Even young children are susceptible to dental diseases, since the enamel and gums of children are not yet strong enough to resist the effects of negative factors. However, most parents believe that there is no need to treat children’s baby teeth, since they will fall out sooner or later anyway. This is an erroneous opinion, because the condition of the baby teeth largely determines what kind of molars will grow. Untreated baby teeth can serve as a source of infection.
There are many reasons that worsen the condition of the oral cavity and teeth in children: poor hygiene, unlimited consumption of sweets, insufficient intake of vitamins. Against the background of these reasons, immunity decreases and the risk of oral diseases increases.
Prevention of dental caries in children
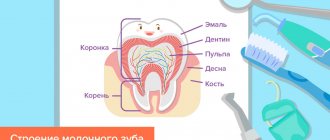
During their short existence, baby teeth have a long-term impact and serve for proper biting and chewing, for the formation of vowels, and also preserve space for permanent teeth.
Children from 0-4 years
Teeth and gums hurt as a result of the action of certain bacteria. In the warm and moist oral cavity, they wait for the appearance of sugar or other sugar-containing products, and quickly begin to multiply, create a sticky mass - plaque - and secrete acid and cellular toxins, which harm the teeth and gums.
It is enough to follow simple rules:
- feed your child foods low in sugar;
- offer sweets that are friendly to teeth, i.e. sweet in taste and safe for teeth;
- care for children's teeth and gums from birth.
Treatment of pulpitis
If the infection is located near or has already reached the pulp chamber of the tooth, completely different treatment methods are used.
- Direct pulp capping. With this method of treatment, the viability of the entire pulp is preserved.
- Pulpotomy (vital amputation). The infected coronal part of the pulp is removed, its root part is preserved for further development of the tooth.
- Pulpectomy (pulpoextraction). The pulp is completely removed, after which the root canals are filled.
If a small patient is brought to the clinic in a timely manner, pulpitis can be cured in one visit.
Dentist recommendations
Your baby needs to brush his teeth 2 times a day from the moment the first tooth erupts. This must be a mandatory and strictly observed rule. In this case, teeth cleaning should be of high quality; the recommended duration of the procedure is 3 minutes.
- How to choose a toothbrush for a child?
The toothbrush should be of medium hardness; pay attention to the markings according to the child’s age.
- Which toothpaste should you choose?
From 3 years of age, it is better to use toothpaste with fluoride, selected according to the child’s age.
- Oral hygiene
Teach your child to use dental floss to clean spaces between teeth that are difficult to clean with a brush.
- Reduce your intake of sweets
If possible, reduce your consumption of sweets - sweets, lollipops, cookies, sweet soda! If a child has eaten a product with a high content of carbohydrates - and they are dangerous for baby teeth - be sure to brush the teeth and do not leave food for bacteria on the teeth. If your child has a sweet tooth, give preference to marshmallows and marmalade, but, of course, in limited quantities.
- Scheduled visit to the pediatric dentist
Visit your dentist twice a year for professional hygiene, starting at age 3. Medical examinations twice a year should also be on your list of mandatory events.
- Child's diet
Include more hard foods in your child's diet - fresh apples, carrots, and boiled meat are useful. Food should not only be soft or pureed.
More detailed and individual recommendations are given after examination and consultation in our clinic.
When all the baby teeth are there
How strong are they? Already in the 6th week of pregnancy, baby teeth begin to form. All of their 20 crowns are already fully developed by the time the child is born and take their permanent place in the jaws, even those that appear by the end of the first year of life.
Between 6 and 8 months of life, the first teeth appear. Alternately, they cut through the swollen gums. Sometimes this is a painful process, and the child worries and cries more often. In some cases, teething toys help, but how to deal with mom's loving concern? After all, in fact, there is no such disease as “teething.” Research shows that rising temperatures and other ailments during this period of life are a coincidence.
By the time all 20 baby teeth have erupted—which takes about 2 years—each one needs care.
Do I need to treat rotten teeth?
Of course, it is necessary to treat any damage to baby teeth. The loss of one or more milk units can affect the correct formation of the bite in later life. In addition, the destruction of hard tissues inevitably leads to inflammatory processes in the surrounding soft tissues. If you do not deal with the problem in a timely manner, then there is a high risk of developing an abscess, meningitis, sepsis, etc.
Quite often, dental caries does not manifest itself in any way until the child’s immune system is weakened due to illness or a common cold. The consequences can be quite serious: sinusitis, pain in the ears (otitis and other problems), digestive problems, intestinal disorders and stool disorders, as well as severe stomach pain.
In addition, rotten teeth look very unsightly even in a child. Older children may begin to feel complex about their appearance; they will develop self-doubt and tightness. That is why it is very important to periodically check the condition of your baby’s teeth, because it is much easier to eliminate the problem at an early stage.
previous post
The difference between paid and free anesthesia
next entry
Dental prevention. ATTENTION: SUGAR!
Sugar is found in breast milk and therefore cannot be excluded from the diet of infants. It is also present in healthy fruit juices and is the main cause of tooth decay. And in order to prevent it from appearing on children’s wonderful teeth, you, dear parents, must help them from the first day.
For children in the first year of life, special baby brushes are made of very soft bristles or completely made of rubber. Systematically, after each meal, the gums and baby teeth should be cleaned on all sides, for example, using a cosmetic spatula wrapped in dry cotton wool. Then you can start using the first soft toothbrushes as early as possible. You need to practice everything that brushes your teeth with fun and humor: open your mouth, show your teeth, brush them, rinse your mouth. Try to effectively use children's curiosity and desire to imitate adults - and brushing your teeth will become real fun associated with pleasant emotions.
At 2 years old, your child already has his own brush with a small, soft head and a small, thick handle. Cleaning is done “from red to white”, i.e. sweeping movements from the gums to the teeth, chewing, internal and external surfaces of the teeth. Proper and good cleaning is not such a simple matter. Be sure to monitor the child and repeat the procedure if necessary.
Vulnerability zone
Let's look at gum disease in children. Your child's healthy gums are delicate and very vulnerable tissue of a pale pink color. Unlike adult gums, they can be easily injured, but they are capable of rapid regeneration. Another peculiarity of children's gums is that they often reflect the general condition of the body, being a litmus test for systemic diseases.
The most common diseases of the gums and periodontal tissues: gingivitis is an inflammation of the gums that occurs as a result of the adverse effects of local and general factors, occurring in 80% of children; gum atrophy, which develops in more than half of the child population; various types of childhood stomatitis, which most often occurs in infants and preschoolers; Periodontitis is a disease in which all periodontal tissues become inflamed and affects up to 5% of young patients. Periodontal disease (dystrophic changes in periodontal tissue) and other pathologies practically do not occur in childhood.
Prevention of dental caries
Children 4-6 years old
Baby teeth are often underestimated, but they play a very important role in the future development of a child.
First, the child uses his baby teeth to bite and chew. When they are positioned correctly, food is properly ground and prepared for digestion.
Secondly, baby teeth make it possible for a child to speak correctly. A lisp, for example, is a consequence of too early loss of baby teeth.
Third, baby teeth hold space in the jaw for permanent teeth. The child's molars should remain until they are 11-12 years old.
Baby teeth cannot resist caries. Therefore, you need to remember that after eating and drinking, especially sticky sweets, food remains remain between the teeth, get stuck in the recesses of the molars, along the edges of the gums. The oral cavity is home to millions of bacteria that convert sugars and carbohydrates into harsh acids, which in turn attack and dissolve tooth enamel. To protect yourself from caries, you need to remember:
At what age should a child be taken to the dentist for the first time?
According to the WHO schedule, you should go to the dentist for the first time when the child is 9 months old. Some doctors indicate an age of 11-12 months. During a dental examination, several parameters are assessed.
1. How many teeth are there?
Based on the number of teeth present, the child’s development is assessed and pathologies are diagnosed. It is normal for children to erupt 5-8 milk teeth by the age of 9-12 months.
2. What condition are the teeth in?
From the first days of teeth appearing there is a danger of caries. Also, teeth should be examined for non-carious lesions - hypoplasia, in order to exclude the appearance and development of caries.
3. What is the condition of the mucous membranes?
Small children put everything in their mouths, so they are at risk for infectious diseases - stomatitis and intestinal infections. The more common fungal form of stomatitis, which must be treated promptly to avoid complications.
At the age of 9-12 months, a dental examination is more necessary for preventive purposes. The doctor will tell you what toothpaste to use, what toothbrush to choose, and how to teach your child hygiene. Until the child reaches two or three years of age, visits to the dentist should be regular - every 3-5 months.
Prevention of dental treatment - brush correctly
about rinsing your mouth or chewing sugar-free gum after every meal and sweets.
Children 6-12 years old
When new teeth are on the way
Something happens in your mouth, or more precisely in the upper and lower jaws: one baby tooth after another says goodbye to you, and new permanent teeth appear in their place. This process will last up to 12 years! Exception: at the age of 6, the permanent one is visible behind the last milk tooth, although none falls out. This is a six-year-old molar. It is important for the further development of the dentition. Therefore, it needs special care and must be coated with a special sealing compound. The reason: the enamel of the “new” teeth is not yet completely hard at the time of eruption and is therefore at risk of caries. The same applies to the remaining molars.
Do baby teeth need to be treated? What are the consequences of ignoring problematic baby teeth in the future?
The doctor’s answer to this question is clear, says FAN’s .
"Of course yes. Baby teeth need to be treated! If you leave everything to chance, the child will inevitably suffer from pain and discomfort. Moreover, it is advisable not to delay this process so that the little patient does not have a negative experience in dental treatment,” explains Victoria Arutyunova.
Of course, it is better to limit ourselves to preventive measures, but if, after all, time has already been lost, then therapeutic manipulations are absolutely necessary, since the infection gets into the tooth, and then through the nerves and canals it enters the bone and ultimately can infect and damage the germ of a new tooth . If this happens, then there are several scenarios for how the situation could develop further. The rudiment may die altogether and stop developing, or the tooth may erupt with a slight visual defect. Typically, this phenomenon is called enamel hypoplasia. In addition, possible complications include swelling, periostitis, inflammation of the gums with subsequent release of infection and pus and, accordingly, painful removal and an incision to drain the exudate.
Naturally, this procedure, which is unpleasant for the child, causes persistent negativity and provokes difficulties in further interaction with the pediatric dentist.
“In addition, during such removals, anesthesia may not work well, since the infectious exudate does not allow the anesthetic to penetrate deep enough. The child will remember such a visit for a long time, so it is better to treat without leading to such complications,” says our expert.
What are the consequences of a frivolous attitude towards children's health? If you still have to remove a baby tooth, the place will be empty, and nature, as we know, does not tolerate emptiness. As a result, neighboring teeth will begin to tilt towards the missing one. As a result, the further appearance of permanent teeth will be difficult; they will erupt in the wrong position and at the wrong time, which will cause orthodontic problems. With a high degree of probability, in the near future, parents will have to seek the services of an orthodontist to correct the situation with the help of plates or braces.
pixabay.com/
Stored hermetically
Your teeth can cause you a lot of problems, because they have so many vulnerable places: the cavities of the chewing surfaces of the molars, the interdental spaces, the necks of the teeth and the edges of the gums. This is where the sticky coating forms. The bacteria in it greet everything sweet with great joy. Then they multiply millions of times. Their waste products - acids - cause caries.
Filling the chewing surfaces of teeth with special compounds (sealing) means their protection and safety and is performed by a dentist. Despite this, all teeth should be thoroughly brushed and floss should be used between teeth. Ask your dentist to tell you more about sealants and flossing.
Almost half of children have an incorrect bite. Make sure that your child does not encounter such a problem. A significant role in the prevention of dental caries is played by the prevention and elimination of developed dentoalveolar deformities. Orthodontic treatment aimed at normalizing the bite, eliminating crowding of teeth, and reducing the likelihood of caries.
13-18 years old
Communication between people is becoming easier: for on-line surfing on the Internet, just a mouse click is enough... Only one thing complicates the communication process. Each serving of fast food with ketchup, ice cream, cola and other similar daily snacks throws our most important communicative organ - the mouth - out of ecological balance. When there is not enough systematic oral care, caries naturally occurs and gums hurt.
Dental status of children
The condition of the oral cavity directly affects the entire body:
- pathological changes can lead to malfunctions of internal organs (kidneys, gastrointestinal tract) and the appearance of diseases;
- with an incorrect bite, breathing through the nose is impaired, which leads to dysfunction of organs and organ systems;
- caries and the complications caused by it cause sore throat and other diseases, the causative agents of which are streptococci, which cause carious changes in the teeth.
The body characteristics of young children and their underdeveloped immune system determine that they are at risk for developing diseases. Since the body is a single interconnected whole, the condition of the oral cavity is given the same close attention as other organs. That is why WHO has proposed that dental examinations be carried out according to a specific schedule. If a child has a toothache, an immediate unscheduled visit to a pediatric dentist is necessary for an examination and prescription of a course of treatment.
Prevention of dental diseases
Two phases characterize caries :
Phase I – “demineralization” of teeth. Dissolution of enamel crystals under the tooth surface. Outwardly, everything looks OK, only white, chalk-like spots signal danger. At the first stage, everything is curable, but with the condition of intensive dental care. If sugar continues to be present, your teeth will have a particularly hard time.
Phase II - the appearance of a hole in the tooth - caries. But this is already incurable!
Fluorine is nature itself
Fluoride is not only found in our saliva, it is a natural component of our environment and a mineral that can be called an absolute “power” for teeth and bones. Fluoride increases the resistance of enamel to acids.
Stages of tooth decay
Any damage to a child’s teeth does not develop immediately, but gradually. The first stage is characterized by the accumulation of a large number of pathogens on the enamel, which over time form a dense dark film - spots. Also, the beginning of the destruction process may be indicated by the appearance of bad breath.
At the same time, tissue sensitivity increases, and the baby may experience discomfort when eating cold or, conversely, hot food. Also at this stage, small black spots and cavities can be found on the teeth. At this time, the deeper tissues of the tooth begin to deteriorate. As a result, the child may complain of severe pain with any mechanical impact and even without it.
Further, the process affects the nerve endings, so the pain may decrease or disappear completely. This suggests that very soon the decay will reach the root of the tooth, as a result of which the unit will most likely have to be removed surgically. The sooner parents seek help from a professional dentist, the greater the chance of saving the tooth.
Prevention of children's teeth - care
Our body’s “laboratory” produces fluoride in saliva, but it is no longer enough to effectively protect our teeth. Too many Big Macs, Snickers, and chewy candies have made it difficult for saliva to perform this function. She needs help:
- brush your teeth twice a day with a toothpaste containing fluoride;
- once a week, carry out intensive fluoridation with products containing fluoride (gels, for example);
- coat your teeth with fluoride varnish monthly;
- eat fluoridated salt.
If plaque is not regularly removed from teeth, it turns into tartar, visible on the surface of the teeth. Tartar increases in size and imperceptibly “grows” under the gums towards the root of the tooth. A thin layer of tartar is stained by exposure to nicotine, tea or red wine.
Fluoride varnish coating is professional protection against caries. Professional cleaning means removing tartar, incl. deposits invisible to the eye, which should be carried out by the dentist at least twice a year.
But that is not all. Only polishing finally rids the roots of residual layers of tartar.
Moreover. Polishing makes it more difficult for stone to form. Polishing all surfaces of the teeth after removing plaque using brushes, polishing heads, superflosses, strips, brushes and pastes allows you to make your teeth very smooth. Only with the help of professional cleaning can gum disease be cured. And the degree of its success can be checked with the tip of your tongue!