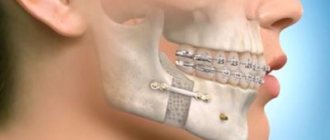
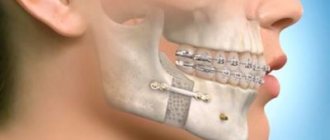
You can contact Dr. Granov's clinic for treatment of jaw injuries. This is one of the areas of treatment that we do.
The jaw is the bony structure that holds the teeth in place. The upper jaw does not move, only the lower jaw moves. Its movements are necessary for eating food and for producing speech. Both jaws connect at a point called the temporomandibular joint (TMJ).
Jaw injuries include cracks, dislocations and fractures. With a fracture or crack, the bone breaks; with a dislocation, the bone changes location and flies out of the joint. Such injuries occur after physical activity (bruise, blow, fall). After appropriate treatment, they heal safely, but the dislocation may appear again.
Jaw injuries are dangerous because they can lead to various complications. Among them:
- breathing disorder,
- bleeding,
- blood entering the lungs
- problems with chewing food,
- problems with diction,
- infection of the jaw or facial structures,
- joint pain,
- numbness of the jaw or face,
- tooth displacement,
- edema.
Symptoms of a jaw fracture:
- pain in the cheek next to the ear, which increases with jaw movement;
- swelling of the face, blood in the mouth;
- immobility of the jaw, inability to open or close the mouth;
- when opening the mouth, only one side of the jaw moves;
- jaw pain that gets worse when chewing;
- dental injuries;
- swelling of the face or changes in the contours of the jaw;
- numbness of the face in the lower lip area.
Symptoms of a dislocated jaw:
- pain in the cheek next to the ear, which increases with jaw movement;
- feeling that the jaw is not positioned correctly in the joint;
- violation of diction;
- inability to close your mouth;
- drooling due to open mouth;
- spasm of the masticatory muscles or protrusion of the jaw forward;
- dental injuries.
First aid for jaw injuries
Jaw injuries require immediate medical attention. Call an ambulance or go to the nearest hospital. Before doctors arrive, you can put a bandage on your jaw to keep it immobilized. The bandage should be easy to remove.
Do not try to set a dislocation yourself or wait for the fracture to heal on its own. Be sure to contact a traumatologist.
Treatment of a jaw fracture
Treatment depends on the extent of the fracture. If the patient has a small crack in the bone, it will heal on its own. The doctor will only prescribe a painkiller.
Severe fractures require surgery to allow the bones to heal properly. After surgery, a bandage is applied to the jaw to allow it to heal quietly. The jaw takes 6 to 8 weeks to heal. At first, elastic bandages are additionally applied, which are then removed to allow the muscles to be developed and their mobility restored.
During treatment you can eat only liquid food. You should always have scissors with you to cut bandages in case the patient suddenly chokes on something or starts vomiting. Then go to the hospital to have a new bandage applied.
Comparative assessment of the effectiveness of three methods of gentle immobilization of the lower jaw for fractures
G. A. Khatskevich Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Head of the Department of Pediatric Dentistry with a course of Maxillofacial Surgery at St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova (St. Petersburg)
V. G. Avetikyan Candidate of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor of the Department of Pediatric Dentistry with a course of Maxillofacial Surgery at St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova (St. Petersburg)
I. G. Trofimov Candidate of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor of the Department of Pediatric Dentistry with a course of Maxillofacial Surgery at St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova (St. Petersburg)
Zhang Fan , doctor, postgraduate student at the Department of Pediatric Dentistry with a course in Maxillofacial Surgery at St. Petersburg State Medical University named after. acad. I. P. Pavlova (St. Petersburg)
I. Yuan Ph.D., Lecturer at Shanghai University (Shanghai, China)
V. B. Nekrasova Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor of St. Petersburg MAPO (St. Petersburg)
Patients with injuries of the maxillofacial area make up about 30% of all patients treated in hospitals for maxillofacial surgery, while fractures of the lower jaw make up about 70-85% of all fractures of the facial bones (Ivasenko P.I., Zhurko E. P., Chekin A.V., Konvay V.D. et al., 2007; Inkarbekov Zh.B., 2009; Bakardjiev A., Pechalova P., 2007).
An analysis of data published in the scientific literature showed that the frequency of complications of mandibular fractures reaches from 10 to 41% (Mubarkova L.N., 2008; Mirsaeva F.Z., Izosimov A.A., 2009), which does not allow us to talk about effectiveness existing treatment methods.
An important pathogenetic link in the development of inflammatory complications in fractures of the lower jaw is a violation of local immune defense, regional blood circulation and innervation in the fracture zone, deterioration of oral hygiene and impaired chewing function (Timofeev A. A., 2004; Berkhman M. V., Borisova I. V., 2007; Magomedgazhiev B. G., 2008; Inkarbekov Zh. B., 2009). Moreover, these changes can be provoked not only by the injury itself, but also by inadequate fixation methods. This especially applies to round aluminum or tape dental splints. Their application is extremely traumatic for the patient and dangerous for the surgeon due to the possibility of hand injury and infection.
In addition, dental splints, used for an average of 30 days, complicate oral hygiene and injure the periodontal border. This leads to the development of pronounced inflammatory changes in the periodontium. Fractures of the lower jaw occur quite often, in which there is no displacement of the fragments and mobility is low. In this case, the immobilization provided by dental splints turns out to be redundant. In this regard, the development of gentle immobilization methods is of particular relevance.
Material and research methods
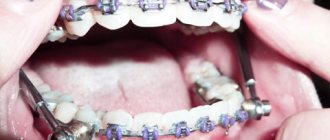
The work is based on the experience of treating 90 patients with fractures of the lower jaw. Of these, in 48 patients, the method of gentle immobilization—intermaxillary fixation using fixed orthodontic equipment—was used as the main and auxiliary (during osteosynthesis surgery) method of fixation (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1a. The stage of gluing Protekt dental buttons-braces. Immobilization of the lower jaw using elastic rings (the least traumatic method).
Rice. 1b. The stage of gluing Protekt dental buttons-braces. Immobilization of the lower jaw using elastic rings (the least traumatic method).
The comparison methods used were: immobilization of fragments with wrapping transmaxillary sutures - 18 patients (Fig. 2).
Rice. 2a. Immobilization of the lower jaw using two wire wrapped sutures.
Rice. 2b. Immobilization of the lower jaw using two wire wrapped sutures.
Intermaxillary suspension using orthodontic mini-implants - 24 patients (Fig. 3).
Rice. 3. Immobilization of the lower jaw using intraosseous implants of fixators and elastic rings.
The control group included 16 males (22.9 ± 1.2 years), practically healthy.
In the main group of patients, where Protekt braces and lingual buttons were used, biologically active additives (dietary supplements) "Lesmin" for oral administration and individual oral hygiene using dental Fitolon pastes.
For diagnosis and evaluation of results, clinical and radiological immunological, index-hygienic methods, electromyography and Doppler flowmetry were used to assess vascular microcirculation.
Indications for choosing the immobilization method using fixed orthodontic equipment (Protect) are as follows. The independent method of immobilization of the lower jaw, as an alternative to splinting, was used in the following cases: unilateral fractures without displacement or with slight displacement; bilateral fractures without displacement or with slight displacement; fracture of the condylar process without clinically detectable and functionally significant displacement (slight limitation of movements in the temporomandibular joint due to pain, the bite is not disturbed). In case of bilateral fractures of the lower jaw, in a number of cases where osteosynthesis was performed with titanium plates, bracket fixation was used as an additional method (Fig. 4).
Rice. 4. Bilateral fracture of the lower jaw. Immobilization was carried out using osteosynthesis and braces.
The analysis included only those cases where the method of gentle immobilization was used as the main method of fixation of fragments and the patients fully followed the recommendations for oral hygiene proposed by the authors. A total of 66 clinical cases were analyzed. Variants of fractures in percentage and their ratio are presented in Figure 5.
Rice. 5. Variants of mandibular fractures with gentle immobilization methods.
Research results
Patients of all 3 groups were observed from the start of treatment and for 3 months. The final assessment of treatment results was carried out 3 months after injury. Inflammatory complications were taken into account throughout the treatment. Consolidation of fragments occurred in all patients, regardless of the method of gentle immobilization. Malocclusion was detected in only one patient, whose jaw was immobilized using orthodontic mini-implants. In this case, it was possible to restore the bite by selective grinding of the teeth. The effectiveness of treatment with the methods under consideration was the same.
Inflammatory complications were observed with all methods of gentle immobilization, while in the case of using fixed orthodontic equipment (group 1), only one patient (4.2%) had a limited osteomyelitic process due to a tooth fracture left in the gap with pulp necrosis versus 12. 6% when fixed with mini-implants and 16.6% when fixed with wrapping transmaxillary sutures (Fig. 6).
Rice. 6. Frequency (%) of inflammatory complications with different methods of gentle immobilization.
In the second group (using mini-implants), 1 patient had a hematoma suppuration, and 2 patients had a limited osteomyelitic process. In the third group (wrapping transmaxillary sutures), 2 patients had suppuration of postoperative hematomas in the tissues of the floor of the mouth and one patient had chronic traumatic osteomyelitis. Thus, in the group of patients in whom gentle immobilization was performed using fixed orthodontic equipment, the number of inflammatory complications is minimal, which is due not only to less additional trauma during the procedure for immobilizing fragments, but also to the systemic use of dietary supplements.
Questionnaires to study self-assessment of quality of life were filled out by patients 1 month after the injury when the fixation structures were removed. A comparative analysis of the study results was carried out in samples of 12 patients from each group. A study of the “quality of life” profiles in patients using different methods of gentle immobilization showed that the quality of life decreases to a lesser extent in patients with fractures of the lower jaw when fixed using fixed orthodontic equipment and mini-implants (Fig. 7).
Rice. 7a. Comparative assessment of relatively healthy respondents’ QoL profiles with different methods of gentle immobilization. OTMS - wrapping transmaxillary sutures.
Rice. 7b. Comparative assessment of relatively healthy respondents’ QoL profiles with different methods of gentle immobilization. OMI - orthodontic mini-implants.
Rice. 7th century Comparative assessment of relatively healthy respondents’ QoL profiles with different methods of gentle immobilization. NOT - fixed orthodontic technique.
One month after the injury, self-assessment of the quality of life in patients with fractures of the lower jaw with a gentle method of immobilization using fixed orthodontic equipment on all scales of the physical component of health and one scale of the mental component (vitality) was higher than in patients with fixation using wrapping transmaxillary sutures.
When determining the level of oral hygiene, the Fedorov-Volodkina Hygiene Index (FHI) and the severity of periodontal inflammation according to the papillary-marginal-alveolar index (PMA) were recorded; at the initial examination, no statistically significant differences were found in patients of the three groups.
The highest RMA values were found in the group of patients where fixation of fragments was carried out using wrapping transmaxillary sutures - 43.3 ± 2.4%
Subsequently, when examined after 7 days, the level of oral hygiene worsened regardless of the method of gentle immobilization and was assessed in all groups as unsatisfactory. When examined a month later, a further increase in IGPV was observed in all groups, however, in the group using fixed orthodontic technology, the increase in IGPV was found to a lesser extent - 2.4 ± 0.03 versus 2.64 ± 0.07 points (p < 0.01) in the group where fixation was carried out using orthodontic mini-implants.
Compared to the initial values, an increase in inflammation during treatment was observed in all groups of patients. At the same time, the highest RMA values were established in the final study in the group of patients where the fixation of fragments was carried out using wrapping transmaxillary sutures - 43.3 ± 2.4%, and the lowest with the gentle method of immobilization we proposed using fixed orthodontic equipment - 26.4 ± 0.8% (Table No. 1).
Table No. 1. Comparative analysis of the dynamics of dental indices with gentle methods of immobilization of the lower jaw, used as the main ones.
| № | groups | n | IGFV (points) | RMA (%) | ||||
| 1 time | 2 times | 3 times | 1 time | 2 times | 3 times | |||
| 1 | NOT | 24 | 2,08±0,04 | 2,3 ±0,06 ** | 2,4±0,03 *** | 22,0±0,8 | 27,5 ±1,0 *** | 26,4±0,8 ** |
| 2 | OMI | 24 | 1,98±0,07 | 2,32±0,07 ** | 2,64±0,07 *** | 22,2±1,0 | 26,9±1,36 ** | 34,9±1,3 *** |
| 3 | OTMS | 18 | 2,17±0,04 | 2,35 ± 0,09 | 2,5±0,09 ** | 25,1±2,1 | 32,2±1,75 * | 43,3 ±2,4 *** |
| P1-2 | >0,05 | >0,05 | <0,01 | >0,05 | ||||
| P1-3 | >0,05 | >0,05 | >0,05 | >0,05 | ||||
Note: the differences relative to the initial examination are statistically significant: * - p<0.05; ** — p<0.01; *** — p<0.001; 1st time during the initial examination; 2nd time after 7 days (at discharge); 3rd time after 1 month. (when removing structures).
This result is associated with the use of surgical intervention in the comparison groups that stimulates the inflammatory response. Less severe inflammation in the final study could have been influenced by the use of the Lesmin dietary supplement by patients in the experimental group and the use of Fitolon toothpaste.
The study of factors of nonspecific protection and local immunity in the oral fluid of victims with fractures of the lower jaw during the initial examination revealed that in all groups there was a significant decrease in lysozyme activity compared to healthy individuals against the background of activation of mucosal immunity (increased levels of immunoglobulins) with a pronounced imbalance of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines (increased IL-8 and decreased IL-4). When examined a week later, a decrease in lysozyme activity relative to the initial data was found only in patients with entwined transmaxillary sutures (65.5 ± 2.1 versus 73.1 ± 2.3% at p < 0.01). In the same group, the lowest levels of lysozyme activity were found after a month (63.6 ± 2.2%), although upon admission in this group the activity of lysozyme was the highest (Fig. 8).
Rice. 8a. Dynamics of lysozyme and sIgA activity in patient groups. Note: NOT - 1st group, OMI - 2nd group, OTMS - 3rd group.
Rice. 8b. Dynamics of lysozyme and sIgA activity in patient groups. Note: NOT - 1st group, OMI - 2nd group, OTMS - 3rd group.
When examined after 7 days, in groups 1 and 2 the level of sIgA decreased slightly, and in group 3 it increased just as slightly. The final examination a month later showed a slight decrease (normalization) of sIgA in group 1, where we used the gentle immobilization method we proposed using fixed orthodontic equipment - 56.1 ± 3.8 versus 72.5 ± 5.78 μg/mg of protein ( p < 0.01) and 77.7 ± 11.4 μg/mg protein.
Studies have shown that when using fixed orthodontic equipment as the main method of fixation, inflammatory complications in the fracture zone are detected in 4.2% of cases
When examined after 7 days, IgG was still at high levels in all groups. Against this background, only in the experimental group of patients was there a decrease in IgM to the control level (from 2.3 ± 0.2 to 1.37 ± 0.1 μg/mg protein, with p < 0.001). A month later, a study confirmed the normalization of IgM levels only in the experimental group, where we used the gentle immobilization method we proposed using fixed orthodontic equipment (1.38 ± 0.1 versus 1.9 ± 0.13 and 2.49 ± 0.26 μg/ mg protein in comparison groups). Moreover, after a month in the experimental group, IgG decreased most significantly (3.77 ± 0.3 versus 4.6 ± 0.45 and 5.0 ± 0.4 μg/mg of protein in the comparison groups).
During the initial examination, the level of IL-8 was 9 times higher than that of the control group; in some patients it was more than 5000 pg/ml, and in some cases IL-4 was not detected at all. Against the background of such large-scale changes in the regulators of the immune response, the smallest were found in patients in the experimental group. Thus, after 7 days they showed a decrease in IL-8 (from 2707.9 ± 198.7 to 1916.3 ± 199.0 pg/ml, with p < 0.01), and when examined a month later, it was in this group has the lowest level of IL-8 (1488.2 ± 183.3 versus 1953.3 ± 202.1 and 2247.1 ± 304 pg/ml in the comparison groups) (Fig. 9).
Rice. 9. Dynamics of IL-8. Note: NOT - 1st group, OMI - 2nd group, OTMS - 3rd group.
The dynamics of IL-4 are less pronounced. In the experimental group, its amount practically does not change during treatment, remaining 2 times lower than in the control group, and in the comparison groups it further decreases. After a month, in patients of group 1, the level of IL-4 was 2.7 ± 0.2 versus 1.12 ± 0.4 and 1.0 ± 0.5 pg/ml in the comparison groups.
Thus, the study of the activity of lysozyme, mucosal immunity and the level of cytokines in the oral fluid showed that in response to a fracture of the lower jaw, the body responds with an acute-phase inflammation reaction, accompanied by a decrease in lysozyme activity against the background of activation of mucosal immunity and a pronounced imbalance of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines. When using the method of gentle immobilization developed by us against the background of systemic administration of the Lesmin dietary supplement, the normalization of disorders proceeds faster (in some cases, improvement occurs after 7 days), and when examined a month later, it is more pronounced, which is due to the less traumatic method of fixation and systemic administration of the biomodulator Dietary supplement "Lesmin"
conclusions
- As a support for mandibulo-maxillary fixation, it is proposed to use non-removable orthodontic equipment: dental braces and lingual buttons, which will eliminate surgical intervention, which complicates the course of the restoration process in periodontal tissues, and will simplify and increase the effectiveness of treatment for patients with mandibular fractures.
- When using fixed orthodontic equipment as the main method of fixation, inflammatory complications in the fracture zone were detected in 4.2% of cases. When using Fitolon toothpaste and Lesmin dietary supplement, better results were registered in comparison with the control. IGFV 2.4 + 0.03 versus 2.65 + 0.1 points at P < 0.05, and a decrease in the intensity of periodontal inflammation RMA 26.4 + 0.1 versus 36.8 + 2.0% at P < 0.001 .
- Our data confirm the regulatory effect of cytokines in the development of inflammation. The initial increase in IL-8, as a consequence of injury, is physiologically determined and stimulates the mucosal immune system, without having a negative effect on such a factor of nonspecific defense of the oral cavity as lysozyme. However, high values of IL-8 after a month negatively affect the restoration of lysozyme activity. At the same time, a decrease in the level of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-4, established at all stages of the study, is accompanied by an increase in lysozyme activity.
- Restoration of lysozyme activity against the background of a decrease in elevated immunoglobulins in the oral fluid and a decrease in the degree of imbalance between pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines leads to a decrease in the inflammatory reaction in the periodontium and an improvement in the hygienic state of the oral cavity, which confirms the effectiveness of the use of Fitolon toothpaste and the systemic use of the Lesmin dietary supplement. in patients with fractures of the lower jaw against the background of a gentle immobilization method using fixed orthodontic equipment.
- A comparative analysis in three groups of patients with gentle immobilization showed that in the case of using fixed orthodontic equipment, the number of inflammatory complications is minimal, which is apparently due not only to less additional trauma during the procedure for immobilizing fragments, but also to the systemic use of dietary supplements. Moreover, a month after the start of treatment, these patients’ self-assessment of quality of life is higher than with other methods of gentle immobilization.
- With the gentle immobilization method we developed, the normalization of identified violations of local nonspecific and immune defense proceeds faster - in some cases, improvement in indicators occurs within 7 days (decrease in sIgA, IgM and IL-8), and when examined a month later, the normalization is more pronounced (decrease in sIgA, IgM and IL-8 with an increase in lysozyme activity), which is due to both a less traumatic fixation technique and systemic administration of the biomodulator dietary supplement "Lesmin", which increases nonspecific resistance of the oral cavity and has an antioxidant effect.
Treatment of jaw dislocation
A dislocated jaw is treated simply: the doctor realigns the joint, placing the bone in the right place. Muscle relaxants or painkillers may be needed to relax tight muscles.
Then the jaw must be secured in a stationary state. To do this, the doctor applies a bandage. If the dislocation does not appear for the first time, then surgery will be needed to straighten it.
Recovery after a dislocation lasts 6 weeks. At this time, you should not open your mouth wide. When yawning and sneezing, the lower jaw should be supported with your hands.
Features of recovery
After removing the plaster, the patient feels discomfort. Joints lose elasticity. They become motionless. Rehabilitation will help. It will allow you to achieve the following results:
- Muscle recovery after injury;
- Stimulation of blood circulation from the day the cast is removed;
- Strengthening blood vessels;
- Protection against thrombosis;
- Reduced swelling;
- Return of mobility.
For complicated fractures and long-term immobility, rehabilitation prescribed by a professional is required. It must be carried out strictly according to the doctor’s recommendations from the removal of the plaster. Neglecting the rule will lead to complications.
Recovery in a supine position
Exercise and loading after a limb injury should be started immediately. The muscles relax. The fragments grow together correctly. Here is an approximate complex of therapeutic exercises for the rehabilitation of a patient:
- Elbow and shoulder raises.
- Leg flexion and extension.
- Foot movements.
- Hand rotations.
Manipulations with the load should be performed approximately 10 times. They are carried out by healthy parts of the body. As for the sore leg, here it is necessary to lower, raise, abduct, and bring the leg to the body. At the initial stage, gymnastics should be performed with an assistant. Then, during rehabilitation, you can study independently.
At the initial stage of rehabilitation, the patient has swelling. To remove it, it is useful to wear support bandages and perform the following movements:
- Lying in bed, raise your legs slightly, hold them, lower them.
- Contraction and relaxation of the muscles of the limb.
- Flexion, subsequent extension of the fingers.
- Rotation of the feet.
- Pulling your legs to your chest.
As soon as the doctor realizes that the patient can walk, he is prescribed another exercise. The load increases. Medication treatment is stopped. The process of resuming walking is carried out with the help of a crutch. You can use a cane. After removing the plaster, do gymnastics:
- Lying on your back, hug your leg with your arms. Unbend, bend it.
- While sitting, move your leg quickly back and forth.
- Move your foot, drawing a figure eight.
From the day the cast is removed, the load is increased gradually, not quickly, under the supervision of a doctor. This is expressed in the use of weighting agents. The number of repetitions and the total load also increases.
Stages
In order not to harm your health after a hip or lower leg injury, it is important to follow a certain course of action during rehabilitation. It consists of the following stages:
- The first stage from the date of plaster removal. Thoroughly rubbing the affected area. Carrying out a massage. Doing light exercises. Application of local drugs to stimulate bone regeneration.
- Second phase. Performing complex sets of exercises. Exercise therapy is prescribed. Physiotherapy is carried out.
- Third stage. Activity increases. Walks are available. Referrals for spa treatment are given.
It is important to accompany each stage of rehabilitation after removing the cast with a diet. It will speed up your metabolism. Quickly strengthens bone tissue and muscles after injury.
Technical features of installing and removing fasteners
If the structure with an external location is installed correctly, removing the spokes after a fracture is not difficult - the spokes are simply removed. If the fixation is intraosseous, inside the joint, using nails and screws, then a full-fledged operation is required.
Fixation with knitting needles is used to connect the joints of the limbs and fingers. It can be performed externally, when the end of the needle rises above the surface, or internally, when the entire structure is under the skin. The technique is used as a temporary measure. In some cases, if patellar fractures, clavicular or elbow injuries are fixed, stable fixation and a longer time for fusion are required.
When a hand is broken, osteosynthesis techniques are used - metal structures, knitting needles and an Ilizarov apparatus is installed. They are removed only after complete healing.
Using plates you can fix any bone. This is a convenient and reliable method. Today, many variants of such plates are used, varying in size, shape, and functionality. The plate is used for fractures of the tibia and ankle, when there is a need to fix bone fragments. Its removal occurs as planned. The time of the operation is determined by the doctor.
Intraosseous rods (pins) are used to fix tubular bones - for example, in case of a fracture of the collarbone or leg. Such operations are performed quickly and are characterized by minimal trauma. After fixation, loading is allowed in just a few days.
Removal of the structure is carried out in half an hour if the installation was carried out correctly. If there is damage to the threads or screws, it becomes necessary to drill out the elements.
Activities and auxiliary things
If the fracture of the limb was uncomplicated, it is enough to wear insoles. They will help not to overload the injured limb. If a person breaks a hip, the recovery time will be more difficult and lengthy. You can’t do it without a special program and devices.
Even in the clinic, the patient’s bed is equipped with a belt. A person grabs it with his hands in order to sit or rise comfortably. Doctors prescribe physical therapy in the first week after an injury, when canes and crutches are still used.
First, breathing exercises are prescribed for the patient. Balloons are used for this. Afterwards, exercises are prescribed, aimed at developing the mobility of the torso. After about a month, the doctor prescribes the following complexes:
- General. Designed for general human health.
- Special. To restore a diseased limb from the day the cast is removed.
Well-thought-out treatment and rehabilitation based on physical education can achieve the following goals:
- Restoring blood circulation through massage;
- Prevention of dangerous complications;
- Serious strengthening of the muscles at the fracture site;
- Restoration of motor ability.
To achieve the above goals, it is important to start exercising while lying down. After this period, quitting classes is not recommended. The features of each gymnastics option should be studied in more detail.
Working with gait
Along with the listed exercises, you need to add a complex for quick gait restoration and rehabilitation. Here are some effective options:
- Use your toes to grab and hold a small object;
- Roll a ball with the foot of the sore limb;
- Standing on your toes, on your heels;
- Walking sideways and backwards.
If possible, you can exercise on exercise bikes. The listed exercises and prescribed treatment after an injury cannot be neglected. Physical education during rehabilitation quickly restores and heals the body from the day the cast is removed.
Recovery after a fracture should continue until the body is completely restored. You can stop exercising after you have regained mobility, swelling has subsided, and there is no pain. The success of rehabilitation depends not only on the will of the patient and the treatment program.