Symptoms Causes Degrees of mobility Diagnostics Treatment methods Splinting Treatment at home Prevention
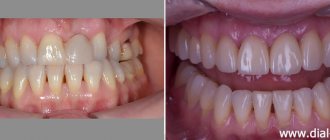
Normally, healthy teeth have little mobility due to the elasticity of the ligamentous apparatus and the need to absorb the chewing load. Physiological mobility is 0.06 - 0.15 mm, completely invisible to humans. Excessive mobility, noticeable when pressing on the tooth, is an anomaly that requires the intervention of a dentist. Even if a mobile tooth looks normal and does not hurt, loosening indicates a violation of the dentogingival connection, which is fraught with loss of a dental unit.
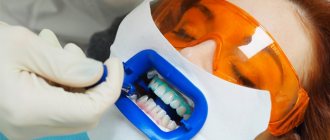
Pathological tooth mobility occurs due to various dental problems or injuries. What to do if a tooth is loose? Go to the dentist. Timely diagnosis and treatment will preserve the integrity of the dentition, restoring the functioning of the ligamentous apparatus. The treatment method is selected according to the severity of the defect, its location, and the presence of associated factors. After a comprehensive diagnosis, specialists from the RUTT clinic in Moscow will select treatment taking into account the clinical picture and indications for one or another method.
Anatomical structure
Going to the mirror, opening your mouth, you can examine your teeth in detail. A person sees only the vernal shell - these are hard enamel crowns. The protective layer reliably hides vulnerable internal tissues.
Incisors, canines, and molars have different shapes and numbers of roots, but they are united by a common structure.
Let's take a closer look at the histological structure of the tooth in section.
- Enamel is a hard protective layer of a whitish-cream color, consisting of 96% inorganic substances. The fabric has increased strength, but is also fragile, prone to abrasion, and susceptible to adverse environmental influences. If the enamel is injured by the attachment of pathogenic microorganisms, caries develops. On the surface of the chewing teeth there are fissures, depressions and grooves. They most often accumulate food particles that are difficult to remove. This causes the development of the disease. When the pathology occurs, it gradually affects the healthy protective layer, leaving internal tissues defenseless.
- Dentin - located directly under the enamel, consists of 70% inorganic substances. Dentin is a hard tissue, but it is much more vulnerable than the surface protective layer. If the carious process reaches the dentin, the pathological process occurs rapidly, and in the absence of timely assistance from the dentist, inflammation of the neurovascular bundle occurs. When dentin is damaged, medium or deep caries develops. Signs of the disease are clearly visible - violation of the integrity of enamel and dentin, the appearance of pain sensitivity upon contact with negative environmental factors;
- The pulp chamber and root canals contain nerve endings and blood vessels and have a soft, loose structure. Thanks to the pulp, the tooth receives the necessary nutrients. It protects periodontal tissues from penetration of pathogenic microorganisms and promotes dentin regeneration. When the neurovascular bundle is damaged, an inflammatory process occurs. The person feels acute paroxysmal pain. Taking analgesics only briefly relieves the pain symptom. If pulpitis develops, you must immediately visit the dentist. If help is not provided in a timely manner, the dead nerve fiber will become a source of infection. Pathogenic microorganisms will penetrate into the surrounding dental tissues, and periodontitis will develop;
- Cementum is a hard tissue lining the outer surface of the root. Periodontal ligamentous fibers are attached to the cement, which securely fix the tooth in the alveolar socket.
The detailed structure of the tooth and methods of their treatment are described in the video: The crown part of the incisors, canines and molars is located above the surface of the gum, the root is hidden deep in the internal tissues of the jaw.
Treatment methods
The treatment regimen and the scope of medical manipulations are selected according to the patient’s somatic status. The inflammatory process is eliminated, professional oral hygiene is performed, and antimicrobial therapy is prescribed. Treatment of mobility is aimed at eliminating the underlying cause that led to the weakening of the ligamentous apparatus. If it is periodontal disease, then infection and inflammation are treated; in case of malocclusion, orthodontic treatment is carried out; in case of injury, a temporary splint is applied.
Treatment includes various methods, including grinding crowns, normalizing occlusion, splinting, and prosthetics.
- Thanks to bite correction, the load on the periodontium is normalized, the teeth occupy a more stable position in the sockets.
- Wearing a special mouthguard that prevents clenching or grinding of the teeth will help strengthen loose teeth in the gums during bruxism or clenching.
- In case of physiological changes, hormonal levels and nutrition are corrected, vitamin therapy is carried out, and the immune system is strengthened.
- In case of injury, a special device is installed on the dentition - a splint, which helps to fix loose units and correctly distribute the load between healthy and injured teeth.
In some cases, it is impossible to save a loose tooth. Direct indication for extraction
is mobility of 3-4 degrees with loss of bone tissue by 70%, atrophy of the jaw bone by more than 50% with damage to the dental pulp. In such situations, it is advisable to remove the loose tooth, preserving the bone tissue for subsequent implantation.
Types of teeth. Classification
There are certain features in the structure of human jaws and teeth. The incisors are located in the very center, followed by the canines, small molars and large molars.
Each unit performs its primary functions. The incisors help to grasp and bite food, the canines hold and separate it, and the molars and premolars chew and grind it.
External structure of teeth and their types:
- The incisors are the weakest teeth. They consist of a flattened crown and have 1 root. The front surface of the incisor is convex, and the back is slightly curved. At the base of the coronal part there are small serrations (cutting cusps).
- Fangs - located behind the incisors, have 1 powerful root, and are equipped with a pointed cusp at the top of the crown.
- Premolars - capable of withstanding powerful loads, are involved in chewing and grinding food. Dentists call them small molars. The units have a prismatic shape and may contain from 2 to 5 tubercles. The lower premolars have 1 root, and the small molars located immediately behind the canines are equipped with 2 roots. Children have no small molars; they are temporarily replaced by baby molars.
- Molars are chewing units, equipped with a massive crown and designed for chewing food. Molars have 4 - 6 cusps, between which there are deep grooves and fissures. The teeth of the upper jaw have 3 roots, the lower 2. The exception is the 8th molar, in which 3 or even 4 roots can be found.
The value of each tooth is very significant. Important organs, together with the tongue, the inside of the cheeks and lips and the salivary glands, contribute to the formation of the food bolus. If even one tooth is missing, the digestion process becomes difficult. This leads to the formation of gastrointestinal diseases. After removal of an incisor, canine or molar, without subsequent prosthetics, the jaw row shifts, the bite is disrupted, and the likelihood of developing caries increases. With pathology or absence of frontal teeth, a person is embarrassed by his smile, becomes withdrawn and uncommunicative.
The structure of the human jaw: teeth and their formula
When citing one number for any tooth, the dentist means its anatomical and functional affiliation. If you conditionally divide the dentition into two halves and start counting from the first incisor, you will get 8 teeth in each direction (top and bottom). The first incisor is a one. The second, accordingly, is a deuce. And so on until the last molar, which is called the figure eight. If the doctor says - bottom seven on the left, then we are talking about the bottom left second molar. As you can see, everything is very simple!
This can be expressed schematically as follows (permanent teeth):
For baby teeth, everything is the same, only the teeth are designated by Roman numerals (there are no premolars in the primary dentition):
As for the two-digit designations, they were invented in order to simplify the written recording of medical history. The above is preserved, but a number appears before the number indicating which jaw and on which side the tooth is located. Conventionally, the oral cavity is divided into segments - upper right (number 1), upper left (number 2), lower left (number 3), lower right (number 4). As you noticed, the report is conducted starting from the top right and clockwise. The segment is written first, and then the tooth number. For example, the third canine from the top right would be designated tooth 13. The lower incisor on the left is 32 teeth. In children, the segments are designated by numbers 5 to 8, so as not to confuse the primary bite with the permanent one. Let's take the same third fang on the right. In a child, it will be designated as tooth 53. And so on by analogy. The main thing is to always start the report from the right side at the top, then you won’t get confused. These are not snails with 25 thousand teeth! Can you imagine their dental formulas?
Teeth of the upper and lower jaw. Structural features
On each of the human jaws there are incisors, canines, premolars and molars. The teeth of the lower jaw are smaller in size, have a narrow crown and a flattened root. The incisors and canines of both jaws, as well as the lower premolars, have 1 root. The small molar of the upper jaw, located near the canine, is attached to the socket by 2 roots.
To facilitate diagnosis and treatment, dentists invented a special teeth numbering system. The distinctive features of incisors, canines and molars, as well as their functions, are clearly visible in the photo:
Features of baby teeth
The rudiments of baby teeth appear during the period of intrauterine formation of the fetus. The baby's first teeth begin to erupt at the age of 5-8 months. The appearance of teeth is a long-awaited event in the family, which brings young parents and children not only joy, but also anxiety. During teething, changes in the toddler's behavior (lethargy, moodiness, tearfulness), increased salivation, fever, and disturbances in appetite and digestion may be observed.
Distinctive features of baby teeth:
- small sizes;
- roundness of the crown shape;
- milky color;
- the presence of an enamel ridge near the gum;
- vertical arrangement. Permanent teeth are inclined in the lip and cheek areas.
The incisors, canines and molars of babies have a similar structure to permanent teeth. The significant difference is the thin enamel coating and the voluminous neurovascular chamber. Due to these features, children experience rapid development of caries and the occurrence of pulpitis.
Question answer
How to detect caries?
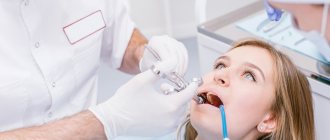
Timely diagnosis helps reduce the percentage of dental disease. To identify pathologies in dentistry, visual examination, probing, temperature tests, and caries test are used. Hardware diagnostic methods (radiography, CT) help to see changes in tissues inside the body, establish the correct diagnosis and carry out adequate treatment.
Despite the fact that only a doctor can identify the initial manifestations of caries, you can try to conduct an independent examination.
Healthy human enamel: smooth, light in color (white-cream-milky), without inclusions or roughness. An important criterion for ill health is pain. If it occurs while eating and goes away immediately after rinsing, it may be a sign of caries.
Self-examination is not a reason to refuse preventive dental care. It often happens that a pathological cavity is hidden from human sight and it is impossible to detect it on your own.
If adverse symptoms appear, visit your dentist as soon as possible.
What are the characteristics of wisdom teeth?
The structure of a wisdom tooth is similar to the first and second molars. Sages have a coronal part and a root, have an enamel coating, dentin and pulp. A distinctive feature of figure eights is their curved roots, which contribute to difficulties during endodontic treatment.
Interestingly, sages do not have milk precursors. This type of molar is a rudiment and in most cases, upon birth, it brings a lot of inconvenience. Very often, third molars erupt in the wrong direction, injure the soft tissues of the oral cavity and are removed.
At what age do wisdom teeth appear? What complications occur during teething?
Eights erupt between the ages of 18 and 30. Possible complications during the growth of eights: pericoronitis (inflammation of the gingival hood), traumatic periodontitis of adjacent molars, inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, gum abscess, submandibular lymphadenitis.
In some cases, figure eights erupt only halfway or remain in the gums forever (impacted teeth).
Dentures: what is included in this concept?
Logically, false or removable jaws should completely imitate the dentition, but this is what people usually call any removable dentures. Before the advent of prosthetics and implantation technology, this solution was the only possible one. Teeth were made from porcelain and animal bones (especially in ancient times), but due to the lack of planning and manufacturing technology, such a design could hardly help. From a functional point of view, these products were ineffective, and the aesthetics were, to put it mildly, not at a high level. Such prostheses were needed to hide obvious defects, but at close range the forgery was always obvious. Today the situation has changed dramatically. The so-called false jaw is sometimes impossible to distinguish from natural teeth even upon closer examination, and modern materials and technologies make it possible to produce not only beautiful, but also comfortable and functional dentures. Next are photographs and types of false jaws.
Partial dentures
In simple terms, the so-called artificial jaws are divided into two broad categories: partial and complete dentures. They are united by the fact that the patient can independently remove them from the oral cavity for cleaning, maintenance or other purposes. Partial structures imitate a fragment of the dentition or even almost the entire jaw, but the key difference between such products is their attachment to natural teeth. There are several types of these dentures, which differ in design and number of teeth replaced.
- Butterfly prosthesis, or immediate prosthesis. A removable product, which in the photo resembles the wings of a butterfly and imitates one or two teeth. Immediate is translated from English as “immediate”, and this fully characterizes its purpose. The product is installed after tooth extraction to hide the aesthetic defect until implantation or permanent classical prosthetics is performed. On average, a butterfly prosthesis lasts about two years and is considered a temporary solution, but some patients wear it for many years, replacing it from time to time;
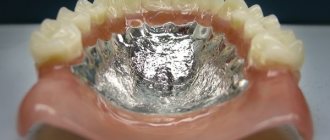
- Plate and clasp dentures. A large group of products that replace a large fragment of the dentition and in appearance really resemble an artificial jaw. These prostheses can be divided into two categories. The first is the so-called laminar dentures: structures with a soft base and artificial teeth. The second is clasp dentures with a metal frame, which do not require an artificial palate and optimally distribute the chewing load. The only drawback of such a prosthesis is the rather high price and the possibility of an allergic reaction to the metal. However, there are also metal-free options, for example, the Quadrotti prosthesis, in which the frame is made of plastic.
Partial removable jaw attachment
Fixation of a partial structure is carried out in several ways, each of which has its own nuances and advantages.
- Clasps are arches made of plastic, silicone or metal that clasp healthy teeth and thereby help to hold the entire structure in place.
- Attachments are a more complex system consisting of a groove and a lock that snaps into place upon contact. One part of the fastening is on the prosthesis itself, the other on the tooth. This option allows for more reliable fixation, but will cost a little more.
- Telescopic crowns are a less common method of fixation, when abutment teeth are prepared for the installation of a special cap - a telescopic crown, which serves as a support for a partial false jaw. The most common solution is the fairly well-known “Sandwich” prosthesis, developed by Russian specialists.
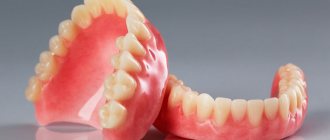
Full dentures
A complete denture imitates the entire dentition and is placed when the patient has lost all of his natural teeth. By and large, this is a completely false jaw in the classical sense. Complete dentures differ from partial dentures primarily in their fastening. If in that case the fixation was carried out using hooks, micro-locks or telescopic crowns, then a full false jaw can only rest on the mucous membrane. Despite the fact that modern complete structures are very comfortable and cause virtually no discomfort, the absence of supporting teeth significantly reduces the stability of the product. However, there is a much better solution - a complete denture supported by implants, when the patient is implanted with artificial roots, on which a removable denture is subsequently placed. As a rule, a removable denture is a temporary solution, but it may well last for several years.
Everything you need to know about dental hyperdontia
During normal development, a person grows 20 primary and 32 permanent teeth during their lifetime. A phenomenon is considered abnormal when these numbers are exceeded. In medicine, this pathology is called hyperdentia, polyodontia or supernumerary teeth. Most often, excess bone elements appear in the anterior part of the upper jaw. However, there are often cases when they erupt near the molars or outside the dentition.
Content
In size, supernumerary teeth rarely correspond to the parameters of a normal bite. They often have defects, are smaller in size and do not erupt completely.
In most cases, the appearance of additional elements in the general row causes insufficient space for the full growth of permanent teeth, provokes crowding, changes in their position and inclination, and deformation of the dental arch.
In accordance with ICD-10 (international classification of diseases), polyodontia belongs to the group “Disorders of development and eruption of teeth” and is divided based on the placement of elements in the dentition:
- area of canines and incisors;
- area ;
- area ;
- unspecified area (additional teeth).
Males are more at risk of this disease. In general, hyperdentia is observed in 2% of the world's population.
The manifestation of hyperdentia can be different. There are several types in dentistry. Based on the characteristics of its appearance, the disease is divided into two types:
- False polyodontia. It manifests itself when the temporary tooth does not fall out, has a natural appearance and location, is firmly attached to the jaw arch and performs the necessary functions. This also includes fused bone elements located in the neighborhood.
- True polyodontia. It has all the signs of the disease and is characterized by the formation and eruption of excess tooth germs.
On this topic
All about bite trainers
- Maria Konstantinovna Tevs
- October 4, 2022
Considering the location of abnormal teeth, experts identify:
- Atavistic or typical polyodentia. In this case, there is an anomaly in the number of teeth, but they do not go beyond the boundaries of the dentition. It is assumed that this feature is hereditary in nature, since our ancestors had a more developed chewing apparatus, and the number of teeth exceeded the norms in force today. In most cases, this pathology does not cause discomfort to a person, especially if there is sufficient space in the bite.
- Atypical polyodentia. Its distinctive feature is the eruption of supernumerary teeth outside the alveolar socket. The formation of rudiments can sometimes be observed on the side of the gum, on the palate and even outside the oral cavity.
The appearance of supernumerary teeth can be either natural or abnormal. There are several forms of pathological deviations:
- Spiked teeth. Their crowns are narrowed from the neck to the apex. They can be placed near the lateral and central incisors of the upper row. The pointed end often leads to injury to the oral mucosa.
- Paramolars are additional molars that usually do not fully erupt, are small in size and are located on the side of the cheek or palate relative to the other lateral teeth of the upper jaw. They can be conical in shape and differ in the number of tubercles.
- Premolars - located in front of the large permanent teeth. Usually appear in the lower dentition.
- Extra canines are the most common type of supernumerary teeth that are found in the upper bite.
- Emenalomas (pearl dew) - refer to microdentia. Their dimensions are less than 2.0 mm and do not cause any clinical disturbances.
How to replace teeth with missing molars: bridge
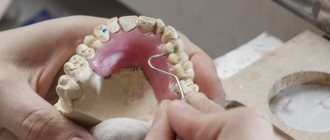
A bridge is the only applicable method of permanent prosthetics in the absence of several adjacent teeth. It consists of connected crowns, the outer ones are put on healthy teeth (close to those that are missing).
The need to grind down the supporting teeth is the main disadvantage of this type of prosthetics, which often forces patients to look for other methods. Today bridges are secured in alternative ways:
- on metal plates;
- using a special adhesive.
Crowns for bridge structures are made from the following materials;
- ceramics;
- metal ceramics;
- plastic.
For the most part, the price of the issue depends on the material from which the prosthesis is made, as well as whether it is necessary to restore one tooth or whether prosthetic teeth are needed in the absence of a large number of them. The cost of one crown in our clinic is from 15,000 rubles. for metal ceramics up to 25,000 rubles. and more for ceramics.
Plastic crowns are installed as temporary crowns. Installing crowns made of plastic on chewing teeth is not advisable - this material is not sufficiently stable, and the crown can easily break.
The service life of a prosthesis depends on the number of missing teeth it replaces: the more crowns it has, the less it will last. On average, you should expect 5-7 years of using a bridge.
Over time, bridge structures become mobile, which can lead to unpleasant consequences:
- bleeding gums;
- exposure of the neck of the supporting tooth;
- food residues getting under the structure.
Symptoms
Hyperdentia more often affects molars than milk teeth. In adult patients, impacted, displaced or incorrectly positioned supernumerary elements are usually diagnosed.
On this topic
6 effective methods for correcting deep bites
- Maria Konstantinovna Tevs
- October 4, 2022
If they develop outside the dentition, a person experiences:
- abnormal position and inclination of normal teeth;
- injuries of soft tissues of the oral cavity;
- excessive saliva production;
- compactions, pain and swelling in the eruption area;
- increased temperature and general weakness.
Impacted teeth remain in the bone tissue of the jaw and are not visible externally. Before complications begin, no signs are observed.
Which prosthesis to choose if all teeth are missing?
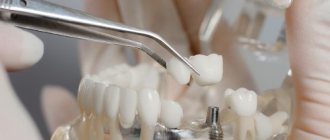
In Russia, classical implantation is more in demand, since the immediate loading protocol is not used by all specialists due to the complexity of the procedure and subsequent prosthetics. To apply modern implantation concepts, it is necessary that the clinic meets all the requirements of the product manufacturer, and the doctor has undergone special training and internship. This requires large expenses from clinics and specialists, in addition, many patients cannot undergo the implantation procedure using the immediate loading technique due to clinical indications or due to limited budget. When choosing budget models, you cannot guarantee the result, since budget implants do not have such high reliability indicators as top manufacturers. Therefore, performing implantation in one stage when using cheap implants is a high risk for the patient. Experts do not recommend installing untested systems using the instant load protocol, since the result is unpredictable and if the operation is performed incompetently, the risk of jaw injury increases. Therefore, despite the delayed result, patients still choose the classic implantation technique for prosthetics in the absence of teeth.
When carrying out classical implantation, two stages are carried out. At the first stage, artificial roots are installed in the patient’s bone tissue, covered with a mucoperiosteal flap and sutures are applied. Without pressure or load, the implants take root in the bone ridge. When choosing budget implant models, the survival rate depends on the type of implant and the manufacturer. Modern clinics, as a rule, use high-quality products with a high degree of reliability. Engraftment occurs in 97-99% of cases when installed in two stages.
At the second stage, after complete engraftment, a gum former is installed inside the implants to create an aesthetic and natural gingival contour that will adhere to the prosthesis and cover the necks of the implants, protect against plaque formation, and prevent the development of peri-implantitis. If the fit is not precise, cavities are formed in which plaque quickly accumulates. It is difficult to remove, resulting in bad breath, inflammation of the gums, and the formation of tartar. To avoid such consequences, it is recommended to use an individual gum former, which will help create a beautiful contour and prevent the appearance of deposits between the denture and the gum.
After creating the gingival contour, the prosthesis is installed. To fix it, an abutment is used - an element connecting the implant and the prosthesis. Since the implant is completely immersed in the bone tissue, additional elements are used to fix the orthopedic structures. The abutment ensures correct load distribution over the entire surface of the implant and prosthesis. Its use prevents breakage and reduces the risk of loosening. If excessive pressure was nevertheless applied to the prosthesis, then if it breaks, only the removable part (abutment) will need to be replaced, while the implanted implant will remain undamaged.
When using a custom abutment, the bridge portion of the prosthesis can be fixed at the correct angle. Unlike standard types of abutment, when making an individual element, the angle of inclination of the prosthesis can be changed and made it most suitable for the patient. The angle of inclination determines how much load the prosthesis can withstand. For any deviations from the pressure axis, the implant and abutment will experience overload. If the lines of the abutment angle do not correspond to the natural position of the teeth and pressure on the fracture, the abutment may break when chewing hard food, even if the material is durable and made of high quality. Only if properly positioned can this element last for a long time. Standard abutment models are used if the location of the implants inside the bone allows them to be installed at a specific angle. In this case, the risk of breakdown is minimal. For this reason, implant manufacturers produce components for installing prostheses - abutments, formers, screws, plugs, etc. With a wide range of products, the doctor can select a standard product for prosthetics without risk to the patient.
The use of individual components such as an individual gum former, abutment and impression tray will allow, after installation of the prosthesis, not to experience discomfort when wearing the prosthesis, easy oral hygiene, and reduce the risk of complications.
Indications for classical dental implantation are complete or partial absence of teeth, the need to install a permanent prosthesis with permanent fixation in the oral cavity, an open palate and a natural volume of the prosthesis that corresponds to natural teeth and has an aesthetic appearance.
Contraindications to classical implantation are the presence of chronic diseases of the heart, lungs, blood, such as tuberculosis, hemophilia, oncology, type 1 diabetes mellitus, osteoporosis, disorders of bone tissue regeneration, weakened condition after a heart attack, stroke, long-term treatment. If the patient has chronic diseases that prevent surgical procedures, it is necessary to obtain additional consultation from the attending physician to eliminate the risk of complications. In the presence of atrophy, the installation of implants is contraindicated. In this case, it is recommended to undergo the procedure of osteoplasty - increasing the volume of bone tissue. After increasing the volume of the alveolar ridge, implantation can be performed. However, it is necessary to plan the procedure first of all in conjunction with the general plan for implantation and prosthetics.
Causes
Modern medicine has not yet been able to establish the true causes of supernumerary teeth. However, there are three supposed factors influencing the development of this pathology:
- Splitting of tooth germs. According to this theory, the anomaly manifests itself during the development of the embryo at the stage of the formation of a tooth germ. Permanent teeth begin to form in the fetus in the tenth week of pregnancy. However, this theory does not explain the reasons for the simultaneous increase in the number of teeth in one area of the jaw, and their shortage in another place due to the underdevelopment of the rudiments.
- Atavism. It is characterized by the appearance in a person of signs that were characteristic of his ancestors, but such an anomaly was not observed in the next generations. Proponents of this idea argue that supernumerary teeth appear due to a return to the past, when humans had six incisors on the lower and upper jaws. Their arguments are based on the fact that polyodontia most often manifests itself in the anterior part of the bite. On the other hand, the disadvantage of the theory is the lack of explanation for the appearance of extra lateral teeth.
- The cumulative influence of genetic abnormalities and characteristics of embryo development.
- Heredity. The likelihood of supernumerary teeth increases if close relatives have such an anomaly.
- Past illnesses or negative impact on the mother’s health during pregnancy
- Pathology occurs when baby teeth do not fall out, but permanent teeth erupt nearby.
- Facial dysplasia. This is a congenital disease that affects the abnormal development of bones and teeth.
In general, people with supernumerary teeth often have other associated syndromes and diseases.
Which removable jaw is better?
Which dentures are best to insert is perhaps the main question among patients faced with the need for complex dental restoration. You can answer right away that the best option is to install a removable denture supported by dental implants or at least mini-implants. This allows you to restore both aesthetics and functionality to the highest possible quality. However, implantation is a completely different direction. Most often, removable dentures are chosen by people who have restrictions on implantation or simply do not have enough funds. In this case, completely different criteria come into play. Of the partial structures, the best (and most expensive) are clasp dentures with a frame. The quality of a full denture depends largely on the material of the prosthesis. It is better to give preference to products made from acrylic-free plastic (for example, Acry Free), since they do not cause allergies and are more comfortable to wear. Nylon dentures also perform well, but they cannot be used in the absence of teeth due to excessive softness.
Diagnostics
Hyperdentia is detected on both the upper and lower jaws, symmetrically on both sides or only on one. Most often, the number of extra bone elements is 1–2 units (more than 90% of cases of detection of this pathology), but there are situations in which there are three or more extra teeth.
Multiple supernumerary formations can be located in different parts of the jaw separately from each other or in groups of several units located close to each other. Sometimes they fuse with each other or with normal teeth partially or completely.
With a single increase in the number of teeth, the doctor does not prescribe additional diagnostics to identify other diseases. With multiple supernumerary elements, concomitant pathology or deviations in the development of the body are usually diagnosed.
Everything you need to know about dental hyperdontia
During normal development, a person grows 20 primary and 32 permanent teeth during their lifetime. A phenomenon is considered abnormal when these numbers are exceeded. In medicine, this pathology is called hyperdentia, polyodontia or supernumerary teeth. Most often, excess bone elements appear in the anterior part of the upper jaw. However, there are often cases when they erupt near the molars or outside the dentition.
Content
In size, supernumerary teeth rarely correspond to the parameters of a normal bite. They often have defects, are smaller in size and do not erupt completely.
In most cases, the appearance of additional elements in the general row causes insufficient space for the full growth of permanent teeth, provokes crowding, changes in their position and inclination, and deformation of the dental arch.
In accordance with ICD-10 (international classification of diseases), polyodontia belongs to the group “Disorders of development and eruption of teeth” and is divided based on the placement of elements in the dentition:
- area of canines and incisors;
- area ;
- area ;
- unspecified area (additional teeth).
Males are more at risk of this disease. In general, hyperdentia is observed in 2% of the world's population.
The manifestation of hyperdentia can be different. There are several types in dentistry. Based on the characteristics of its appearance, the disease is divided into two types:
- False polyodontia. It manifests itself when the temporary tooth does not fall out, has a natural appearance and location, is firmly attached to the jaw arch and performs the necessary functions. This also includes fused bone elements located in the neighborhood.
- True polyodontia. It has all the signs of the disease and is characterized by the formation and eruption of excess tooth germs.
Symptoms
Hyperdentia more often affects molars than milk teeth. In adult patients, impacted, displaced or incorrectly positioned supernumerary elements are usually diagnosed.
On this topic
6 effective methods for correcting deep bites
- Maria Konstantinovna Tevs
- October 4, 2022
If they develop outside the dentition, a person experiences:
- abnormal position and inclination of normal teeth;
- injuries of soft tissues of the oral cavity;
- excessive saliva production;
- compactions, pain and swelling in the eruption area;
- increased temperature and general weakness.
Impacted teeth remain in the bone tissue of the jaw and are not visible externally. Before complications begin, no signs are observed.
Tooth roots
The processes of bone tissue - the roots of the tooth, hold it in the jaw - and in this they are very similar to the roots of plants. But, in addition, in each root process there is a void inside - this is the root canal. The same nerve fibers and capillaries that go higher into the pulp, and from below are brought out into the jaw through a tiny hole at the tip of the tooth root, are laid in it, like wires in a protective cable. This hole is called apical.
Depending on the type and size of the tooth, there may be one root, or there may be two.
Causes
Modern medicine has not yet been able to establish the true causes of supernumerary teeth. However, there are three supposed factors influencing the development of this pathology:
- Splitting of tooth germs. According to this theory, the anomaly manifests itself during the development of the embryo at the stage of the formation of a tooth germ. Permanent teeth begin to form in the fetus in the tenth week of pregnancy. However, this theory does not explain the reasons for the simultaneous increase in the number of teeth in one area of the jaw, and their shortage in another place due to the underdevelopment of the rudiments.
- Atavism. It is characterized by the appearance in a person of signs that were characteristic of his ancestors, but such an anomaly was not observed in the next generations. Proponents of this idea argue that supernumerary teeth appear due to a return to the past, when humans had six incisors on the lower and upper jaws. Their arguments are based on the fact that polyodontia most often manifests itself in the anterior part of the bite. On the other hand, the disadvantage of the theory is the lack of explanation for the appearance of extra lateral teeth.
- The cumulative influence of genetic abnormalities and characteristics of embryo development.
- Heredity. The likelihood of supernumerary teeth increases if close relatives have such an anomaly.
- Past illnesses or negative impact on the mother’s health during pregnancy
- Pathology occurs when baby teeth do not fall out, but permanent teeth erupt nearby.
- Facial dysplasia. This is a congenital disease that affects the abnormal development of bones and teeth.
In general, people with supernumerary teeth often have other associated syndromes and diseases.
Methods of dental prosthetics in case of large absence of teeth
Before proceeding with methods of prosthetics in the absence of a large number of teeth, it is necessary to define the concept of prosthetics itself and the features of each of its types. After all, it is precisely these features that determine the possibility of recreating the dentition in the event of the loss of several adjacent teeth at once.
Dental prosthetics refers to the professional reconstruction of the lost form or function of both missing and significantly damaged teeth. Therefore, prosthetics include restoration methods such as inlays, veneers and crowns, which are inappropriate to describe in relation to the situation under consideration (they are applicable for restoring destroyed or damaged teeth).
Here are the main groups of prosthetic methods, each of them includes those that are applicable when prosthetics are needed in the absence of one , two or more teeth:
- Fixed prosthetics is a method of installing a long-term structure in the patient’s mouth. Used to recreate one or two adjacent teeth (lost or damaged). Fixed prosthetics has the following features:
- the device cannot be removed without breaking it;
- the prosthesis is not able to evenly distribute the load on the gums; all the pressure falls on the teeth to which the device is attached;
- For permanent prosthetics, the following materials are used: metal alloy;
- ceramics;
- do not require filing and depulpation of nearby supporting teeth;
- according to the size of the prosthesis;
By mounting method:
- By redistributing the chewing load.
- Implantation is the insertion of a pin into the jawbone on which an artificial tooth is installed. Based on implantation, both fixed prosthetics are performed (artificial crowns are installed on the implant) and conditionally removable (a removable structure is attached to the implants). The second method is optimal in a situation of complete loss of teeth.
Next, we will describe all possible methods of dental prosthetics in the absence of them, indicating the advantages and disadvantages of each.
Diagnostics
Hyperdentia is detected on both the upper and lower jaws, symmetrically on both sides or only on one. Most often, the number of extra bone elements is 1–2 units (more than 90% of cases of detection of this pathology), but there are situations in which there are three or more extra teeth.
Multiple supernumerary formations can be located in different parts of the jaw separately from each other or in groups of several units located close to each other. Sometimes they fuse with each other or with normal teeth partially or completely.
With a single increase in the number of teeth, the doctor does not prescribe additional diagnostics to identify other diseases. With multiple supernumerary elements, concomitant pathology or deviations in the development of the body are usually diagnosed.
{SOURCE}