Modern solutions offered by clinics allow an individual approach to each patient and selection of the optimal method of restoring teeth in case of their destruction or absence. Prosthetics allows you to restore the aesthetics of the dentition and natural chewing functions, while prolonged absence of teeth always leads to serious health consequences - it affects the bite, jaw joints, and facial appearance. Therefore, it is so important to undergo prosthetics as soon as possible and enjoy the result. But what if instead of “pleasure” you get pain after dental prosthetics?
Reasons for installing a crown
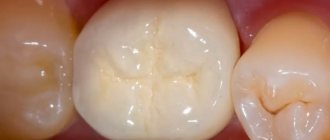
A crown is a kind of cap that is placed on a tooth, covering and protecting its tissue. Installed in three cases:
- If the natural crown of the tooth is destroyed by more than half and it is impossible to restore it with filling material or other restoration methods;
- To improve the aesthetics of the dentition - correct the shape of the tooth, hide visual flaws;
- When using prosthetics using a bridge. In this case, crowns are placed on the supporting teeth.
A crown can only be installed on a tooth with an intact root. If the upper part is significantly destroyed and the carious process has reached the pulp, before installing the crown, the tooth is depulped and the root canals are filled.
When installing a bridge, the supporting teeth are covered with dental crowns, even if they are not destroyed. If the tooth is relatively healthy, the dentin and pulp are not affected, crowns can be installed without depulpation.
Our clinic’s specialists do not recommend that patients install bridges, but offer alternative types of prosthetics if the supporting teeth are healthy. To place a crown, the doctor must prepare (grind) the tooth, that is, completely remove the enamel. Without a natural protective layer, even if covered with a crown, the tooth becomes vulnerable and gradually collapses. A bridge should only be placed on teeth that have “nothing to lose.”
What is a dental bridge?
A dental bridge can replace a tooth or several teeth. Artificial teeth in dental bridges look and function like real teeth.
A person can see a podiatrist, a dentist who specializes in restoring and replacing missing teeth, or a regular dentist. Either way, there are many options for filling the smile gap.
One option is to have a crown, a false tooth attached to a small part of the real tooth that the dentist has ground down.
However, when a person has lost a tooth or the dentist has had to remove it, a crown alone is not suitable - then a dental bridge may be a better choice.
The term "bridge" refers to a structure that contains one or more false teeth. The structure is often secured in place with one or more crowns on either side of the tear in the mouth.
- For example, if a person loses several front teeth due to injury or decay, the doctor may use a bridge to fill the gap.
- A person may not want to have gaps in their teeth after a tooth extraction, for example, because they need the tooth in the chewing area or because of cosmetic concerns.
- For some people, a permanent dental implant is an alternative to a bridge. Dental implants are fake teeth that dentists surgically insert into the bone in your mouth.
- For others, dentists recommend implants to help protect a bridge, especially if many teeth are missing.
Benefit
A dental bridge can help a person feel more comfortable with their smile. This may also allow them to chew normally.
When a person loses one or more teeth, it can affect their bite, causing pain or making it difficult to eat. Replacing these teeth prevents these complications.
A person may need a bridge if:
- the tooth is so damaged that it falls out or the dentist removes it
- an accident or injury damages the tooth beyond repair
- decay or infection so deep inside the tooth that neither a filling nor a root canal is sufficient
Types
Dentists use several types of bridges:
- A traditional bridge includes two crowns, sometimes called abutments, that secure the artificial tooth or teeth. This is the most popular type of bridge and can be fixed or removable.
- A cantilever bridge requires only one crown for support. This involves a less intensive procedure and may be a good option for people who do not want to damage healthy teeth. However, a single crown can act as a lever, increasing the risk of damage to the teeth and jaw.
- Maryland bridges are more conservative and less aggressive than traditional or cantilever bridges. The bridge is supported by metal or porcelain frames attached to the roots of the teeth on either side of the gap. These bridges can preserve healthy teeth, but they are less secure.
- Implant supported bridges use dental implants as anchors. This type of bridge is more expensive and aggressive, but safer.
What to expect
The specific procedure depends on the type of bridge.
When a person receives a traditional bridge, the process begins by preparing the teeth on either side of the gap. The dentist will grind down these teeth to remove any decay. Next, they will take a picture of your mouth, which will help with fitting the bridge.
- The dentist will place a temporary bridge over the damaged teeth to protect them.
- Temporary bridges include structures that look like real teeth, but they are not permanent, so it is important to return to your dentist within a few weeks.
- Once the actual bridge is complete, the dentist removes the temporary structures and attaches the bridge using strong adhesives.
The process is similar for cantilever bridges, although the crown only needs one tooth. The Maryland bridge requires less preparation because there are no crowns. Both of these bridges also require at least two designations.
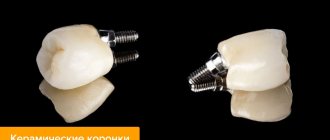
Materials for making crowns
Modern dental crowns are made from:
- Metal.
Metal dentures are considered obsolete due to their lack of aesthetics, but are still used because they are the cheapest option; - Metal ceramics.
A relatively inexpensive and durable option, but due to the metal base it is difficult to achieve a “healthy” whiteness of an artificial tooth; - Ceramics.
Ceramic crowns are more aesthetically pleasing than metal-ceramics, but are inferior in strength, so they are usually installed only on the front teeth; - Porcelain.
A type of ceramic crown. Porcelain dentures are indistinguishable from living teeth, since the optical properties of the material are almost identical to tooth enamel. They are also installed on the front teeth; - Zirconia.
They are made on the basis of zirconium dioxide and covered with ceramics on top. Durable, aesthetic, but quite expensive crowns.
Zirconium dentures can be installed on any tooth.
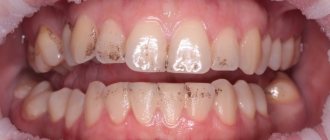
The material, contrary to popular belief, does not cause toothache, but may be the answer to the question of why the gums hurt after installing a crown. Inflammation of the mucous membrane and gums can cause an allergic reaction to the metal in a metal-containing crown. Patients with ceramic and zirconium prostheses do not encounter such problems.
Dental prosthesis made of metal-ceramics - features, types, pros and cons, prices
Article navigation
- Metal-ceramic bridge
- Design advantages
- Varieties
- Manufacturers
- Indications and contraindications
- Disadvantages and complications
- Manufacturing
- How to install and remove the structure
- Warranty and service life
- Rules for wearing and care
- Repair features
- What is better to put
- Price
question for a specialist
Several decades ago, “gold” and “iron” bridges gave way to their leading positions to another design - aesthetic and durable. We are familiar with it under the name “metal-ceramic bridge”. In today’s material, we will reveal the most important characteristics of a dental bridge made of metal ceramics – what the structure looks like, its pros and cons, how it is placed and how it is removed from the teeth. We will also dwell on other, no less interesting questions on the topic.
Why can a tooth hurt under a crown?
Toothache can occur for several reasons, most of which are associated with poor preparation of the tooth for the installation of a crown. First of all, these are errors when filling root canals after depulpation.
Causes of inflammation
Inflammation under the crown can cause:
- Insufficient filling of canals. If the canal is not filled with filling material to the top, the empty space is quickly populated by pathogenic microflora. Its waste products cause inflammation.
- Poor obturation (filling of canals). If the doctor was in a hurry or, due to inexperience, did not fill the canals tightly with filling material, bacteria will settle in the resulting pores, which will ultimately cause inflammation. Crown pain may occur months or years later.
- Perforation of the canal wall. Most often this happens when the doctor mechanically expands a canal with an uneven axis with a rasp. For example, in a curved or bent root. In order to properly seal the canals in such roots without breaking through the wall, a specialist needs extensive practical experience. The doctor may also damage the wall when installing the pin. If the hole is immediately closed with a special material, there will be no complications. But if the doctor simply fills the canal without closing the “gap,” problems may arise. The filling material is not completely biocompatible with the periodontium - the connective tissue surrounding the root. If, through the resulting hole, it extends beyond the canal, the periodontium becomes inflamed. A complication of the inflammatory process can be a cyst or granuloma.
- A fragment of an instrument in the canal cavity. Unfortunately, this is a common occurrence. The instrument may break due to improper use technique, and this will be the doctor’s fault. Or due to the physiological characteristics of the root. For example, if it is strongly curved and difficult to pass. In this case, the specialist is not to blame. The main problem in such situations is that it is often impossible to remove the tool fragment from the canal. But no matter why the foreign body ended up in the canal, it can cause inflammation, even if the canal is sealed.
- Pulp burn. This happens when a crown is installed on a living (non-pulpless) tooth. During turning, the specialist must strictly adhere to the protocol. In particular, use water cooling and prevent tissue overheating. If the doctor does not adhere to the protocol and is in a hurry, the dentin overheats from the friction of the bur and “burns” the neurovascular bundle hidden underneath it. As a result, the pulp becomes inflamed, the tooth reacts to cold and hot, and acute pain may occasionally occur, turning into aching pain.
- Poor quality crown installation. For example, the denture does not fit well; there is a gap between the crown and the tooth. Another possible mistake is that the ledge for seating the prosthesis is made too low; the crown puts pressure on the gum and causes inflammation. In this case, the patient may feel that when pressing, the tooth hurts under the crown.
What are the advantages of the design?
Metal-ceramic dental bridges have important advantages, due to which they are chosen by the vast majority of orthopedic dentists’ patients. Let's take a closer look at the positive characteristics:
- high aesthetics combined with a relatively low cost: this is the main advantage of a metal-ceramic bridge, which often becomes the “factor of choice” for the patient,
- fast production,
- Possibility of installation on both natural teeth and dental implants,
- quick adaptation and easy care.
South Korean implant Osstem - from 35,000 rubles.
Hurry up to sign up for a free consultation and lock in promotional prices.
Call now or request a call
Opening hours: 24 hours a day - seven days a week
How to treat a tooth under a crown
Treating prosthetic teeth is difficult and expensive. Inflammation can only be relieved by eliminating its cause. To do this, you need to unseal the canals, carry out anti-inflammatory therapy, which can last 2-3 months, then fill the canals again.
The patient will not only have to endure several unpleasant procedures, but also pay for a new prosthesis, since in most cases the crown has to be removed. Sometimes the doctor manages to refill the canals without removing the prosthesis. A hole is drilled in the crown, which is closed with a filling after treatment. But this is not always possible.
Not all specialists agree to treat a tooth under a crown. This is very labor-intensive work and there is no 100% guarantee that refilling will save the tooth. Many doctors in such situations immediately refer the patient for removal. Our clinic’s specialists take on even the most difficult cases and use every opportunity to save patients’ teeth.
If inflammation occurs due to underfilling of the canal, but it is impossible to treat with conservative methods, the doctor may suggest that the patient solve the problem surgically - perform resection (cutting off) of the root apex. In this case, the unfilled area, together with the granuloma or cyst formed on it, is removed through an incision in the gum area. The operation is performed under local anesthesia and lasts from 30 to 60 minutes.
The doctor determines the method of treatment in each situation individually, based on the cause and stage of the inflammatory process. Unfortunately, there are situations when it is truly impossible to save a tooth and the only option is extraction and subsequent prosthetics.
How long does it take to get used to dental bridges?
There are many reasons why people lose their own teeth: neglect of hygiene, poor nutrition, gum disease, general health problems. As a result, few people reach middle age and can boast of a full set of teeth.
Of course, inexpensive prosthetics can practically work a miracle and return a person to the ability to chew food normally and smile from ear to ear. Moreover, externally such teeth cannot be distinguished from real ones. Of course, dentures are an excellent option for losing teeth, so many people think that this is the solution to all “dental” problems: after all, there is nothing left to hurt and fall out. In fact, you will have to first adapt to any structures in the mouth, even the best and perfectly fitted ones. And then take proper care of them. Only in this case will artificial teeth meet all expectations.
This is what experts advise those who have recently installed dentures and are just getting used to them.
Dentists say that it is easiest for a person to get used to fixed and single dentures. Most likely, if everything is done efficiently, a few days will be enough. The situation is more complicated with the so-called “bridges”, and it takes the longest to get used to removable structures.
Features of product repair
Is it possible to repair a dental bridge made of metal ceramics? It is possible, but only if, for example, part of the ceramic coating has chipped - then it is built up with new ceramics or composite. If the metal frame is cracked or falls apart, then even soldering will not help, because... the structure will soon break again at a “weak” point.
“I wore a metal-ceramic bridge without problems for a couple of years. But one day after eating I noticed that a small piece of ceramic had fallen off. I was all worried while I was waiting for an appointment with my dentist. But the doctor repaired this damaged crown very well, it looked perfect. But I was warned not to chew anything hard on this side, because it could break off even harder.”
Lyudmila A., review from the site irecommend.ru
Indications and contraindications
The indication for the installation of a classic metal-ceramic bridge is the absence of 1 or several teeth in a row (but no more than 4 adjacent ones). Moreover, 2-4 healthy teeth or roots should be preserved along the edges, which will be used for supports. If there are 1 or several teeth missing at the end of the row, then it is better to install not a console, but a bridge on implants.
Contraindications to metal-ceramic bridge prosthetics are as follows:
- end defects (no tooth at the end of the row) for classical designs,
- absence of 5 or more teeth in a row,
- inflammatory processes in the oral cavity,
- mobile, diseased or collapsing supports that cannot be cured or strengthened with a pin/stump,
- the presence of cysts or granulomas under the roots,
- the supports are too low: ideally the height of the stump should be 5 mm or more,
- allergy to materials,
- intolerance to anesthesia: preparation for prosthetics includes depulping supports or installing implants, and this cannot be done without an anesthetic injection,
- exacerbation or late stages of periodontitis/periodontal disease,
- the presence in the mouth of dentures with inclusions of other metals: this way, an electrical impulse will arise between the old and new dentures - galvanism,
- inability to carry out proper oral hygiene.