Dental practice involves a large number of manipulations, accompanied by pain of varying severity. Fear of pain in the dentist's chair often forces the patient to refuse medical care until the last minute.
The most popular method of administering an anesthetic is infiltration with an average effect of up to 2 hours
Today, high-quality anesthesia is one of the criteria for which patients put forward the highest demands. People want to receive treatment in a comfortable environment, without unnecessary stress. There are several types of painkillers. Depending on the method of administration and the composition of the drug, anesthesia after dental treatment can last from a couple of hours to a day. The doctor chooses an option based on the complexity of the upcoming intervention.
Inhalation anesthesia
This is the most commonly used type of anesthesia, which is characterized by ease of implementation, relatively easy control and short duration of action, which is important for minor surgical interventions. Inhalation anesthesia is the administration of drugs through a mask, which ensures their entry into the organs of the respiratory system. Most often, Narcotan, nitrous oxide, Trilene, Ftorotan and Etran are used for this type of anesthesia. There is a certain problem - to achieve the desired result, it is necessary that the effect of anesthesia be deep, and this is fraught with serious complications. Therefore, this type of anesthesia is most often used in pediatric surgery. Children under anesthesia administered by inhalation feel excellent, they do not experience respiratory dysfunction, and complications are extremely rare.
Drug sedation is a type of general anesthesia. Sedation is used for short-term operations or diagnostic procedures and, unlike general anesthesia, does not require the administration of a large dose of strong anesthetics. During the administration of anesthesia, the anesthesiologist gradually puts the person into deep sleep, during which the patient is unconscious. When going into anesthesia, the patient goes through three stages:
- Analgesia. At this stage, sensitivity decreases and diction is impaired. The specialist can only perform simple operations that do not provoke acute pain.
- Excitation of the nervous system. The stage at which the pulse quickens, the heartbeat noticeably accelerates, a slight respiratory arrhythmia appears, muscle tone increases, and dilation of the pupils is observed.
- Surgical stage. At this stage, the person is in a state of deep sleep, there is no sensitivity to pain of any level of intensity.
The involvement of a qualified anesthesiologist to perform the procedure under general anesthesia is a necessary condition in world practice.
Preparation for the general anesthesia procedure
Our goal is to ensure your safety and comfort during surgery, research or treatment.
Before the procedure, you should consult with a specialist anesthesiologist. Our doctors will carefully examine your situation: the presence of chronic and infectious diseases, allergies, recent vaccinations and pregnancy, and if necessary, they will refer you for additional examinations, which can be completed at each of our clinics in Sergiev Posad, Khotkovo, Pushkino and Korolev. If there are no contraindications to the use of general anesthesia, the doctor will tell you about the specifics of preparing for the procedure.
It is recommended to limit food and liquid intake 6 hours before applying general anesthesia.
Following the doctor's recommendations will allow specialists to carry out the anesthesia procedure and surgery in the most comfortable way for you. After treatment, you will be under the supervision of our highly qualified specialists for two hours.
Is sedation harmful?
The medical community believes that the use of modern anesthetics (namely, they are used in the Family Clinic Network) is one of the safest types of anesthesia (in comparison, for example, with spinal or epidural anesthesia). In some cases, according to indications, doctors may use combined anesthesia. Such anesthesia includes, for example, nitrous oxide and propofol.
Dreams during anesthesia
If you are a patient preparing for anesthesia, you are probably worried about what will happen to you during anesthesia.
Will you see hallucinations, nightmares or light at the end of the tunnel? We dare to dissuade you. Anesthesiologists at the Network of Family Clinics, who have more than 29 years of experience, claim that when using general anesthesia using modern anesthetics, patients, as a rule, have pleasant dreams, and the process of waking up from anesthesia does not cause headaches or other side effects. The main thing is to come to the doctor calmly and without unnecessary fears, and the doctor will do the rest for you.
Intravenous anesthesia
This type of anesthesia refers to non-inhalation types of anesthesia, which are characterized by a long-lasting effect and a greater depth of effect compared to inhalation anesthesia. Intravenous anesthesia can be performed using the following drugs:
- Thiopental, Recofol, Oxybutyrate and Propofol - classic pain relief
- Fentathyl with diphenhydramine - neuroleptanalgesia, which can be carried out on spontaneous breathing or combined with artificial ventilation
- Sibazon with Fentathyl is ataralgesia, which provides superficial, gentle anesthesia and can be carried out with other types of anesthesia.
This type of anesthesia is used to remove abscesses and phlegmons that occur with complications; it is also possible to treat small benign tumors if their removal under general anesthesia is not possible.
How does the drug affect the body?
The mechanism of action of Propofol has not yet been fully studied. Its main effect is associated with the fact that it enhances and prolongs the action of GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid), an amino acid that plays the role of an inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, responsible for calm, relaxation and sleep.
When administered, Propofol begins to act almost immediately - it instantly penetrates the brain and causes rapid onset of sleep. Next, a maintenance dose of the drug is administered through an intravenous catheter. An anesthesiologist, using special equipment, controls the depth of sleep, the dosage of incoming medication, the patient's breathing, blood oxygen saturation, blood pressure and heart rate. After completing the treatment procedures, the supply of Propofol is stopped, and the patient wakes up after 5-10 minutes as if from a normal sleep.
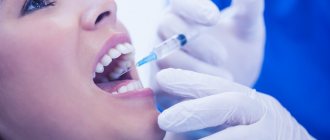
Local anesthesia
Treatment under anesthesia is the only option for providing surgical care to a patient or performing complex manipulations. Often, a doctor will numb a specific area, which is achieved by injecting it with an anesthetic solution and is called local anesthesia. This type of anesthesia is used for opening ulcers, treating teeth, and excising a hernia. Local anesthesia is the injection of an anesthetic into the skin and other anatomical structures of the place where surgery is expected to be performed.
The anesthetic injections are superficial; only in exceptional cases can the doctor administer the drug more deeply. Local anesthesia is performed by injecting the drug through a very thin needle, so the actual anesthesia procedure is minimally painful. Often, the administration of an anesthetic is combined with sedation - sedatives are introduced into the patient’s body, which normalize the person’s psychological state, reducing feelings of anxiety and restlessness.
Despite the fact that local anesthesia is used very widely in medicine, the consequences of anesthesia can be quite serious. For example, local anesthetics can have a negative effect on the heart and brain, leading to heart rhythm disturbances, seizures and loss of consciousness. At the same time, doctors claim that local anesthesia, compared to general anesthesia, is safer for the patient’s health.
Types of anesthesia, how it is done
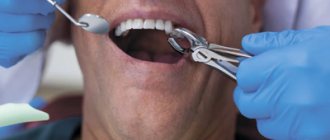
The dentist can use application, infiltration and conduction anesthesia. In each case there will be a different depth of impact. Accordingly, anesthesia after tooth extraction will weaken, depending on the location of exposure and the concentration of the drug.
- The application type of anesthetic is a solution or gel that is applied to the surface of the mucous membranes. The effect is on receptors in the mouth and peripheral nerve endings. This type of anesthesia is used to relieve pain before injections, as well as when removing children's baby teeth.
- Infiltration is a shallow injection that allows you to locally “freeze” the peripheral nerves. This is the option most often used for dental treatment, extractions and simple surgical interventions.
- The conduction type of anesthesia allows you to “turn off” nerve channels and trunks. When it is necessary to desensitize half of the jaw, this option is used. It is used for tooth extraction, surgical interventions, and severe inflammatory processes. The injection is performed closer to the temporomandibular joint, in the branch of the trigeminal nerve.
Anesthetic for applications - a solution or gel applied to the mucous membranes
In complex cases, when the patient is treated using sedation with analgesia or general anesthesia, the anesthesiologist is responsible for deactivating the effects of the drugs. In this case, there is an effect on the central nervous system, suppressing not only the patient’s consciousness, but also all reflexes. General anesthesia after tooth extraction is completely removed within 24 hours. After such manipulations, the patient is transferred to intensive care, where he is under the supervision of specialists.
Endotracheal anesthesia
One of the most commonly used methods of anesthesia when performing complex surgical interventions is endotracheal anesthesia, which involves immersing the body in a state of deep narcotic (medicinal) sleep. At the same time, the muscles completely relax, and the patient does not breathe independently. To achieve the desired state, doctors carry out a set of measures for the patient:
- Tracheal intubation is the insertion of an endotracheal tube into the lumen of the trachea, which is needed to provide artificial ventilation of the lungs.
- Intravenous administration of narcotic anesthetics, sedatives and tranquilizers.
- Administration of muscle relaxants – they block neuromuscular transmission.
- Artificial ventilation.
The quality of endotracheal anesthesia depends not only on the experience of the anesthesiologist, but also on how correctly the patient’s condition is monitored. It is imperative to monitor blood pressure, pulse, and oxygen saturation.
Before general anesthesia: preparation
Preparation for surgery under anesthesia has a great influence on the effectiveness and safety of general anesthesia and the course of the postoperative period. You will have to undergo a comprehensive diagnostic examination, including detailed blood tests, coagulogram, and ECG. According to indications, consultations with narrow specialists are prescribed.
The presence of chronic diseases of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems is of great importance. Be sure to tell your doctor about the following diseases:
- bronchial asthma;
- chronic obstructive bronchitis;
- arterial hypertension;
- IHD;
- history of stroke.
Do not under any circumstances hide the fact that you have a history of chronic diseases and acute vascular events (heart attack, stroke). Not only the outcome of the operation, but also your life depends on this! Also provide your doctor with a complete list of medications you take, including “harmless” analgesics for headaches or menstrual pain.
As practice shows, excess weight negatively affects the rate of recovery after operations under general anesthesia. If you are planning plastic surgery in advance, pay attention to weight loss issues. It is advisable to quit smoking in about six months. If you have not done this, stop smoking a week before the operation, but you should not “quit” the day before anesthesia - this may complicate the rehabilitation period.
On the eve of the operation, pay special attention to nutrition and hydration. You should not drink alcohol 24 hours before plastic surgery. On the day before surgery, you should limit yourself to breakfast and lunch. On the day of surgery, eating and drinking is strictly prohibited!
Consultation with an anesthesiologist
First of all, the anesthesiologist’s task is to assess how ready a person is for surgery and anesthesia. If the answer is yes, then the method of pain relief is selected based on the volume of intervention and the patient’s health condition. The following factors are taken into account:
- whether the patient had previously undergone surgical interventions under anesthesia, and if so, under what kind;
- whether there is an allergy to medications;
- what chronic diseases are there;
- whether there have been recent injuries;
- whether the patient is currently taking any medications (this is especially important because when combined with each other, drugs can change the effect or cause side effects).
All this must be taken into account and analyzed even if an outpatient operation under local anesthesia is planned.
The patient must provide the doctor with all available medical documentation and test results. You can and should ask a specialist all the questions that interest and concern you. You should not go into surgery feeling very scared and anxious.
Shadrina Vera Vladimirovna
Anesthesiologist-resuscitator
“At the SM Clinic we treat anesthesia very responsibly; we take into account the development trends of modern anesthesiology and use effective and safe methods of pain relief. The patient is carefully prepared for general anesthesia. They inform you about the progress of the manipulations, examine the nasal passages for patency, and find out your allergy history. Every little detail is important. The operation will be rescheduled if the anesthesiologist has doubts about the patient’s readiness for surgery.”
How long does Propofol take to leave the body?
Propofol is eliminated through its breakdown in the liver with the formation of inert metabolites and further removal through the kidneys. Only 1-2% of propofol is excreted unchanged. The time it takes to remove half of the substance contained depends on the duration of its administration.
The fact is that the substance penetrates unevenly into different tissues. At the very beginning of the administration of the drug (so far it has penetrated only into tissues directly supplied with blood through large arteries), it takes from 1 to 8 minutes for its concentration to drop by half after stopping the supply.
If Propofol is administered within 8 hours, then it has time to penetrate all tissues of the body, therefore, when the supply is stopped, it begins to enter the blood from those tissues into which it penetrated slowly over all these hours, and therefore the same half-life is already increasing up to 40 minutes. The drug is completely eliminated from the body after a few hours.
Complications of anesthesia
Therapy is carried out taking into account the reasons that caused the pathological condition. In case of respiratory disorders, the composition and volume of the gas-air mixture is adjusted, and the endotracheal tube is sanitized using an electric suction. If it is not possible to completely clear the airways, call the endoscopic team on duty to perform emergency bronchoscopy. To relieve laryngospasm, narcotic analgesics, atropine, antispasmodics, and adrenergic agonists are used. To saturate the blood with O2, the device is set to enhanced oxygenation mode (100%). Maintaining a sleepy state is ensured by intravenous anesthetics.
Cardiac dysfunction is treated symptomatically. For bradycardia, administration of atropine and adrenaline is required. A decrease in blood pressure against the background of weakened cardiac activity is an indication for transferring the patient to the administration of pressor amines through a syringe pump. The dose of anesthetic may need to be reduced. Arrhythmias are stopped using cordarone, amiodarone, procainamide, lidocaine. Fibrillation that is not amenable to chemical treatment requires electrical defibrillation. When blood pressure increases, antihypertensive drugs are administered; when blood pressure decreases, hypotonic drugs, infusion solutions to replenish blood volume, and steroid hormones are administered.
Short-term postoperative psychosis cannot be relieved with medications. In case of severe psychomotor agitation, the prescription of neuroleptics and narcotic analgesics is allowed. Long-term disorders of the central nervous system require therapy with the use of nootropics, antioxidants, and general strengthening agents (multivitamin complexes, adaptogens). Intestinal tone usually recovers on its own within 1-2 days. In case of prolonged paresis, proserin is administered.
Malignant hyperthermia is an indication for the administration of datrolene, a muscle relaxant that can block ryanodine receptors. In addition, symptomatic treatment drugs and physical methods of reducing the temperature are prescribed (ice on large vessels, wetting the sheets and the patient’s body with cold water, ventilating the patient’s body). For allergic reactions, antihistamines, glucocorticosteroids, and symptomatic medications are infused. Severe manifestations require mandatory tracheal intubation and transfer to mechanical ventilation, if this has not been done previously.
Possible risks
There is a risk of complications even with very small volumes of intervention. It is associated with the presence of chronic diseases in the patient, his general health, the volume of work of the surgeon, the method of pain relief, etc. However, the specialists of SM-Clinic do everything to reduce risks to an absolute minimum:
- A thorough preoperative examination allows us to identify the slightest contraindications. If they are present, the operation is postponed or not performed.
- The clinic widely uses modern minimally invasive methods that minimize tissue trauma and reduce the duration of the operation.
- SM-Clinic uses only certified modern drugs that meet international standards.
- The staff of doctors consists of experienced anesthesiologists and surgeons who thoroughly know their business.
- During the entire operation, an anesthesiologist is with the patient to monitor the vital signs and general condition of the patient.
- Both during surgery and during the rehabilitation period, we bear full responsibility for the patient’s condition and health.