Liquororrhea (from Latin liquor
- liquid and Greek
rhoia
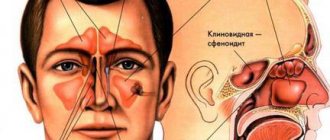
- outflow) - outflow of cerebrospinal fluid. Depending on the location of the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid from the cranial cavity, several types of spontaneous liquorrhea are distinguished: nasal, auricular and orbital.
Spontaneous nasal liquorrhea (SNL) - the leakage of cerebrospinal fluid from congenital or resulting from various non-traumatic causes of defects in the bones of the skull and dura mater - is a rare disease that accounts for 3-4% of all cases of nasal liquorrhea [1, 2]. It can be constant or periodic, drip or jet. Intensification of liquorrhea is possible when changing the position of the head or straining. In some cases, SNL is hidden, and cerebrospinal fluid flows into the nasopharynx. SNL is also divided into primary (idiopathic), the obvious cause of which cannot be determined, and secondary, when a pathological process in the paranasal sinuses and bones of the base of the skull leads to the formation of a fistula (defect).
There are a small number of reports in the literature summarizing the experience of monitoring patients with SNL. Thus, a number of foreign scientists consider SNL a symptom of idiopathic intracranial hypertension [3], other researchers consider defects of the ethmoid bone and the walls of the sphenoid sinus as the cause of this pathology [4]. However, it is generally accepted that the reliable cause of SNL cannot be established.
Computed tomography (CT) as a method of non-invasive radiation diagnostics has been used since the 70s of the last century. It allows, even before surgery, to create a visual model of the nasal cavity and its paranasal sinuses - a kind of “visual reality”, taking into account which the surgeon can plan adequate treatment measures [5]. The advantages of K.T. are the ability to eliminate the summative effect inherent in a conventional radiograph, visualize organs and tissues separately, as well as assess their density characteristics.
The purpose of the study is to develop a diagnostic algorithm for examining patients with SNL using CT.
The authors conducted a detailed analysis of the CT results of patients with SNL, assessed the anatomical features of the ethmoid bone structure, their possible impact on the development of this disease and the condition of the bone structures of the paranasal sinuses and pathological changes in them.
How do we treat sinusitis?
Sinusitis (sinusitis) is inflammation of the maxillary sinuses. Microorganisms (bacteria or viruses) enter the maxillary sinus through the nose or through the bloodstream and cause inflammation of its mucous membrane, often accompanied by the accumulation of pus in the sinus. To drain pus, “punctures” are used - punctures of the maxillary sinus. Unfortunately, many patients, fearing such “punctures,” delay seeing a doctor for sinusitis, thereby harming themselves: creating the threat of developing severe complications of sinusitis associated with the possible spread of infection, as well as conditions for the formation of chronic sinusitis.
Is it possible to treat sinusitis without a puncture?
Very often - yes. Subject to timely contact with an ENT doctor. At the initial stage of sinusitis, it is quite possible to do without a puncture. A “puncture-free” method of treating sinusitis is nasal lavage using the fluid displacement method (“cuckoo”) in combination with laser therapy. The rinsing procedure clears the nasal passages and nasal cavities of pus and mucus, and the laser relieves inflammation. The course is designed for 5-7 procedures. Already after the 1st procedure, patients see a significant improvement in their condition. Another way to avoid a puncture for sinusitis is to use a device that creates negative pressure in the nasal cavity, and thereby helps remove secretions from the maxillary sinuses. A modern method of ensuring outflow from the inflamed sinus and the possibility of carrying out therapeutic actions in it is balloon sinuplasty, performed in our center. It is possible to cure sinusitis without a puncture only if there is nasal discharge, indicating that there is an outflow of the contents of the maxillary sinus. Even the anatomical features of the structure of the ENT organs are important. That is, to determine the optimal treatment tactics for sinusitis, it is necessary to contact an otolaryngologist as early as possible. In our clinic, puncture-free treatment of sinusitis is possible!
- Without pain and blood
- Without piercing the maxillary sinuses
- In just an hour and a half
Healing sinusitis is a huge relief for your body.
Acute sinusitis. Symptoms Treatment. Prevention.
- home
- For patients
- Articles
- Acute sinusitis. Symptoms Treatment. Prevention.
»
»
»
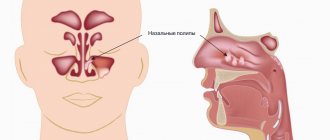
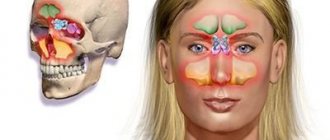
Some bones of the human skull are hollow formations, that is, they have sinuses inside (maxillary (maxillary), ethmoid, frontal (frontal), main (sphenoidal)). Inflammation of the mucous membrane of one or more of these sinuses is called the general term sinusitis (from the Latin sinus - sinus).
The largest sinus is the maxillary sinus.
The entry of a bacteria, virus or allergen into the sinus provokes the development of edema, the lumen of the sinus decreases, and an excess amount of mucus is formed, which disrupts the movement of air flow. Bacteria begin to multiply in the cavity, producing pus.
Sinusitis is an inflammation of the maxillary (maxillary) sinus.
Symptoms:
• Increased body temperature, chills.
• General malaise. • Runny nose (nasal discharge is usually mucous at first, and on the 5-7th day it becomes purulent). • Nasal congestion. • Sneezing. • Pain in the maxillary sinuses (infraorbital-buccal region), radiating to the teeth, forehead, and root of the nose. • Pain intensifies when bending the head forward, sneezing or coughing. • Nasality. • Decreased sense of smell.
Forms
According to the type of inflammation, they distinguish: • acute catarrhal sinusitis (viral) usually does not differ from a runny nose and is manifested by congestion, nasal discharge, and sometimes there is a slight heaviness in the buccal-infraorbital area. Acute catarrhal sinusitis can end in recovery or go into the second stage, that is, the stage of acute purulent sinusitis; • acute purulent sinusitis (bacterial) is characterized by the accumulation of pus in the maxillary (maxillary) sinuses. Facial pain becomes more intense, a headache occurs, and the patient’s general condition worsens significantly.
In any of the forms, sinusitis can be: • unilateral (inflammation of the sinus on one side); • bilateral (inflammation of the sinuses on both sides).
Causes
Acute sinusitis develops: • as a complication after acute respiratory infections; • in the presence of foci of infection in the nasopharynx (rhinitis (runny nose), tonsillitis (inflammation of the tonsils)); • against the background of disease of the teeth of the upper jaw (odontogenic sinusitis); • as a result of allergies; • as a result of injuries and wounds of the upper jaw (traumatic). A predisposing factor is also seasonal hypovitaminosis, that is, a state of decreased body tone due to a lack of vitamins (usually in the autumn-winter period).
Diagnostics
• Analysis of complaints and medical history: nasal congestion, thick nasal discharge (possibly green), headache or facial pain, aggravated by bending the head forward, nasal tone, increased body temperature, the presence of a runny nose or colds that preceded the disease, the fact of treatment by a dentist etc. • General examination: the presence of swelling in the cheek area; when pressing in the area of the maxillary sinuses, discomfort is noted - from increased sensitivity and mild pain to sharp pain radiating to the orbital area, etc. • Rhinoscopy - instrumental examination of the nasal cavity, during which signs of the development of the inflammatory process (swelling and redness of the mucous membrane, purulent discharge). • Endoscopic examination of the nose reveals pus in the middle meatus, which indicates the presence of purulent sinusitis. • X-ray diagnosis: in some cases, an X-ray of the maxillary sinuses shows the fluid level. • Diagnostic puncture of the maxillary sinus: the wall of the maxillary sinus in the nose is pierced with a special thin needle under local anesthesia. Then, using a syringe, the contents of the sinus are drawn out. When pus is obtained, the sinus is washed and a medicinal substance is injected into it. • Ultrasound of the paranasal sinuses is sometimes used as an alternative to x-ray examination. • Oropharyngoscopy (examination of the oral cavity) to identify carious teeth, assess the condition of fillings, etc. If necessary, a consultation with a dentist is indicated.
Treatment
Drug treatment: • vasoconstrictor drugs in the form of sprays or drops into the nasal cavity (drugs in this group relieve swelling of the mucous membrane and help remove stagnant fluid from the maxillary sinuses). The products are used in a short course, lasting 5-7 days; • nasal sprays containing antibiotics and steroid hormones (have an anti-inflammatory effect); • antihistamines, if the disease develops against the background of allergic reactions; • mucolytics – drugs that help liquefy the contents of the maxillary sinuses and, as a result, improve its excretion; • for purulent sinusitis, it is possible to prescribe antibiotics (in the form of tablets or injections).
Non-drug treatment. • Puncture (puncture) of the maxillary sinuses. The method allows you to quickly remove purulent contents (which leads to a rapid reduction in headache and facial pain, and improve your general condition) and inject medicinal substances directly into the sinus. Carrying out punctures of the maxillary sinuses in many cases allows you to do without prescribing antibiotics. • Rinsing the nose with saline, herbal and antiseptic solutions: The procedure can be carried out independently at home using special devices for a nasal shower, sprays or syringes; • Physiotherapy (treatment using natural and artificially created physical factors) is prescribed only when there is a good outflow of contents from the sinuses. • Taking general strengthening medications.
Surgical treatment is performed in the presence of orbital (eye) and intracranial complications. Treatment comes down to opening the purulent cavities and their sanitation, that is, removing the pus.
Complications and consequences
• Inflammation of the soft tissues of the face. • Spread of inflammation into the respiratory tract: inflammation of the bronchi (bronchitis), lungs (pneumonia), and ears (otitis). • Spread of the inflammatory process into the cranial cavity with the development of meningitis (inflammation of the meninges), encephalitis (inflammation of the brain substance) or brain abscess (formation of purulent cavities). • Purulent inflammation of the skull bones (a complication requiring surgical intervention). • Inflammation of the eyeball and its membranes, which can cause vision loss. • Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve (the large nerve in the face), accompanied by severe pain. • Sepsis is a severe complication that develops when the pathogen enters the bloodstream, with the further formation of secondary foci of inflammation in vital organs. • Risk of death.
The sooner you seek help from a specialist, the greater the chances of maintaining health and reducing the risk of complications!!!
Prevention
• Timely and adequate treatment of runny nose (rhinitis). • Treatment of nasal diseases accompanied by difficulty in nasal breathing (chronic rhinitis, deviated nasal septum). • Timely sanitation (treatment) of carious teeth. • Timely treatment of allergies. • Prevention of colds and strengthening the immune system:
hardening in the autumn-winter period; avoid hypothermia; taking multivitamin complexes in the autumn-winter period; wearing protective bandages during periods of mass morbidity, for example, influenza; balanced and rational diet (eating foods high in fiber (vegetables, fruits, herbs, etc.).
The information was prepared by an otorhinolaryngologist of the highest category, Doctor of Medical Sciences I. V. Raitselis
Sources: “Otorhinolaryngology”, manual for doctors V. T. Palchun, A. I. Kryukov, Moscow “Medicine”, 2001 “Otorhinolaryngology: national guide” edited by V. T. Palchun, GEOTAR-Media, 2008 G.
Causes and development of sinusitis
- rhinitis (runny nose) - infectious or allergic,
- deviated nasal septum (congenital or acquired)
- difficulty in nasal breathing due to hypertrophy of the nasal turbinates and adenoids (in children);
- the existence of foci of chronic infection in the body (for example, staphylococcus);
- weakening of the immune system.
ENT medical doctors have all the technical capabilities necessary to diagnose and treat sinusitis. Extensive experience and attentive attitude of doctors to your problem and your concerns will ensure timely and correct treatment of sinusitis at the modern level and prevent the development of complications. With a runny nose, inflammation of the nasal mucosa can also affect the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus. There, mucus production, reproduction and accumulation of pathogenic microorganisms increase. The outflow of the contents of the nasal sinus is difficult due to the swollen nasal mucosa, which blocks the opening connecting the nasal cavity and the maxillary sinus. This is how sinusitis develops. The accumulation and stagnation of mucus leads to increased pressure on the walls, which is felt as pain. The formation of pus and the absorption of toxins produced by microbes cause symptoms of intoxication - fever, malaise, headache.
Symptoms and main complaints of sinusitis
- Runny nose, nasal discharge (if the drainage is not blocked), often due to yellowish-greenish pus
- Difficulty in nasal breathing
- Pain in the nose and inflamed maxillary sinus (right or left of the nose)
- General symptoms: fever, headache, weakness.
Sinusitis is confirmed by the results of radiography or computed tomography. As soon as the diagnosis of sinusitis is confirmed, full-fledged qualified treatment is required under the guidance of an ENT doctor (in no case self-medication!).
Material and methods
The article analyzes the CT results of 45 patients with SNL who were treated in the department of otorhinolaryngology of the Kursk Regional Clinical Hospital from 2000 to 2014. Among the patients there were 39 women aged 37 to 66 years and 6 men aged 34 to 66 years . The studies were carried out in axial and coronal projections with a slice thickness of 0.625-3.0 mm on a computed tomograph, followed by evaluation of diagnostic images on a workstation. All patients underwent biochemical analysis of nasal discharge.
Possible complications of sinusitis
If adequate treatment of sinusitis is not carried out, then pus and inflammatory effusion from the maxillary sinuses can penetrate into the surrounding tissues. First of all, the tissues of the eye react, since in the area of the eye sockets there is a lot of loose fiber that easily absorbs liquid. Swelling and redness of the eyelids appears, and exophthalmos may even develop - protrusion of the eyeball forward. If pus destroys the wall of the maxillary sinus, there is a danger of developing osteomyelitis - inflammation of the bone tissue, in this case the upper jaw. With proper and timely treatment, the risk of such complications is low.
Cyst in the maxillary sinus and sinus lift
Many patients are interested in the question of whether it is possible to simultaneously extract a cystic formation and perform bone grafting of the upper jaw. The answer to this question depends on several factors, which include:
- The degree of severity of bone tissue atrophy at the site of the cyst (in some cases, the deficiency is so pronounced that sinus lifting becomes impossible, and patients can only hope for the installation of removable dentures);
- The presence of an active inflammatory process (cysts are often complicated by infectious pathologies, especially sinusitis, which are a direct contraindication for surgery);
- The size of the cystic formation (small cavities can be removed immediately before sinus lifting, but if the cyst occupies the entire space of the sinus, then bone grafting is out of the question);
- The location of the cyst (if it is located on the lower wall, then problems with removal during sinus lifting usually do not arise, but if the formation is located higher, the dentist simply will not be able to reach it without injuring the walls of the sinus).
Performing a sinus lift with preliminary removal of a cystic formation is performed quite rarely and only in cases where the process has just begun to develop and was accidentally discovered by instrumental studies. The doctor must correctly weigh the benefits and risks of future surgery. Most often, patients are transferred for treatment to ENT specialists, and the sinus lift is postponed to a later time.
Treatment of sinusitis
The earlier treatment for sinusitis is started, the better the prognosis. If you consult a doctor before the accumulation of pus in the maxillary sinus (in the first days of the onset of symptoms of sinusitis), the treatment effect is the best (without puncture). Early use of vasoconstrictor drops and sprays will help relieve swelling of the nasal mucosa and restore the outflow of secretions from the maxillary sinuses. Antibacterial therapy and antiallergic treatment are mandatory. Local rinsing of the nose with antiseptic solutions, physical treatment - UHF, UV irradiation of the nasal cavity.
How is the treatment carried out?
We respect the patient’s personal time and strive to carry out all activities comprehensively, in one day :
- Professional hygiene Preparation of the oral cavity to ensure sterility during surgery to avoid secondary sinus infection
- Surgery to eliminate inflammation Performed while you sleep; the method of access to the sinus is selected depending on the location of the foreign body and the presence of tumors
- Temporary prosthetics If the causative tooth had to be removed, a temporary crown or immediate prosthesis is installed to mask the defect
Surgical operations in our Center are performed under sedation. The patient does not feel anything, fears and worries are excluded. Sedatives put you into a controlled drug-induced sleep without falling into unconsciousness - this is not general anesthesia! They do not contain toxic components, act gently, preserving reflexes. The artificial lung ventilation device is not connected, hospitalization is not required.
The surgical intervention is completed by a mandatory CT examination , which is necessary to assess the quality of the work performed.
After 10-14 days, the patient is invited to the clinic for suture removal and a control CT image. A schedule of professional inspections is drawn up.
Puncture of the maxillary sinus
If sinusitis is advanced and there is thick pus in the sinuses, then a puncture is necessary. After removing the pus through a needle, the doctor rinses the maxillary sinuses with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs. After the puncture, catheters are inserted into the sinus through the hole - thin tubes, which allow the sinuses to be washed every day in the future without additional punctures. Relief occurs immediately upon completion of the procedure. And recovery is going very quickly. If the doctor insists on performing a puncture, it means that it is necessary for your health.
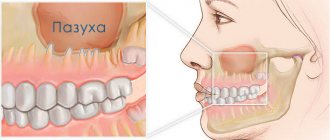
Causes of sinus perforation during dental treatment
The maxillary sinuses or maxillary sinuses are located inside the upper jaw. They are separated from the oral cavity by a septum and the alveolar process, which contains the roots of the teeth. Treatment of the canals of such teeth is complicated by the risk of sinus perforation for a number of reasons:
- Anatomically thin septum Sometimes the height is only 1 mm. It happens that the teeth penetrate the cavity with their roots and only the sinus mucosa separates.
- Treatment of teeth with inflammation on the roots If there is inflammation on the roots of the teeth (periodontitis, cyst), the surrounding bone melts and becomes thinner.
- Excessive efforts by the doctor If the dentist does not calculate the efforts when passing the canals, the canal may rupture, damage the root, or perforate the bottom of the sinus.
Without a preliminary diagnosis, the endodontist, having no idea about the size of the sinus septum and the location of the roots, may not calculate the effort and damage the tooth and the thin bone layer that lies between the maxillary sinus and the root. As a result, infection penetrates into the sinus cavity, and fragments of instruments and filling material may fail. In our practice, there are cases when a foreign body in the sinus attracts secondary infections with the development of neoplasms - fungal colonies, cysts, polyps.
A fragment of an endodontic instrument in a tooth canal