Hello! Today we will talk about a procedure used in dental practice, x-rays. And the most common question we hear from our clients is how safe is this procedure?
Our clinic performs two types of X-ray examinations using a radiovisiograph and a computed tomograph. Using them, we can take a picture of one or several teeth, as well as a panoramic picture of the entire oral cavity.
What is the difference between a radiovisiograph and a computed tomograph? On a radiovisiograph we see all teeth in a two-dimensional projection. It's essentially a photograph of a tooth. On a computed tomograph we can see all organs in a three-dimensional projection.
What can a doctor see on an x-ray?
He can see:
- total number of teeth;
- anatomical features of the structure of the maxillofacial region;
- level, bone height;
- possibility of installing implants.
X-rays are also done for the purpose of establishing a diagnosis, when the doctor cannot make one based solely on the patient’s complaints.
X-rays are also done to monitor the doctor’s work. It shows how:
- canals are sealed;
- tooth removed;
- an implant was installed.
What types of photographs are there and what is better to choose?
As for the classification of OPTG, there are 2 types of panoramic X-rays of the jaw - film and digital orthopantomogram. Sometimes you can also hear about three-dimensional, but in fact this type of OPTG does not exist - all X-ray results here are only two-dimensional, “flat”.
- 1. film – this type of OPTG appeared first. Initially, models of devices were used that involved the use of a special film. It was placed on one side of the patient's head, while the X-ray tube was on the other side. After the procedure, the image was transferred to film, after which it was processed and developed,
- 2. digital – a modern version of the examination involves recording images on a medium in digital format. The obtained data is loaded into a special computer program, and the doctor can carefully study the already processed image from the computer screen.
What is better to choose – digital or film orthopantomogram? Of course, it is better to give preference to the digital option. It is more modern, accurate, and the image can be enlarged many times on a computer to examine the pathological area in detail.
What is an x-ray?
This is one of the types of radiation. If you think that X-ray radiation is present only in the X-ray room, then we can say right away that you are very mistaken. Let's remember physics lessons. We receive small doses of radiation every day:
- outdoors, from a natural source of radiation - the sun;
- at home from household sources located in the apartment: from a TV, various gadgets, a refrigerator, etc.
Radiation is measured in sieverts. What is the rate of radiation that a person can consume? Acceptable is 1000 sieverts per year.
Now let's remember mathematics and calculate how many X-rays can be taken for a person. A targeted image of one tooth is equal to 2-3 microsieverts. You can take 300-500 x-rays per year. A panoramic photograph (all teeth) is equal to 16-18 microsieverts. You can take 60-70 x-rays per year.
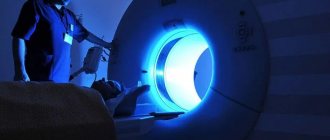
Now let's look at computed tomography. 1 photo taken on this device is equal to 60-80 microsieverts. You can take 16-20 x-rays per year.
We are now considering the maximum dose limits for X-ray equipment. Our clinic has a radiovisiograph and a computer tomograph of the latest generation made in Germany. The load on the devices is reduced to a minimum.
Previously, when taking an x-ray, the exposure time (you hear it as a beep) was approximately 2-3 seconds. Now this time has been reduced to 0.05 seconds.
Now let's talk about household radiation. If you watch TV for 3 hours at a distance of less than 2.5 meters from the screen, you get approximately 0.5 millisievert, i.e. Watched TV for 5 days, get 1 x-ray. If you sit in front of a computer monitor for more than 3 hours, you get 1 microsievert, 1 x-ray. We flew by plane to Turkey, where the flight is 3-3.5 hours, you get 10 millisieverts or 5 targeted shots. And add radiation from TVs, refrigerators, microwave ovens and you will understand that you will not receive terrible radiation in the X-ray room.
17-hydroxyprogesterone is a precursor to cortisol, a hormone produced by the adrenal glands and involved in the breakdown of proteins, glucose and fats, maintaining blood pressure and regulating the immune system.
Synonyms Russian
17-OPG.
English synonyms
17-hydroxyprogesterone, 17-OHP, 17-OH progesterone, progesterone -17-OH.
Research method
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
Units
ng/ml (nanograms per milliliter).
What biomaterial can be used for research?
Venous blood.
How to properly prepare for research?
- Do not eat for 2-3 hours before the test; you can drink clean still water.
- Unless directed by a doctor, women should be tested on days 3-5 of the menstrual cycle.
General information about the study
The test determines the amount of 17-hydroxyprogesterone (17-OPG) in the blood. 17-Hydroxyprogesterone is a precursor to cortisol and is used by the body to produce it.
Cortisol is a hormone produced by the adrenal glands; it is involved in the breakdown of proteins, glucose and fats, maintaining normal blood pressure and regulating the activity of the immune system. The production of cortisol is stimulated by adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), which is produced by the pituitary gland. Cortisol concentrations typically fluctuate throughout the day, with hormone levels peaking at 8 a.m. and then decreasing in the evening. In addition, the level of cortisol in the blood increases during illness and stress.
Several special enzymes are required to produce cortisol. When one or more of these are deficient or dysfunctional, abnormal amounts of cortisol and its precursors are produced, causing 17-hydroxyprogesterone to accumulate in the blood. The adrenal glands use excess amounts of 17-hydroxyprogesterone, producing a lot of androgens. Excess androgens, in turn, can cause masculinization and promote the development of male sexual characteristics not only in men, but also in women.
So, hereditary deficiency of special enzymes and, as a result, excessive amounts of androgens lead to a whole group of functional disorders in the body, collectively known as “adrenal hyperplasia.” Most often it is caused by a deficiency of the enzyme 21-hydroxylase, which is the cause of the disease in 90% of cases. Adrenal hyperplasia is inherited in mild or severe form.
In more serious cases of congenital adrenal hyperplasia, 21-hydroxylase deficiency and excess androgens can result in a female child being born with blurred genitalia, making it difficult to determine the baby's sex. Boys with this disease appear normal at birth, but subsequently their sexual characteristics begin to develop prematurely. In girls, hirsutism is likely, first in childhood and then during puberty, then irregular menstruation occurs and signs of masculinization appear. Almost 75% of patients of both sexes affected by 21-hydroxylase deficiency due to congenital adrenal hyperplasia produce less aldosterone, a hormone that regulates salt retention. In newborns of both sexes, this can lead to a life-threatening “salt loss crisis”: too much fluid accumulates in the body and therefore too much salt is excreted in the urine. In some cases, patients with these symptoms may have low blood sodium levels (hyponatremia), high potassium levels (hyperkalemia), low aldosterone, and increased renin activity. This severe, although less common, form of the disease is often detected during a preventive medical examination of newborns.
In the milder, most common form of the disease, only partial enzyme deficiency may be observed. Sometimes this form is called late, or non-classical, congenital adrenal hyperplasia - its symptoms can appear at any time in childhood, puberty or in adults. However, they may be mild and may develop slowly over time. And although this form of adrenal hyperplasia does not pose a threat to life, it is still dangerous for problems with growth, development of the body, as well as abnormal puberty in children, which can cause further infertility.
75% of newborns with 21-hydroxylase deficiency caused by adrenal hyperplasia also produce less aldosterone, a hormone that regulates salt retention in cells. The loss of too much fluid and salts along with urine threatens acute insufficiency of the adrenal cortex and the so-called salt loss crisis.
What is the research used for?
- For a preventive medical examination of newborn children - in order to find out whether the baby has congenital adrenal hyperplasia or any hereditary disease that is caused by specific gene mutations associated with a deficiency of enzymes involved in the formation of cortisol. Almost 90% of cases of congenital adrenal hyperplasia are caused by mutations in the CYP21A2 gene, which leads to 21-hydroxylase deficiency and accumulation of 17-hydroxyprogesterone in the blood.
- To screen for congenital adrenal insufficiency before symptoms appear, or to confirm adrenal hyperplasia if symptoms of the disease already exist.
- For the diagnosis of congenital adrenal hyperplasia in older children and adults who have a milder form of “late” hyperplasia. If a diagnosis of 21-hydroxylase enzyme deficiency is made, treatment is prescribed that involves suppressing the production of adrenocorticotropic hormone and replacing deficient cortisol with glucocorticoid hormones. However, a 17-hydroxyprogesterone test may be periodically necessary to monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
- Together with tests for other hormones - to exclude adrenal hyperplasia in patients with symptoms such as hirsutism and irregular menstrual cycles.
- To monitor the condition of women suffering from polycystic ovary syndrome, infertility, and occasionally to monitor the condition of patients with suspected adrenal or ovarian cancer.
When is the study scheduled?
- During preventive medical examination of newborns. If increased values are obtained, it is repeated to confirm the initial result. It may be prescribed if the child has symptoms of adrenal insufficiency or disorders associated with the loss of salts from the body. Signs of the disease may include lethargy, weakness, lack of appetite, dehydration, and low blood pressure.
- If congenital adrenal hyperplasia is suspected in a child (indistinct genitalia, signs of masculinization, acne and early growth of pubic hair). Sometimes - if a milder (late) form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia is suspected in older children or adult patients.
- Girls and women with hirsutism, irregular menstrual cycle, masculinization or infertility (these symptoms are very similar to the symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome).
- Periodically in case of 21-hydroxylase enzyme deficiency (to monitor the effectiveness of treatment).
What do the results mean?
Reference values
| Reference values | ||
| Up to 2 months | 0.96 - 10.46 ng/ml | |
| 2 months - 1 year | 0.66 - 2.81 ng/ml | |
| 1-10 years | 0.2 - 0.8 ng/ml | |
| For 10-18 years old - Tanner stage: | ||
| I | ||
| II | ||
| III | 0.33 - 1.98 ng/ml | |
| IV | 0.33 - 2.31 ng/ml | |
| V | 0.33 - 2.64 ng/ml | |
| Men | 0.2 - 3.1 ng/ml | |
| Women | Folliculin phase | 0.4 - 1.51 ng/ml |
| Luteal phase | 1 - 4.51 ng/ml | |
| Postmenopause | 0.2 - 0.9 ng/ml | |
| Pregnancy | 1-6 weeks | 1.32 - 3.30 ng/ml |
| 7-14 weeks | 1.1 - 2.8 ng/ml | |
| 15-24 weeks | 1.65 - 4.62 ng/ml | |
| 25-33 weeks | 1.98 - 10.2 ng/ml | |
| 34-40 weeks | 2.64 - 13.20 ng/ml |
Reasons for increased 17-OPG levels
Normal levels of 17-hydroxyprogesterone indicate the absence of congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency.
A significantly increased concentration of 17-hydroxyprogesterone in a newborn most likely indicates the presence of congenital adrenal hyperplasia.
Moderately elevated levels of this enzyme may indicate a less severe form of adrenal hyperplasia, and 11-beta-hydroxylase deficiency (another enzyme defect associated with congenital adrenal hyperplasia) is also likely.
Reasons for decreased 17-OPG levels
Low or decreasing concentration levels in patients diagnosed with hyperplasia indicate a positive effect of treatment.
What can influence the result?
- In prematurely born children, increased levels of 17-hydroxyprogesterone are often observed.
Can X-ray examinations be performed on pregnant women?
In the first half of the term, the study is done only according to strict indications. In the second half of the term, you can do as much research as you like.
Another interesting fact. People often ask X-ray technicians to wear more protective lead aprons. Let's say right away that this is useless. You receive the same dose of radiation from covered and exposed parts of your body.
And remember that a doctor will never order an x-ray just out of curiosity. X-ray is one of the types of diagnostics of the area of proposed treatment and the anatomical features of the oral cavity.
Come to our clinic and we will make every effort to make your stay comfortable and enjoyable!
Orthopantomogram - the essence of the study
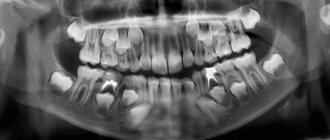
An orthopantomogram is a complete panoramic x-ray of all teeth at once, which allows you to get a general picture of the condition of the dentofacial apparatus. Today, this technique is actively used in cosmetology and various fields of dentistry, including dental implantation and maxillofacial surgery. The procedure is carried out using a special device - an orthopantomograph or computed tomograph (this is more powerful and modern equipment that is installed in clinics that also offer computed tomography services).
Thus, the snapshot allows you to examine the status of the following elements:
- jaws and bite,
- teeth, their shape, position, roots, as well as the rudiments of future teeth, including eights, impacted elements, bone tissue,
- gingival tissue, vascular system, dental canals - examination allows us to identify possible pathological conditions, such as periodontitis or the presence of neoplasms,
- soft fabrics,
- fillings, crowns, dental bridges.
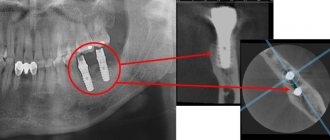
An orthopantomogram (OPTG) is a mandatory procedure in preparation for dental implantation. The examination allows you to identify hidden pathologies, eliminate possible contraindications to treatment and avoid many problems even at the preparatory stage. The diagnosis itself lasts about a minute. After this, the received data is loaded into a computer, where further image processing is carried out.
Important! In addition to OPTG of the dentition, computed tomography is often also prescribed, which allows you to obtain not just a flat, but a three-dimensional image - on it, of course, all elements can be viewed in 3D. This is especially important when all teeth are implanted, immediate loading methods are used, or complex osteoplastic surgery is required.
DENTAL PROSTHESIS WITH 4 OSSTEM IMPLANTS - RUB 170,000!
Implantation even with bone tissue atrophy. Work guarantee! Save RUR 20,000.
on promotion >> Free consultation with an implantologist +7 (495) 215-52-31 or write to us
Features of conducting OPTG for children
We figured out what is visible in panoramic photographs and why they are taken, and found out that this is a completely safe diagnostic method. Now it should be noted that an orthopantomogram for children is carried out taking into account some nuances. A radiation exposure of 55 μSv (1 shot) is completely safe for a child, so a similar procedure is allowed from 5-6 years of age. The examination assumes that the patient must stand still for some time, but for young children this task can be quite difficult . When it comes to small patients, the procedure is carried out in exposure mode - the area of exposure is reduced, and the sensor is adjusted to a trajectory of movement corresponding to the small size of the jaws.
“My son also recently had a panoramic photo taken. He's 10, everything went great. Now there are new technologies everywhere, everything is safe. The procedure took less than a minute, and the doctors assured me that there was nothing wrong with it. How else can you start correcting your bite? The orthodontist prescribed OPTG for us. So far I’ve made the plate, but in a couple of years we’ll get braces. There’s no place here without pictures!”
In pediatric dentistry, OPTG is used to detect the rudiments of permanent teeth, assess the correctness of their formation, to diagnose adentia and identify malocclusions. Most often, this procedure is prescribed by an orthodontist before starting to correct defects in bite and teeth position. The procedure is completely safe for the child
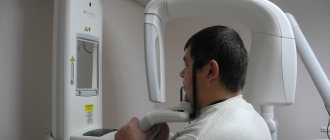
How is OPTG performed?
The patient is put on a special protective apron and asked to sit inside the orthopantomograph. In this case, the hands are placed on the handles of the orthopantomograph, the chin is placed on a special holder, and a special mouthpiece is placed in the teeth.
After this, the orthopantomograph is turned on, after 20-30 seconds the procedure is completed, and the study data is transferred to the PC.
How is the procedure performed?
We have figured out why an orthopantomogram is done in dentistry, and now we will look at the progress of the procedure. Diagnostics is completely painless for the patient, and the operation of the device itself takes no more than a minute. In this case, the patient immediately receives the examination results. Immediately before the procedure, the specialist will ask you to remove all metal items and jewelry and put on a protective vest. The doctor will indicate the place where you need to stand during the diagnosis. After that, he will raise the working area of the device and fix it at head level.
“I took a panoramic photo before implantation - this is the most harmless procedure I have ever undergone in dentistry, especially compared to the operation itself! I don’t understand the reason for the excitement of some patients, after all, they probably underwent fluorography, everything is similar here, only they examine not the chest, but the jaw. Everything really takes no more than a few minutes. Moreover, the doctor immediately showed me the result on the computer screen, gave some comments, gave me the picture, and I also wrote it down on a flash drive, just in case. In general, don’t be afraid, there’s nothing scary there at all...”
Mila1989, Moscow, from correspondence on the woman.ru forum
After this, the person’s head is fixed using a special plate. At one end it is attached to the equipment, and its second free end is opposite the mouth. A sterile tip is fixed on it so that the patient can clamp it in his teeth - this helps ensure the immobility of the jaw apparatus during the examination and eliminate any distortions.
When all the equipment settings are ready, the specialist will definitely warn the patient about the start of the examination, and also remind him of the importance of remaining still. After turning on the tomograph, the plates will gradually rotate around the head, making two revolutions. Next, the doctor will be able to evaluate and show the patient the result on the computer screen, and will offer to print the image or record it on a digital medium.
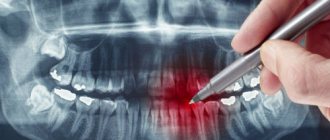
How to decrypt a photo
In good clinics and specialized centers, the radiologist often provides a detailed description of the image, which identifies all the identified problems. However, such an approach to work is not found in all medical institutions today. Usually, the patient is given only an envelope with an image, and its detailed study and analysis is carried out by the attending physician.
If you try to “read” the results of an X-ray examination yourself, then, if you wish and have some skill, you can assess the position of your wisdom teeth, detect inflamed areas, and identify a decrease in the level of bone tissue. In addition, on the Internet today you can find a lot of sources with visual examples of dental problems shown in panoramic photographs of different patients - they can be used for comparison with your results.
Indications and restrictions
The procedure is completely painless, carried out as quickly as possible and without any discomfort for the patient. OPTG is prescribed in the following cases:
- as part of implantation – carried out to study bone tissue, select implant models and places for their implantation. Based on the data obtained, the doctor will be able to draw conclusions about the advisability of building up the jawbone;
- to assess the quality of dental canal treatment and the condition of the roots - before prosthetics;
- before starting orthodontic treatment - before installing braces and other corrective structures;
- before an upcoming operation, complex removal, including wisdom teeth;
- to examine the dental system in children, assess the correctness of its formation and identify possible deviations;
- in order to determine the extent of damage to periodontitis and periodontal disease;
- to identify neoplasms in hard and soft tissues.
This procedure may be required in various clinical cases. X-ray diagnostics is not advisable in the first and last trimester of pregnancy - it is carried out only in the presence of emergency indications and with the permission of a gynecologist.