suppuration at the site of the extracted tooth.
Complications that a gum abscess can cause
Without treatment of the disease and inadequate medical care, complications may develop. Adverse consequences arise due to the spread of inflammation to neighboring organs and tissues, as well as the spread of infection throughout the body with the formation of secondary septic foci. The most common pathological conditions that occur are:
- lymphadenitis - infection of the lymph nodes;
- sinusitis - infection in the maxillary sinuses;
- periostitis of the jaw (inflammation of the periosteum);
- osteomyelitis of the jaw bones (destruction of bone tissue due to purulent-necrotic melting of osteocytes);
- phlegmon - diffuse odontogenic inflammation of soft tissues, accompanied by progressive swelling of the face;
- destruction of the alveolar processes with significant loosening of teeth or their loss;
- peri-implantitis with implant rejection;
- sepsis.
Purulent lesions of soft periodontal tissues are always accompanied by general intoxication of the body. The temperature rises and chills appear. There is a headache, tachycardia, and the pulse quickens. Pain relief with medications brings short-term relief, but symptoms return after the medication wears off.
Prevention and treatment
Abscess prevention is simple. It is enough to follow the rules of daily oral hygiene and regularly come for examinations to the dentist.
If an abscess does form, it should be treated by a doctor. Even if the abscess opened on its own. Usually, after the pus is released, the pain goes away, and the person considers the problem solved. But even in this case, there is a risk that the infection continues to develop deep in the soft tissues. A visit to the dentist is a must.
Various methods are used to treat an abscess:
- Therapeutic antibacterial treatment. Antibiotics are not always used. Which drugs will best cope with the problem depends on the clinical picture. Usually in the early stages you can do without potent drugs.
- Surgical intervention. The surgeon opens the abscess and cleans the abscess cavity. After this, anti-inflammatory therapy is mandatory. It is necessary in order to eliminate the risk of inflammation.
Lack of qualified medical care for an abscess can lead to the development of serious complications. Suppuration is fraught with the development of tooth mobility, their loss, and bone destruction. If any alarming symptoms appear, contact our clinic. The dentist will make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Breakthrough of purulent masses with an abscess
Often the “bump” grows, swells, and then bursts. Then the pus inside it flows out. After this, the pain goes away and the patient’s well-being improves significantly. But this does not mean that the problem is a thing of the past. It should be remembered that with an abscess, fistula tracts often form. They serve as a protective reaction of the body - they ensure the unhindered outflow of pus and prevent the inflammatory process from further progressing.
The disease may recur. Purulent exudate is able to penetrate into the tissue surrounding the tooth. Therefore, even if the “bump” has burst, you still need to make an appointment with the dentist so that the doctor can conduct an examination and tell you what to do to prevent the disease from returning.
Basic methods of treating abscess
After carrying out all diagnostic measures, the dentist determines the treatment tactics necessary in a particular clinical case. Abscess therapy is complex, including eliminating the cause of the pathology, alleviating symptoms and accelerating tissue regeneration. If the patient turned to dentistry in the early stages of the development of the disease, a conservative method can alleviate the condition. During this procedure, tissues affected by caries are removed and the canals of the tooth that are causing the abscess are cleaned. The source of inflammation is washed with antiseptic solutions, a course of antibiotics, painkillers, anti-inflammatory and hyposensitizing agents is prescribed.
With a more pronounced inflammatory process and the development of signs of suppuration, it is necessary to use a surgical method of treatment. After opening the abscess, conditions are created for the unhindered exit of exudate from the lesion and the gradual subsidence of symptoms. Rinses and mouth baths with an antiseptic effect speed up healing. Another method of surgical treatment of an abscess is tooth extraction. After extraction, the purulent contents of the abscess are released through the hole, which is cleaned and treated with antimicrobial agents.
At the Dentistry Academy Dent, located in the south-west of Moscow, abscess treatment is carried out using modern methods of high efficiency. The clinic is equipped with advanced dental equipment and materials, the quality of which is recognized throughout the world. A specialist with many years of experience in the successful treatment of inflammatory and destructive gum diseases, after a thorough diagnosis, will create an individual treatment package and give professional recommendations.