November 29, 2021
194
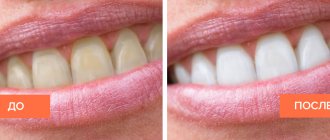
Cosmetology involves performing various procedures that require pain relief. To do this, patients are injected or applied anesthetic drugs. Most solutions used today are non-invasive. In other words, they do not need to be injected under the skin. This is necessary to eliminate any discomfort.
General anesthesia
Anesthesia or general anesthesia is a procedure in which a person is put into a special state - the body does not react to external stimuli, one of which is pain. General anesthesia is performed using anesthetics that act on the central nervous system.
General anesthesia is given if there is a need to perform surgical procedures. The technique has a high level of complexity, so an anesthesiologist accompanies the operation. It calculates the correct dosage for a particular person. The well-being and even the life of the patient depends on it.
As a rule, local anesthesia is often used for aesthetic cosmetology, and anesthesia is done in rare cases, for example, if it is necessary to do deep peeling.
Anesthesia is perceived ambiguously by people. So, some are sure that anesthesia shortens life by several years. There is also a myth that says that drugs of this type make a person mentally ill. However, such statements are incorrect. Of course, risks exist, as in other areas of medicine, but experienced doctors can minimize them. Possible side effects include dizziness, headache, diarrhea, and vomiting.
Advantages and disadvantages of the technique
The main advantages of topical anesthesia:
- Performance. Painkillers used for topical anesthesia have an immediate effect.
- High efficiency. The treated surface loses sensitivity in 99% of cases.
- Safety. An experienced dentist will perform the procedure in such a way that no complications will arise.
The disadvantages of topical anesthesia are mainly related to the specifics of the procedure:
- The substance penetrates shallowly. Its area of influence is limited to the upper layers of the epithelium and tooth enamel.
- It is quite difficult to control the exact dosage of the drug.
- Small concentrations of anesthetic enter the blood.
- Painkillers have a vasodilating effect. Therefore, after their action stops, many patients' gums begin to bleed.
- Quite a short period of validity. The maximum duration of the anesthetic effect is 25-30 minutes. This fact limits the scope of application of topical anesthesia. It is impossible to cure deep caries using this delicate technique.
Local anesthesia
Local anesthetic injections are designed to numb the area the doctor is working on. Such pain relief can be:
- Application. Special creams or gels are applied to the skin to help cope with discomfort.
- Infiltration. The medicine is injected under the skin, which blocks nerve impulses.
- Regional. The medication is injected into the area of the nerve trunk, which is responsible for a certain area of the body.
In injection cosmetology, anesthesia is selected taking into account factors such as the area of manipulation and the individual characteristics of the patient.
Application in pediatric dentistry
The technique is popular in pediatric dentistry, as it allows you to completely anesthetize any dental procedure, creating a trusting attitude towards doctors in young patients.
The porous structure of children's primary teeth is especially susceptible to topical anesthesia. The drug easily penetrates tissue, turning off sensitive receptors even in the deep layers of the gums. This allows the method to be used as the main method of pain relief - not only for superficial procedures, but also for the treatment of deep caries of primary teeth.
ATTENTION! In pediatric dentistry, drugs with a low level of toxicity are used. Drugs such as Dicaine are contraindicated for use in patients under 10 years of age.
Effective pain relief with Anesta-A cream
Cosmetologists must carefully select a local anesthetic, and the products used must have registration and permits for use in the Russian Federation. One of the most popular local anesthetics is Anesta-A. This drug is registered and has a certificate, so it can be used in medical clinics, beauty salons, tattoo parlors, etc. The drug is intended for topical anesthesia and is based on lidocaine and its derivatives. Differs from analogues in minimal allergy risks.
Indications for use in dentistry
Application anesthesia is indicated for all patients with increased anxiety to create a favorable mood at the dentist’s appointment. However, the direct purpose of this method is to relieve pain from superficial procedures, such as:
- removal and application of sutures;
- injections (intermediate pain relief reduces any discomfort to zero);
- prosthetics (fitting of crowns and bridges);
- taking impressions (if the gag reflex is pronounced, the anesthetic is applied to the basal area of the tongue);
- procedure for cleaning teeth and removing tartar;
- treatment of periodontal pockets, treatment of periodontitis and gingivitis;
- treatment of uncomplicated caries of superficial and moderate severity;
- any manipulations with increased sensitivity of tooth enamel (preparations are rubbed directly into the tooth enamel and adjacent tissues);
- treatment of pulpitis (for local anesthesia of the inflammatory process, the drug is placed at the bottom of the carious cavity);
- removal of baby teeth or teeth with pathological mobility (for example, with periodontal disease);
- opening of gingival abscesses.
The main contraindication to topical anesthesia is an allergic reaction and hypersensitivity to the drug.
In rare cases, when infiltration anesthesia is strictly contraindicated for a patient, application anesthesia is the only way to somehow reduce pain.
Prevention of anaphylactic shock
Although deaths from anesthetics (or insect bites) account for a minority of the statistics, preventative measures should be taken to reduce the risk of anaphylactic shock.
- Detailed and in-depth analysis of the client’s allergic history, data on drug intolerance; pharmacological history included in the medical documentation.
- Conducting tests to identify the allergen before administering the required dose of anesthetics for patients with a more complex allergic history.
- Assessment of the system of medications that the patient is taking (pharmacotherapy) at the moment.
- Mandatory and constant monitoring of the client throughout the entire time after the introduction of the allergen (especially the first 30 minutes).
- Refusal of immunotherapy for uncontrolled bronchial asthma.
- Arrangement of an office or clinic (emergency medical kit with the presence of adrenaline), and training of all members of the staff in case of drug-induced AS or similar serious conditions of patients.
Even after the active elimination of acute manifestations of anaphylactic shock, there are no favorable and definitive prognoses for the completion of the pathological process. We can talk about a positive prognosis for the patient only after 5-7 days of rehabilitation.
The TOTIS company takes care of its clients and offers drugs for safe contouring and biorevitalization procedures from the Austrian pharmaceutical giant CROMA and the SAYPHA line:
- Saypha Rich (18 mg/ml) is a sterile, purified, transparent, isotonic, biodegradable gel for skin biorevitalization procedures. Provides a long-lasting “anti-age” effect + prolonged hydration.
- Saypha Filler (23 mg/ml) is an intradermal hyaluronic acid filler for the correction of superficial and medium-deep wrinkles, as well as for increasing lip volume.
- Saypha Volume (23 mg/ml) is an intradermal hyaluronic acid filler for correcting deep wrinkles and creating volume in the middle third of the face, as well as voluminous modeling of the lips.
Very soft fillers that are easily and painlessly distributed under the skin and guarantee the most natural result. These products can be combined with each other and not worry about comfortable administration, thanks to the unique CROMA syringe + ultra-thin terumo needle.
The article was written with the information support of a dermatocosmetologist, methodologist of the medical information section of the TOTIS company - Natalia Malichenko
Pathogenesis of anaphylactic shock
The pathogenesis of anaphylactic shock is caused by a type I allergic reaction, which develops in a highly sensitized organism.
The mechanism of development of the immune response occurs as follows: recognition of the allergen, its processing and presentation, the union of T and B lymphocytes, the formation of duplicate plasma cells that form antibodies and immune memory cells.
A very large amount of IgE during anaphylactic shock leads to an immediate hyperergic reaction.
Phases that form an immediate allergic reaction:
Immunological phase
- The antigen comes into contact with the nasal mucosa, with the surface of the skin, bronchi, gastrointestinal tract, or with the macrophages themselves.
- The latter absorb the allergen and transmit it to type 2 T helper cells, which begin to produce cytokines that stimulate the proliferation of B lymphocytes, their transformation into plasma cells with the subsequent production of IgE antibodies.
- Combination of antibodies (lgE).
- IgE antibodies are fixed on the surface of mast cells and basophils in the blood.
- Repeated contact with a familiar allergen.
- Communication of the allergen with antibodies on the surface of basophils and mast cells.
The pathochemical phase is characterized by the release of mastocytes + basophils, after the formation of immune complexes on the cell surface. Mediators C3, C5a-anaphylotoxins become part of the basophils and mast cells formed during degranulation.
The pathophysiological phase is the direct activity of these mediators on specific receptors of tissues and organs. This hypersensitive reaction is characterized by dilation of peripheral blood vessels, spasm of smooth muscles of organs, release of fluid from blood vessels (cardiovascular dysfunction), formation of edema of the respiratory tract and excessive secretion of mucus.
The clinical phase is final. It manifests itself in the form of anaphylactic shock and similar allergic reactions of the IgE-dependent type.
The nature of the course of anaphylactic shock
a) Malignant is characterized by a rapid decrease in blood pressure - BP (diastolic - up to 0 mm Hg), impaired consciousness and the appearance of bronchospasm. This form of AS is quite resistant to intensive therapy and progresses rapidly in parallel with the development of severe pulmonary edema, a stable drop in blood pressure and deep coma.
b) Acute benign (typical) course of AS is described as a depressed state, which is accompanied by a moderate and functional change in vascular tone + signs of respiratory failure. “Benign” in terms of real chances for a quick recovery, with timely and adequate treatment from a specialist.
c) The protracted nature of AS is observed after active anti-shock therapy, which provides a temporary / partial effect. The symptoms are mild, unlike the 2 previous conditions, but quite often lead to complications (pneumonia, hepatitis, encephalitis). The prolonged course of anaphylactic shock is directly related to the administration of long-acting drugs.
d) Recurrent course (repeated state of shock) occurs due to the localization of the first symptoms of anaphylactic shock. After re-entering the body, allergens become more resistant to therapy and have more serious consequences.
e) The abortive nature is considered favorable from the point of view of the speed of localization. It is expressed in the form of a typical form of anaphylactic shock + hemodynamic disturbances (including blood pressure) are minimally expressed.
Each stage of anaphylactic shock requires immediate response and action from a specialist.
Anaphylactic shock as one of the most dangerous types of complications
In everyday life, systemic allergic reactions can occur after contact with many substances. An international study (ISAAC) showed that 20-25% of the world's population has one or another type of allergic disease. Moreover, this figure has tripled over the past 25 years.
Unfortunately, in Ukraine, we do not have reliable data on the incidence of this complex pathological condition among adults and children. However, the incidence of anaphylaxis deaths in the US and UK, which is 0.4 per million people (1-3 people annually), highlights the importance of training and awareness.
The most threatening type of allergic reaction in the human body is anaphylactic shock (AS). This reaction can develop due to the interaction of the antigen with immunoglobulin (IgE), which leads to the release of mediators and various systemic manifestations (skin, respiratory, cardiovascular failure, gastrointestinal).
Anaphylactic shock is an acute systemic reaction of the body's hypersensitivity to an allergen, which threatens human life and is accompanied by severe hemodynamic disturbances (failure of the circulatory system and hypoxia in all vital organs). Typically, the speed of reaction to an antigen can vary from a few seconds (minutes) to 5 hours from the moment of contact.