- A little about the paranasal sinuses
- What to do if pathological changes are detected in the images?
- Which is better: radiography or CT of the paranasal sinuses?
- Prices for x-ray of the nose
- The clinic is located a three-minute walk from the Ulitsa 1905 Goda metro station
X-ray of the paranasal sinuses is a diagnostic procedure that is often prescribed by ENT doctors. First of all, it is carried out in order to diagnose the inflammatory process in the paranasal sinuses - sinusitis. But other pathologies can also be identified, because the photographs show the adjacent bones of the skull and the dental system of the upper jaw. The advantages of radiography are that it is a fast, affordable and non-invasive diagnostic method. In the images, the doctor can immediately see pathological changes and prescribe further examination and treatment for the patient. The quality of diagnostics depends on how modern the model of the device is used in the clinic, and how clear the images it allows to obtain. At the ProfMedLab clinic you can undergo testing using good equipment and quickly receive an accurate diagnosis.
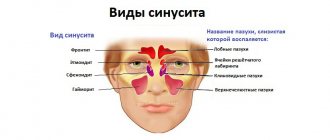
A little about the paranasal sinuses
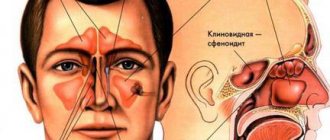
The paranasal sinuses, or sinuses, are located in the bones of the skull. They are lined with mucous membrane and communicate with the nasal cavity. These formations perform many useful functions: they reduce the mass of the skull bones, warm and moisturize the inhaled air, soften blows to the face, participate in the formation of the timbre of the voice, and help to sense changes in environmental pressure.
Humans have four types of paranasal sinuses:
- The most famous are the maxillary ones. As the name suggests, they are found in the upper jaw. These sinuses are also called maxillary sinuses, and inflammation in them is called sinusitis.
- The frontal sinuses are located in the frontal bone, just above the bridge of the nose. When inflammation develops in them, frontal sinusitis is diagnosed.
- Inside the skull, in the thickness of the ethmoid bone, there is a ethmoid labyrinth. Inflammation in its cells is ethmoiditis.
- The sphenoid sinus is the only unpaired sinus. It is located in the bone of the same name, which is located deep in the very center of the skull. Only its wings protrude outward. The inflammatory process in the sphenoid sinus is called “sphenoiditis”.
The general term for inflammation in any of the paranasal sinuses is “sinusitis.”
Briefly about sinusitis
Sinusitis is inflammation of the mucous membrane in the maxillary sinuses. Nathaniel Gaymore was the first to describe these sinuses: the name came from his name. And Leonardo da Vinci was the first to draw the maxillary sinuses.
Essentially, sinusitis is sinusitis caused by various reasons, which are associated with infection in the sinuses and the accumulation of pus in them. It can be rhinogenic, odontogenic, traumatic, allergic.
Rhinogenic occurs due to untreated rhinitis, when the infection penetrates from the nasal cavity into the sinuses. Odontogenic sinusitis develops as a result of infection through a diseased tooth and inflamed tissue around it.
Traumatic rhinitis is a consequence of damage to the nasal septum, maxillary sinus or jaw.
Finally, allergic rhinitis occurs due to allergies to pollen, animal dander, dust mites, medications and other allergens.
Acute sinusitis lasts less than 3 months, recurrent acute sinusitis occurs up to 4 times a year, chronic sinusitis lasts from 3 months or more. An exacerbation of chronic sinusitis is also possible, when new symptoms are added to existing ones.
In what cases is radiography of the paranasal sinuses necessary?
Most often, the reason for prescribing radiography of the paranasal sinuses is a suspicion of sinusitis. Symptoms of this disease: constant nasal congestion, pain in the forehead, upper jaw, swelling in the affected sinuses, discharge of yellow or green mucus from the nose, increased body temperature. Sinusitis can manifest itself in the form of toothache and bad breath.
Also, radiography of the paranasal sinuses is prescribed for injuries to the nasal area, suspected hemorrhage, benign and malignant tumors, and other pathological formations. In dentistry, this study is usually carried out before surgical interventions on the upper jaw. In addition, radiography of the paranasal sinuses helps clarify the diagnosis for the following symptoms and conditions:
- Chronic headache. If it is persistent and cannot be treated, the neurologist may refer the patient for a consultation with an ENT doctor.
- Chronic cough.
- Secretory otitis media. With this disease, mucus accumulates in the tympanic cavity, the ventilation of the middle ear is disrupted and hearing deteriorates.
- Chronic pharyngitis is an inflammation of the pharyngeal mucosa.
- Dacryocystitis is an inflammatory process in the lacrimal sac of the eye.
- Hypertrophy (pathological enlargement) of the nasal turbinates.
- Deviation of the nasal septum.
After sinus surgery, radiography is used to monitor the results of treatment.
What is an x-ray of the paranasal sinuses?
X-ray of the paranasal sinuses is one of the types of X-ray examination that allows you to clarify the condition of the organ and identify the causes of unpleasant symptoms. X-rays of the paranasal sinuses are taken in two projections: chin and nasomental, which allows visualization of all structures of the paranasal sinuses. For already diagnosed tumors in the sinus cavity and paranasal sinus, this research method is not suitable, since the structure and size of the tumors are poorly captured by x-rays. Therefore, a study is ordered to confirm the occurrence of pathology.
Study safety and contraindications
X-ray radiation is ionizing and can damage cells and genetic material. However, its doses, especially in modern digital devices, are very small and do not cause harm. If you have to undergo x-rays again and you are worried about the possible risks, you can keep a list of all the procedures and show the doctor when he prescribes the examination.
Any diagnostic methods using x-rays are contraindicated during pregnancy (especially in the first trimester) and breastfeeding.
Preparation for the procedure
Before starting the procedure, you must remove your outer clothing, metal and other jewelry, earrings, piercings, and remove dentures. Next, you need to tell the doctor whether similar procedures have been performed previously, whether there are dental implants, fractures of the nose or facial bone.
During the diagnosis, the patient must stand still and not move. He should rest his nose and chin on the stand of the X-ray machine, which has been previously adjusted to the patient’s height. After this, the doctor will take several pictures from another room and give further instructions to the patient. During the procedure, the patient will sometimes need to hold their breath for a few seconds (no more than 10 seconds). The radiologist will take pictures in two projections, and sometimes while lying down.
The whole procedure will take about 10 minutes.
Which is better: radiography or CT of the paranasal sinuses?
Computed tomography is more informative, and it is used when pathological changes cannot be identified and comprehensively studied using radiography. But this is not always necessary. In addition, CT scans are more expensive and involve higher radiation exposure to the body.
Modern digital X-ray machines allow you to obtain very clear, detailed images, which are often enough to establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment. This is exactly the device that is used in the ProfMedLab clinic. In our clinic, based on the results of the study, you can get a consultation with one of the leading ENT doctors.
Indications for the purpose of the study
Mainly, radiography of the paranasal sinuses is prescribed to confirm or exclude sinusitis, sinusitis and other inflammatory processes in the nasal cavity, as well as if cysts or neoplasms are suspected, bleeding, the cause of which has not been identified. X-rays of the paranasal sinuses are taken throughout treatment to monitor the disease, before and after nasal surgery. This is a mandatory procedure for injuries to the nose and face, as well as foreign objects entering the nasal cavity. Typically, x-rays of the paranasal sinuses reveal problems hidden from the doctor’s traditional equipment, so its importance cannot be overestimated.
What can diagnostics show?
X-ray of the paranasal sinuses reveals defects and anomalies in the structure of the bones and cartilage of the face, as well as the nature of their damage, if any. The x-ray clearly shows fluids and their quantity, which most often turn out to be purulent inflammation of the paranasal sinus, which invariably accompanies many diseases of the nose. An X-ray examination of the nose reveals tumors and cysts, which can be distinguished by their outlines. This is an indispensable diagnostic method when foreign objects enter the nasal cavity - to identify their location.
Prices for x-ray of the nose
| Name of service | Price |
| X-ray of the nasopharynx | 1900 |
| X-ray of the lower jaw joints | 1700 |
| Printing an x-ray image on film | 500 |
| Consultation of radiographs, interpretation of studies performed in another health care facility | 700 |
| X-ray of the paranasal sinuses in the naso-mental projection with the mouth open (1 projection) | 1500 |
| X-ray of the nasal bones (2 projections) | 1700 |
| Interpretation of radiographs (from other health care facilities) | 1200 |
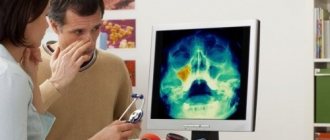
What does sinusitis look like in the picture?
Healthy paranasal sinuses in the picture are similar in shade to the eye sockets. If inflammation develops, they acquire a darker shade with whitish, “milky” contents. The usually smooth edges of the sinus may be curved, and thickening may be observed locally or along the entire edge of the sinus. This picture indicates that pathology has developed in the sinuses.
An otolaryngologist and a radiologist interpret the X-ray. Photos of the sinuses highlight potential abnormalities and darkened areas. The analysis can determine: the presence of potentially affected areas - darkened or sub-darkened areas, whether there is sinusitis - lightened areas of the sinuses.
After treating a runny nose and congestion, the doctor can also determine the nature of the disease - sluggish, stopped, chronic, acute, the presence of tumors or cysts.
Lesions on MRI of the brain: what does it mean?
The result of magnetic resonance imaging is a series of layer-by-layer images of the area under study. In the images, healthy tissue appears as alternating light and dark areas, depending on the concentration of fluid in it and the pulse sequence used. Based on the sections, the radiologist evaluates:
- development and position of individual structures;
- compliance of the MR signal intensity with the norm;
- condition of the gyri and grooves;
- size and structure of the ventricular system and subarachnoid space;
- parameters of the ear canals, orbits, accessory sinuses;
- structure of the vascular bed;
- structure of cranial nerves and cerebral membranes;
- the presence of signs of pathology (focal changes, swelling, inflammation, damage to the walls of arteries and veins).
Lipoma of the quadrigeminal cistern on MRI (circled)
MRI is prescribed if the patient has neurological abnormalities due to damage to brain tissue. Symptoms may include:
- headache;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- dysfunction of the organs of hearing or vision;
- disturbances in concentration;
- memory disorders;
- sleep problems;
- psychoemotional disorders;
- paresis/paralysis of the limbs and/or facial muscles;
- sensory disorders;
- seizures, etc.
Magnetic resonance imaging of the head allows the doctor to accurately determine the location of focal changes and find out the nature of the patient’s poor health. At the Magnit DC, specialists are armed with the latest MR scanning devices, which allow them to conduct research with high reliability.
How are x-rays taken of the paranasal sinuses?
X-rays of the paranasal sinuses are carried out in specially equipped diagnostic rooms using an X-ray unit. Before the procedure, you will need to remove metal objects and outer clothing, and put on a protective apron with a lead coating. If it is necessary to take a picture in the nasomental projection, the patient presses his nose and chin to the device, opening his mouth. In the chin projection, the chin is pressed against the installation, and the nose is located 2 cm from it. Patient position for x-ray of the paranasal sinuses
corrected by the doctor. The patient is then asked to hold his breath and not move while a photo is taken.
X-ray with contrast
The contrast agent blocks x-rays and thus makes the image clearer. It is inserted into the paranasal sinus before the x-ray. The administration of contrast is an unpleasant procedure, so the doctor first administers anesthesia. However, recently, contrast X-rays of the paranasal sinuses have been used less frequently, as MRIs
And .