Full text of the article:
Working with diseases of the internal organs is especially difficult because they cannot be seen. Previously, doctors had to treat patients literally “blindly,” since it was possible to examine a person’s internal organs only during surgery. Nowadays, doctors don’t have to pick up a scalpel; various types of scans help make a diagnosis. However, patients are wary of this type of examination. This is due to the high cost of some procedures and the fear of radiation. Let's try to figure out what the features of certain scans are and when to resort to them.
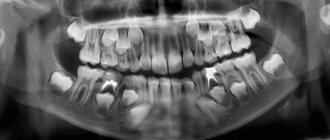
X-ray
The oldest and most common method of visualizing the human body. X-rays are used everywhere, from surgery to dentistry. The method is simple and clear: a person is irradiated with special rays that easily pass through soft tissues and linger in hard ones. Thanks to this principle, an image is transmitted to a photographic film or sensor located on the side opposite the ray source, and radiography or fluoroscopy is available to the doctor.
Main advantages
such an examination: speed and cost. Almost all hospitals are equipped with X-ray machines; the procedure is quick and inexpensive.
Main disadvantages:
exposure and image quality. When performing radiography, the patient is irradiated, and the picture is two-dimensional. The doctor can hardly see the internal organs individually, since their shadows overlap each other. It is also impossible to see the cartilage tissue and brain in detail. The cartilage practically does not block the rays, the brain is securely closed by the skull. X-rays are not suitable for their examination.
It will be most effective to carry out radiography for damage to bones, joints and teeth.
What is the difference between X-ray and digital X-ray?
The principle of digital diagnostics in medicine is completely similar to the method that is used for research in industry, construction and even, for example, at customs, in veterinary medicine. Modern X-rays in any advanced clinic or hospital are a special method of radiation diagnostics, during which all images are processed digitally.
Radiography of this type has many advantages, thanks to which it is successfully displacing analogue techniques from absolutely all areas of medicine. Even hospitals are striving to acquire such equipment, not to mention advanced paid medical centers, which have long forgotten about the old analog equipment.
The essence of the digital radiography method in medicine
The main and, perhaps, the most fundamental change affected the very method of capturing the image. If previously a special material with a special photosensitive coating was needed, now such a need has disappeared completely. The image is immediately generated in electronic form and is ready for viewing and processing.
During the shooting process, a special system of converters and detectors is used, which allows you to display the image immediately on a computer monitor. The sensitivity of flat panel detectors is several times higher than that of film, so a specialist can reduce exposure time and the radiation dose itself, and still get an image of exceptional quality.
Fluorography
Another type of examination that all residents of our country regularly undergo. Fluorography was “invented” almost a hundred years ago. This is a kind of accelerated radiography. Scientists proposed photographing a screen with an image obtained from radiography. This made the procedure faster and more widespread. Screening tests began to be administered to everyone in order to detect latent pulmonary tuberculosis.
Main plus
The procedure is fast,
the main disadvantage
is the image quality. The patient also receives a dose of radiation, and the doctor has a rather blurry picture, so fluorography is recommended to be supplemented with questionnaires and laboratory tests for the presence of tuberculosis.
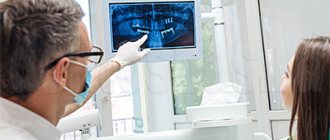
Expert opinions
Ilya Gipp, Ph.D., Head of MRI-guided therapy:
— Many of these devices can be used for treatment. For example, a special installation is attached to an MRI machine. It focuses ultrasound waves inside the body, increasing the temperature in a targeted manner, and burns out tumors - for example, uterine fibroids.
Kirill Shalyaev, director of the largest Dutch manufacturer of medical equipment:
- What seemed impossible yesterday is reality today. Previously, during CT scans, a drug was administered to slow down the heart. The newest CT scanners make 4 rotations per second, so there is no need to slow down the heart.
| What radiation doses do we receive* | ||
| Action | Dose in mSv** | Over what period of time will we receive this radiation in nature? |
| X-ray of a hand | 0,001 | Less than 1 day |
| X-ray of a hand using the very first machine in 1896. | 1,5 | 5 months |
| Fluorography | 0,06 | 30 days |
| Mammography | 0,6 | 2 months |
| Mammography with MicroDose characteristic | 0,03 | 3 days |
| Whole body CT scan | 10 | 3 years |
| Live in a brick or concrete house for a year | 0,08 | 40 days |
| Annual norm from all natural radiation sources | 2,4 | 1 year |
| Dose received by liquidators of the Chernobyl accident | 200 | 60 years |
| Acute radiation sickness | 1000 | 300 years |
| Epicenter of a nuclear explosion, death on the spot | 50 000 | 15 thousand years |
| *According to Philips **Microsievert (mSv) is a unit of measurement of ionizing radiation. One sievert is the amount of energy absorbed by a kilogram of biological tissue. | ||
Mammography
A separate type of radiography designed to diagnose breast diseases, which is why women undergo mammography. There is no consensus on the recommended age for the procedure. Mammography helps ensure the absence of a malignant tumor with an accuracy of 89%. It is believed that women should be screened regularly starting at age 39, although some cancer societies recommend screening at a younger age.
Mammography is prescribed to diagnose breast cancer, the procedure is quick
, this is a plus, but the patient
is irradiated
, and the risk of an incorrect diagnosis remains, this is a minus. Mammography can be digital or film; digital mammography provides a clearer image.
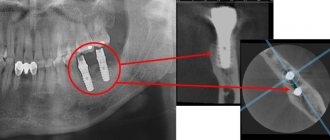
Computed tomography (CT)
Computed tomography is also carried out on the principle of radiography, but as a result the doctor receives not a flat two-dimensional picture, but a three-dimensional image. This is achieved by simultaneously taking a large number of images, which are assembled into a single image. CT scanner sensors are highly sensitive and distinguish a huge number of shades, so the doctor can examine in detail all the bones and organs of the patient. The image quality can be further improved by injecting the patient with a special substance, the so-called “contrast”. The contrast helps to distinguish healthy tissues from altered ones and detect abnormal structures in the body, and also makes it possible to study the condition of blood vessels in detail. CT with contrast is not prescribed in every case; often a simple computed tomography is sufficient.
CT scan is done quickly
, with its help to screen for lung cancer. You can also use computed tomography directly during surgery.
Disadvantages of CT
can be considered a high radiation dose to the patient. Therefore, CT is not prescribed to pregnant women, children and overweight patients (more than 200 kilograms).
Ultrasound examination (ultrasound)
X-ray is not the only way to “look inside” the human body; another technology is ultrasound. Some animals, such as bats, use sound waves to orient themselves in space. People have also learned to use waves to solve some problems, including in medicine. A picture of the internal organs can be obtained by sending a sound wave into the human body and monitoring its return. The computer helps process the results and present them in the form of a three-dimensional picture.
The main advantage of this research method is safety.
. Ultrasound can be performed even on pregnant women; in addition, ultrasound devices are mobile and can easily be placed in the patient’s room to monitor the condition of organs and blood flow in real time.
However, ultrasound cannot provide a high-definition image, so the use of this method of research is limited, for example, gastrointestinal diseases cannot be diagnosed using ultrasound.
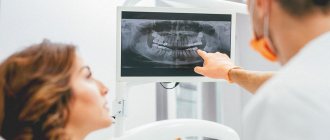
Digital X-ray: capabilities and practical applications in medicine
Digital technologies in radiography open up quite broad horizons for physicians. The technique is absolutely not inferior to the analog method of research and is excellent for:
- Assessing the condition of soft tissue and bone tissue after injury or any negative impact.
- Checks for various types of neoplasms. Can be used to work with both benign and malignant tumors.
- Search for foci of active inflammatory processes.
- Assessment of pathological deviations from the norm, abnormal scenarios of development of the congenital type.
- Diagnosis of the condition of the spinal column.
- Finding the location of foreign bodies if they are swallowed. This is especially true when working with young children, for whom such situations are not uncommon.
- In preparation for surgical treatment.
For example, by checking the head area, a specialist can detect metastases, lesions, strokes, or even a hematoma. When checking the lungs using digital radiography, bronchitis, changes due to oncology or tuberculosis, and fibrosis can be detected. When assessing the condition of the spine, the doctor will see a hernia, disc displacement, cancerous lesions and many other abnormalities.
Digital X-rays can be used not only to quickly make a diagnosis, but also to track progress in the treatment process. Timely assessment of dynamics allows you to quickly adjust prescriptions, avoid side effects and achieve the best possible result.
The use of digital x-rays today not only simplifies the work of specialists and reduces diagnostic costs. With its help, it is possible to detect those pathologies for the search for which previously it was necessary to use more serious invasive methods.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
The principle of MRI is based on the property of atomic nuclei to respond to a strong magnetic field. The calculation is based on the reaction of hydrogen nuclei, of which there are many in the composition of water molecules, and the human body, as is known, consists of 60% water. When entering a magnetic field, the nuclei of atoms are oriented along it; they can be excited and the energy that they will give off when the influence weakens can be recorded, i.e. “relaxation”. Computer analysis allows you to convert the information received and determine the location, density and structure of tissues in the body.
MRI allows you to “see” cartilage, soft tissue and the human brain without causing harmful effects
, so the procedure can be performed by anyone and as many times as desired.
However, the examination takes a long time
, and closed-type tomographs can cause attacks of claustrophobia. True, there are open-type devices. MRI procedures should not be performed on people who have electrical devices (such as pacemakers) or metal implants implanted in their bodies.
MRI will be effective in studying tumors, brain and vascular abnormalities.
Scintigraphy, SPECT, PET
Perhaps these are one of the rarest procedures on our list. These examination methods are based on radiation diagnostics, but it is used in reverse. The patient is not irradiated from the outside, but a special radioactive drug is injected into him to make him “glow from the inside.” First, scientists invented and tested scintigraphy. With its help, it was possible to obtain two-dimensional images. Then research went further and single photon emission computed tomography ( SPECT)
), followed by positron emission tomography (
PET
). The difference between these methods is rather technical; they use different radiopharmaceuticals and different types of detectors that record radiation from the patient’s body.
The question arises: “Why such difficulties?” The fact is that thanks to these procedures, you can see formations in the pictures that are not visible in pictures obtained by external irradiation. Metastases and tumors can appear inside bones or organs and remain silent for a long time. The radiopharmaceutical is injected into the body and accumulates in the tissues, which allows it to “illuminate” certain areas.
Main disadvantage
of this examination method is the cost. The radiopharmaceutical is developed individually for each patient; in addition, the patient receives radiation exposure, and the procedure itself is more complex than those we described earlier. However, in some cases it cannot be avoided, for example, in cases of oncological and neurological diseases, diagnosis of heart and thyroid diseases.
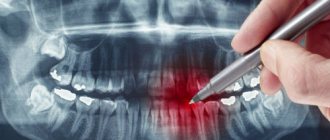
What an x-ray will show and how to properly prepare for it
18.10.2021
Radiological examination using X-rays requires us to follow certain rules, and this is not always advisable when diagnosing this disease. Particular caution should be taken by pregnant women or those who are not sure if they are expecting a baby. X-rays are inexpensive and are also covered by the National Health Fund. They always require a referral from a general practitioner or specialist. How to prepare for the examination, what determines its price and when is the best time to choose computed tomography? We answer these and other questions in this article.
X-ray (colloquially x-ray , x-ray examination) is one of the fastest and most accessible diagnostic imaging methods. Using a small dose of radiation, it allows you to image a specific area of the body. The following article will answer questions about the indications for x-rays and how to prepare for them, as well as provide information about the safety of the examination.
What is X-ray examination
X-ray examination is one of the main diagnostic tests that involves exposing the patient to a beam of x-rays (x-rays, X-rays) to produce an image of a given area of the body. The duration of the examination depends on the number of projections required (patient position). The entire diagnostic procedure takes between 5 and 10 minutes for non-contrast tests or up to an hour for tests that require the patient to take a contrast agent. X-ray examination is available and can be performed in a hospital or private diagnostic facilities. Most x-ray laboratories are already equipped with digital x-ray machines and x-ray results are provided to the patient on CD/DVD.
The health care provider may also have the patient tape the result. However, the examination recorded on disk is the best solution, since it can be sent to the doctor via the Internet. Additionally, by bringing the CD to your doctor's , the specialist can change the recorded image. It should be added that the result obtained in the form of a photo cannot be changed. However, this is useful if the doctor does not have a computer - viewing the film on film allows you to evaluate the area being examined without causing unnecessary confusion or scheduling another appointment.
What is radiological contrast? When should you take an x-ray with contrast and when without? Radiological contrast, otherwise known as a contrast agent or opacifying agent, is a substance that is administered to a patient to better visualize a given area before or during an examination. X-ray examination with contrast allows you to visualize the organs of the digestive system - the esophagus , stomach , duodenum and intestines . They are also performed during some studies of the urinary system - urography, pyelography, cystography and ureterography.
How to prepare for an x-ray examination
Most non-contrast X-rays do not require special preparation. When examining the head, it is important that the patient does not wear any jewelry, hairpins, or other objects that may interfere with the image. When examining the lower spine , pelvis and lower ribs, diet is recommended , preferably two days before the examination. In the case of an X-ray with contrast, the patient must fast. This means that he should not eat or drink for at least 6-8 hours before the test. It is also recommended to refrain from smoking on the day of the examination.
In case of X-ray examination of the intestine or urinary system with contrast, a low-fiber diet diet and the use of laxatives.
In the case of an x-ray of the small intestine, the patient should empty the bladder immediately before the examination. To have a photograph of the designated organ, each patient must bring a referral, identification, and results of previous imaging tests (if any). In a situation where the person is a minor, he must also have the child’s medical record with him.
Women are a special case of patients who undergo diagnostic imaging using X-rays. If the patient signed up for an x-ray without being sure that she is not pregnant, then before the examination she should undergo a pregnancy , since pregnancy is a contraindication. regarding X-ray examination.
X-ray examination is important in the diagnosis of trauma, especially fractures, gastrointestinal perforation and intestinal obstruction. The test is also indicated for many diseases of the respiratory and urinary systems. A referral for an x-ray is required for both NHS-funded and private examinations.
As mentioned above, pregnancy is a relative contraindication to x-ray examination. This means that X-rays are only possible if they cannot be taken after delivery , they are necessary for diagnosis and cannot be replaced by another diagnostic method that does not use radiation. X-ray examination has a low radiation dose and has no consequences when diagnosing an adult using this method.
There is no set number of x-rays that can be taken in a given period of time. During X-ray exposure, the patient receives a relatively small dose of X-ray radiation, and shields over unexamined areas of the body provide additional protection. As with any procedure performed using radiation, X-ray examination should only be performed in justified cases based on the direction of a physician .
X-rays and CT scans are both ionizing radiation tests that differ in many ways. An X-ray image requires a much lower dose of rays than a CT scan. However, tomography is characterized by higher image resolution, greater ability to differentiate tissues, and visualization of pathological conditions such as neoplastic changes or strokes. The examination technique also differs - during a tomography, the patient lies on a diagnostic table, which moves during the examination. During an x-ray, the patient can stand, sit, or lie on a table that remains stationary.
Published in Diagnostics and examinations of Premium Clinic
Hybrid Imaging Techniques
Probably, science would not be science if it did not constantly move forward and try to create something new from the old. So, doctors began to combine different scanning methods to obtain even more detailed and high-quality images. PET and SPECT are combined with CT, MRI complements PET. Such experiments are not cheap, but can sometimes help make decisions about further treatment for the patient.