Author of the article:
Soldatova Lyudmila Nikolaevna
Candidate of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Clinical Dentistry of the St. Petersburg Medical and Social Institute, Chief Physician of the Alfa-Dent Dental Clinic, St. Petersburg
Candidiasis or, otherwise, thrush is an infectious disease, the main cause of which is infection with Candida fungi. These fungi belong to the same species as yeast and are part of the natural microflora of the vast majority of healthy people. The maximum concentration of these opportunistic microorganisms is observed in the intestines, nasopharynx, and vagina; Some fungi can also be found on the surface of the skin.
In a normal, healthy state of the body, the fungus does not cause any unpleasant symptoms. However, when the immune system is weakened and other provoking factors appear, Candida actively multiplies, resulting in discomfort, itching, burning and other manifestations of thrush. This disease can affect various tissues and organs; Candidiasis of the oral mucosa is also common.
Most often, infants suffer from this disease: according to statistics, up to 20 percent of children under the age of one year have suffered from candidiasis at least once. About 10 percent of people over 60 also suffer from symptoms of this infection. It occurs more often in women than in men; very often, signs of the disease appear in smokers. There are many other factors that contribute to the development of candidiasis in the mouth.
Causes of oral candidiasis
The main reason for the occurrence is a decrease in immune status, as a result of which the uncontrolled proliferation of microflora begins. Reduced immunity is observed in older people and infants, in patients suffering from HIV, AIDS and other diseases associated with immunodeficiency, in those who regularly expose the body to excessive stress, neglect the rules of a healthy diet and violate work and rest patterns. Risk factors include reasons such as:
- Use of medications.
Taking antibiotics, immunosuppressants (drugs that suppress the immune system) and some other medications leads to disruption of the immune system and the natural balance of microflora in the body. Oral contraceptives, which affect hormonal levels, have a similar effect. - Pregnancy.
During pregnancy, a sharp and significant change in hormonal levels occurs, which can lead to a surge in the activity of pathogenic and opportunistic microflora. - Radiation and chemotherapy.
Often occurs in patients undergoing drug and radiological treatment for cancer. - Injuries to mucous membranes.
Violation of the integrity of the mucous membranes leads to loss or deterioration of the barrier function, as a result of which the fungus enters deep into the tissues, causing inflammation and other symptoms. Small, but constantly recurring injuries are especially dangerous - for example, when wearing incorrectly fitted dentures or braces. - Overwork and stress.
Prolonged stress of physical and mental forces leads to a deterioration in the protective function of the body. Similar consequences are caused by hypothermia or overheating, regular lack of sleep, insufficient, excessive or simply unbalanced nutrition, abuse of alcohol, nicotine, and narcotic substances. - Hypo- and vitamin deficiency.
May be caused by a lack of nutrients, in particular vitamins B and C. - Somatic diseases.
Frequent companions of candidiasis include tuberculosis, dysbacteriosis and other pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, diseases of the adrenal glands and other endocrine glands. Candidiasis is a contagious disease. A large number of pathogenic microorganisms are transmitted through kissing and sexual contact, through the use of shared dishes, towels and other household items. Infection can also occur during childbirth (vertical transmission from mother to fetus). In addition, there is a risk of infection through contact with infected pets.
Complication
With timely treatment, candidiasis does not cause any particular harm to health. But the symptoms of candidiasis can cause a lot of discomfort. Long-term, it can lead to damage to other organs, most often the urethra, bladder and kidneys. In particularly severe cases, the progressive disease can affect the reproductive organs, leading to infertility in both men and women. But candidiasis poses the greatest danger to pregnant women, because... the risk of fetal damage is very high.
Types of disease
The clinical picture of oral candidiasis is classified:
- For clinical and morphological.
- With the flow.
- By localization.
Clinical and morphological is divided into:
- Hyperplastic.
- Erosive-ulcerative.
- Pseudomembranous.
- Atrophic.
The clinical picture, classified according to the course, is divided into:
- Chronic.
- Spicy.
By localization:
- Cheilitis.
- Gingivitis.
- Glossitis.
- Stomatitis.
- Tonsillitis, etc.
Based on the clinical picture, oral candidiasis comes in several types:
- Chronic hyperplastic.
- Candida infection.
- Chronic atrophic.
- Acute pseudomembranous.
- Chronic pseudomembranous.
- Acute atrophic.
Menu (Power Mode)
Based on the principles of proper nutrition for candidiasis , you can create a varied menu. You need to alternate protein dishes daily, supplementing them with vegetable side dishes.
Breakfast usually consists of porridge cooked in water, vegetable salad or stewed vegetables, cottage cheese or omelet, and a decoction of herbs. Try to prepare vegetable soups, borscht and cabbage soup, including permitted vegetables in the first courses.
For main courses, choose boiled chicken, meat cabbage rolls, baked meat or fish, meat and fish meatballs and cutlets. As a side dish you should use stewed or fresh vegetables and occasionally porridge. Limiting salt and sugar certainly affects the taste of food. For dinner you can make cheesecakes and cottage cheese casserole. All snacks should consist of yogurt or biokefir; you should also drink rosehip infusion, unsweetened compotes, fruit drinks, and herbal teas during the course.
Symptoms
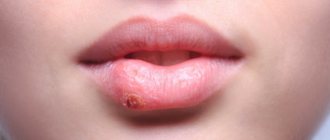
Infection of the oral mucosa by Candida fungus can take various forms, each of which has its own characteristics of symptoms. The most common forms of the disease are candidal angulitis, glossitis, cheilitis, and stomatitis. There are both acute and chronic forms of the disease.
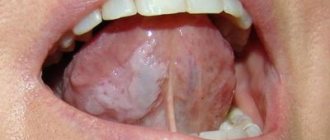
- Pseudomembranous acute candidiasis is the most common form and most often occurs in infants and the elderly. This form is characterized by the appearance of severe swelling and hyperemia (redness) of the mucous membranes. In addition, a characteristic whitish coating forms on the surface of the lips, palate, back of the tongue and the inside of the cheeks. If the plaque is scraped off, the surface of the mucous membrane underneath will be macerated (softened) or ulcerated and bleeding. In this case, patients complain of pain, burning or itching in the mouth; Eating becomes very difficult. Very often the process spreads to the esophagus and pharynx.
- Acute atrophic candidiasis of the oral mucosa usually develops due to the lack of adequate treatment. The upper part of the mucous membranes (epithelium) is exfoliated, the mucous membrane becomes thin, red or, on the contrary, swollen. The patient’s tongue and the corners of the lips also acquire a bright red color; the papillae on the tongue atrophy and smooth out. The plaque is absent or is found only in hard-to-reach places.
- Hyperplastic chronic candidiasis is characterized by the formation of a large number of papules and plaques of irregular or round shape. They are located close to each other on the mucous membrane of the tongue and cheeks and often become soldered and fused. Around each such formation there is a thin rim of reddened, inflamed tissue. It is difficult to scrape off or otherwise remove such a plaque. The oral cavity becomes dry and rough; When chewing, speaking, and even at rest, patients experience significant discomfort and pain. It should be noted that this disease most often affects men over 30 years of age.
The main cause of the chronic atrophic type is constant injury to the mucous membranes, for example due to wearing a prosthesis. Symptoms of the disease are localized in the affected area. Redness of the mucous membrane occurs (often along the contour of the lesion), plaque forms, pain and burning occur, and the membranes become dry.
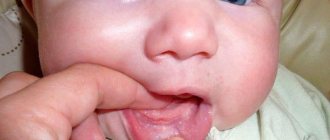
How does the disease manifest in children?
In children, the disease occurs in an acute form and is accompanied by the appearance of redness and swelling in the oral mucosa. The child sleeps poorly, may have no appetite, and becomes tearful.
The disease can occur in children for the following reasons:
- Weakening of the immune system.
- Infection during breastfeeding.
- Transmission of the fungus during childbirth.
- Infection through household items.
If the disease is not diagnosed and treated in a timely manner, a whitish coating resembling cottage cheese will soon appear in the child’s mouth, and in an advanced stage, ulcers will appear, which are accompanied by bleeding and cause severe pain in children.
Diagnostics
To make an accurate diagnosis, a combination of several methods is used - from a simple examination and questioning of the patient for complaints to laboratory methods, such as culture, microscopic examination of biomaterial, analysis of the degree of contamination of the oral cavity with fungal mycelium.
Oral candidiasis is accompanied by a number of characteristic external signs, in particular the formation of plaque, bad breath, ulceration and hyperemia of the mucous membranes. However, laboratory methods make it possible to accurately determine the type of pathogen and exclude the possibility of a secondary infection, which may affect the nature and duration of treatment.
Differential diagnosis is used to separate cases of candidiasis from aphthous stomatitis, leukoplakia, lichen ruber, streptococcal infection and other infectious pathologies of the oral cavity.
Advantages and disadvantages
| pros | Minuses |
|
|
How to treat oral candidiasis?
Treatment is carried out using local and general, specific and symptomatic remedies. Among the main goals of therapy are the elimination of foci of infection in the oral cavity (sanitation), treatment of diseases that accompany candidiasis and are risk factors, and stimulation of the body's defenses. The total duration of treatment is usually at least 7-10 days.
As a means of local therapy, rinses are used - using solutions of boric acid, soda, sodium tetraborate. For a longer and more effective effect, such products can be used in the form of applications - moistening a cotton swab or bandage with the solution.
Nystatin for oral candidiasis is used to combat the main cause of the disease - a fungal infection. Treatment of candidiasis in the mouth may also include the use of other antimycotic (antifungal) drugs - for example, levorin ointment. The best effect is achieved by using several drugs, alternating them for several days.
Antifungal drugs are also prescribed for systemic therapy - in this case, medications for oral candidiasis and other infections such as Lamisil, Diflucan, Levarin, Nizoral, etc. are taken orally. In the most severe cases of the disease, the treatment regimen includes taking immunomodulatory drugs, as well as the use other agents that have a stimulating effect on the immune system and help strengthen the body’s own defenses.
An equally important task is to protect against additional fungal and bacterial infections that can join the Candida infection and complicate the course of the disease. For this purpose, rinses with antiseptic solutions - fucorcin, iodinol and others.
As an alternative, you can use ASEPTA antiseptic mouth rinse, which contains the active ingredients chlorhexidine and benzydamine. Both of these substances have broad antimicrobial effects. Regular use of ASEPTA rinses also has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect and helps not only eliminate unpleasant symptoms, but also reduce the risk of complications.
Authorized Products
- Protein low-fat foods (fish, meat, poultry). Dishes are prepared boiled or baked. cabbage rolls, stuffed zucchini, meat casseroles with vegetables.
- You can eat non-starchy vegetables - they are boiled, stewed or baked. Most vegetables should be used fresh. Season vegetable dishes with cloves, cinnamon, garlic and bay leaves, which have an antifungicidal effect.
- Non-starchy vegetables include broccoli, eggplant, Chinese cabbage, beet tops, Brussels sprouts, watercress, cucumbers, spinach, celery, sorrel, and tomatoes. Moderately starchy - turnips, carrots, zucchini. Zucchini, pumpkin, beets, potatoes, Jerusalem artichoke, radishes, squash and radishes contain a large amount of starch, so they are excluded from the diet.
- It is better to eat beets, carrots and pumpkin raw, since when these vegetables are cooked, their sugar content increases, and this is not desirable for candidiasis. Eliminate potatoes, and if you cannot do without them, then you need to soak them before cooking to reduce the starch content. Sauerkraut populates the intestines with microorganisms and should be present in the diet. To salads you need to add seaweed and sprouted grains, which are immunostimulants.
- It is better to use vegetables rather than porridge as a side dish for meat and fish. Porridges (buckwheat, oatmeal and brown rice) should be a separate meal, but they should be consumed limited, since they are sources of carbohydrates, albeit complex ones.
- Natural yogurt and biokefir are allowed among dairy products. These are useful products, since lactic acid bacteria inhibit fermentation in the intestines and exhibit an antifungal effect. You should choose yoghurts from baby food (unsweetened, without dyes or preservatives). You can eat cottage cheese because it prevents the activity of pathogenic flora.
- The therapeutic effect of fermented milk products is associated not only with the presence of live bacteria, but also with the organic acids contained (lactic, phosphoric, citric), which acidify the intestinal pH, and this has a probiotic effect.
- Eliminate all yeast baked goods and replace the bread with yeast breads. You can bake them yourself from whole grain flour, adding bran and flax seeds.
- Choose unsweetened fruits: lemon, orange, grapefruit, currants, cranberries, lingonberries, blueberries, pomegranate. Cranberries and viburnum are the best berries in the fight against candidiasis. The polyphenols they contain stop the growth of yeast.
- For drinks, we recommend rosehip decoction, decoctions of cranberries, lingonberries, fruit drinks from these berries, decoctions and teas from herbs and dried berries - chamomile, alfalfa, plantain, rose hips, rowan, black currant, hawthorn, rowan, oregano. Green tea is allowed with restrictions. Carrot juice, pomegranate juice, oat broth, water with lemon juice are useful for this disease.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| spicy vegetables | 2,8 | 0,5 | 5,3 | 36 |
| vegetables legumes | 9,1 | 1,6 | 27,0 | 168 |
| artichoke | 1,2 | 0,1 | 6,0 | 28 |
| cabbage | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,7 | 27 |
| Brussels sprouts | 4,8 | 0,0 | 8,0 | 43 |
| sauerkraut | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,4 | 19 |
| cabbage | 1,2 | 0,2 | 2,0 | 16 |
| green onion | 1,3 | 0,0 | 4,6 | 19 |
| bulb onions | 1,4 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 41 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| parsley | 3,7 | 0,4 | 7,6 | 47 |
| beet tops | 2,1 | 0,5 | 5,5 | 17 |
| celery | 0,9 | 0,1 | 2,1 | 12 |
| asparagus | 1,9 | 0,1 | 3,1 | 20 |
| dill | 2,5 | 0,5 | 6,3 | 38 |
| garlic | 6,5 | 0,5 | 29,9 | 143 |
| spinach | 2,9 | 0,3 | 2,0 | 22 |
| sorrel | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2,9 | 19 |
Fruits | ||||
| oranges | 0,9 | 0,2 | 8,1 | 36 |
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
| lemons | 0,9 | 0,1 | 3,0 | 16 |
| plums | 0,8 | 0,3 | 9,6 | 42 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Berries | ||||
| cowberry | 0,7 | 0,5 | 9,6 | 43 |
| strawberry | 0,8 | 0,4 | 7,5 | 41 |
| cranberry | 0,5 | 0,0 | 6,8 | 26 |
| sea buckthorn | 1,2 | 5,4 | 5,7 | 82 |
| Rowan | 1,5 | 0,1 | 10,9 | 50 |
| blueberry | 1,1 | 0,4 | 7,6 | 44 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| oat groats | 12,3 | 6,1 | 59,5 | 342 |
| wheat bran | 15,1 | 3,8 | 53,6 | 296 |
| brown rice | 7,4 | 1,8 | 72,9 | 337 |
| brown rice | 6,3 | 4,4 | 65,1 | 331 |
Bakery products | ||||
| whole grain bread | 10,1 | 2,3 | 57,1 | 295 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| carnation | 6,0 | 20,1 | 27,0 | 323 |
| cinnamon | 3,9 | 3,2 | 79,8 | 261 |
| Bay leaf | 7,6 | 8,4 | 48,7 | 313 |
Dairy | ||||
| kefir | 3,4 | 2,0 | 4,7 | 51 |
| acidophilus | 2,8 | 3,2 | 3,8 | 57 |
| yogurt | 4,3 | 2,0 | 6,2 | 60 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese | 17,2 | 5,0 | 1,8 | 121 |
Meat products | ||||
| beef | 18,9 | 19,4 | 0,0 | 187 |
| veal | 19,7 | 1,2 | 0,0 | 90 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Bird | ||||
| chicken | 16,0 | 14,0 | 0,0 | 190 |
| turkey | 19,2 | 0,7 | 0,0 | 84 |
Eggs | ||||
| chicken eggs | 12,7 | 10,9 | 0,7 | 157 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| seaweed | 0,8 | 5,1 | 0,0 | 49 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| peasant unsalted butter | 1,0 | 72,5 | 1,4 | 662 |
| corn oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
| olive oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| sunflower oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| lingonberry juice | 0,1 | 0,0 | 10,7 | 41 |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| carrot juice | 1,1 | 0,1 | 6,4 | 28 |
| tomato juice | 1,1 | 0,2 | 3,8 | 21 |
| pumpkin juice | 0,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 38 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Disease prevention
Preventive measures are aimed at improving the condition of the microflora. These include:
- Proper oral hygiene.
- A thoughtful diet with a high amount of protein foods and reduced consumption of foods containing glucose.
- Quitting smoking and alcoholic beverages.
- Timely examination by the attending dentist for the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of the disease.
- Avoid taking medications, such as antibiotics, without first consulting your doctor.
- If the patient has dentures, then one of the preventive measures will be their regular treatment in a special solution.
Sources:
- The role of anti-inflammatory rinse in the treatment of periodontal diseases (L.Yu. Orekhova, A.A. Leontyev, S.B. Ulitovsky) L.Yu. OREKHOVA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department; A.A. LEONTIEV, dentist; S.B. ULITOVSKY, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof. Department of Therapeutic Dentistry of St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova
- Report on clinical trials to determine/confirm the preventive properties of commercially produced personal oral hygiene products: mouth rinse "ASEPTA PARODONTAL" - Solution for irrigator." Doctor of Medical Sciences Professor, Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation, Head. Department of Preventive Dentistry S.B. Ulitovsky, doctor-researcher A.A. Leontiev First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after academician I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry.
- Study of the clinical effectiveness of treatment and prophylactic agents of the Asepta line in the treatment of inflammatory periodontal diseases (A.I. Grudyanov, I.Yu. Aleksandrovskaya, V.Yu. Korzunina) A.I. GRUDYANOV, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Prof., Head of Department I.Yu. ALEXANDROVSKAYA, Ph.D. V.Yu. KORZUNINA, asp. Department of Periodontology, Central Research Institute of Dentistry and Maxillofacial Surgery, Rosmedtekhnologii, Moscow
Fully or partially limited products
- Products containing additives and preservatives that can disrupt the balance of microflora.
- Eliminate all types of simple carbohydrates and products containing fructose, galactose, sorbitol, glucose, maltose. Fruit juices and sweet fruits should not be consumed.
- Use caution with nuts and dried fruits, which may contain invisible mold, and dried fruits may be high in fructose.
- Products containing yeast (kvass, baked goods and beer) are excluded. It is better not to eat grapefruits, lemons, pineapples, oranges, or tomatoes for a month, as they create an alkaline environment favorable for the growth of fungi.
- You should not consume all products that have an irritating effect: mayonnaise, ketchup, hot seasonings, horseradish, vinegar, mustard, salty and pickled foods, canned food and smoked meats. Mushrooms and blue cheeses are prohibited.
- Avoid fatty pork, duck and goose meat, fatty and smoked fish, and canned fish. Remember that fried foods promote the growth of yeast.
- From drinks you should exclude strong coffee and tea, beer, sweet juices, kvass, sweet water with carbonation and alcohol - all of them are provocateurs of candidiasis infection.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| canned vegetables | 1,5 | 0,2 | 5,5 | 30 |
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| potato | 2,0 | 0,4 | 18,1 | 80 |
| corn | 3,5 | 2,8 | 15,6 | 101 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| canned cucumbers | 2,8 | 0,0 | 1,3 | 16 |
| squash | 0,6 | 0,1 | 4,3 | 19 |
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| turnip | 1,5 | 0,1 | 6,2 | 30 |
| beet | 1,5 | 0,1 | 8,8 | 40 |
| canned tomatoes | 1,1 | 0,1 | 3,5 | 20 |
| Jerusalem artichoke | 2,1 | 0,1 | 12,8 | 61 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
Fruits | ||||
| avocado | 2,0 | 20,0 | 7,4 | 208 |
| pineapples | 0,4 | 0,2 | 10,6 | 49 |
| oranges | 0,9 | 0,2 | 8,1 | 36 |
| watermelon | 0,6 | 0,1 | 5,8 | 25 |
| pears | 0,4 | 0,3 | 10,9 | 42 |
| melon | 0,6 | 0,3 | 7,4 | 33 |
| figs | 0,7 | 0,2 | 13,7 | 49 |
| tangerines | 0,8 | 0,2 | 7,5 | 33 |
Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
| marinated mushrooms | 2,2 | 0,4 | 0,0 | 20 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| raisin | 2,9 | 0,6 | 66,0 | 264 |
| dried apricots | 5,2 | 0,3 | 51,0 | 215 |
| dried apricots | 5,0 | 0,4 | 50,6 | 213 |
| dates | 2,5 | 0,5 | 69,2 | 274 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| corn grits | 8,3 | 1,2 | 75,0 | 337 |
| white rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
Bakery products | ||||
| bread | 7,5 | 2,1 | 46,4 | 227 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| cake | 3,8 | 22,6 | 47,0 | 397 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| yeast | 12,7 | 2,7 | 0,0 | 75 |
| ketchup | 1,8 | 1,0 | 22,2 | 93 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
| sugar | 0,0 | 0,0 | 99,7 | 398 |
| soy sauce | 3,5 | 0,0 | 11,0 | 58 |
| vinegar | 0,0 | 0,0 | 5,0 | 20 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk | 3,2 | 3,6 | 4,8 | 64 |
Meat products | ||||
| pork | 16,0 | 21,6 | 0,0 | 259 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
Alcoholic drinks | ||||
| beer | 0,3 | 0,0 | 4,6 | 42 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| cola | 0,0 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 42 |
| coffee | 0,2 | 0,0 | 0,3 | 2 |
| lemonade | 0,0 | 0,0 | 6,4 | 26 |
| Pepsi | 0,0 | 0,0 | 8,7 | 38 |
| sprite | 0,1 | 0,0 | 7,0 | 29 |
| black tea | 20,0 | 5,1 | 6,9 | 152 |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| apricot juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,0 | 38 |
| Orange juice | 0,9 | 0,2 | 8,1 | 36 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||