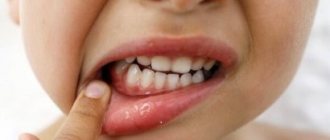
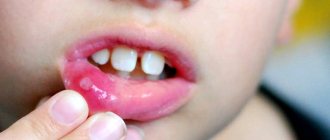
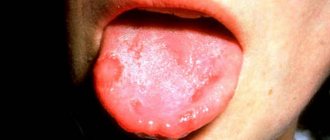
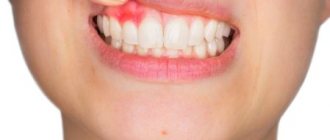
Stomatitis is a disease characterized by the appearance of ulcers on the gums. The reasons for its occurrence are different. Aphtha, or as it is called in simple terms - a sore on the gum - can appear due to allergies, herpes virus, bacteria, etc.
Mouth ulcers or gum stomatitis most often occur in children, since the child most often comes into contact with dirty toys, household items and, at every opportunity, puts everything into his mouth. It occurs less frequently in older people.
Varieties of stomatitis have different causes, symptoms and require different treatments. We will provide more detailed information about them below, this will help you navigate.
Stomatitis is a disease characterized by the appearance of ulcers on the gums.
What is stomatitis
Stomatitis is an inflammatory disease of the gums that appears externally as white spots or sores on the gums.
You should not ignore stomatitis or try to treat it yourself. Mouth ulcers occur for various reasons, sometimes quite serious. If a white sore appears on the gum, it is important not only to get rid of the symptoms, but to understand the cause of its appearance, because stomatitis in adults often manifests itself as a secondary process of some disease, which is best diagnosed with the help of doctors in a timely manner.
What does stomatitis look like?
Stomatitis is an inflammation of the lining of the mouth that causes ulcers, blisters and spots.
White sores can appear throughout the mouth: a white spot can be on the gum, tongue, lips, cheeks, and so on. Ulcerative damage to the integrity of the oral mucosa can cause severe discomfort, pain, provoke an increase in the sensitivity of nerve endings, and an increase in body temperature. It would seem that a minor white sore on the gum not only prevents you from eating normally, but also from sleeping and drinking, which can lead to problems with the gastrointestinal tract. If you have developed stomatitis, its signs are quite obvious - a white sore appears on the gum, and your general condition may worsen significantly. In this case, you should not delay visiting a doctor.
Stomatitis causes inflammation of the oral mucosa, which causes ulcers, blisters and spots to appear.
Symptoms of the disease
Stomatitis has its own characteristic signs, by which a specialist quickly identifies the disease:
- sores, vesicles, blisters on the gums;
- inflammation of the gums;
- swelling, pain, redness of the oral mucosa;
- hyperemia of the gums and mucous membranes;
- white or yellow coating;
- increased salivation (hypersalivation);
- bleeding gums;
- bad breath;
- unpleasant putrid taste in the mouth;
- enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes;
- increase in temperature;
- general deterioration of health.
With stomatitis, the patient's well-being can seriously deteriorate.
Where can stomatitis occur:
- most often stomatitis occurs on the gums, both the upper and lower jaws;
- buccal mucosa;
- lips;
- sky.
The mechanism of development of stomatitis and causes of occurrence
The mechanism of development of this disease has not been precisely established, and today it is believed that it is based on an immune reaction to various irritants - presumably, their role is played by molecules that the immune system is not able to recognize. As a result, lymphocytes attack unidentified molecules, which leads to stomatitis on the gums in adults and children.
Stomatitis is often a manifestation of a number of systemic diseases, such as vitamin deficiency, endocrine diseases, blood diseases, gastrointestinal tract and others.
Among the local factors for the formation of ulcers on the gums, the following causes of stomatitis are distinguished:
- microorganisms (viruses, mycoplasmas, bacteria);
- diseases of the oral cavity and gastrointestinal tract (for example, colitis, gastroduodenitis, gastritis) can provoke catarrhal stomatitis;
- poor oral hygiene;
- herpes on the lips;
- dehydration;
- dentures of low quality, as well as incorrectly installed ones;
- use of certain medications;
- mechanical injury to the gums and mucous membranes of the mouth;
- vitamin deficiency and hypovitaminosis;
- insufficient intake of vitamins;
- smoking;
- chronic systemic diseases;
- oncological diseases of the neck and nasopharynx;
- side effects of chemotherapy;
- hormonal imbalances.
Sometimes stomatitis appears after dental treatment. If the cause of the disease is identified and eliminated in time, it is possible to cure it quickly and effectively.
Is stomatitis contagious and how is it transmitted?
Stomatitis itself is not a contagious disease, but the underlying cause is contagious, for example, the herpes simplex virus in herpetic stomatitis or an RNA virus in vesicular stomatitis. In these cases, stomatitis can develop as a consequence, as a variant of the body’s response to the causative virus.
If stomatitis occurs due to other reasons: mechanical damage, vitamin deficiency, hormonal imbalance, it does not pose any danger in terms of infection.
Causes of herpes
Getting infected with herpes is easy. Kissing, sexual contact or using someone else's household appliances is enough. The virus can also be transmitted from mother to child through the placenta or during childbirth. As a rule, herpes does not appear immediately: a person may not know about its existence for years. However, under the influence of certain factors, herpes can awaken.
Causes of herpes on the gums:
- weakened immunity, colds;
- hypothermia;
- stress, overwork, lack of sleep;
- lack of hygiene;
- taking antibiotics;
- avitaminosis;
- teething;
- imbalance of microflora in the mouth.
Most often, herpes on the gums appears in the autumn-winter period, when the immune system is weakened and the body lacks vitamins.
Types of stomatitis
In modern periodontology, several types of stomatitis are distinguished:
- Aphthous stomatitis. It may be accompanied by the appearance of single ulcers or multiple rashes. At the initial stage, these ulcers have a pinkish tint with pronounced red edges, but after an exacerbation, yellowish aphthae form with general swelling of the oral mucosa. Aphthous stomatitis occurs with high fever, enlarged lymph nodes, sharp pain and burning sensation while eating. There is also a chronic form that can occur in a person with a weakened immune system. In this case, this disease can manifest itself from period to period.
- Ulcerative stomatitis. It is an inflammatory disease characterized by focal destruction of the mucous membrane.
- Catarrhal - caused by poor oral hygiene, insufficient hydration of the oral cavity, the introduction of bacteria and fungi of the genus Candida. In the latter case, the disease is called candidal or fungal stomatitis, popularly known as thrush. The immediate cause of inflammation is the activity of fungi and their penetration into the mucous membrane. Candida is normally always present on the body and mucous membranes in small quantities. The disease appears when their active reproduction begins. Candidiasis is a contagious disease. It can be infected by contact, by using the same utensils and hygiene products. A characteristic manifestation of the disease is a cheesy white coating. It appears in different areas of the mucosa in the form of spots of different sizes. Associated symptoms are dryness, burning, itching. The latent period of the disease can last up to 20 days. With proper treatment, the disease resolves without complications.
- Traumatic. Injuries that cause stomatitis can be mechanical, chemical or physical and may be acute or long-term, such as improperly manufactured or installed dentures. The sharp edges of the prosthesis can irritate the mucous membranes and tongue. This provokes the appearance of stomatitis.
- Vesicular. This is one of the types of contagious stomatitis. It is caused by an RNA virus of the genus Vesiculorus of the Rhabdoviridae family. Patients should use separate hygiene products and utensils so as not to infect their household.
- Enteroviral vesicular stomatitis is caused by enteroviruses.
- Herpetic or cold sore. The disease lasts 8 days, is accompanied by weakness, drowsiness, a sharp increase in body temperature, and possible inflammation of the lymph nodes. In addition, with this type of stomatitis, gingivitis occurs and the saliva becomes viscous. The mucous membranes of the oral cavity become covered with a rash consisting of blisters that burst after three days. Accompanied by gingivitis, viscous saliva.
- Allergic. Autoimmune reactions and allergies can manifest themselves in the oral cavity. The frequency of this disease is increasing, which is associated with the emergence of new allergens and environmental deterioration. The drugs and materials used in dentistry also play a role—some people may also be allergic to them. The symptoms of allergic stomatitis in general do not differ from the manifestations of other types of inflammation of the oral cavity. Swelling, redness, pain, and the formation of various elements of a rash are observed. Ulcers and erosions may also appear. Allergic stomatitis can develop against the background of autoimmune disorders. At the same time, many variants of mucosal lesions are associated with them, when it is not possible to establish connections with other possible causes.
In addition, stomatitis can take acute and chronic forms, depending on the characteristics of its course:
- acute stomatitis is accompanied by a significant deterioration of the condition,
- Chronic is a disease that occurs periodically.
How to distinguish stomatitis from other diseases
Since stomatitis can appear for a variety of reasons, and the forms of its manifestation can be very different, it is highly not recommended to self-medicate, since in this case you can only aggravate the course of the disease and cause the appearance of new symptoms. Due to such diversity, methods of treatment and prevention of this disease can also be very different.
Manifestations of stomatitis may be similar to a number of diseases, from each of which a doctor, when examining a patient, will definitely be able to distinguish this ailment:
- Sore throat or stomatitis: you can determine a sore throat, which may be similar to stomatitis, by damage not only to the mucous membranes of the mouth, but also to the pharynx. It is very painful for the patient to swallow.
- Herpes or stomatitis: In the case of herpes, the rashes first look like blisters and appear later.
- Cancer or stomatitis: the first disease is distinguished by the fact that ulcers appear, which grow together over time. As a result, one ulcer forms and begins to grow.
- Thrush or stomatitis: when examining the mouth, if there is a disease such as candidiasis, a yellow or white coating is detected, redness, the wounds are round in shape, and the ulcers are small.
- Syphilis or stomatitis: the first disease is distinguished by the nature of the ulcers. They appear in the form of eosis and do not hurt. Sometimes there is a depression in the center of the wound.
The doctor selects the treatment for stomatitis based on the cause of the disease, the complexity of its course, the form of manifestation, the individual characteristics of the body, and so on - in general, you will have to take into account a lot of things in order to choose the correct and most effective treatment. A specialist usually easily determines that it is stomatitis and not another disease.
What does a fistula on the gum look like?
Fistulas are small holes. Initially, white bubbles appear on the gums. Inside the seals, pus collects and harmful microorganisms multiply. Holes or canals appear when the soft jaw tissue remains in an inflamed state for a long time.
Before the perforating channels appear, the fistula looks like a red lump. A white dot is clearly visible on the side or above it - this is a purulent accumulation.
The fistula can reach 1 centimeter in diameter. Most often it occurs next to a diseased tooth, which ultimately requires removal. In fact, a fistula is a symptom that indicates other diseases in the oral cavity. Before it forms, the gums may become red and swollen, and sometimes the formation process is accompanied by painful sensations. Chewing becomes especially uncomfortable. Fistulas appear with advanced caries, pulpitis and periodontitis.
Can stomatitis go away on its own?
Patients often delay visiting a doctor, hoping that stomatitis will go away on its own. Stomatitis in non-advanced forms can actually go away on its own within a week. But given the risk of complications and, as a rule, a fairly high degree of discomfort from which the patient suffers with this disease, it is much wiser to seek help from a doctor and receive competent medical care.
Correctly prescribed treatment, following the recommendations of the attending physician, will bring rapid relief and improved quality of life. In addition, this will speed up the process of curing stomatitis, avoid the unpleasant consequences of untimely treatment, and also, thanks to diagnostics, learn about the causes of stomatitis and, if necessary, take care of your health. It is difficult for a patient who does not have special knowledge to assess the severity of his disease and the causes that caused it, so seeking medical help is necessary.
Possible consequences and complications of stomatitis
Recurrent stomatitis can be cured quickly if you follow your doctor’s recommendations. But sometimes patients may experience some complications:
- lung diseases;
- damage to the entire mucosa;
- digestive problems;
- loss of some teeth.
Typically, such complications are the result of self-medication or lack of treatment, which is why you should consult a doctor in a timely manner.
Diagnosis of stomatitis
Only a doctor can make a diagnosis. Typically, the doctor reviews the medical record and then examines the patient's mouth. Today, no special medical diagnostic methods, such as laboratory culture analysis or biopsy, are used to detect stomatitis, since they do not exist for this disease. In diagnosis, the doctor is guided by the main and main signs of stomatitis:
- This is the appearance of the ulcers and their location
- The condition of the oral tissues around the ulcers - with stomatitis they look normal and healthy
- The fact of recurrence of episodes of the disease
- The patient has no deterioration in general health, high temperature and other significant general symptoms. This symptom does not apply to advanced forms of stomatitis, mainly in children, when there are a large number of ulcers and just a high temperature and poor health. The diagnosis of stomatitis can only be made by a doctor.
Treatment of stomatitis
Only a doctor can prescribe correct treatment for stomatitis in adults or children. If you want to quickly cure stomatitis, it is best to consult a doctor in the early stages of the disease. Remember that improper self-medication can lead to generalization of the infection and serious consequences for your health.
Remember that improper self-medication of stomatitis can have serious consequences for your health.
Depending on the type of damage to the oral mucosa, the doctor will prescribe the correct and effective treatment for your stomatitis, most often with medication - these can be antifungal, antiviral, anti-inflammatory, antiseptic, antihistamine and other medications. In addition, the doctor will recommend a gentle diet and prescribe mouth rinses using decoctions of various plants with antiseptic properties or tinctures of them, ready-made rinses. Sometimes the use of medicinal lozenges may be prescribed - in addition to the antiseptic effect, they improve salivation and provide a distracting effect.
In case of severe pain symptoms and the need for rapid treatment of stomatitis, the doctor may prescribe anesthetics for local use. When treating recurrent stomatitis, it is especially important not to miss repeated appointments with the doctor, since specialist supervision is necessary for complete cure and prevention of relapses of the disease.
In some cases, as prescribed by a doctor, a modern and effective method of treating stomatitis can be used - laser therapy. Its essence is the impact of a laser device on areas of the oral mucosa affected by stomatitis, during which the inflamed areas are disinfected and pain is reduced. As a result, recovery occurs very quickly.
In cases where, in addition to stomatitis, the patient is also concerned about caries, the primary task is to cure stomatitis. Planned dental treatment for stomatitis is not carried out; first you need to cure stomatitis, and then start dental treatment. Of course, this does not apply to acute cases, and the treatment procedure is determined by the attending physician.
Recommendations during treatment of stomatitis
- follow the treatment method for stomatitis prescribed by your doctor,
- It is especially important when treating children: eat food several times a day in small portions, crushed and not hot, so as not to injure the mucous membranes,
- exclude salty, spicy and sour foods during treatment - pickles, marinades, pepper and mustard, tea with lemon, sour juices and fruit drinks, let them wait until better times.
How many days does stomatitis treatment last?
You should not delay visiting a doctor to treat stomatitis in the mouth, because the sooner you contact a specialist, the sooner you will begin proper treatment and the faster you will get rid of the disease. It is worth considering that treatment of chronic stomatitis takes a little longer, since the disease has already developed into a more complex form.
Most often, if the doctor’s recommendations are fully followed, stomatitis is completely cured in 3-10 days, sometimes it may take about 2 weeks.
Pimple on the gum - what to do?
The treatment scenario depends on the reasons that caused the rash on the gums. In addition to clinical treatment, a number of home measures can be taken. For example, if the rash is associated with the spread of Candida fungus in the mouth or with stomatitis, regular rinsing, taking special medications and treating the mucous membrane help. A purulent pimple on the gum may be a consequence of a viral infection of the body, in which case antiviral drugs are prescribed. The treatment must be selected by the dentist. The doctor will explain how to rinse a pimple on the gum and what habits will need to be reviewed. If a rash appears, it is recommended to exclude certain foods from the diet:
- fried foods and dishes high in oil;
- solid foods - nuts, raw vegetables such as carrots, etc.;
- very hot or cold dishes - food should be at room temperature;
- spicy, sweet and sour.
It is important that the diet does not contain foods that can further irritate the mucous membrane. Dentists also recommend abstaining from soda during treatment. Mostly you will need to switch to a liquid diet; you can leave purees and well-cooked porridges.
A white pimple on the gum may be fatty. In this case, the dentist should observe the changes for some time without intervention - the fat will resolve on its own. They rarely increase, but such development is possible. Then surgical removal is necessary.
A rash on the gums may indicate stomatitis, candidiasis or herpetic infection. An individual treatment regimen is selected for each situation. Taking medications is combined with preventive measures such as adjusting the diet. Severe inflammation is treated with a course of antibiotics. If the rash is accompanied by pain in the mouth, the doctor prescribes antiseptic solutions or gels to reduce pain.