From this article you will learn:
- what to do if the gum around the tooth is inflamed,
- what are the causes of inflammation,
- Medicines for gum inflammation are fast-acting and inexpensive.
The article was written by a dentist with more than 19 years of experience.
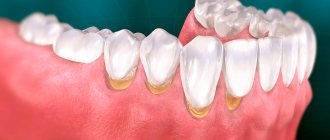
Depending on the cause of its occurrence, gum inflammation can be observed either in the area of most teeth (which is typical for gingivitis and chronic generalized periodontitis), or there can be a local inflammatory process developing in the area of just 1-2 teeth. The latter is typical for localized periodontitis, as well as for purulent periodontitis of the tooth.
How to treat gum inflammation (including medications) will depend on the cause of the inflammation, as well as the severity of the inflammatory process. If we are talking about gum inflammation due to gingivitis or periodontitis, in this case treatment will consist of anti-inflammatory therapy (antiseptic rinses, gel applications on the gums, sometimes antibiotics), as well as procedures for removing supragingival and subgingival dental plaque.
Inflammation of the gums: photo of catarrhal gingivitis
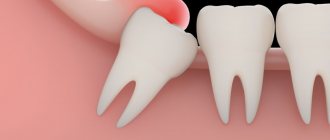
A completely different treatment is required if the inflammation of the gums near the tooth is local in nature (in the area of only 1-2 teeth). The causes of such inflammation can be - 1) overhanging edge of the filling and crown, injuring the gingival margin, 2) traumatic supercontacts between the upper and lower teeth, 3) inflammation at the apex of the tooth root. Therefore, if the gums near the tooth become inflamed, what to do in such situations is always to eliminate the specific causative factor that caused the inflammation. But drug treatment with drugs will not play a very big role in these cases.
The author of this article worked as a periodontist for more than 10 years, treating gum disease in patients, and therefore our recommendations really work (state-issued documents on advanced training in the Periodontology program can be seen in the editorial section). Below we will talk about inexpensive and effective drugs for the treatment of gum inflammation.
What is gum disease
This is a lesion of periodontal tissues, that is, the tissues surrounding the tooth. This general definition combines deep and superficial inflammatory processes.
Damage to soft tissue occurs gradually. At the initial stage, only the marginal part of the gum is inflamed. If the inflammation is not cured at this stage, the infection penetrates deeper, the deeper layers of the periodontium are affected, and the disease becomes severe.
Read also
The gum under the tooth hurts
Gum inflammation
Inflamed and bleeding gums
If the pain suddenly overtakes a person, and he does not have the opportunity to visit the dentist at the moment, you can reduce the pain by following these recommendations:
- To avoid aggravating gum inflammation, do not apply warm compresses to it;
- to relieve the pain caused by a wisdom tooth, take 1-2 tablets of analgin, paracetamol or tempalgin;
- It is recommended to rinse your mouth with a weak solution of soda at room temperature;
- do not take anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics without a doctor’s recommendation;
- At the first symptoms of pericoronoritis, contact your dentist immediately.
It should be noted that all of the above methods only temporarily reduce gum inflammation caused by an erupting wisdom tooth, and in order to completely eliminate the causes of pain, the help of a professional dentist is necessary.
Why does inflammation occur?
Plaque is the main cause of the first stage of gum disease, gingivitis. It contains bacteria that irritate soft tissues, causing inflammation and redness. At the initial stage, this does not cause severe pain, but if the inflammation is not treated, it can progress and develop into periodontitis, a more severe stage of the disease that can cause tooth loss.
Injuries - brushing your teeth too intensely or aggressively can injure the soft tissue, causing inflammation and pain.
Hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy or puberty make gums more sensitive and prone to developing gingivitis.
Systemic diseases change the composition of saliva, disrupt the composition of the blood, metabolism, and therefore can affect the condition of the gums. These include cancer, HIV, and diabetes.
Medicines can affect oral health because some of them reduce the flow of saliva, which has a protective effect on teeth and gums. Some medications cause abnormal growth of gum tissue.
Bad habits such as smoking make it difficult for soft gums to heal themselves.
Poor oral hygiene , for example if a person brushes their teeth irregularly or does not floss.
Heredity - a family history of dental diseases - is a factor contributing to the development of periodontitis.
Harmful effects of microorganisms . Various microorganisms form the natural microflora of the oral cavity. However, when the immune system is weakened or due to poor nutrition, pathogenic microorganisms begin to multiply in the mouth, which negatively affects the soft tissues of the mucous membrane.
Clinical researches
ASEPTA® mouth rinses are designed to protect gums from inflammation and improve oral hygiene. The main indications for their use are:
- acute and chronic gingivitis;
- acute and chronic periodontitis;
- stomatitis;
- post-extraction alveolitis;
- toothache of infectious origin.
Clinical trials conducted in laboratories have shown that after 3 weeks of using ASEPTA® rinse, gum bleeding is reduced by 28.3%, inflammation is reduced by 32.3% and the hygienic condition of the oral cavity is improved by 33.5%*.
Sources:
- Clinical and laboratory assessment of the influence of domestic therapeutic and prophylactic toothpaste based on plant extracts on the condition of the oral cavity in patients with simple marginal gingivitis. Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor Elovikova T.M.1, Candidate of Chemical Sciences, Associate Professor Ermishina E.Yu. 2, Doctor of Technical Sciences Associate Professor Belokonova N.A. 2 Department of Therapeutic Dentistry USMU1, Department of General Chemistry USMU2
- Clinical experience in using the Asepta series of products Fuchs Elena Ivanovna Assistant of the Department of Therapeutic and Pediatric Dentistry State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education Ryazan State Medical University named after Academician I.P. Pavlova of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation (GBOU VPO RyazSMU Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia)
- Report on clinical trials to determine/confirm the preventive properties of commercially produced personal oral hygiene products: mouth rinse "ASEPTA PARODONTAL" - Solution for irrigator." Doctor of Medical Sciences Professor, Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation, Head. Department of Preventive Dentistry S.B. Ulitovsky, doctor-researcher A.A. Leontiev First St. Petersburg State Medical University named after academician I.P. Pavlova, Department of Preventive Dentistry.
Types, symptoms and treatment of gum diseases
The initial stage of the disease usually takes place in the form of gingivitis. Untreated inflammatory processes progress and lead to the development of more serious pathologies, such as periodontitis.
| Disease/Symptoms | Gingivitis | Periodontitis | Periodontal disease | Periostitis (flux) |
| Gum color | Bright red/purple | Bright or dark red | Close to natural | Red (in the area of the diseased tooth) |
| What happens to the gums | Inflamed, swollen. Growth of gum tissue (in pregnant women) | Inflammation, swelling, pus from under the gums, exposure of the necks of the teeth | Gum recession with virtually no signs of inflammation | Painful lump with a purulent tip (abscess) |
| Painful sensations | Moderate to strong, depends on shape | Strong during exacerbation, weak during chronic course | No, but there is an itch | Severe pain, radiates to other parts of the jaw, neck, head |
| Bleeding while brushing teeth | Eat | Eat | No | No |
| Unpleasant smell | Eat | Eat | No | Eat |
| Other symptoms | Increased salivation, gray-green film on the gums (in advanced forms) | High temperature, intoxication, loosening of teeth, interdental spaces | No obvious signs | Swelling of the face, neck, ear, lymph nodes, fever up to 38-39°C, intoxication |
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is a form of gum disease that causes inflammation of the marginal tissue of the gums. In mild cases of gingivitis there may be no discomfort or visible symptoms, but in more severe cases the symptoms are more severe.
How is gingivitis treated?
Treatment begins with diagnosis. To do this, a specialist conducts an instrumental and visual inspection. Subsequently, the optimal treatment plan is selected taking into account the clinical picture of the development of the disease, as well as the individual characteristics of the patient.
In standard situations, treatment of gingivitis occurs in stages:
- Professional oral hygiene.
- Antibacterial, anti-inflammatory therapy.
- Treatment of caries (if necessary).
- In severe clinical situations, hormonal therapy or surgery may be indicated (in the presence of hypertrophic gingivitis).
Read more about the cost of treatment for gingivitis.
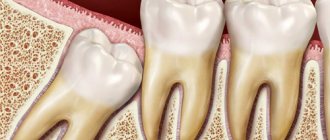
Periodontitis
Periodontitis is a more serious inflammation of the gums, which damages not only the soft, but also the hard periodontal tissues that support the teeth. Their destruction can cause loosening and loss of teeth.
Non-surgical treatment methods are used if periodontitis is not in advanced form. This treatment involves less invasive procedures:
- Hygienic teeth cleaning. Eliminates bacteria and hard deposits from the surface of teeth. The procedure is carried out using mechanical tools, sandblasting, and an ultrasonic device.
- Curettage. During the procedure, deposits under the gums and on the tooth roots are removed, and their surfaces are polished to prevent the re-accumulation of soft/hard deposits.
- Local antibiotics in gels are injected into periodontal pockets after cleaning. However, oral antibiotics may be required to completely eliminate the microorganisms causing the infection.
Surgery. If the patient has advanced periodontitis, more invasive procedures may be required:
- Flap surgery. The dentist cuts the gum to lift the edge of the gum, thereby exposing the roots of the teeth. Thanks to this, he can efficiently remove plaque and, if necessary, build up bone tissue.
- Transplantation (transplantation) of soft tissues. If gum tissue is lost, it may need to be strengthened by grafting a small amount of tissue from the surface of the mouth (palate). This will help stop tissue recession and restore lost tissue.
- Osteoplasty. This procedure is performed when the bone around the root is destroyed. A bone graft preserves the tooth by holding it in place. In addition, it serves as the basis for the restoration of natural bone.
- Regeneration of destroyed tissues. A special gel is applied to the root of the diseased tooth. This gel contains proteins that stimulate the restoration of destroyed bone and connective tissue.
To increase the chances of successful treatment of periodontal disease, and to reduce the likelihood of developing it, it is recommended that you brush your teeth at least twice a day and floss every day, and it is also important to see your dentist regularly.
Learn more about the types of periodontitis.
Periodontitis and Periodontitis: what is the difference?
Periodontitis is a pathological inflammatory process in which harmful microorganisms penetrate the periodontium through the root canals. Unlike periodontitis, which affects the gums, periodontitis develops against the background of caries, pulpitis, or tooth trauma. That is, periodontitis is actually a disease of the teeth, not the gums, and only subsequently can the pathology spread to the soft tissues in the form of a purulent lump or fistula.
The first symptoms are a feeling of discomfort and tension in and around the affected tooth. When suppuration occurs, the pain becomes throbbing, the tooth visually appears higher than the rest. In severe cases, the lymph nodes become enlarged and there is malaise or fever.
Periodontal disease
The disease is very similar to periodontitis. It is essentially a form of periodontitis. The key differences are:
- No obvious signs.
- No bleeding as opposed to periodontitis.
- Itchy gums (as opposed to periodontitis, where there is increased sensitivity).
Reasons for development:
- malocclusion;
- metabolic disorders or hormonal changes.
The choice of treatment method depends on the main cause of the disease. The dentist’s first task is to eliminate the root cause of the pathology.
Prevention of periodontal disease is: normalization of hormonal levels, vitamins, careful hygiene, gum massage.
Learn more about the stages of periodontal disease and the cost of treatment.
Periostitis (Flux)
Periostitis is an inflammatory disease that occurs due to infection from the periodontium into the area between the bone and the periosteum. Occurs as a complication of periodontitis.
Within a few hours, severe swelling of the face and neck may occur. Associated symptoms are unbearable pain and tumor formation. The pus is located in a sac, its location is also very individual, most often it appears in the form of a protruding lump.
Periostitis can occur even after extraction (pulling out) of a tooth. In addition, it occurs as a result of severe sore throat, colds, and also after injury to the teeth, soft tissues or jaw.
During surgical treatment, the pus must be drained, and the periodontal pocket must be cleaned and disinfected.
Care
To avoid problems with structures, you should properly care for them. For teeth with crowns, you can use an irrigator and specialized solutions for it, for example, ASEPTA with extracts of medicinal herbs. This will ensure proper cleaning in hard-to-reach places and will be a good prevention of problems with crowns.
In addition, the specialized ASEPTA ACTIVE paste, made on the basis of natural herbs and special enzymes, will help you maintain a healthy state. It eliminates pathogenic bacteria, relieves gum inflammation and prevents bleeding, providing comprehensive protection to tooth enamel.
Daily use of ASEPTA mouth rinse will also help to avoid inflammation; it combines analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects. It increases the effectiveness of periodontal treatment and prevents the development of many diseases.
How and with what to relieve inflammation
⛔ Only a doctor can prescribe anti-inflammatory therapy. There is no point in trying to heal yourself. If you can't see a dentist right away, here are some effective home remedies to reduce pain and inflammation before you can see a doctor:
- Rinse with salt water. Reduces the number of bacteria, which means it slows down damage to the oral cavity. At least 2 times a day until the swelling subsides.
- Cold compress. Wrap the ice pack in a clean cloth and apply it to the sore area. This will prevent swelling or at least reduce it.
- Herbal poultice. Some herbs and spices can be used as home remedies to relieve inflammation and pain. The analgesic effect is exerted by: clove and spilanthes powder; anti-inflammatory - turmeric. Apply a paste of herbal powder and water to your gums, wait until the pain subsides, and rinse.
- Tea bags. Brew a tea bag in boiling water (5 minutes). Cool, apply the cool bag to the sore gums for at least 5 minutes. Simple black or green tea or anti-inflammatory herbs (chamomile, ginger) are better suited.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers. Regular pain relievers and NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) such as aspirin, acetaminophen, ibuprofen can help in a pinch. Follow the directions on the bottle labels to determine dosage.
Are folk remedies effective? Dentists do not recommend treating gum disease at home. If an oral infection is suspected, the patient is advised to contact a dentist and immediately visit an emergency dental care office. Painkillers in such cases are unnecessary and ineffective. Home remedies won't help either.
What to do if the gums under a denture or crown become inflamed?
In dental practice, there are also cases when, after installing a crown or prosthesis, the patient begins to complain of pain in the gums or the presence of blood when brushing his teeth. First of all, it is important to understand that this may not be due to improper dental care. As a rule, the process is triggered by trauma to the gums with burs when adjusting the shape of the crown or preparing the tooth itself for prosthetics.
This can happen if the doctor carelessly processed the tooth with a rotating drill or bur, and accidentally caught the edge of the gum. Inflammation can also be caused by an incorrectly selected crown size: if it protrudes far beyond the row of teeth, the edges of the prosthesis can injure the delicate gum tissue, and the food accumulated under the crown will be an excellent environment for the development of pathogenic bacteria.
If your gums become inflamed after dental prosthetics, you should immediately consult a doctor. A qualified dentist will remove the crown, treat the inflamed gum and install a new denture that is more suitable in size.
What are the dangers of gum disease?
Untreated inflammation is fraught with penetration of infection into the deeper layers of the periodontium.
Periodontal pockets create a favorable environment for the growth of bacteria, which causes their abnormal expansion and receding gums. Harmful microorganisms also penetrate hard dental tissues, corroding them. These processes can lead to exposed roots, loosening or tooth loss. In the future, the infection can cause tonsillitis, bronchitis, pharyngitis, adenoiditis, and spreads hematogenously throughout the body.
When do you need to see a dentist urgently?
Contacting a dentist is required in the following cases.
- Pericoronitis
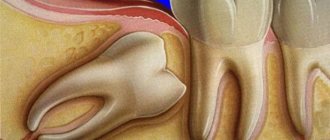
– the “hood” will be excised. - The figure eight puts pressure on neighboring teeth
- it needs to be removed. - Initial caries
– treatment will be carried out. - Medium, deep caries or rotten tooth
- a clear removal of the figure eight. - The wisdom tooth is loose
- a diagnosis of its condition will be carried out, according to the results of which the molar will be treated or removed. - Pulpitis
– if the root canals are passable, they will be filled.
This list should also include the above symptoms of pathological teething - pain when opening the mouth, swallowing, high temperature. If they appear, you should contact your dentist immediately, since this is a serious inflammatory process, the localization of which requires adequate treatment.
The reason for contacting a specialist may also be the “normal behavior” of the number eight. In this case, the doctor will simply make a small incision on the gum, thereby facilitating the eruption of the wisdom tooth. After a simple procedure, the process will be less painful, and the incision site will heal quickly, after pain for 2 to 4 days.
When should a tooth be removed?
Direct indications for wisdom tooth removal are the following pathologies and conditions.
- There is no place in the dentition for a number eight.
- Dystopic tooth (molar occupies an anatomically incorrect position).
- The appearance of wisdom teeth threatens the molars in front.
- Severe forms of caries that destroy the tooth.
- The third degree of mobility of the figure eight.
- Upcoming installation of braces.
If removal is not carried out, the development of complications is inevitable. The number eight will destroy adjacent teeth and provoke the development of pulpitis, periodontitis, and extensive caries. Eventually it will fall out on its own, but at too great a cost to the patient.
There is no need to be afraid of wisdom tooth removal. Depending on the complexity of the problem, third molar extraction will last from 20 minutes to 2 hours. The operation is performed using local anesthesia or sedation, which ensures that the procedure is painless.