Dry tooth socket: features of the disease
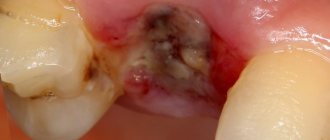
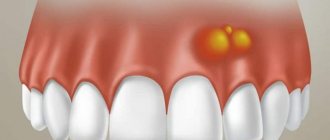
A dry socket appears in two cases after tooth extraction. In the first, a blood clot may fall out or dissolve, while in the second, it may not form initially (usually due to severe bleeding). On average, a similar diagnosis is made to two to five percent of people who have undergone a tooth extraction procedure, but dry socket after wisdom tooth removal is much more common. In the absence of timely treatment, the disease can progress to the stage of alveolitis, which in turn threatens the appearance of phlegmon or an abscess. What does a dry socket look like? Visually, a dry tooth socket is easy to identify: in the absence of a blood clot, part of the bone is exposed.
Symptoms of dry socket
- After 2 - 3 days, the gums begin to become inflamed and pain appears.
- As the inflammatory process develops, pain increases and manifests itself not only in the oral cavity, but also in the cervical region, as well as in the ear area.
- The appearance of an unpleasant odor and specific taste in the mouth is another characteristic symptom.
- Partial hearing loss may occur.
Alveolitis photo of the hole
Often the hole may look normal, that is, without pronounced deviations, but this can be seen in the photo. But here you can consider the presence of a narrow inlet. It is also not very clear whether a clot is present in this case. Of course, making a diagnosis under such circumstances is very difficult. To do this, the doctor will have to conduct a full examination, which is performed using modern technology. And only because of the constant, very often in the form of increasing pain, smell from the open socket, tumor of the gingival tissue, can alveolitis be suspected.
Causes of dry socket after tooth extraction
- Smoking (especially immediately after tooth extraction).
- Poor oral hygiene over a long period of time.
- Poor blood clotting or taking blood thinners.
- Frequent rinsing of the mouth.
- Mechanical impact on the socket and soft tissue in its area.
In addition to the factors mentioned above, much depends on the extraction procedure itself: improperly performed tooth extraction contributes to a number of complications, including dry socket and alveolitis. To prevent this unpleasant phenomenon, dentists recommend limiting physical activity for a few days after tooth extraction, and also not chewing on this side of the jaw (especially hard foods). Under no circumstances should you touch the hole and the area around it with your hands or foreign objects. Bad habits (drinking alcohol and smoking) should be eliminated during healing. The doctor usually prescribes anti-inflammatory drugs for rinsing the mouth (miramistin, chlorhexidine or furatsilin), but this procedure should be carried out no more than 2 - 3 times a day.
After operation
After three hours, the painkillers are still strong, so patients do not feel pain or it is mild. All this time, pure blood or ichor may be released from the hole. If a figure eight was removed, this can last all day, since the surgical area of the wisdom tooth is larger than that of other teeth.
Bleeding from the socket
On the second day, the hole has an unattractive appearance: a blood clot with a grayish coating. It looks like pus, but you shouldn’t be afraid of it: it’s fibrin, a substance that facilitates wound restoration. If everything goes well, the pain will be aching and will subside by the end of the day. If the nature of the pain is different - sharp, pulsating, and there is scarlet blood from the wound, you should urgently see a dentist.
At first, the hole may smell foul. There is no need to be afraid of this: blood accumulates there, and since it cannot be rinsed out, bacteria settle in the wound. If you feel normal, there is no fever, there is no reason to worry.
The rehabilitation process is normal if:
- What medicine is put into the hole after tooth extraction?
- when touching the wound, the ichor does not appear;
- the aching pain gradually disappears;
- feeling normal (temperature up to 38° is possible only in the first two hours);
- swelling on the cheek decreases (if it was not there before extraction, it should not appear at all);
- after 3 days the wound no longer bleeds.
2 weeks after removal
To reduce bleeding, you can make a tampon yourself. Positioning it so that the edges do not injure the blood clot, hold the napkin for half an hour. In the pharmacy chain you can buy a hemostatic sponge, which can be used in cases of heavy bleeding, for example, in liver failure.
Hemostatic sponge
The hole is closed with a hemostatic sponge.
You can take one or two tablets of Dicinone or Etamzilate (no more than 8 pieces per day).
Dicynone tablets
You cannot experiment with hydrogen peroxide: it reacts with blood components, destroying the blood clot and increasing blood flow.
Treatment methods for dry tooth socket
If you discover symptoms of a dry socket, immediately contact your dentist: in this case, you should not self-medicate, although on the Internet you can find a lot of advice on how to treat a dry socket at home. Can a dry socket heal on its own? Without therapeutic and preventive measures, the healing process is not always successful and takes longer. What kind of dry socket treatment will be carried out after tooth extraction depends on the degree of development of the inflammatory process.
| Degree of complication | Treatment method |
| Lightweight | Antiseptic and anti-inflammatory drugs available without a prescription. |
| Average | Antibacterial therapy, cleaning the hole and filling it with anti-inflammatory gel. |
| Heavy | In severe stages of the disease (cellulitis, abscess), the patient is sometimes hospitalized, and a number of measures are taken for his rehabilitation, including physical therapy and ultraviolet irradiation. |
Treatment of a dry socket after the removal of a wisdom tooth is carried out in the same way as in the case of other teeth, however, access to the area of inflammation can be complicated due to the distance of the “eight” location.
A few words about the procedure
Tooth extraction is a full-fledged surgical procedure. The operation consists of four stages.
- Treatment of the area around the tooth that is to be removed.
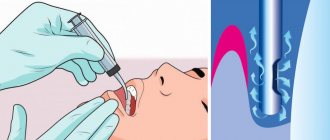
- Anesthetic injections - ampoules in carpules, where an anesthetic is combined with drugs to constrict blood vessels. Usually local anesthesia is used in the area where the nerve that innervates the problem tooth exits; if this is not enough, anesthetics are added without additional effect. When the medicine is injected into the inflamed gum with an acidic environment, part of it is inactivated, so additional anesthesia is used.
- Tooth extraction after the anesthesia has started working (the gums become numb, the blood vessels narrow). A scalpel is used to cut off the ligaments that fix the tooth. The choice of instruments and duration of the procedure depend on the condition of the tooth.
- Treatment of the oral cavity after removal: sutures (if the wound is torn or its edges are located far from each other) and a gauze swab soaked in a hemostatic agent (it must be held in the teeth for 20 minutes, since the effectiveness of the hemostatic drug increases compression of the wound). Do not rush to remove the tampon.
Gum section
Preparing for removal
Removal of a tooth
Installing a tampon
Stitching
Bleeding from the hole itself does not pose a mortal danger. In medical practice, only one case of death was recorded when blood from a wound entered the respiratory tract because the patient was intoxicated. The bleeding was complicated by cirrhosis of the liver, which interferes with clotting, and the woman had three teeth removed at once.
How long does it take for a dry socket to heal?
Many people are interested in the question of how long it takes for a dry socket to heal. In the absence of complications, the wound heals in 5 - 7 days, and within a month the hole is filled with epithelial tissue. If you have dry socket, the healing process may take longer than two weeks (with proper treatment, of course). As already mentioned, extensive inflammation may occur and even require surgical hospitalization of the patient: in this case, the healing of the dry socket may be very delayed.
Possible forms
The table shows the forms of alveolitis:
| Form | Features of the flow |
| Acute inflammatory process | Pain, swelling of the gums, no discharge, body temperature is normal |
| Chronic inflammatory process | Granulations are present, the pain is mild, droplets of pus may be released, the general condition is unsatisfactory, there is weakness, malaise |
| Purulent-necrotic inflammatory process | There is a sharp pain radiating into the ear, a strong increase in body temperature, swelling of the gums, a dark coating is revealed at the bottom of the socket, pus is released when pressed, and there is a persistent bad breath. The most complex form, often requiring surgery |
Clinical diagnosis
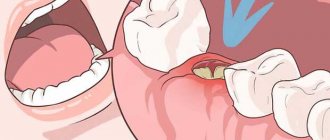
Externally, the hole looks like a deep hole in the gum that has an unhealthy color. You can diagnose this disease yourself using the above symptoms, but visiting a doctor in this case is mandatory.
If severe pain, general weakness, redness of the gums and high fever appear in the socket area, you should suspect the development of alveolitis.
The dentist most often makes a diagnosis based on external signs. Visually, he is able to determine the degree of damage to the hole, on the basis of which the treatment method is selected. Additional blood tests may be required to confirm the diagnosis.
Based on the results obtained, the specialist prescribes appropriate medications to the patient.
The process of diagnosing a disease begins with an examination of the dentist and a survey of the patient. Already at the first pathological manifestations, you need to consult a doctor, because when the disorder starts, irreversible purulent-necrotic processes can arise and actively progress.
Immediately after removal, several preventive visits to the doctor are required. Usually, to identify alveolitis, it is enough to ask the patient about complaints and visualization; less often, radiography, computed tomography, and electromyography are additionally performed. When a disease occurs, the doctor detects a plaque with a green or yellow tint in the oral cavity.
Differential examination is not difficult, since the clinical picture of alveolitis is specific. It is important to distinguish it only from alveolar neuritis. But with neuritis, the temperature does not rise, the lymph nodes remain normal, there is no inflammation. Therapy proceeds faster, and the pathology itself is not dangerous if proper, timely assistance is provided.
Why is pathology dangerous?
If you do not pay close attention to the problem, then within a few days after the operation severe pain will begin, indicating inflammation of the socket of the extracted tooth, that is, alveolitis. The disease is dangerous because, if treated improperly and not seeing a doctor in a timely manner, it can lead to the development of gumboil, when the cheek swells and an abscess appears on the gum. But flux is not the worst thing. Advanced alveolitis can lead to a purulent abscess, phlegmon of the soft tissues of the face and osteomyelitis of the jaw, damage to internal organs, sepsis (blood poisoning), and death.
What to do to prevent alveolitis
Alveolitis most often develops after the removal of third molars - wisdom teeth. This is due to the high traumatic nature of the doctor’s manipulations. Often, additional cutting is required, peeling off the gums, sawing the tooth into several parts to make it easier to remove it if the roots are bent.
After 30 years, alveolitis in the current situation occurs several times more often, since the jaw itself becomes denser, not enough blood flows into it, and the socket often remains dry.
After the removal of third molars, the doctor may recommend the implementation of prophylaxis. The main goal is to prevent complications. To do this, you need to strictly follow all the dentist’s advice so that the blood clot in the socket is preserved and healing proceeds as it should.
What to do for prevention:
- avoid intensive rinsing;
- avoid foods that are too hot, because heat provokes inflammation;
- do not chew on the operated side;
- do not touch the wound with your hands;
- do not pick the hole with improvised objects;
- do not try to remove the blood clot;
- organize proper care.
The patient should visit the dentist twice a year for preventive examinations.
When performing an operation, the doctor observes the following precautions:
- proper treatment of the patient’s hands, instruments, and mouth;
- carrying out the operation in accordance with the regulations and stages;
- after removal, the edges of the hole must be connected so that it fills with blood;
- placing a hemostatic sponge in the socket to prevent alveolitis and stop bleeding;
- suturing in cases of severe soft tissue injury.
The most common complication after tooth extraction is dry socket. You should know why this disorder occurs and what to do when symptoms appear.
Dry socket syndrome (alveolitis) is the definition of a disorder when a blood clot does not form after tooth extraction.
This is dangerous because it is accompanied by bleeding and the risk of infection. Complications are possible for two reasons: when a clot does not form at all, and when it falls out after a while.
General rules for caring for the tooth socket after surgery
It is important to pay attention to oral care in order to avoid infection. Thanks to antiseptics (Chlorhexidine or Furacilin), unsanitary conditions and inflammatory complications can be avoided. In order to use antiseptic solutions, you should know that use is prescribed after 24 hours from the date of tooth amputation.
The rinsing is gentle, so as not to wash the protective layer in the hole. After a few days, the antiseptic can be replaced with folk remedies: herbal infusions, soda or salt solutions, strong tea. The solution should be of such a consistency that it does not cause additional drying or damage to the oral mucosa. Don't overuse antibiotics. They should be prescribed by the attending physician only in case of severe symptoms in the form of inflammation or suppuration.
List of other means and methods for care and treatment of the affected area in case of complications:
- rehabilitation, i.e. medical therapy to remove pus, dead tissue and tooth fragments from the socket;
- drainage procedures (installation of a drainage tube to drain purulent deposits);
- suturing.
What should everyone know after tooth amputation?
Here are the rules that must be followed. Abuse of bad habits or an indifferent attitude towards such wounds can turn out very badly and affect the health of not only the oral cavity, but the entire body as a whole. What rules do you need to know?
Wait 2-3 hours after tooth extraction and do not take any food or water.
- Find the strength to hold the gauze under pressure for 20 minutes, which the doctor left in the wound after the amputation of the tooth.
- Ban yourself from visiting steam rooms and swimming pools; you will be forced to give up even sports and active recreation.
- Consuming alcohol, tobacco products, as well as eating hard, hot, spicy or sour foods will have an extremely negative impact. This can irritate or dry out the oral mucosa, increasing pain and increasing the risk of developing inflammation or infectious diseases.
- Protect the affected area of the mouth from damage and temperature changes, and try not to sleep on that side.
- Remember the most important thing: a blood clot formed in the socket of an extracted tooth performs protective and antiseptic functions. Removing it will lead to the wound opening and suppuration.
- Do not drink liquid from a straw. This will also help remove the blood clot.
- Try to protect the affected part of the jaw from damage by chewing food only in the untouched area.
- On the first day after tooth amputation, refrain from brushing your teeth. In the following days, it is advisable to brush your teeth twice a day, paying special attention to the affected areas of the gums.
- Your immunity will be weakened, try to avoid contact with sick people, as well as visiting cool places.
wisdom tooth
Thus, your health and consequences after tooth extraction directly depend on your attitude to care and proper treatment. Don’t be afraid to visit your doctor often and in a timely manner; this can protect you from serious illnesses and serious consequences. If you find that:
- bleeding does not stop after amputation;
- unbearable pain is felt for several days;
- 4 or more days body temperature is above average;
- noticeable inflammation forms, the formation of a malignant odor from the oral cavity - do not hesitate. You urgently need a doctor’s consultation, and perhaps the right course of treatment!
Prevention at home
After the operation, certain rules should be followed that will significantly reduce the chance of alveolitis occurring:
- do not rinse your mouth on the day of the operation;
- eliminate smoking;
- Avoid eating hot and spicy foods , as well as foods that require effort to chew;
- do not touch the hole even with your tongue>;
- exclude physical activity and visiting the sauna.
Treatment for severe cases and restoration of the socket
As mentioned above, if you do not see a doctor in time, complications may arise. In this case, treatment consists of the following steps:
- The hole is treated and a swab soaked in antibiotics is inserted into it. You can also add to this remedy drugs that relieve the inflammatory process.
- An antistatic blockade is carried out.
- Proteolytic drugs are used to clean the upper part of the wound from dead tissue.
- The nerve is blocked using Lidocaine.
- A warm rinse is carried out with potassium permanganate.
Plus, to all of the above, measures used for the usual form of the disease are added.
The healing process takes about a week; if we are talking about a wisdom tooth, then this period may increase slightly. The inflammatory process goes away completely within two weeks. A dry socket after tooth extraction, photo proof of this, begins to recover, forming granulation tissue on the inner walls of the hole. Painful sensations become less, swelling subsides, the gums become pink and return to their original state. The wound is filled with granulation tissue. The first layer of epithelium begins to appear.
Pathology prevention measures
Every patient can protect himself from the occurrence of an unpleasant problem. To do this, you must initially choose professional dental surgeons who specialize in surgical interventions. At the stage of planning the operation, you need to inform the specialist about the diseases you have and the medications you are taking, so that the doctor, based on the data received, can draw up an individual treatment plan.
At home, you need to follow all the recommendations of specialists without exception. It is especially important to follow those that prevent damage and dissolution of the protective clot. Namely: you need to stop eating hot and solid foods, you shouldn’t engage in sports or physical activity, and you shouldn’t touch the wound with any objects or hands. For a while, you should stop smoking and drinking alcohol, as well as actions that lead to overheating, a rush of blood to the head and severe swelling of the tissues.
Treatment of alveolitis - how is it carried out?
If there are any complications after tooth extraction, you should contact your dentist. Independent attempts at treatment often only aggravate the situation, since a focus of infection remains at the bottom of the hole. Only a dentist can eliminate it. The doctor should clean the hole and fill it with medicine.
You should not postpone your visit to the doctor if the pain does not go away after tooth extraction. In the absence of appropriate treatment, the inflammatory process can spread to the bone, and osteomyelitis develops against the background of alveolitis.
To successfully treat alveolitis, the doctor completely cleans the socket of any remaining blood clot, purulent plaque, or food particles that have gotten into the wound. All manipulations are performed under local anesthesia. Cleaning the hole is a key point on which the success of treatment depends.
After cleaning, the doctor rinses the hole, puts medicine in it and schedules a time for the next visit to replace the medicine. In addition, to treat alveolitis, the dentist will prescribe antiseptic baths, antibiotics, and for severe pain, an anesthetic drug.
Treatment at home
Treatment at home is carried out for mild inflammation.
For this purpose, the drugs Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, and potassium permanganate solution are used.
The mouth is rinsed with the products after each meal.
Additionally, you can use decoctions of chamomile, sage, calendula, and oak bark.
The doctor may prescribe Solcoseryl dental paste. It has an analgesic effect and promotes the healing of damaged tissue.
It is introduced into a hole pre-washed with an antiseptic. The paste gradually dissolves, so there is no need to remove it. Periodically it needs to be added to the hole.
How to rinse the hole from food debris
In some situations (when the turunda has fallen out of the hole, and there is no way to see a doctor right away), it may be necessary to wash the hole. After all, after each meal, the hole will become clogged with food debris, which will cause new inflammation. Rinsing will not help here, but you can easily rinse the hole with a syringe.
Important : from the very beginning you must bite off the sharp edge of the needle from the syringe! Next, bend the needle a little and fill a 5.0 ml syringe with a solution of Chlorhexidine 0.05% (it is sold ready-made in every pharmacy for 20-30 rubles). Screw the needle tightly so that it does not fly off when pressing the syringe plunger! Place the blunt end of a bent needle into the upper part of the socket (do not insert too deeply to avoid injuring the tissue), and rinse the socket under pressure. If necessary, do this after every meal.
In principle, after this the hole can be dried with a gauze swab and treated with Solcoseryl.
Dental care
Stages of dry socket treatment at the dentist:
- Anesthesia.
- Removing food particles and necrosis from the hole.
- Washing with an antiseptic.
- Drying and filling the hole with iodoform turunda.
Important! Without removing the necrosis, any other therapeutic measures will be useless.
This is interesting: Diagnosis and treatment of acute focal pulpitis in children and adults
After curettage, the dentist prescribes medications and gives recommendations on how to care for the hole. The medicine in the hole needs to be changed every 3-5 days. You will have to visit the dentist at least 3 times.
Curettage of the tooth socket for alveolitis
- Under anesthesia, a festering blood clot, food debris, and necrotic plaque from the walls of the socket are removed. Without removing the necrotic plaque and the disintegration of the blood clot (containing a huge amount of infection), any treatment will be useless.
- The hole is washed with antiseptics, dried, after which it is filled with an antiseptic (iodoform turunda). Usually, the turunda needs to be changed every 4-5 days, i.e. you will have to go to the doctor at least 3 times.
- The doctor will prescribe you antibiotics, antiseptic baths, and painkillers, if necessary.
Doctor's prescriptions after tooth socket curettage –
- NSAID-based analgesics (for pain),
- 0.05% Chlorhexidine solution for antiseptic rinses (2-3 times a day for 1 minute),
- Antibiotics: usually either Amoxiclav 625 mg tablets (2 times a day for 5-7 days) or Unidox-solutab 100 mg (2 times a day for 5-7 days) are prescribed. These antibiotics are better, but not cheap. Inexpensive ones are Lincomycin capsules 0.25 (2 capsules 3 times a day), but keep in mind that after this antibiotic, problems with the stomach and intestines develop more often.
Method for creating a secondary blood clot
However, there are 2 situations in which a different treatment method can be used. This method involves the creation of a secondary blood clot in the socket and, accordingly, if successful, the socket will heal much faster than after constantly placing iodoform turundas into it for 2-3 weeks. It is preferable to use this method only in the following two situations...
Firstly, when you consulted a doctor immediately after, for example, you rinsed the clot out of the socket or it fell out on its own (that is, when the socket is not yet filled with infection and food debris, and there is no necrotic disintegration of the clot or suppuration). Secondly, when the patient has a sluggish alveolitis for a long period of time, and the socket is filled with inflammatory granulations.
How this technique is carried out - if the hole is empty, then under anesthesia the bone walls of the hole are scraped out with a curettage spoon to create bleeding and the hole fills with blood (video 3). If the hole is filled with granulations, then they are carefully scraped out, i.e. do the same curettage (video 4). Then, in both cases, after the hole is filled with blood, an anti-inflammatory medicine (Alvogel) is placed deep into the hole, and several sutures are placed on the mucous membrane to bring the edges of the wound closer together. Antibiotics are immediately prescribed.
How to keep a clot in the socket and what to do if it falls out?
Alveolitis occurs on average in only 3–5% of cases, however, when wisdom teeth are removed, the probability of complications reaches 30% (we recommend reading: how many days does gum pain persist after wisdom tooth removal?). The site of the extracted tooth becomes inflamed and festers, causing the patient to experience acute pain and symptoms of intoxication of the body: weakness, dizziness, fever.
A guarantee of proper and safe healing is a blood clot, which forms after tooth extraction and protects the socket from infection.
To prevent the clot from falling out, you must adhere to the following rules:
- Do not rinse your mouth for the first 2-3 days (see also: Do you need to rinse your mouth with anything after tooth extraction?). On the recommendation of a doctor, it is permissible to take antiseptic baths by holding a lukewarm liquid in the mouth and spitting carefully.
- Do not touch the site of the extracted tooth. Try not to touch the clot with a fork, toothpick, or tongue. On the first day, it is recommended not to even brush the area with a toothbrush.
- Avoid active physical activity. It is also recommended to limit your facial expressions and move your mouth muscles extremely carefully. If stitches are placed, they may come apart due to sudden movements.
- Avoid exposure to heat. Do not visit the sauna or bathhouse, do not consume hot drinks or food.
- Avoid alcohol and smoking for at least 1-2 days.
- Follow a diet. For the first 2–3 hours after surgery, do not eat at all, after which eat only soft, warm foods.
- Maintain hygiene. Use a soft brush morning, evening and after every meal. Clean around the blood clot especially carefully.
- Do not drink through a straw. It is a common belief that after a tooth extraction it is best to consume food and liquids through a straw, but the suction may dislodge the clot.
If the blood clot does fall out, you should consult a dentist. The doctor will clean the hole from clot and food residues, treat it with an antiseptic and fill it with a special product - iodoform turunda, which will need to be changed every 4-5 days. There is also a secondary clot method: if the inflammatory process has not yet begun in the hole, then it is processed (scraped out) so that bleeding begins and a new clot forms.
Medication assistance
After cleaning the hole, the following medications are prescribed:
- painkillers based on NSAIDs - Ibuprofen, Nise, Diclofenac;
- antibiotics - Amoxiclav, Lincomycin, Unidox-solutab;
- Chlorhexidine solution 0.05% for rinsing.
Causes of the disease
Traumatic tooth extraction.
Alveolitis is often caused by a traumatic dental procedure. Injury can occur if a tooth is removed in fragments (parts). During the operation, sometimes the gums are damaged or the bone walls of the socket are partially destroyed. In this case, healing takes longer compared to uncomplicated removal and is often accompanied by the appearance of alveolitis.
Foreign particles entering the hole.
Sometimes pain after tooth extraction occurs as a result of the contents of the carious cavity, dental plaque, fragments of the extracted tooth, or bone fragments of the alveoli entering the socket. In addition, the cause of pain and alveolitis can be the destruction of a blood clot.
Failure to maintain socket hygiene.
Healing of the alveoli occurs due to the formation of a blood clot. This biological barrier protects the socket from infections and inflammation. After some time, the clot is replaced by newly formed bone tissue. It is not recommended to eat rough, hot or spicy foods within 24 hours after a dental procedure, as this can destroy the blood clot. In addition, brush your teeth and rinse your mouth with caution. Failure to follow the dentist's recommendations can lead to blood clot disruption, alveolitis and pain after tooth extraction.
Presence of infection.
Sometimes the cause of dental surgery is chronic periodontitis - inflammation of the tissues that surround the root. If you have had a tooth removed and its socket hurts, this may be caused by an infection getting into it.
Up to contents