26.11.2019
Many patients have itchy gums after tooth extraction. This is a dental problem, which is a fairly common consequence of surgery. The phenomenon occurs quite often in both adults and children. The operation can lead to other consequences, which will also be described in this article.
Correct oral care after tooth extraction
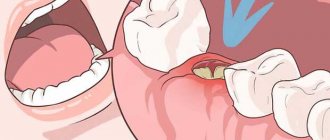
When dental problems arise, the dentist treating a person may recommend removing one or more affected teeth that cannot be restored. This operation is considered a minor surgical procedure. It is important to know not only how to properly prepare for it, but also what to do immediately after the operation. Of course, you can get more detailed recommendations from your doctor, but there are certain tips that will help the damaged gum heal faster and prevent gum scratching after tooth extraction.
Depulpation before prosthetic crowns
Depulpation is unconditional if there is serious tooth decay. It is preferable to remove the dental nerve during prosthetics in the following cases:
- The size of the teeth determines the low position of the crown (too small or short teeth);
- The inclination of the prosthetic tooth is from 15°;
- Increased sensitivity of teeth;
- According to aesthetic requirements.
The need to remove the dental nerve during prosthetics is dictated by deep removal of the top layer of dental tissue: if the doctor is not sufficiently qualified, heating or touching the nerve can cause an attack of unbearable pain. However, cases of nerve-sparing crown installation also occur in modern dental practice.
If over time the nerve under the crown becomes bothersome, it is possible to remove the pulp through the top of the crown and fill the hole after removal.
The danger of such a procedure is associated with the risk of complications in the future due to surgery on the exposed dental nerve.
Taking painkillers
If the doctor left a cotton-gauze swab in the tooth socket, then check exactly when it can be removed from the oral cavity. Thanks to this tampon, the wound heals faster. To get a positive result, you should not pull it out earlier than the dentist advises.
When the anesthetic drugs stop working, quite severe pain and discomfort may occur in the injured area of the oral cavity. Most dentists allow you to take painkillers, but you should check in advance which remedy will be most effective in your situation.
It must be remembered that even a simple tooth extraction is quite a lot of stress for the human body. That is why experts advise forgetting about strong physical activity at least for a few days. It’s better to rest a little these couple of days so that the body has time to recover from a stressful situation.
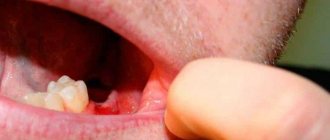
If the doctor does not give other advice, then you will be able to perform your usual regular oral hygiene within 24 hours after the operation. Remember that you need to brush your teeth carefully, especially in the place where the damaged hole is located and near it. Especially if your gums itch after tooth extraction. It is advisable to add socket rinsing to regular teeth cleaning and additionally use antiseptic agents. Rinsing and brushing teeth are allowed one day after surgery.
Proper oral care, especially after surgery, is very important. Bacteria or infections can enter an open wound, so it’s worth making sure they don’t have a chance.
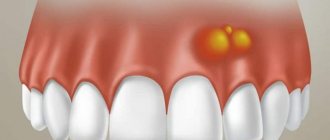
If you notice that the gums are very swollen, suppuration has begun, or the wound is dry, the itching is too strong, then you should immediately seek advice from a specialist. The same should be done if severe pain occurs that does not go away after a long time after the operation.
What can the patient do after removal?
To help the wound heal, the patient must take steps to prevent secondary infection. To do this, immediately after the intervention you need to accurately follow the general recommendations of the dentist.
- Press the cotton swab placed in the hole firmly with your teeth. This is important to stop bleeding and blood clot formation.
- For the same reasons, you should not eat or drink for 3 hours.
- Once a clot has formed, it is necessary to exclude the possibility of injury and removal. Do not rinse your mouth vigorously, inspect the wound with your fingers or a toothpick, smoke, drink alcohol, hot foods and drinks, or solid foods.
- Visits to the fitness center, sauna, and beach should be excluded for several days. Physical activity and overheating can lead to complications.
Likely consequences
In addition to the fact that the gums may begin to itch after the removal of a wisdom tooth and other teeth, there is the possibility of other consequences of dental surgery. Even a minor surgical intervention has many features that must be taken into account. Initially, it is worth understanding why the gums itch after tooth extraction. Also an important topic for discussion are the factors that provoke the appearance of various disorders. Today, there are several main factors that provoke itching of the gums and other ailments after the removal of a diseased tooth.
When nerve removal is indispensable
In modern dental practice, both complete and partial resection are used. Indications for the procedure:
- deep carious tissue damage;
- chronic pulpitis (including asymptomatic);
- bactericidal infection spread by the apex of the tooth root;
- the presence of an extensive pulp area, the threat of developing periodontitis or transition to periodontitis;
- trauma leading to nerve exposure and tooth destruction;
- the need to correct a medical error;
- the need for prosthetics with low crowns.
Unbearable pain can also be an indication for depulpation.
The dentist will never prescribe such a serious intervention as long as it is possible to save the tooth.
Important : problematic “eights” when affected by caries, as a rule, are removed. This is due to the location of the “wisdom” teeth at the end of the dentition, which makes cleaning them from plaque and stone and filling the canals very problematic. Indications for removal are also the wrong direction of eruption, displacement of the dentition, malocclusion, and the development of pulpitis.
Damage to the mucous membrane
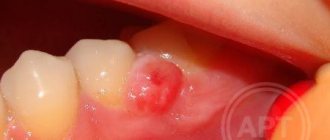
If a person consumes a lot of very hot or cold food, spicy dishes, drinks, then various types of injuries, ulcers, and erosions can form in the oral cavity. This also occurs due to fairly intensive brushing of teeth or incorrect, very careless actions of the dentist who carried out the treatment. This occurs especially often after one or more teeth have been removed. The cause in this situation is damage to the gums, so the gums very often itch after tooth extraction during healing.
Classification
Depending on the nature of the healing of the hole, dentists distinguish several main forms of dental alveolitis:
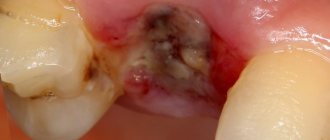
- Serous. The initial stage of the disease usually appears 2–3 days after tooth extraction. This form is characterized by continuous pain that worsens while eating. Although the patient does not yet complain of feeling unwell, his lymph nodes are not enlarged, but he already feels that the disease is progressing.
- Purulent. If the serous form of alveolitis is not treated, the disease turns into a purulent form. Most often it is diagnosed 6–7 days after tooth extraction. The painful sensations can no longer be ignored, the pain intensifies, radiating to the ear or temple. Exploring the affected area also causes severe pain. Purulent alveolitis is characterized by a dirty gray coating inside the socket, significant swelling around the wound, thickened alveolar process and other problems. The patient's general health deteriorates significantly. Lymph nodes enlarge and become painful on palpation. Often the patient cannot even eat or open his mouth.
- Hypertrophic. At this stage, the symptoms of the disease subside. The patient notes a decrease in body temperature, improved well-being and decreased pain. However, at the hypertrophic stage, dangerous tissue proliferation occurs, which is clearly visible upon examination. When touched, pus is released from the inflamed area, and the mucous membrane acquires a bluish tint.
Ask a Question
Diseases of an inflammatory or infectious nature
This group of reasons includes the development of dental pathologies such as gingivitis, stomatitis, periodontitis, and candidiasis. Diseases occur due to the rapid proliferation of pathogenic microflora of various types. Also, a factor that provokes the appearance of pathology may be improper oral care.
Quite often you may encounter the fact that along with the development of an inflammatory or infectious disease, bleeding appears, the gums become very sensitive to various irritants, and a very unpleasant odor appears from the mouth. For this reason, the gums may itch after tooth extraction.
Injuries during tooth extraction
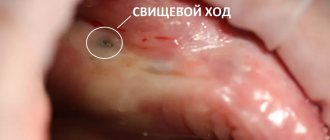
They are considered a complication, most often appear on the upper jaw, the highest risk is when removing premolars and molars. If removal is difficult, there is a risk of perforation of the floor of the maxillary sinus. It becomes damaged, and a hole appears in the bony septum between the nasal and oral cavities. This may be due to the anatomical features of the jaw structure (there is no bone septum or the roots of the teeth being removed are located close to the bottom of the sinus). Another possible cause is chronic inflammation in the area of the tooth root, due to which the bone septum becomes thinner and destroyed. Such an injury is eliminated immediately. If this is not done, liquid may enter the nose when swallowed or chewed. If such a symptom appears, you should contact your dentist so as not to provoke inflammation.
Leukoplakia
This disease is characterized by a special condition, which, as a rule, appears immediately before the development of oncology. In this case, leukoplakia can manifest itself not only as very severe itching in the gum area. Other symptoms also occur: a feeling of numbness, white spots and a dense coating form on the affected area of the gums or oral cavity. Almost all patients suffering from leukoplakia complain about this. In most cases, the disease affects people who have a long history of smoking and smoke more than a pack of cigarettes per day.
When do you need specialist help?
You should contact your dentist even if you have minor discomfort in your mouth. It is easier to cure any disease at an early stage of development. The help of a specialist is necessary if itching in the gums is accompanied by:
- bleeding,
- unpleasant smell,
- redness of soft tissues,
- erosions and suppuration,
- pain of different localization.
These symptoms indicate serious problems that require medical or surgical treatment.
Allergic reaction
The most common cause of itching of the gums after tooth extraction and discomfort in the oral cavity can be called a direct allergic reaction. It can occur not only due to medications that were used during tooth extraction, but also due to food products, stabilizers, preservatives, and dyes that they contain. Sometimes allergies occur due to improperly selected hygiene products or household chemicals that somehow got onto the oral mucosa.
Complications during tooth extraction
They occur rarely and may be associated with the actions of the surgeon and the condition of the dental system:
- damage to adjacent teeth or artificial crowns. The appearance of chips, fractures, other mechanical defects, weakening, loosening is possible. More often it occurs when working with molars, access to which can be complicated, due to crowding. Requires additional treatment;
- incomplete removal. After resection, a root fragment may remain in the bone. If the area is close to a nerve or there is a higher risk of additional injury, the dentist may leave it. Doctors at the DentoSpas clinic recommend atraumatic removal to prevent such situations from arising;
- removal of a section of the alveolar ridge. If the forceps were applied to the bone tissue surrounding the tooth, it can be removed along with it. This results in a serious bone defect. To remove it, plastic surgery is performed, protective membranes and bone tissue blocks are installed;
- jaw fracture. The risk of such a complication is increased with a weak jaw bone structure. Its changes may be associated with osteoporosis and other diseases.
Itchy gums after tooth extraction: how to treat
The gums can itch for a variety of reasons; therefore, today there is no single treatment regimen approved by dentists.
Initially, you need to remove all those factors that can provoke the development of a particular pathology. Also visit the dentist to eliminate plaque, sources that injure the gums and mucous membrane of the oral cavity, foci of inflammation or infection. To eliminate itching of the gums, you can use antihistamines, antibiotics, and oral disinfectants. Before starting use, you should definitely consult with your dentist so that he can select the most suitable means, having previously established the causes of such a problem as itching of the gums after tooth extraction. Category: Tooth extraction Published by Mister stomatolog
Allergy - itchy gums
If a person says that his gums are very itchy, this is not always evidence of a serious illness. A similar process can occur when taking any food products (chocolate, dyes, citrus fruits, spices, honey, etc.), or as a side effect when using toothpaste. In this case, it is better to stop consuming allergens or replace the toothpaste.
Often, an adult's gums itch when taking certain medications in contact with the mucous membrane. This is due to the rapid entry of mediators and allergens into the blood.
Implant rejection: should you be afraid?
In very rare cases, implant failure occurs, requiring surgical intervention. The following symptoms indicate this problem:
- acute pain;
- strong bad breath;
- mobility of the structure;
- redness and swelling of the mucous membrane near the implant plug.
We will look at the symptoms of complications in more detail below. Again, implant failure is extremely rare. According to statistics, new teeth do not take root in only 3-5% of cases. For example, German or Swiss implants will take root in 98% of procedures, and Russian or Israeli implants in 95%.
Therefore, if you detect even all of the listed symptoms, you should not set yourself up for negativity. Most likely, inflammation of the gums after installation of an implant is caused by more harmless reasons. Which ones? Let's deal with all the questions in order.
What not to do
In order to avoid any complications after surgery to remove any tooth, you must follow the following rules:
- Do not eat or drink anything for 3 hours after surgery;
- It is not recommended to eat hot, spicy, hard and fine-grained foods, or drink hot drinks. The load when chewing food must be transferred to the healthy side of the jaw;
- For 3 days, limit physical activity and procedures that increase blood pressure or increase blood flow. Do not take hot baths. Bathhouse, sauna, solarium, visiting the beach are prohibited;
- Do not touch the hole with your tongue, finger, toothbrush, or toothpick;
- Do not rinse your mouth;
- Do not ignore the advice, recommendations and prescriptions of the dentist. Do not violate your medication schedule.
If the patient has any doubts about his condition or questions for the doctor, he should not put off calling the clinic “for later.”
Tooth hurts after nerve removal and filling
Only a dentist after an examination will help you figure out why a tooth hurts after removing a nerve and filling its canals. Treating teeth on your own without a diagnosis is highly discouraged.
In dental practice, the procedure for treating tooth canals by removing a nerve is a rather complex manipulation. Cases of medical error are common. They are fraught with various complications, in which the filled tooth continues to hurt.
The main reason why a “dead tooth” (without a nerve) is bothersome is:
- removal of the filling material beyond the apex of the tooth - this occurs due to incorrect definition
- working tooth length;
- the doctor filled the canal incorrectly;
- a tool broke off in the canal;
- root perforation of the tooth;
- If your tooth aches, you may be allergic to the filling material.
It is worth considering that a tooth under a filling can hurt even without a nerve. After all, during the extraction procedure, only a small part of it is removed from the root canal, which branches off from the main nerve trunk. In addition, when removing and filling canals, dental tissues are damaged. When an anesthetic is applied to a tooth, pain is not felt; it begins to be felt after the anesthesia wears off. Such painful sensations are called post-filling.
After removal of a nerve, neighboring teeth can often be bothered, but it seems as if it is the treated tooth that is hurting. An experienced doctor will examine the dentition to identify and eliminate this problem. However, it is worth sounding the alarm when the nerve has been removed for a long time, and the tooth continues to hurt - this symptom may signal the development of chronic pulpitis or periodontitis.