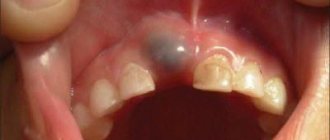
When visiting a dentist, you have probably heard them more than once say such phrases as, for example, “lower left five” or “16th tooth” or “2nd premolar.” Experienced patients know that this is the numbering of the teeth, which is necessary for the doctor to describe the condition of the oral cavity when filling out the card. There are several systems used in dental practice for this purpose.
What is a dental formula
A dental formula or diagram is a brief description of the dental structure of the human dentition using numbers and Latin letters.
The letters are abbreviations from the Latin names of teeth accepted in medicine:
- I – these are dentes incisivi or incisors.
- C is for dentes canini or fangs.
- P stands for dentes premolars or premolars.
- M stands for dentes molars or molars.
The alphanumeric dental formula is common in many countries, including America, which is why it is sometimes called American. After the letters in the formula there is always a digital fraction, where the numerator indicates the number of teeth on the upper jaw, and the denominator on the lower jaw.
The dental formula of a healthy adult with a normal bite and 32 teeth looks like this:
This formula indicates that on each human jaw there is:
- 2 pairs of incisors;
- 1 pair of fangs;
- 2 pairs of premolars;
- 3 pairs of molars.
Dental formula in the absence of some teeth
It is not difficult to correctly number dental units with a healthy dentofacial apparatus; it is much more difficult to indicate the location of the teeth if a person does not have any molars, incisors, canines or premolars. In this case, the dentist indicates the number 0 opposite a certain group of teeth, rather than shifting the number series.
If the patient has any anomalies in the development of the dentofacial apparatus, for example, teething in the wrong place (hyperdontia, polydontia), the dentist prescribes an individual formula. In addition to numerical designations, the doctor generates a detailed report on the structure of a person’s dentition.
Why is tooth numbering necessary?
All human teeth have their own specific location according to numbers. But how can you understand whether it is located on the upper or lower jaw, or on the left or right? You can use full formulations (for example, the first permanent molar of the upper jaw on the right). But such cumbersome names create certain difficulties for dentists and can often cause mistakes, which are especially dangerous if the patient is undergoing extraction of a diseased tooth.
In order to optimize the work of doctors and simplify the designation of tooth numbers as much as possible, special numberings were invented.
Description, structure, functions, name and location of human teeth
It is not without reason that human teeth have different shapes, structures and sizes. Each tooth performs certain functions, and its purpose is, one way or another, reflected in the name:
- The incisors are the front teeth that fall into the smile zone. They are quite sharp as their function is to tear or cut food, hence the name. Normally, every person has lateral and central (larger) incisors.
- Canines are cone-shaped teeth that can be used to tear and hold food. They are located immediately behind the incisors.
- Premolars are the small back molars located behind the canine teeth.
- Molars are the back teeth necessary for mechanical processing of food. Wisdom teeth refer specifically to molars.
The listed types of teeth are also found in animals. But in the process of their evolution, some dental units were slightly modified:
- elephants' upper incisors became tusks;
- Poisonous snakes have poison in their fangs.
Many animals have front teeth similar to human ones, but since they are called differently, they cannot always be identified with the usual incisors and canines.
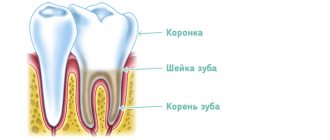
The structure of human teeth
Human teeth consist of a crown and a root part. The first is located above the level of the gum, the second is inside it. The top of the crown is covered with enamel, the strongest tissue in the body. It protects the inner layer of the tooth – dentin – from external influences. Under the dentin there is a hollow chamber with nerves and blood vessels - the pulp.
Despite its strength, enamel is vulnerable to bacteria. If left untreated, caries can affect the dentin and pulp. When the pulp chamber, which contains nerve fibers, is damaged, pulpitis develops, accompanied by acute throbbing pain. If the infection spreads to the root of the tooth, it is highly likely that it will have to be removed.
The basis of the lower part of the tooth is the root canals, which also contain arteries, veins and nerve fibers. Through the apical foramen, all of these structures are connected to the main neurovascular bundle.
The lower part of the tooth is covered with dentin and cement, which is attached to the periodontium using collagen fibers. The roots of teeth are hidden in the alveoli - depressions in the jaw bone.
How many canals are there in teeth?
The number of tooth canals does not always coincide with the number of roots. The number of channels can only be determined using x-rays. The upper incisors usually have two or three canals. Some teeth have only one canal, which branches into two parts.
Number of canals in teeth:
- Upper Lower four – 1, less often 2 channels;
- Upper second – 1, less often 2 and even 3 channels;
- Bottom five – one channel;
- Upper first molar 3, 4 canals;
- Lower first molar – 3, less often 2 canals;
- Upper and lower seven – 3, 4 channels.
On what basis are teeth numbered according to different classification systems?
In addition to the Latin names of teeth, digital designations are used in dentistry. The numbering of teeth is based on the order in which they erupt. It starts from the front incisors (from the middle of the jaw) and runs to the left and right of them.
There are several generally accepted systems for numbering human teeth.
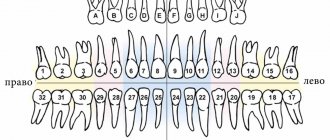
Universal system
Most often, dentists name teeth not by the Latin alphabet, but according to their location in the oral cavity (ordinal number). Moreover, using not Roman, but familiar Arabic numerals.
Names of teeth according to the universal classification system:
- two central incisors are located at number 1 and are called ones;
- the second incisors are numbered 2;
- the fangs are called triplets;
- chewing teeth or premolars are called fours and fives;
- molars are called sixes, sevens and eights.
According to the universal system of classification of dental units, the jaw is divided into 4 segments:
- top left;
- top right;
- bottom right:
- bottom left.
The further name indicates not only the serial number, but also the location of the dental unit in the human oral cavity.
The universal dental numbering system is the most popular and frequently used. It is used by dental therapists and surgeons in various countries.
The picture shows a diagram of the designation of teeth in the oral cavity of an adult according to the universal numbering system:
European system
The European Viola system is one of the newest and most advanced methods for naming human teeth. It is characterized by the division of the jaw into segments (two at the bottom and two at the top). Each segment is numbered (from 1 to 4).
Based on these numbers, each tooth receives a two-digit number. The first digit indicates the segment, and the second is the actual sequence number.
The Viola system is recognized internationally and is therefore popular all over the world. It is used in radiography, making panoramic images and allows dentists from different countries to exchange information about patients, overcoming the language barrier.
Haderup system
To designate dental units according to the Haderup system, Arabic numerals are used and segmentation into the lower and upper jaws is used:
- the “+” sign indicates that it belongs to the upper jaw;
- the “–” sign indicates the lower jaw.
The only disadvantage of such numbering is that it is necessary to additionally indicate whether the dental unit belongs to the left or right side of the jaw.
Zsigmond-Palmer system
The Zsigmond-Palmer system is considered the most imperfect, since it only indicates the numbers of teeth without their location. Standard Arabic numerals are used for numbering.
This tooth numbering system is practically not used in therapeutic and diagnostic procedures. It is used only by orthodontists and maxillofacial surgeons.
Features of treatment of individual groups of teeth
The treatment tactics for incisors, canines, premolars, molars of the upper and lower jaws are different. Each tooth carries a different load. One part of the row is visible when you smile, while the other remains invisible to others. Let's look at the features of treatment for each area of the oral cavity.
Treatment of wisdom teeth
Eights are the outermost molars in the row. They erupt later than others, practically do not participate in chewing food, and regularly cause trouble. 1, 16, 17, 32 teeth can erupt incorrectly, displacing the entire row, injuring the gums, and causing the formation of a soft tissue hood. This increases the risk of plaque accumulation and tooth decay.
| Features of wisdom teeth treatment | |
| Question | Dentist recommendation |
| Do I need to remove wisdom teeth? | In most cases, this is necessary and recommended. |
| Is it possible to treat caries on the 8th tooth? | If they do not disturb the structure of the dentition or cause discomfort, then after consultation with a doctor you can do this. |
In most cases, eights must be removed. If they grow at an angle, disrupt the bite, displace other molars, cause discomfort, or have underdeveloped enamel, it is recommended to get rid of them as quickly as possible. Extraction of teeth 1, 16, 17, 32 does not affect the chewing function or appearance of the patient.
Is caries of eights curable? If they have a normal structure, do not cause discomfort, and are involved in chewing, superficial caries can be treated using the traditional method - drilling, installing a filling. The procedure is performed at the request of the patient. If a person refuses conservative therapy, the extreme molars are removed.
If there is significant damage to the visible part of the figure eights, their removal is indicated. Artificial crowns are not installed on them due to their location and anatomical features. For acute pain, the only way to solve the problem is extraction. The figure eights are located in the far corners of the oral cavity, which makes depulpation and endodontic treatment impossible. Lack of visibility and access to instruments prevents nerve removal and canal filling.
Extreme molars are unreliable and often destroyed, so they are not recommended for use as a support for bridges. If eights are lost, prosthetics are not performed; there is no such need or possibility.
Treatment of molars
2, 3, 14, 15, 18, 19, 30, 31 teeth are molars that bear the main load when chewing. They are large, with a wide crown, have several roots, so they are firmly held in the jaw. They are not visible when you smile, but the defeat or absence of one of them causes severe discomfort to the patient. When treating this group, they pay attention to strength and strive for complete restoration of function.
| Features of treatment of molars | |
| Question | Dentist recommendation |
| What treatment methods are there if a molar is severely damaged? | In case of severe destruction of molars, ceramic inlays are most often used. |
| Which crowns are best for molar prosthetics? | More often, patients are recommended to install metal-ceramic crowns in the molar area. |
| What to do if you lose molars? | The best option in this case is implantation; patients also consider removable dentures. |
The main method of treating caries of sixes and sevens is drilling and filling. If the process does not affect the canal with the neurovascular bundle, the doctor drills out the affected areas and closes the defect with a filling made of composite materials. If the affected area is large, it is advisable to use ceramic inlays. They are made from impressions for each patient and close the cavity formed after treatment. The use of inlays allows you to increase the service life of the molar and ensures its resistance to chewing loads.
If the visible part of the six or seven is significantly destroyed, but the root is preserved, restoration is carried out using a crown. The best material for prosthetics of 2, 3, 14, 15, 18, 19, 30, 31 teeth is metal ceramics. Such designs are very durable and allow you to chew even hard food. A thin strip of metal that is visible between the metal-ceramic crown and the gum is not a disadvantage when restoring molars. It is completely invisible because these teeth are not located in the smile area. You can choose crowns made of zirconium dioxide, but they will cost more than metal-ceramics. Ceramic structures are not installed on chewing teeth.
The loss of molars affects the condition of the gastrointestinal tract and leads to displacement of the entire dentition, so prosthetics are necessary. To replace 6-k bridges, bridges are often used. If nearby units can serve as support, this is the fastest, least expensive, painless option for restoring mastication. For multiple defects, removable clasp and plate prostheses are used.
The optimal way to replace molars is implantation. The condition of adjacent teeth does not matter. With the help of titanium structures, it is possible to restore both one and several units. In most cases, root-shaped prostheses are used for prosthetics. They are able to withstand heavy loads. Such implants can serve as a support for artificial crowns and bridges.
Treatment of premolars
Teeth 4, 5, 12, 13, 20, 21, 28, 29 are premolars. They also perform the function of chewing, but are not as large and massive as molars. Some premolars are located in the smile zone, so when treating them, not only strength and functionality are important, but also beauty and naturalness.
| Features of treatment of premolars | |
| Question | Dentist recommendation |
| What to do if premolars are destroyed? | In case of significant destruction, ceramic inlays or crowns are used. The best material for premolar restoration is zirconium dioxide. |
| What to do if there are no premolars? | In this case, there are several treatment options - bridge structures, butterfly prosthesis or implantation of a missing tooth. |
The most common lesion of fours and fives is caries. Destruction occurs especially often in patients with deep fissures and narrow interdental spaces.
Due to the location of small molars, caries on them can be noticed in the initial stages. Sometimes even patients themselves pay attention to the problem and seek dental help. If a carious lesion is detected at the spot stage, modern clinics carry out treatment without drilling using the ICON system. Careful removal of damaged enamel using an etching gel allows you to save the tooth, and sealing the cavity with a special compound stops further destruction. For deeper lesions, destroyed tissue is removed using a drill or laser. Small defects are restored with durable photopolymer materials. You can choose the shade of the filling that perfectly matches the color of the enamel. In case of significant destruction, leading dentists recommend using ceramic inlays, which are made in a dental laboratory using individual impressions.
The destroyed outer part of the premolar is an indication for the installation of crowns. If only the root remains, a stump tab is installed to securely secure the prosthesis. The choice of crown material depends on the financial capabilities of the patient. The best choice is zirconium dioxide. Such designs are aesthetic and resistant to chewing loads. Their only drawback is their high price. Metal ceramics are available to everyone. It is strong and durable, but the strip of metal under the gum can be very noticeable for some. Ceramics are not suitable for fours and fives. This material is too fragile; with intensive chewing, chips will quickly appear on it.
The absence of premolars in a person is immediately noticeable to others. When they are lost, most turn to dentistry for prosthetics. If you want to quickly restore chewing and restore an attractive smile, installing an inexpensive bridge will help. The design consists of several interconnected crowns made of metal ceramics or zirconium dioxide. The outer crowns are placed on the supporting teeth, and the middle ones cover the defect in the dentition. The main disadvantages of this type of prosthetics are the need to grind healthy teeth and uneven distribution of load on the jaw.
If installing a bridge is not possible, the prosthetist will suggest a removable clasp prosthesis. Typically, the design is used when several teeth are missing. This method saves the budget and has virtually no contraindications. Lightweight butterfly prostheses are used to temporarily replace the defect. They last no more than six months, but this is enough for patients who are awaiting the manufacture of a permanent prosthesis or implantation.
The best method of replacing a lost premolar is implantation. If there are no contraindications and your budget allows, it is better to choose this modern method. A titanium rod is inserted into the jaw bone tissue and becomes a support for an artificial crown. To install such a prosthesis, you do not need to grind down the adjacent teeth. In addition, the load during chewing is distributed physiologically. Externally, an artificial premolar is difficult to distinguish from your own. Even a dentist will not always do this at first glance.
When treating 4- and 5-k, it is important to maintain a balance between practicality and aesthetics. For this reason, this group is the most difficult for dentists.
Treatment of fangs
There are four fangs in the oral cavity. These are 6, 11, 22, 27 teeth according to the universal numbering system. They have a different shape from other teeth, so during restoration it is necessary to have experience working with this group.
| Features of canine treatment | |
| Question | Dentist recommendation |
| What treatment options are there for lost fangs? | In this case, implantation of the lost canine is recommended. |
| How can you correct abnormally growing fangs? | After consultation, the patient is offered options for either orthodontic treatment or the installation of veneers or crowns. |
The fangs do not bear the chewing load. They help you bite off small pieces of food. In the process of evolution, the role of fangs in humans was lost; we do not use them to hold food or tear it into fragments. That is why the treatment of triplets is aimed at restoring their natural appearance.
In case of carious lesions, the preparation of fangs is carried out carefully, trying to preserve healthy tissue as much as possible. This will allow for high-quality restoration. With superficial caries, it is possible to preserve the volume of hard tissue necessary for high-quality filling, but deep lesions serve as an indication for installing a crown. To maintain a natural smile, it is recommended to use structures made of ceramics or zirconium dioxide.
If 6, 11, 22, 27 teeth are lost, implantation is recommended. Manufacturers offer titanium prostheses of a special configuration, taking into account the anatomical features of the jaw. Such prostheses are already classic, they have a special thread that allows you to securely fasten the structure in the narrow alveolar process.
A popular dental service is canine shape correction. Some patients have teeth that are too long, pointed, or significantly narrower than the incisors, which makes the smile less attractive. The best way to give the fangs the ideal shape is to use ceramic onlays made from individual impressions, as well as modeling with composite materials.
Alternative names for human teeth
In addition to the official names, there are also alternative names for human teeth. They are not written in dental records, but have long been used in informal communication, since these teeth in people are located or grow in certain places or at certain times.
Eye teeth
The upper canines are called eye teeth because of their close location to the branches of the facial nerve. When they become inflamed, the pain radiates to the eye area and upper face. How close the incisive canals and the dental nerve are located to each other is shown in the figure:
Wisdom tooth
The wisdom tooth is the posterior third molar. He was called “wise” because he grows up in adulthood - when a person has already gained wisdom (by about 20 years).
Numbering for an abnormal number of teeth
If a person has a normal number of teeth in his mouth, then their numbering does not cause difficulties and remains constant both at a young age and after 60 years.
If some teeth are lost (for example, due to various diseases or developmental anomalies), then in the dental formula next to the corresponding number its absence is simply indicated.
But there are diseases of the dental system, which are characterized by an increase in the number of teeth with an atypical arrangement. With such options, the use of any numbering schemes is difficult and most often dentists refuse to use them. In this case, complete information about the number of teeth, their description and location is entered into the patient’s medical documentation.
Correct names of baby teeth
In Latin, baby teeth in a child are called the same as permanent teeth in an adult. But children do not have all the dental units characteristic of older people. Milk teeth are divided into:
- central incisors;
- lateral incisors;
- fangs;
- first and second molars.
There are different names for teeth, but it is better to focus on Latin terms and serial numbers. In this way, you can identify teeth even without serious knowledge of dentistry.
How to determine the tooth number - practice with examples
Determining which teeth numbers are quite simple, you just need to practice a little with examples.
Tooth number 37 - which one is it?
To an unknowing person who is not familiar with the numbering systems in dentistry, it may seem that we are talking about an extra 5 teeth in the mouth. But that's not true. According to the Viola system, teeth with numbers starting with three are located on the lower jaw on the left. And serial number 7 corresponds to the second molar. This means the 37th tooth is the second lower molar on the left.
What number corresponds to the upper right wisdom tooth (eight)?
The third molar will be designated differently in different systems.
- In the universal number scheme - number 1.
- According to the Zsigmondy-Palmer scheme - “upper right eight”.
- According to the Haderup system - “+8 on the right”.
- In the American scheme - “upper M3 on the right”.
- According to the Viola system - number 18.
For a school-age child, the dental formula says that next to tooth 21 there is tooth 62. How can this be?
In children at 6-7 years old (less often at 8-9 years old), the replacement of milk teeth begins. Therefore, both teeth from a temporary set and already erupted permanent teeth can be located in the mouth at the same time. In this situation, they are numbered according to the Viola system, and their numbers indicate that the central upper incisor on the left (number 21) has already been replaced by a molar, but the lateral incisor is still from the primary bite (therefore it is marked under number 62).
Upper canine
Average age of teething: 10-12 years
Average age of root formation: 13-15 years
Average length: 26.5 mm
As the longest tooth, the canine has an imposing shape designed to withstand strong occlusal forces. Its long crown with a thick layer of enamel is subject to abrasion by the cutting edge. As she ages, she often has deep cervical erosions.
The access cavity corresponds to the shape of the lingual surface of the crown and is oval. To obtain direct access, the cavity must be expanded incisally, but not so much as to weaken the actively functioning cusp. The initial access is made in the middle part of the crown from the palate. If the pulp cavity is deeper, a No. 4 or 6 ball-shaped extended bur may be required. A sweeping motion with this bur will open up the oval pulp cavity.
As it moves through the cervical portion and down apically, it remains oval. Thorough cleaning of this oval-shaped canal is difficult, so attention must be paid to targeted file processing.
The root canal is quite straight and long. Most canines require instruments 25 mm or longer in length. The last 2-3 mm of the top often bends in some direction.
The morphology of the canines rarely changes radically, and lateral and accessory canals are less common than in the upper incisors.
The vestibular cortical plate over the apex of the tooth root is often destroyed to form a fenestration. The apical foramen is usually located close to the anatomical apex, but can be located laterally, especially if there is an apical bend of the root.
Second upper molar
Average age of teething: 11-13 years
Average age of root formation: 14-16 years
Average length: 20.0 mm
The shape of the crown of the second upper molar is very similar to the first upper molar, although it is not as rectangular and massive. Adequate access on both teeth can usually be achieved without disturbing the transverse enamel ridge. The second molar is often easy to prepare due to the straightforward approach to the orifices.
A distinctive feature of the morphology of the upper second molar is the closely spaced and sometimes fused three roots. The shadows of parallel root canals often overlap on the radiograph. Its roots are usually shorter than those of the first molar and not as curved.
The three orifices may form a blunt triangle, and sometimes they are located almost in a straight line. The floor of the pulp chamber is noticeably convex, creating a slightly funnel-shaped shape of the canal orifices. Sometimes the canals extend from the bottom of the pulp chamber at an acute angle, resulting in the need to remove the edge of the dentin in order to create a straight line of access.
Complications during access occur if the molar is tilted distally. Initial exposure is performed with a fissure bur with a cutting tip, and then a short ball-shaped bur is used, which is best suited for opening the pulp chamber and forming an access cavity. Then, small hand instruments are used to establish the patency of the canal and its working length. After this, the bulk of cleaning and shaping can be done by machining the files in the endodontic handpiece.
To improve radiographic visibility, especially when layering the shadow of the process of the zygomatic bone, photographs can be taken in perpendicular and distal projections at an angle.
All infected dentin, leaking fillings and denticles must be removed before endodontic treatment begins. To prevent vertical coronal or crown-root fractures, it is necessary to completely close the access cavity. If indicated, immediately after endodontic treatment it is necessary to apply internal reinforcement with intraradicular pins.