- Operating principles
- Anesthesia methods
- Indications and contraindications
- Types of anesthesia
- pain relief in pregnant women
- Anesthesia for children
- Recommendations
- Complications
- Drugs used
- Price
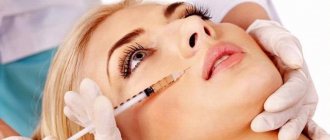
Nowadays, it is possible to receive medical care not only fast and high-quality, but also painless. Almost any action of the doctor that can bring discomfort or unpleasant sensations to the patient is accompanied by dental anesthesia, or in other words, “freezing”. He stops experiencing pain and fear and relaxes, allowing the dentist to calmly do his job.
Operating principles
Anesthesia is carried out immediately before the start of treatment. The anesthetic comes in both liquid and gel form. The doctor injects into the soft tissues that are located near the diseased tooth. After some time, the tongue, gums and cheeks become numb and “freeze”. At this moment, the anesthetic acts as a blocker of nerve impulses that send a pain signal to the brain. The patient calmly endures dental procedures without experiencing stress.
The duration and effectiveness of dental anesthesia depends on the quality of the materials used and the location of the injection. The closer to the problem area the injection was administered, the more intense its effect. Each organism is individual, therefore the drug will be excreted at different rates.
Different types of drugs function in their own ways. For example, gel-like ones applied to the gums or surface of the cheek last only a couple of minutes. If they are installed in the upper part of the jaw, the effect will last for 2-3 hours. To treat the lower group of teeth, a deeper injection is required, so the result lasts up to 4 hours. After the solution is absorbed, the numbness disappears and sensitivity returns to the patient.
Preparations for local anesthesia
The Smile-at-Once clinic uses modern anesthetics of the latest generation - effective, non-toxic and absolutely safe, even for pregnant women, the elderly or children. We do not use drugs based on novocaine or lidocaine due to toxicity and a high risk of allergic reactions. In addition, the articaine group of drugs, which are used today for local anesthesia, are 5-6 times more effective than lidocaine.
"Ultracaine" for all groups of patients
An original drug produced in France, which is used for both infiltration and conduction anesthesia.
It is safe, used even in the presence of allergic reactions, and is suitable for patients with heart disease and pregnant women. Its effectiveness is very high, while it is instantly eliminated from the body and does absolutely no harm. The main active ingredient is articaine, to which epinephrine is added to enhance the anesthetic and prolong its action. It provides local vasoconstriction, which significantly shortens the rehabilitation period after treatment. Depending on the concentration of epinephrine, there are three types of the drug - for different manipulations and categories of patients.
"Ultracaine-Forte" (concentration 1:100,000) is a drug with a high dose of epinephrine, used during surgical operations. "Ultracaine DS" with a low concentration (1:200,000) - is used for therapeutic treatment, including in patients with diseases of the cardiovascular system, high blood pressure, suitable for pregnant and lactating women. Ultracaine D does not contain epinephrine. The effect of the drug is short, but it can be used for allergic reactions, bronchial asthma, and pronounced cardiovascular pathologies.
"Ubistezin"
A cheaper, but no less high-quality analogue of Ultracain, produced by the German company 3M. It contains similar active ingredients: articaine hydrochloride and epinephrine. It has two forms of release, depending on the concentration of the latter (1:100,000 or 1:200,000). Use is allowed during breastfeeding and cardiovascular pathologies.
"Artikain"
An injection solution that consists directly of the main active ingredient - articaine. Inexpensive drug made in Russia. Used for infiltration or conduction anesthesia. Can be used in pure form or with the addition of epinephrine/glucose solution in a certain proportion. Not used for bronchial asthma and severe allergic reactions.
"Scandonest" for the elderly
The main active ingredient of this French-made drug is mepivacaine hydrochloride. It is not used during pregnancy and bronchial asthma, but use is allowed in patients with cardiovascular pathologies, since the drug does not contain epinephrine, adrenaline and preservatives. Suitable for older people, especially those with high blood pressure. It is one of the safest anesthetics for both infiltration and conduction anesthesia. Its disadvantage is its short duration of action, which requires repeated administration of the drug approximately every 30 minutes during long procedures.
"Orablock"
Another drug, the main active ingredients of which are articaine and epinephrine with varying concentrations of the latter, which affects the effect and duration of pain relief. Not used during pregnancy and pronounced cardiovascular pathologies.
"Naropin" for complex surgical operations
A long-acting anesthetic whose main active ingredient is ropivacaine hydrochloride. The duration of pain relief depends on the dosage. Very often, this drug is used for conduction anesthesia during complex surgical operations and the installation of a large number of implants. Among the contraindications is only individual intolerance to amide anesthetics.
Anesthesia methods
Depending on the goals and nature of the problem, the doctor chooses the method of pain relief. In medicine there are two main methods:
Anesthesia
It is most often used in surgery, and in dentistry much less often, in case of urgent need. It affects the entire body of the patient, inducing a state of sleep. At this time, all muscles relax and consciousness turns off. You can administer painkillers intravenously or inhale vapors through a mask. Deep anesthesia is used during complex operations when a person does not have enough strength to cope with pain or it is necessary to completely eliminate body movement. During sleep, the doctor monitors the patient's condition to avoid emergency situations.
Recovery from anesthesia is the body’s return to normal functioning after a long “freeze.” For all people, this process proceeds differently, some experience signs of nausea or a feeling of lethargy, while others wake up well-slept and rested.
General anesthesia in dentistry during pregnancy is applicable only in emergency cases when there is no other alternative.
Local anesthesia
Unlike anesthesia, it occurs locally, affecting only certain areas of the body. Can be used for children and pregnant women, without fear of unwanted consequences. In dental practice, this method is most often used, so we will talk about it in more detail.
Xenon sedation or xenon therapy to prepare for main anesthesia
This is a separate type of anesthesia that can be used in combination with both local and general anesthesia (if necessary). Xenon is an inert gas that quickly begins to act and is just as quickly eliminated from the body. It has a relaxing effect: anxiety decreases, the patient relaxes. Moreover, during the operation he is fully conscious, can communicate with the doctor, and understands everything that is happening around him. The procedure can be interrupted if necessary if there is discomfort. At the same time, local anesthetics are used, since xenon itself does not have a pronounced analgesic effect.
Among the pleasant “bonuses” are saturation of cells with oxygen and restoration of metabolic processes. That is, this is not only a reduction in stress, but also a general improvement in the body’s health.
Indications and contraindications for the use of local anesthesia
Any dental intervention that causes pain must be accompanied by “freezing” of the required area of the oral cavity. There is a list of diseases for the treatment of which it is necessary to administer anesthetic drugs:
- Complex caries;
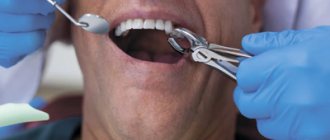
- Removal of a tooth or its roots;
- Periodontitis;
- Inflammatory processes in the dental system;
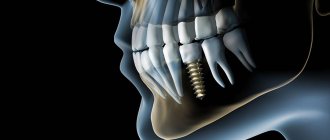
- During prosthetics.
Before drawing up a treatment plan and choosing medications, the doctor must interview the patient and find out from him the presence of contraindications in order to exclude the possibility of complications.
- Allergy to drugs used;
- Heart diseases;
- Diabetes;
- Problems with the endocrine system.
Today, patients have an alternative: the STA system.
Computer anesthesia is a local, imperceptible anesthesia using a device controlled by a computer, the so-called “single tooth anesthesia.” It is approved by the American Dental Association and recommended as the optimal method of pain relief.
This anesthesia is liked by those patients who are afraid of injections, but at the same time want to feel comfortable in the dentist's chair. This is especially important when treating children. When using STA, the child does not experience fear of a traditional syringe, and the anesthesia process itself occurs as delicately and effectively as possible. Thanks to this, the dentist can calmly carry out all the necessary manipulations and leave only positive impressions on the little patient after the appointment.
Types of anesthesia
There are several methods in medicine; they differ in duration, effectiveness and location.
Conductor.
The most common type of local anesthesia in dentistry. Using a special needle, the drug is injected near the nerve trunk, blocking pain impulses that go to the brain. The injection is given in doses not exceeding a volume of 5 ml. To ensure a guaranteed result, the injection is placed at an angle of 90 degrees.
“Freezing” applies only to a certain group of teeth, in the place where the treatment will take place. After about 15 minutes, the medicine begins to work and the doctor can begin work.
The injection site can be additionally lubricated with lidocaine. If during the procedure the patient continues to feel discomfort, another dose may be administered.
Infiltration
It differs from the conductor only in the angle of the needle and the place of application. The drug is injected directly into the root apex area. This type is most effective for teeth and upper jaw. With infiltration anesthesia, you can “freeze” both a small area and a large surface of the oral cavity along with soft tissues.
Applique
This method is performed without a syringe. The dentist applies the necessary product directly to the diseased tooth and the soft tissues surrounding it using a cotton swab or fingers. Some doctors spray anesthetics using a special spray.
It is mainly used during simple and quick operations, since its effect is short-term and does not protect against severe pain. The result is stored for a maximum of 20 minutes. It is often used as the first stage before the injection “freezing” method.
Intraosseous
The dentist resorts to this technique much less often when other types of anesthesia have proven ineffective. An analgesic that is injected directly into the hard tissues between the teeth. The difficulty lies in the technique; to get to the bone, the doctor cuts the gum and drills a hole in it with a bur. This is the most effective method for quickly and permanently freezing the required area.
Intraligamentary
Its peculiarity is the high speed of injection, so numbness occurs almost immediately, but lasts only 20-30 minutes. The advantage of intraligamentary anesthesia in dentistry is that it acts directly on the tooth without touching the cheeks, lips and tongue. That is why the recovery process is much easier.
The mechanism of anesthesia using the Single Tooth Anesthesia System
The STA apparatus itself consists of two main parts. This is a small unit in which a microprocessor is installed that controls the anesthesia procedure. As well as a sterile disposable tube with a special ergonomic tip with a needle. The needle itself is incredibly thin, which ensures the most delicate penetration into the mucous membrane of the oral tissues.
When the doctor makes the first touch with the tip to the gum , the device begins to analyze the density and resistance of the tissue and gradually release an anesthetic solution. As it moves into the tissues, the release of the solution continues in an optimal individual mode, taking into account the anatomical and physiological characteristics of the tissues of each patient.
As the needle penetrates deeper into the gum, the program continuously evaluates the parameters, changing the mode of drug administration . The computer constantly regulates the speed, degree of pressure and amount of administered medication. This is done to ensure that the painkiller travels to the nerve endings along the path of least resistance, without causing a feeling of fullness or burning and excessive pressure on the soft tissue.
evaluates the condition and resistance of tissues , which, in case of any deviations from the norm, gives an audible and visual signal to the doctor. For example, if the resistance and density of the tissues are increased or the needle tip is clogged, the device will signal and automatically stop supplying the anesthetic.
The STA device provides the dentist with all the necessary information in real time . Thanks to this, the specialist can adjust the correct position of the needle without causing pain to the patient. At the same time, the needle moves smoothly and evenly, making the necessary rotational movements to achieve an accurate, fast and most pronounced effect.
Features of pain relief in pregnant women
One of the most common misconceptions is that pregnant women are contraindicated for dental treatment. You should not trust unreliable sources; dentistry and pregnancy are completely compatible concepts. Expectant mothers should undergo a professional examination during planning and at 8, 18 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. Untreated infections in the oral cavity contribute to the development of other dangerous diseases.
The question immediately arises: can the use of dental anesthesia harm the health of the unborn child? Modern technologies allow the use of drugs with lower concentrations of adrenaline. Accepted painkillers are ultracaine, primacaine or mepivacaine*. They do not penetrate the placenta, therefore, do not harm the body of a pregnant woman.
*A verified and accurate list of acceptable medications can be obtained from your doctor.
Tuberal anesthesia
Tuberal anesthesia is so named in connection with the injection site - the tubercles of the upper jaw, which are called tuber in Latin. The posterior alveolar nerves are located here, innervating the area of the alveolar ridge from the third to the first molar. This type of anesthesia is the most dangerous in terms of possible complications due to individual differences in the structure of this area and the location of nerves and blood vessels in it. There are intraoral and extraoral methods of administering tuberal anesthesia. It is believed that the intraoral method is more likely to cause injury, while the external method is safer and it is also easier to ensure adequate antiseptic treatment of the surface before injection.
Anesthesia for children
Painless pediatric dentistry is a hot topic today. All parents know what a trip to the dentist means for a child. If this brings few pleasant emotions to an adult, then what can we say about children. The first scheduled visit is always scheduled for the age of 6-7 years - this is the time when baby teeth are replaced with permanent ones.
The psyche of children is not yet fully formed; one wrong word or action can provoke the development of unpleasant memories. Therefore, it is important to instill confidence in the child, to mentally prepare him for the procedure: explain why he is going there and what the doctor will do. The use of anesthetic agents in pediatric dentistry is an integral part of comfortable treatment.
The most suitable injection methods for babies are infiltration, conduction and application. The place where the drug is administered is “frozen” in advance and only then does the doctor give an injection. The child’s body is not yet fully formed, so in pediatric anesthesia, special medications are used that make it possible to carry out the procedure safely.
Intraligamentary anesthesia
Intraligamentary anesthesia is also called intraligamentous and intraperiodontal. Its difference is in higher pressure when administering an anesthetic, which ensures uniform spreading of a small amount of the drug in the periodontal space, as well as its penetration into the intraosseous space. Drugs should be administered very slowly. When using this type of anesthesia, significantly less drug is required than with conventional infiltration; it occurs within 15-45 seconds and lasts for 20-30 minutes. For intraligamentary anesthesia, special syringes are often used, which make it possible to administer the drug under the required pressure without unnecessary effort and thus achieve the best result.
Recommendations
For the successful use of anesthetics, there are two conditions: 1) the patient must abstain from drinking alcohol at least 24 hours before treatment; 2) feel good.
Often, after the effect of painkillers wears off, the patient experiences pain, swelling, tingling at the injection site, and difficulty opening the mouth (trismus). Within 2-4 days, all residual effects should disappear.
After treatment, sensitivity returns gradually, so take the food carefully so as not to accidentally bite yourself. It is also recommended to quit smoking during this time.
Infiltration anesthesia
This is one of the most common methods of anesthesia in modern dentistry. There are two types of infiltration anesthesia: direct and indirect. Direct anesthesia is injected directly under the mucous membrane near the teeth that require treatment, and acts at the injection site. Indirect spreads to surrounding tissues and covers a larger area, while its prevalence depends on the type of surrounding tissues. For example, on the upper jaw the alveolar process is more porous, while on the lower jaw it is denser, which means that the effect of infiltration anesthesia on the upper jaw will be more effective.
Modern drugs for anesthesia
The choice of anesthetic depends on the patient's individual treatment plan and the method of anesthesia. For local topical anesthesia, gels, ointments and sprays based on lidocaine, dicaine, bumecaine, and benzocaine are currently used. For example, diplen - LH, topex gel, disilane, diseptin, xylonor.
For injection anesthesia, drugs such as procaine, lidocaine, mepivacaine, ultracaine, ubistezin, trimecaine, articaine, chirocaine, bipuvacaine are used. Inhalational sedation uses a mixture of nitrous oxide and oxygen. If you are afraid of visiting the dentist, you can take tranquilizers orally in the form of tablets, for example, diazepam, oxazepam, hydroxyzine, hexobarbital, as prescribed by the doctor.
New effective P-ASA anesthesia
The STA Injection System is excellent not only for single tooth anesthesia, but also for multi-tooth anesthesia techniques with a single injection (such as P-ASA).
P-ASA is a palatal injection that can numb the six anterior teeth and surrounding soft tissue on both the palatal and labial sides without causing collateral numbness to the patient's upper lip and facial skin. This simple technique replaces at least four infiltration anesthesia and a palatal injection, and is indispensable in aesthetic dentistry for the manufacture of composite restorations, veneers and crowns, since the dentist can immediately assess the patient’s smile line.
The P-ASA technique can also be used during endodontic and periodontal interventions, as well as implantation.
Injection using the P-ASA technique is absolutely painless due to the possibility of constant control over the position of the needle and the speed of anesthetic injection, which does not exceed the patient’s pain threshold.
What are the features of anesthesia in dentistry for pregnant women?
It is also important for pregnant women to ensure pain-free dental treatment. However, conventional painkillers are not suitable for them, since vasoconstrictors (also known as vasoconstrictors) are usually added to the anesthetic solution in order to keep it in the right place and prolong its effect. Vasoconstrictors also reduce potential common side effects and reduce bleeding. For example, adrenaline added to a four percent solution of articaine can extend its analgesic effect from three to forty-five minutes.
Only mepivacaine can be used without adrenaline, since, unlike other drugs for local anesthesia used in dentistry (articaine, which is considered the best option today, novocaine and lidocaine), it does not have the ability to dilate blood vessels at the injection site, which means it can be recommended for pregnant women, children, and other categories of patients who should not be administered adrenaline. These include, for example, those suffering from cardiovascular diseases, arterial hypertension, severe forms of diabetes mellitus, and severe thyrotoxicosis.
Our advantages
Our dentistry treats dental caries in Moscow (Ramenki district) at affordable prices. We cooperate directly with many manufacturers of dental materials, avoiding intermediaries. This allows us to provide you with genuine European quality without putting an extra strain on your budget. Polite and helpful staff, comfort and convenience are at your service. Come visit us and appreciate the advantages of the center [email protected] :
Quality of treatment
- Personality. Professional approach to each individual case.
- Subsequence. Medical procedures are carried out only after a full diagnostic examination and agreement on the treatment plan and cost. If necessary, specialists from related fields (periodontist, surgeon, implantologist, orthopedist, orthodontist) will be invited to a consultation. The price of dental treatment depends on the stage of development of caries. The sooner you contact your dentist, the easier and cheaper it will be to get rid of the problem.
- Qualification. The appointment is conducted by an experienced specialist who is fluent in modern and classical techniques in the field of endodontic, therapeutic, and aesthetic dentistry.
- Certificates. We work only with certified drugs. Three-dimensional obturation with liquid gutta-percha (work in the canals). For direct restoration of a damaged crown, innovative nanocomposite filling materials from leading brands (USA, Europe, Japan) are used.
- Guarantee for all types of work.
Safety
- Multi-stage disinfection and sterilization of instruments and apparatus.
- Disposable instruments.
- Painless. Computer anesthesia STA is the most comfortable treatment of caries in dentistry. Reduced dosage of anesthetic (without compromising the effectiveness of anesthesia), absence of unpleasant sensations after the drug has stopped working.
Technologies
- Diagnostic examination using a digital orthopantomograph Planmeca ProOne.
- Application of optical caries detector, laser.
- Treatment of dental caries under a microscope. The most precise passage of channels, complete mechanical and medicinal treatment, without the risk of complications.
- Ceramic inlays for restoring a damaged tooth – inlay, onlay (indirect restoration).
Ultrasound anesthesia
When performing anesthesia, it is very important to choose the right injection site, since a mistake can lead to serious complications. This is especially true for conduction anesthesia, where the drug must be in close proximity to the nerve, but the needle cannot touch it. Ultrasound successfully helps determine the site of anesthetic injection. Under the control of an ultrasound machine, it is possible to calculate down to the millimeter the location of the needle and its proximity to the nerve, thereby ensuring the most effective and safe anesthesia of the desired area.
Computer anesthesia
Computer anesthesia allows dentists to calculate more accurate doses of the drug, administer it at the desired speed, pre-selected by the computer, and painlessly guide the syringe needle, which has a special cutting edge. Anesthesia administered with high precision can last longer - up to 40 minutes, and visual and audio signals provided by the device allow the doctor to position the needle as needed, without the risk of tissue damage, introducing anesthetic into the bloodstream or placing the needle too far from the nerve.