Tooth abscess: what is it - symptoms and treatment
A dental abscess is an acute infectious pathology characterized by a clearly limited accumulation of pus in the root area. The purulent process is often a dangerous complication of periodontitis, periostitis, and other dental diseases. The lack of timely treatment threatens with adverse consequences not only for the affected segment, but also for the entire body. In Moscow, dental services are provided by the Center for Aesthetic Dentistry near the Otradnoye metro station. Our doctors will quickly and efficiently help eliminate any problem with sore teeth and gums.
The dangers of treating periodontitis at home
The desire of some people to avoid visiting the dental office by any means and continue to endure pain cannot be explained. At the same time, patients persistently practice self-medication, search for recipes on the Internet, rinse their mouths with herbs and smear their sore teeth with homemade compounds of dubious content.
Unfortunately, none of the diseases mentioned in the article can be treated at home. Any method that has been proven over the years, which refers to grandmother’s recipes, will not heal, but will only ease the pain and help the outflow of purulent contents. Remember, the use of this or that non-traditional method of treatment must obtain the approval of a doctor.
Painkillers are also only allowed in limited quantities. Many drugs have a strong and negative effect on the liver and gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, it is unacceptable to constantly relieve pain with pills. And heating a sore tooth, trying to reduce the level of discomfort, is strictly prohibited!
Taking self-prescribed antibiotics will not be successful, because the drug is not able to penetrate into the root canals. It will also not be possible to disinfect and eliminate the source of inflammation by rinsing your mouth. In addition to the warnings voiced, let us remind you that the pathogenic microflora of carious tissues is extremely resistant to drugs, so it cannot be destroyed by taking drugs; drilling is required.
It is better to direct all unspent energy to the prevention of dental diseases. Choosing the right toothbrush, getting into the habit of flossing, and getting regular professional teeth cleanings at your doctor's office are the foundations of oral health.
Repeated endodontic treatment of tooth canals for pulp inflammation
Cervical caries on the front teeth: causes and treatment
Root canal treatment for chronic periodontitis
Restoration of tooth enamel, price, drugs
Treatment of tooth enamel erosion, causes, photos, price
Retreatment of tooth canals before prosthetics, with granuloma, cyst and aching pain
Mistakes and complications in the treatment of dental pulpitis
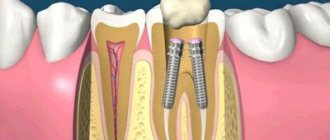
What is a tooth abscess
An abscess in dentistry is an inflammatory process accompanied by the formation of a cavity with pus near a segment or its root. The abscess on the root of the tooth is surrounded by a dense connective tissue capsule, separating it from healthy tissue. Pyogenic bacteria penetrate into the unit through chips, cracks, and carious cavities.
During their life, microbes produce toxins that irritate the pulpal nerve receptors, which causes pain. In addition, toxic products of pathogenic flora increase vascular permeability, resulting in soft tissue swelling.
There are three main types of abscess:
- Periapical - pus accumulates at the root of the tooth (near its apex). A hilar abscess is formed due to an infectious lesion of the pulp. The etiological factor is untreated caries or periodontitis. The progressive inflammatory process spreads to the periosteum and surrounding soft tissue with the formation of a fistula and purulent lump on the gum.
- Periodontal - the focus is located inside the periodontal pockets. The cause is periodontitis. The pulp remains intact, and the infection is localized between the gum and the alveolar ridge.
- Desnevoy. Gum abscess is a purulent formation in the area of the gingival papillae between the segments.
Classification of abscess in dentistry
Doctors say there are three types of tooth abscess:
- Desnev. Only the soft tissues of the mouth are damaged. But, if the disease is started, the periodontal ligaments and periosteum will be drawn into the inflammatory process. Then flux develops.
- Periapical. The pulp is affected. If treatment is not carried out in a timely manner, you will have to perform depulpation or, even worse, tear out the affected unit. More often, this type of disease is diagnosed in children with primary occlusion, which is why dentists have to remove a preschooler’s incisors, canines and molars without waiting for their natural replacement by molars.
- Periodontal. The abscess has a destructive effect on the root, so the tooth becomes loose and falls out prematurely.
The main danger of a purulent tooth abscess is that the pus that has accumulated inside the tumor can penetrate into the blood. Then a general intoxication of the human body will occur. Internal organs, bones, and brain come under attack. A person who ignores the presence of an abscess may develop meningitis, sepsis, and even die.
Why does a tooth fester?
Let's look at why pus forms in teeth. The causes of the pathology can be:
- mechanical damage to the oral mucosa;
- dental diseases of an infectious nature (caries, pulpitis, periodontitis, periodontitis, gingivitis, etc.);
- hematogenous spread of microbes from other foci of infection in the body (sinusitis, pneumonia, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, adnexitis, etc.);
- maxillofacial injuries accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the segment;
- insufficient oral hygiene;
- Iatrogenic causes associated with the introduction of bacteria during dental treatment.
There are risk factors, the presence of which increases the likelihood of pathology: smoking, decreased body defenses, hypothermia, chronic stress. Timely treatment of tooth root periodontitis and other dental diseases reduces the likelihood of an abscess.
Causes of granuloma
What causes dental granuloma? Among the main factors provoking the formation of a focus of inflammation, the following should be highlighted:
- treatment of pulpitis was carried out poorly (for example, tissues affected by caries were not completely removed);
- the dentist filled the root canals in violation of the rules of asepsis and antisepsis;
- the tooth was injured directly due to damage to the maxillofacial area, unsuitable orthodontic design or for other reasons.
Symptoms of gum abscess
The main symptom of the disease is pain. It has a different character (aching, pulsating, acute), is constant or occurs periodically under the influence of stress factors (cold, heat, sour, sweet foods). The pain is often worse when chewing. It can be local or spread to neighboring teeth, ears, eyes. In addition, with an abscess there are other clinical manifestations:
- hyperemia of soft tissues around the affected segment;
- swelling of the inflammation zone;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- foul odor;
- mobility and change in the natural color of the segment;
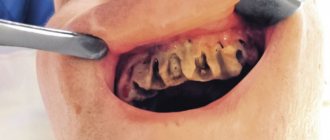
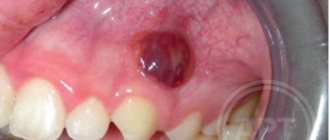
- the presence of an ulcer on the gum with purulent discharge;
- enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes;
- facial deformation due to swelling;
- hyperthermia, lethargy, sleep disturbance.
What to do when you have an abscess
What to do if a tooth breaks: immediately seek help from a dentist. When a fistula forms and the purulent contents drain, the person’s well-being improves and the intensity of pain decreases. However, the pathological process, when the lesion is opened independently, continues to progress and can lead to complications: mediastinitis, thrombophlebitis, sepsis, meningitis, etc.
Therefore, it is important to promptly treat inflammatory diseases of teeth and periodontium. How much it costs to treat pulpitis and other pathologies at North-Eastern Dental Center No. 1 can be found on the corresponding page of the official website.
How to treat a tooth abscess
Treatment of a tooth abscess is aimed at eliminating the infectious process and relieving pain. A comprehensive program may include the following activities:
- Opening and draining the lesion. An incision is made on the gum, a drainage is installed through which the pus can freely come out. The drainage system is installed for several days. During this period, the patient is prescribed rinses with antiseptics and saline solutions.
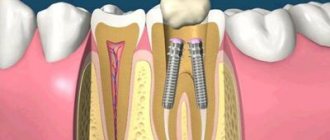
- Endodontic treatment. It involves removing the pulp, treating the root canals with medications and filling them.
- Excision of the root apex. Surgical intervention is performed when the source of infection is located in the periapical area. The surgeon cuts the gum and removes the abscess along with the affected part of the root. The segment itself is preserved.
- Removing a unit. The need for tooth extraction occurs when there is significant destruction of the tooth.
- Therapy with broad-spectrum antibiotics.
- Restoration of the coronal part with a filling or orthopedic construction.
Pus in the gums with periodontitis -
Very often, the patient’s complaints that his gums near the tooth are festering are not associated with inflammation at the apex of the tooth root during periodontitis, but with the formation of periodontal pockets in local or generalized forms of periodontitis. With periodontitis, there is destruction of the attachment of the gingival margin to the necks of the teeth, destruction of the alveolar bone around the teeth, as well as periodontal fibers, with the help of which the tooth is attached to the bone tissue.
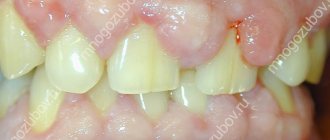
All this leads to the formation of so-called periodontal pockets between the gum and the surface of the roots of the teeth (Fig. 14). They create good conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria and the development of chronic inflammation. When one of the periodontal pockets becomes too deep, this can lead to disruption of the discharge of inflammatory serous-purulent exudate through the lumen of the pocket. As a result, an abscess forms in the projection of the periodontal pocket on the gum, which dentists call the term “periodontal abscess” (Fig. 15-16).
You can immediately suspect that gum swelling is associated with periodontitis, and not with periodontitis, if the tooth is completely intact (i.e., externally healthy and does not have a filling, crown or caries), if it has mobility, and mobility was present in this tooth and before the gums become suppurated, and also if, with slight gentle pressure on the abscess, pus comes out from under the gums (as in Fig. 16).
The differences between local and generalized periodontitis are that they are caused by completely different reasons and, accordingly, the treatment will also be different. With local periodontitis, the inflammatory process occurs only in the area of 1-2 teeth - due to exposure to a traumatic factor. For example, a pocket may appear as a result of trauma to the gum margin by the overhanging edge of a filling or crown. The cause may also be the premature closure of several teeth, which leads to chewing overload and destruction of the bone tissue around them.
But with chronic generalized periodontitis, gum suppuration occurs for other reasons. You can immediately suspect this form of periodontitis if you have symptoms of bleeding and pain when brushing your teeth, swelling, redness or bluishness of the gum margins in the area of most teeth. The cause of generalized periodontitis is soft microbial plaque and hard tartar, which accumulate on the teeth as a result of insufficient oral hygiene.
Bacteria in plaque and tartar produce toxins and various pathogens that trigger an inflammatory reaction in the gums. With prolonged inflammation, first the dental-gingival attachment is destroyed, and then the periodontal fibers and bone tissue around the teeth are destroyed. With this form of periodontitis, pockets are found in almost all teeth, and not just in 1-2 (as with local periodontitis). When the outflow of inflammatory serous-purulent exudate in one of the pockets is disrupted, a periodontal abscess is formed in the gums.
Treatment of local periodontitis –
Based on the examination, the identified amount of tooth mobility, probing the depth of the periodontal pocket and analysis of the x-ray, the doctor will determine the possibility of saving the tooth and the algorithm for further treatment.
If the tooth can be saved, then the first thing to do in case of local periodontitis is to eliminate the impact of the traumatic factor. This means that you need to remove the overhanging edge of the filling or crown, and selectively grind the contacts of the chewing surface of the causative tooth and its antagonists. Next, under anesthesia, the periodontal abscess is opened to allow the outflow of pus and to rinse the periodontal pocket with antiseptics. If pus comes out of the pocket without an incision, but only little by little, then after anesthesia you still need to widen the mouth of the pocket with a stroker. Next, the doctor prescribes systemic antibiotic therapy, anti-inflammatory drugs, and antiseptic rinses.
Opening of periodontal abscess –
Next, the issue of the need to fill the root canals in the causative tooth is resolved. This must be done if the depth of the periodontal pocket reaches 2/3 or more of the length of the root of this tooth. Removing the nerve from the tooth and filling the canals is required here because infection from a deep pocket very easily penetrates through the bloodstream into the neurovascular bundle (tooth pulp), as a result of which the pulp itself becomes a source of infection. But all this is just initial basic treatment!
The main treatment consists of open curettage of the periodontal pocket. This operation allows you to remove inflammatory granulation tissue (which forms at the site of destroyed bone tissue) from under the gums, as well as fill the periodontal pocket cleared of granulations with bone material, which allows you to partially restore the level of bone tissue around the tooth.
Progress of open curettage operation –
During open curettage, the gums are first moved away from the teeth and bone tissue to create good access to the periodontal pocket. Then the granulations are removed from the pocket, the root surface is polished and the pocket is filled with material based on artificial or bovine bone tissue. Next, the flaps of the gum mucosa are placed in place and the gum is sutured. Figure 19 shows that the bone level differs between radiographs taken before and 4 months after surgery (an increase in bone level of approximately 2.5 mm).
Moreover, if an abscess on the gum occurs near a moving tooth, then in addition to all of the above treatment, splinting of the moving tooth may be required. For this purpose, fiberglass and filling material are used, with the help of which the movable tooth is fixed to the adjacent stable teeth. Detailed information on curettage and splinting in the articles:
→ How the open curettage operation is performed, → Teeth splinting technique
Treatment of generalized periodontitis –
With generalized periodontitis, periodontal pockets occur not in 1-2, but in almost all teeth. Typically, this form of periodontitis has a sluggish chronic course. Common complaints from patients include bleeding gums and inflammation of the gingival margin. In severe cases, tooth mobility, changes in the position and inclination of teeth, and suppuration from periodontal pockets occur.
Against the background of decreased immunity, an exacerbation of chronic inflammation may occur, and then abscess formation (i.e., the formation of purulent abscesses) may occur in the area of one or more periodontal pockets. Treatment of the generalized form of periodontitis is very complex, and we have devoted a separate article to this topic, which you can read at the link above. We hope that our article on the topic: What to do if your gums are swollen turned out to be useful to you!
Sources:
1. Dental education of the author of the article, 2. Based on personal experience as a dental surgeon, 3. National Library of Medicine (USA), 4. “Outpatient surgical dentistry” (Bezrukov V.), 5. “Therapeutic dentistry: Textbook” ( Borovsky E.).
Who treats an abscess
Only a dentist can cure a tooth abscess. If you suspect an abscess, you should contact your general practitioner. He will conduct an examination and, if necessary, schedule a consultation with a dental surgeon.
Preventing a tooth abscess is easier than curing it. To do this, it is necessary to carefully observe oral hygiene, promptly eliminate inflammatory processes in the body, and visit the dentist twice a year. A balanced diet and vitamin-mineral complex products will help compensate for the lack of vitamins and minerals necessary for dental health.
Treatment methods
Pathology sometimes does not cause pain at the initial stage, so not everyone goes to the doctor on time. But usually the inflammatory process develops quickly, and within a day a noticeable tumor forms. You definitely need to see a dentist. Only a doctor after an examination can determine how to treat a tooth abscess.
Home remedies such as rinsing the mouth with saline solution or herbal decoctions, as well as taking painkillers, may provide temporary relief, but will not eliminate the cause of the pathology. They can be used if it is not possible to immediately get to the dentist.
Treatment prescribed by a doctor must be comprehensive. Its purpose is to remove pus and destroy infection. The following methods can be used for this:
- drainage of pus;
- cleaning dental canals or sockets after extraction;
- treatment of caries, pulpitis and filling;
- use of local antiseptic and anti-inflammatory drugs;
- taking antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and painkillers.
Opening a tooth abscess is often performed surgically. Some clinics use low-intensity laser. It allows you to painlessly clean the cavity from pus and disinfect it.
If inflammation has developed on a healthy tooth, it can be saved if you consult a doctor in a timely manner. Removal is a last resort; doctors resort to it only in advanced cases. But this is the main method of treatment if an abscess has developed in a baby tooth or wisdom tooth in an adult, as well as in cases where the dental tissue is severely destroyed.